Semester 1 Finals Review
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
8 Characteristics of life
1) Respond to environment
2) Grow and change
3) Reproduce and have offspring
4) Complex Chemistry
5) Maintain Homeostasis
6) Made of cells
7) Pass traits onto offspring
8) Evolution
Lab Question
Question about lab; includes the IV and DV
Independent Variable
The variable you change as the scientist
Dependent Variable
the variable the you measure, the results of lab
Hypothesis
Educated guess
IMPORTANT: If, then, because format
Control group
The trial you compare your results to
What is “usually” done
Experimental Groups
The other trails that are not the control group
Give you results
Materials and Procedure
List of things needed for lab
Includes everything like tools, items etc.
A list of step by step directions from start to finish of how you will go through the lab (specific)
Data table
Organized
Includes all data (qualitative and quantitative)
Adaptation
Heritable characteristics that increases an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce
Metabolism
When all chemicals get carried out in the organism
Constants
Things that don’t change in experiment
Scientific Method
Question—> research—> hypothesis—> test—> conclusion
Cell
Basic units of all forms of life
Cell theory
1) All living things are composed of cells
2) Cells have basic unit of structure/function in living things
3) New cells come from existing ones
Cell Membrane
Flexible, barrier surrounds all cells
Nucleus
Structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in form of DNA
Eukaryote
Cells with a nucleus; animal and plant cells
Prokaryote
Cells with no nucleus; bacteria
Cytoplasm
Fluid portion of cell outside of nucleus
Organelle
Specialized structure that performs cellular functions (only in eukaryotic cells)
Ribosomes
Cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein found throughout cytoplasmic cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Internal membrane system found in eukaryotic cells where lipids are assembled
Golgi Apparatus
Sorts, modifies, and packages proteins for storage in cell or release outside of cell.
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores water, proteins, and carbohydrates
Lysosome
Cell organelle that breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that can be used
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein filaments in a eukaryotic cell that gives the cell its shape and internal organization and is involved in movement.
Chloroplast
Organelle found in cells of plants that do photosynthesis
Mitochondria
Converts chemical energy stored in food compounds that are more convenient for cell to use
Cell Wall
Strong, supporting layer around cell membrane in some cells
Lipid Bilayer
Flexible double-layered sheet that makes up the cell membrane and forms barrier between the cell and it’s surrroundings
Selectively Permeable
Property of membranes that allows some substances to pass across it while others cannot
Homeostasis
Relatively constant internal physical/chemical conditions that organisms contain
Diffusion
Process by which particles tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated
Facilitated Diffusion
Molecules pass across membrane through cell membrane channels
Aquaporin
Water channel protein in cell
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through permeable membrane.
Isotonic
When the concentration of two solutions is same
Hypertonic
The solution with greater solutes
Hypotonic
The solution with less concentration of solutes
Osmotic Pressure
Pressure that must be applied to prevent osmotic movement across a selectively permeable membrane.
What cell has no organelle or nucleus? They are usually unicellular?
Prokaryotic cells
What type of cells have chloroplast, one vacuole, and a rectangular fixed shape (cell wall)?
Plant cells
What cells don’t have cell walls, have different shapes, and have different vacuoles?
Animal cells
Where are proteins assembled?
Ribosomes
Where can ribosomes be located in a cell?
Around the cytoplasm, or in the rough ER
Vesicles
Store and transport material within cell and extracellular environment
Microtubules
Hollow structures made of proteins known as tubilins:
Maintain their shape/vesicle around cell (like highway)
Forms spindles for cell divisioni
Hydrophilic heads
Part of the lipid bilayer, can interact with water
Hydrophobic tails
Part of lipid bilayer, cannot interact with water.
Where can you find cell membranes?
ALL cells
Where can you find cell walls?
Only in prokaryotes and specific eukaryotes (plants and fungi)
Lipids
Creates majority of membrane as a phospholipid bilayer
Creates a semi-permeable membrane
Proteins
A largey variety of proteins are located within the phospholipid bilayer
Functions: assisting materials into and outside of cell, receiving and transmitting messages.
