Lecture 4 - Cell Membrane Composition and Transport
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Plasma membrane composition
Lipid bilayer and proteins in fluid mosaic
- cellular activity
- separates intracellular and extracellular fluid
What are the 3 basic parts of human cells?
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus
Membrane lipids
75% phospholipids
5% glycolipids
20% cholesterol (increases membrane stability)
Membrane protein function
Integral and peripheral proteins with various roles
-1/2 mass of plasma membrane
Integral proteins
penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
- function as transport proteins, enzymes or receptor
6 functions of membrane proteins
1. Transport
2. Receptors for signal transduction
3. Attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
4. Enzymatic activity
5. Intercellular joining
6. Cell-cell recognition
3 Types of membrane transport
1. simple diffusion
2. osmosis
3. active transport
passive transport
Requires NO energy
- movement of molecules from high to low concentration (down gradient)
Fick's first law of diffusion
States that the rate of diffusion, or flux, J of a species is proportional to the concentration gradient.
Fick's second law of diffusion
describes the change in concentration at a particular point in the system with time
Stokes-Einstein Equation
D=KT/6πrη
- liquid diffusion, drag force is related to size and solvent viscosity of spherical particle
Permeability vs diffusion
permeability: rate of flow of liquid/gas through porous material
diffusion: passive movement of molec/particles down conc grad
4 types of diffusion across lipid bilayer:
1. small nonpolar (O2, CO2, steroid, hormones) = rapidly
2. small polar molec = slowly
3. large polar molec = very slowly, need help
4. ions = highly impermeable
2 types of membrane transport proteins
1. channels: aqueous pores
ex - aquaporin
2. transporters: bind specific solute and undergo conformational change
Speed of diffusion is influenced by
size of molecule and temperature
simple diffusion
Diffusion that doesn't involve a direct input of energy or assistance by carrier proteins.
facilitated diffusion
going high to low conc
- certain lipophobic molecules (like glucose, aa, ions) binding protein carriers, or water-filled channels
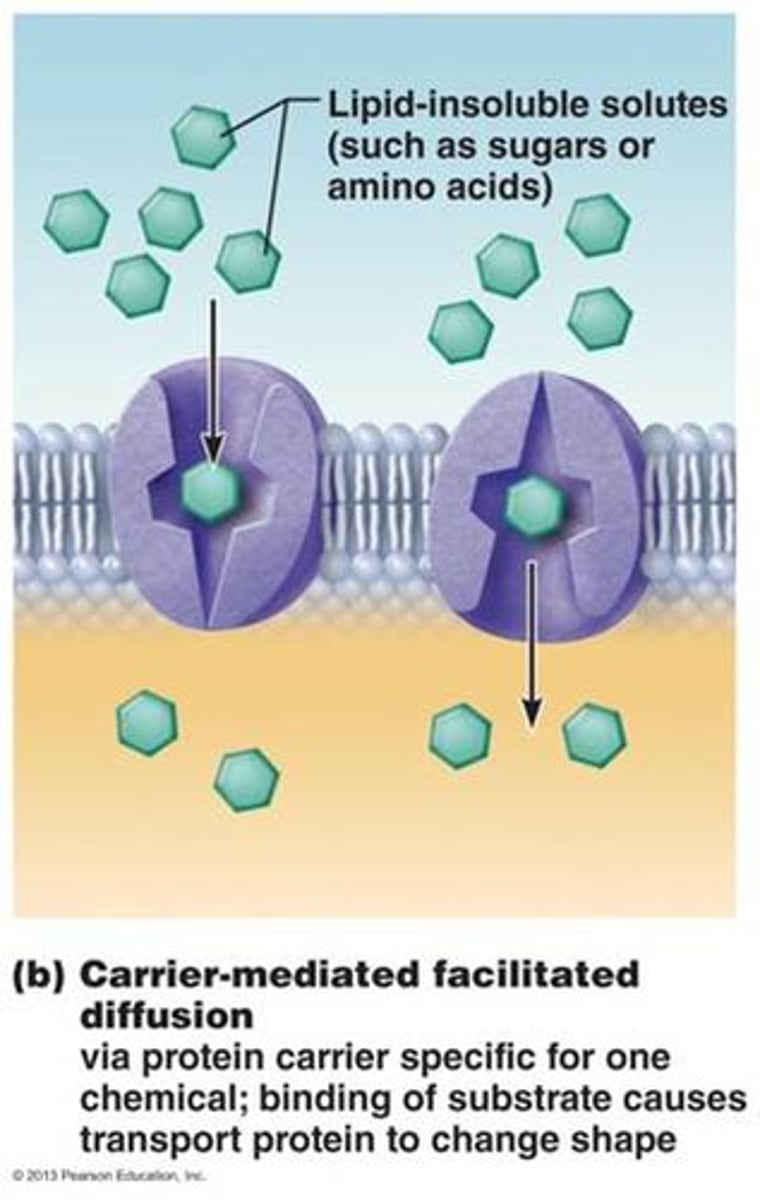
Carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion
Molecule binds to specific protein that changes shape to carry molecule across the plasma membrane
- limited number of carriers present
Channel-mediated facilitated diffusion
through a channel protein; mostly ions selected on basis of size and charge
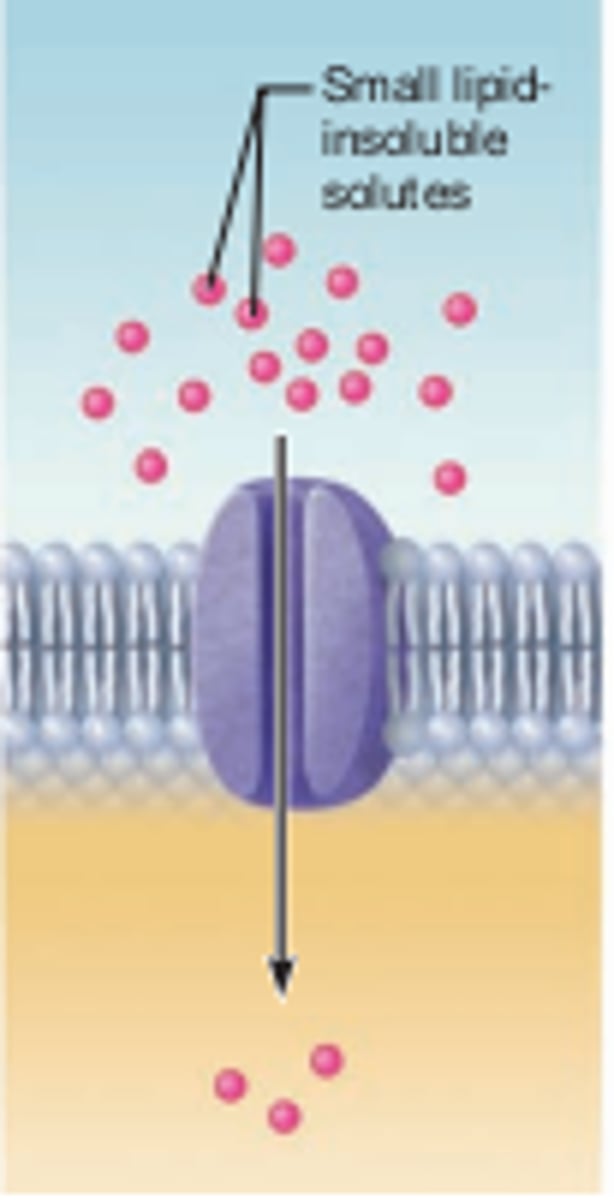
2 types of channel-mediated
1. Leakage channel
2. Gated channel
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
- through aquaporin channels
Osmolarity
measure of total concentration of solute particles
- h2o moves by osmosis until hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure equalize
Tonicity def
the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as another solution.
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than cytosol
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than cytosol
Cholesterol
Lipid that increases membrane stability
Sources of intracellular osmolarity
- macromolecules (little)
- mostly small organic molec (sugars, aa, nucleotides)
RBC osmolarity
hypotonic - water rushes in, cells burst
hypertonic - water leaves cell, shrink
Typical concentrations of ions in cells
K high inside
Na high outside
Cl high outside
2 types of active processes
active transport and vesicular transport
- both require ATP because solute to large, lipid not soluble or solute can't move down conc grad
Uniporter
transporter that carries one specific ion or molecule
coupled transporters
couple the uphill transport of one solute across the membrane to the downhill transport of another
- symporter & antiporter
Active transporters have
one or more binding sites
- undergoes conformational change
How to cells link transporters to energy souce?