Carbohydrates
Attached to proteins, often act as “flags”, identifying the cell in some specific matter
Passive Transport
NO energy is required, molecules with the concentration gradient (high to low)
Equilibrium
In passive transport, where concentration is equal on both sides, no net change.
What can happen to cells in a hypotonic cells?
Vacules can expand and cell can burst!
Active transport
Molecules move AGAINST concentration gradient (low —> high)
ATP energy is REQUIRED!
Protein Pumps
Moves small molecules in and out of cell.
Protein changes shape to allow for membrane
LIKE AN OLD SCHOOL TOLLWAY
Endocytosis
A membrane forms a pocket around a particle. The pocket breaks loose from outer portion and forms a vesicle with the cytoplasm
“Consumes” the particle
Exocytosis
membrane forms a vesicle around material then fusses with cell membrane
contents are forced out of cell
“spits” the contents out
Levels of organization
Species-population-community-ecosystem-biome-biosphere
Biotic
Living
Abiotic
not living
Geographic Range
Area inhabited by a population
Density and Distributions
Number of organisms and how spaced apart they are in an environment (clumped, random, and uniform)
Population Increase Factors
Birth and immigration
Population Decrease Factors
Emigration and Deaths
Exponential growth
In an ideal condition with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially.
Logistic Growth
Three Phases: exponential, slows, stops (at carrying capacity)
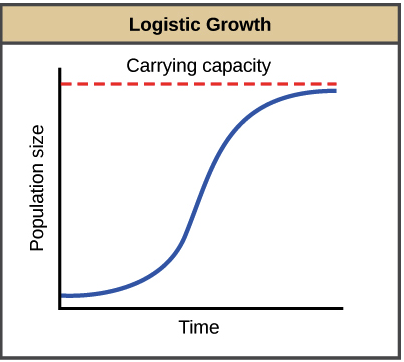
Carrying Capacity
Max # of individuals of a particular species that a particular environment can support.
Limiting Factors
Determines carrying capacity of an environment for a species
Density Dependent Factors
Has to do with affecting the population by competition, parasitism, disease, overcrowding, predation, and herbivory.
Density Independent Factors
Affects all populations regardless of population size/family (natural disasters)
Primary Producers
Autotrophs, organisms that can make own food through photosynthesis
Chemosynthesis
Using chemical energy to produce carbs
Detritivores
Feeds on detritus particles, chewing/grinding them into smaller pieces
Scavengers
Animals that consume carcasses (dead animals)
Food chain
Series of organisms in which energy is transferred from one organism to another (who eats who)
Food web
A network of feeding interactions, more complicated than food chain since animals eat more than one food.
Energy Pyramids
Each step is a trophic level.
Three types: pyramids of energy, pyramids of biomass, and pyramid of numbers.
Mircrohabitat
A tiny part of larger habitat, has own set of environmental conditions called a microclimate
Mircrobiome
Community of bacteria
Tolerance
The range of external conditions within a species can survive and reproduce.
Niche
The role of an organism, or “what it does for a living”, the way it obtains resources.
Intraspecific Competition
Same species
Interspecific Completion
Different species
Competitive Exclusion Principle
No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in the same habitat at exactly the same time
Resource partitioning
dividing resources to try not to compete
Predator-prey relationship
predator population follows prey population and fluctuates accordingly.
Herbivory
Eats plants, can impact plants’ size, growth, distribution, and survival.
Keystone species
A keystone species maintain structure, stability, and diversity of an ecosystem.
Commensalism
A relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Mutualism
two species in which both species benefit
Parasitism
a relationship where an organism lives inside or on another organism and harms it.
Genetic diversity vs Species diversity
Genetic- Different forms of genes (kinda invisible)
Species- # of different species in an ecosystem
Threats to biodiversity
1) Invasive species- disrupt eccosystem
2) Climate change- forces some organisms out of tolerance level
What are ecological services available because of diversity?
Food production, nutrient cycling, soil structure, purifying water, storing carbon, regulating pests and more.
Preserving Biodiversity
The act of aims to preserve and protect natural resources