1. coupled transporters
2. ATP driven pumps
3. light driven pumps (archea/bacteria)
active transport
requires energy and carrier proteins (specific)
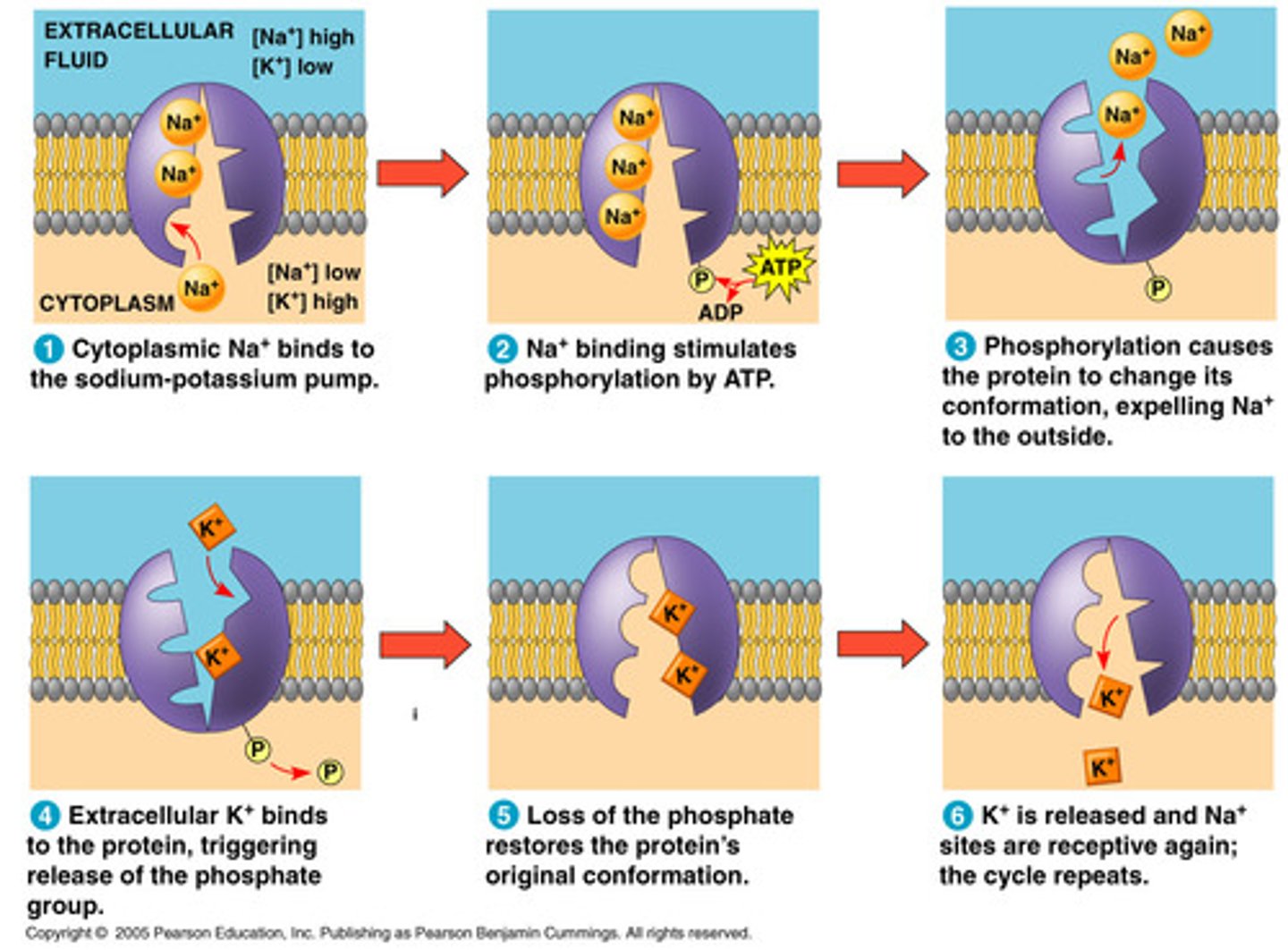
primary active transport
Active transport that relies directly on the hydrolysis of ATP
ex: sodium-potassium pump
secondary active transport
use pre-existing gradient to drive transport of solute
symporter
transporter that carries two different ions or small molecules, both in the same direction
antiporter
A carrier protein that transports two molecules acrss the plasma membrane in opposite directions.
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
- keeps electrochemical gradient
Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
Electrical potential energy produced by separation of oppositely charged particles across plasma membrane in all cells
- -50 to -100 mV
ABC transporter def
ATP binding cassette, contains 2 ATP binding sites in order for transport
ABC transporter function clincally
- cancer (challenge for treatment)
- malaria
- cystic fibrosis
vesicular transport
Transport of large particles and macromolecules across plasma membranes
- requires ATP
Vesicular transport functions
exocytosis, endocytosis, transcytosis, vesicular trafficking
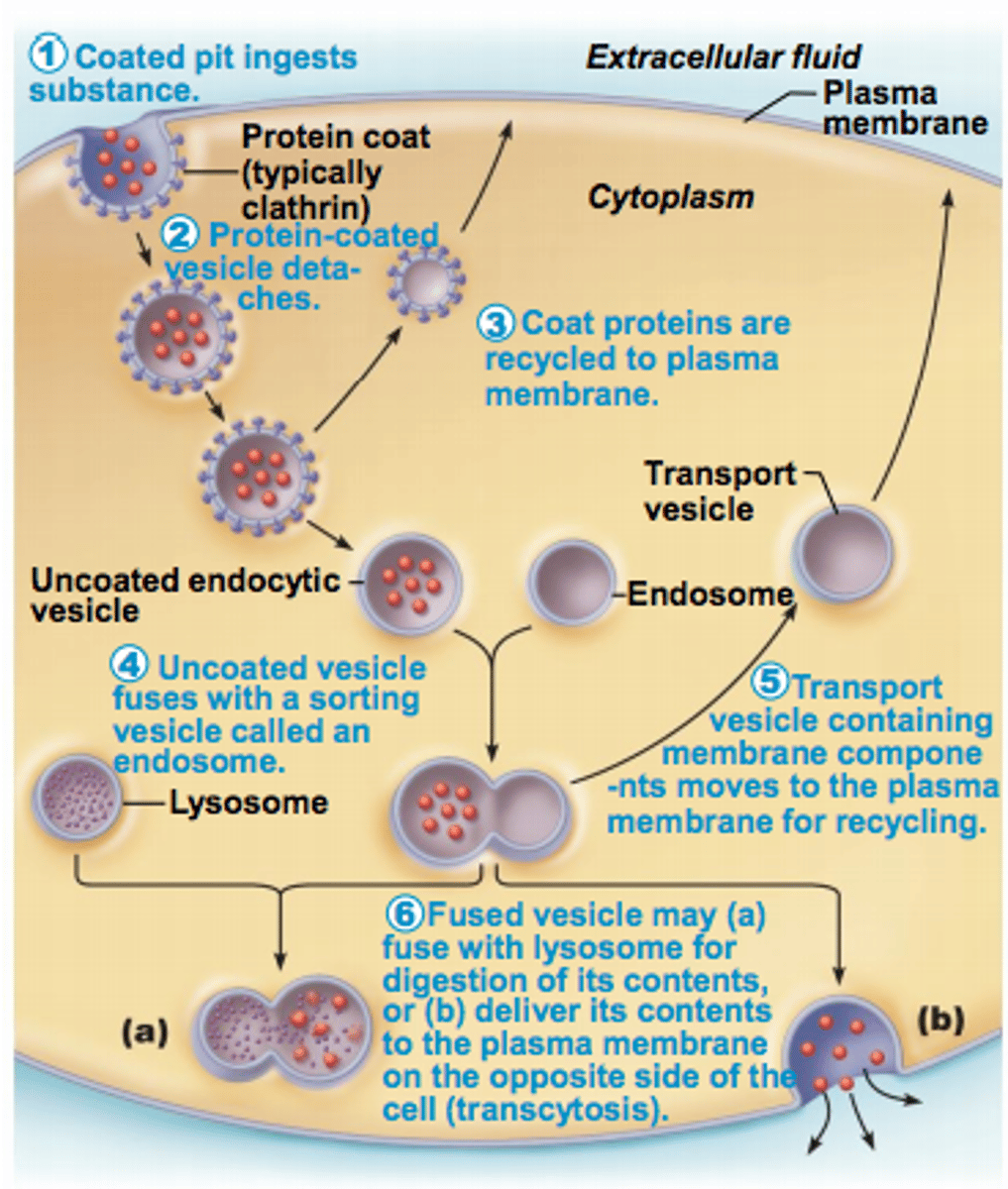
Endocytosis and Transcytosis
Involve formation of protein-coated vesicles
- Often receptor mediated, therefore very selective
endocytosis example
phagocytosis and pinocytosis
Phagocytosis
Cell eating, pseudopods engulf solids
- form phagosome
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking
- plasma membrane infolds
- fuses with endosome
ex: nutrient absorption in small int.
Glycolipid
Lipid with polar sugar groups on outer membrane surface
receptor-mediated endocytosis
The movement of specific molecules into a cell by the inward budding of membranous vesicles
- clathrin-coated pits
types of coat proteins for receptor-mediated endocytosis
1. caveolae: capture specific molecules for transcytosis
2. coatomer: funct in vesicular trafficking
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
- activated by cell-surface signal
- secretory vesicle
Tags exocytosis
1. v-SNARE (v = vesicle) find vesicle
2. t-SNARE (t = target) on membrane and bind
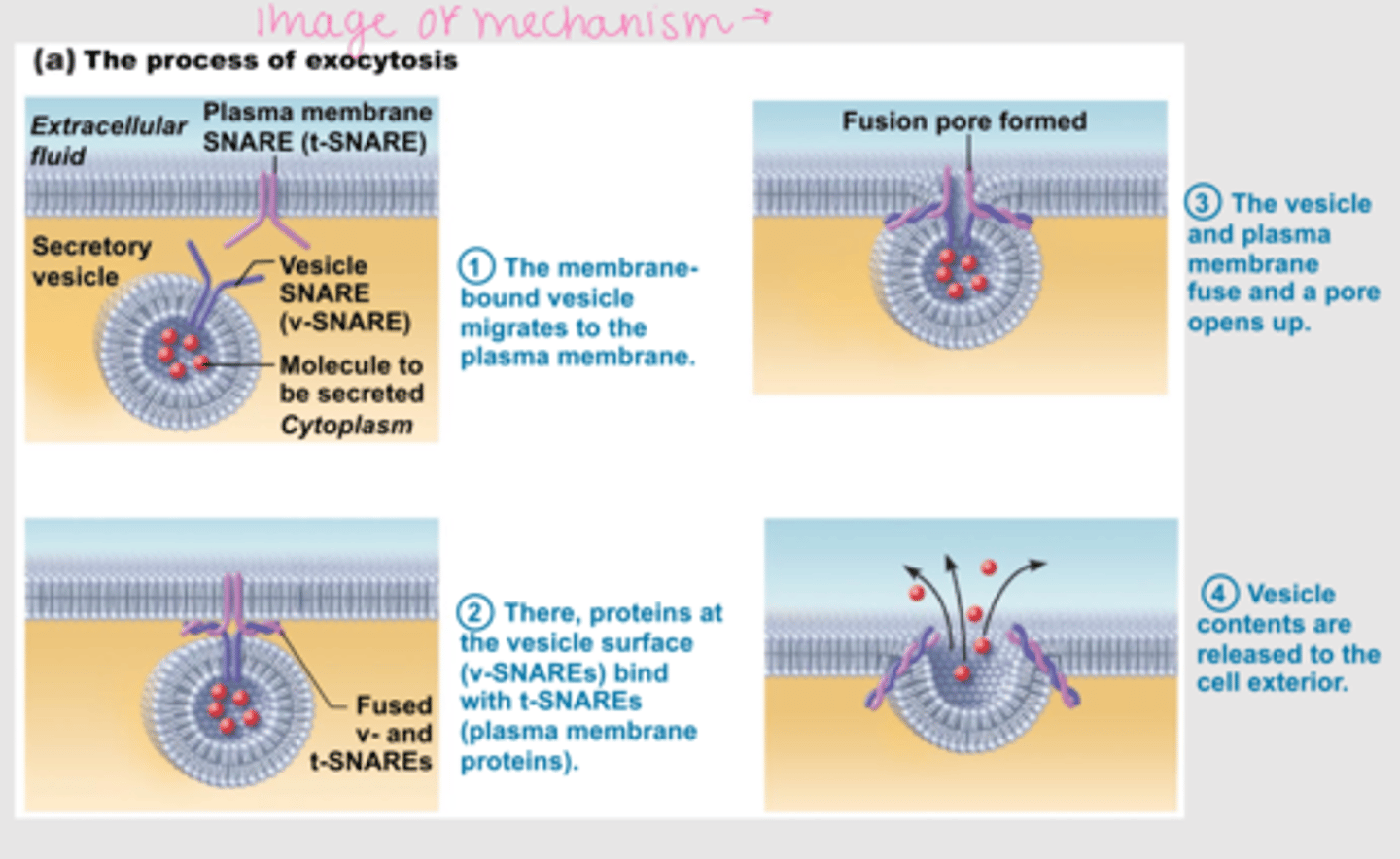
Glycocalyx
sugar coating at surface
- every cell has different pattern of sugars (used for cell-cell recognition)
** immune system to recognize "self" and "non self"
Cell junctions (3 types)
contact points between the plasma membranes of tissue cells
1. tight junctions
2. desmosomes
3. gap junctions
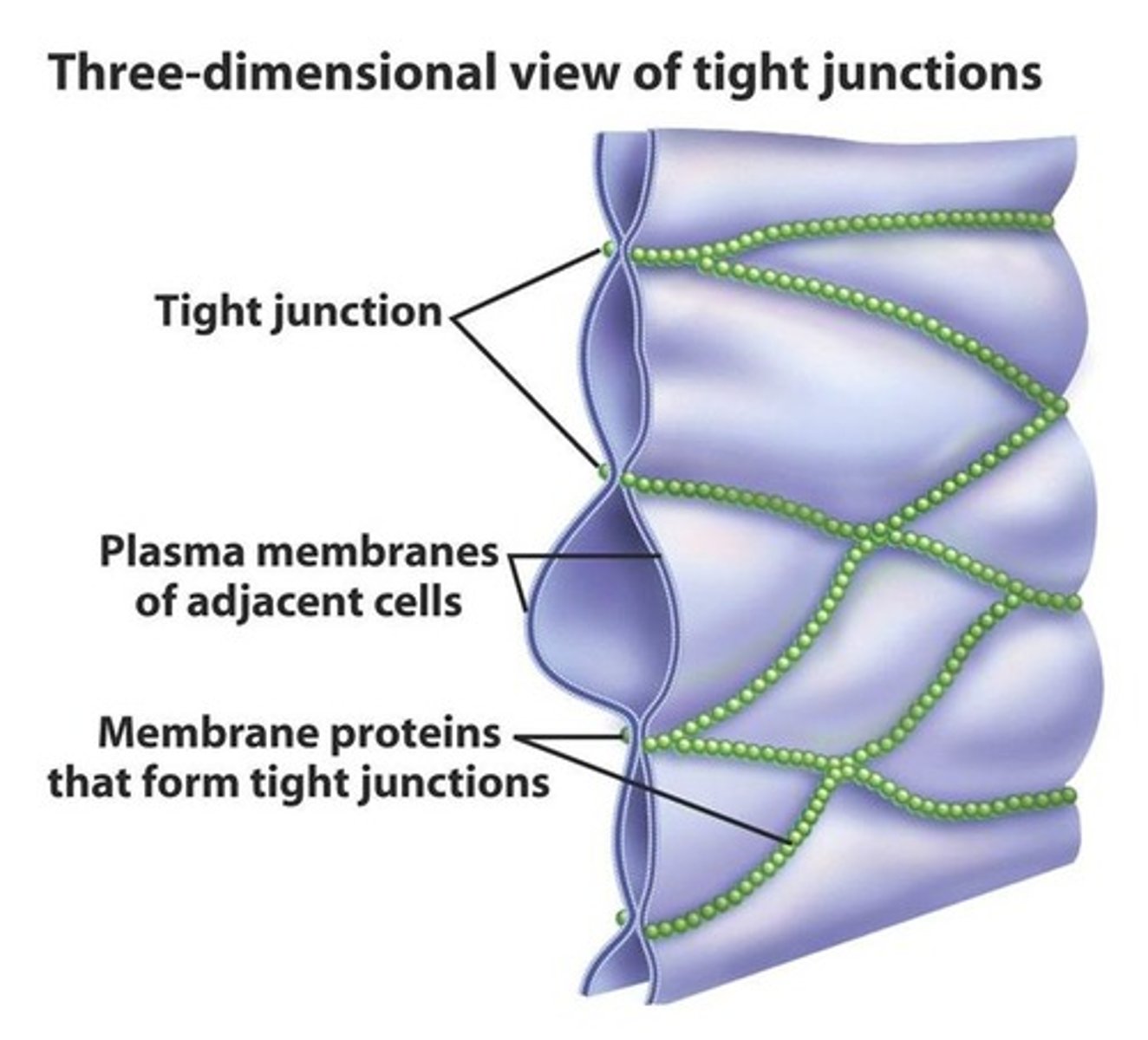
tight junctions
Membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together, preventing leakage of extracellular fluid
ex: endothelial cells, skin
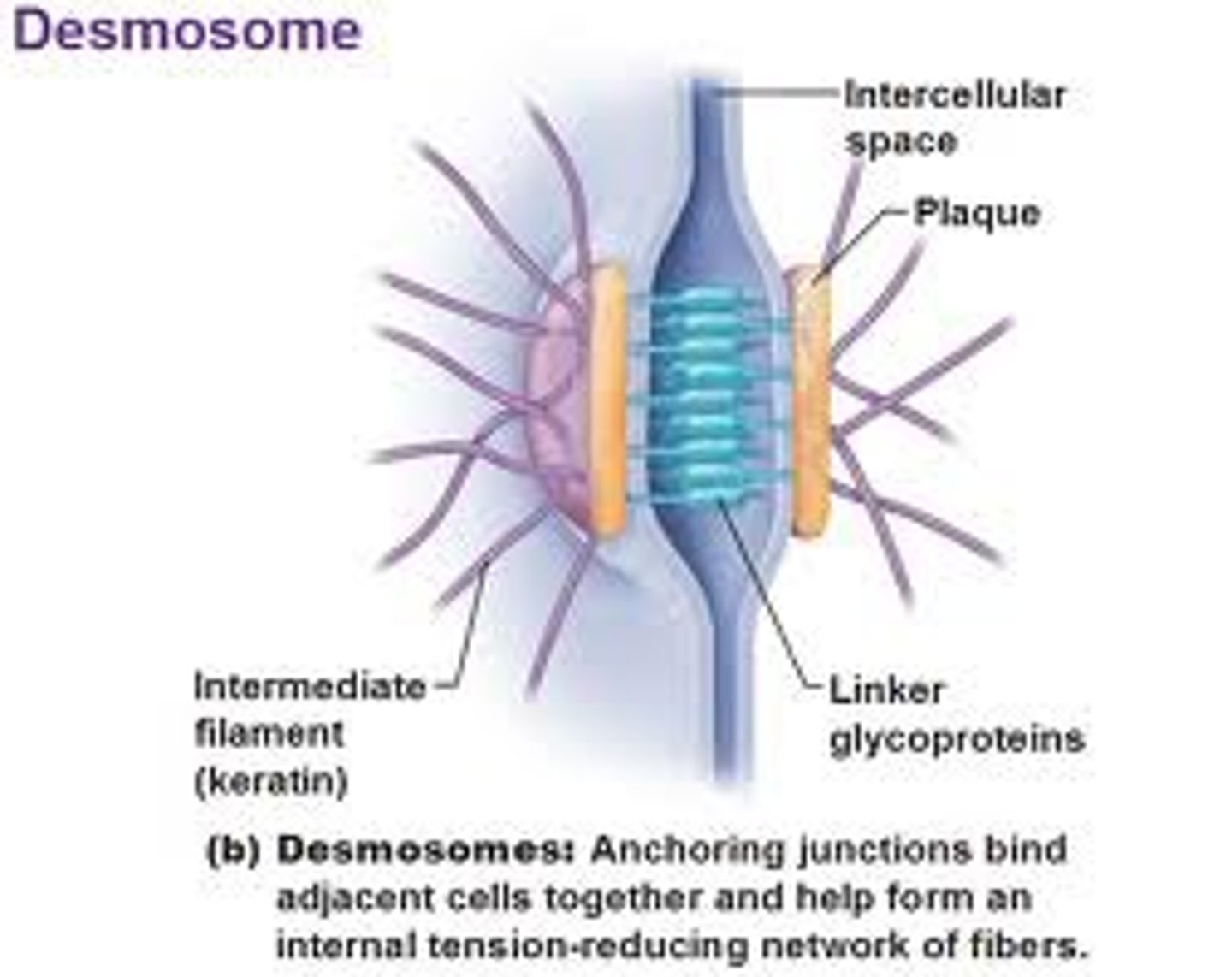
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions at plaques (thickening of plasma mem)
- linker proteins
- prevents cells subjected to mechanical stress from being pulled apart
ex: near joints
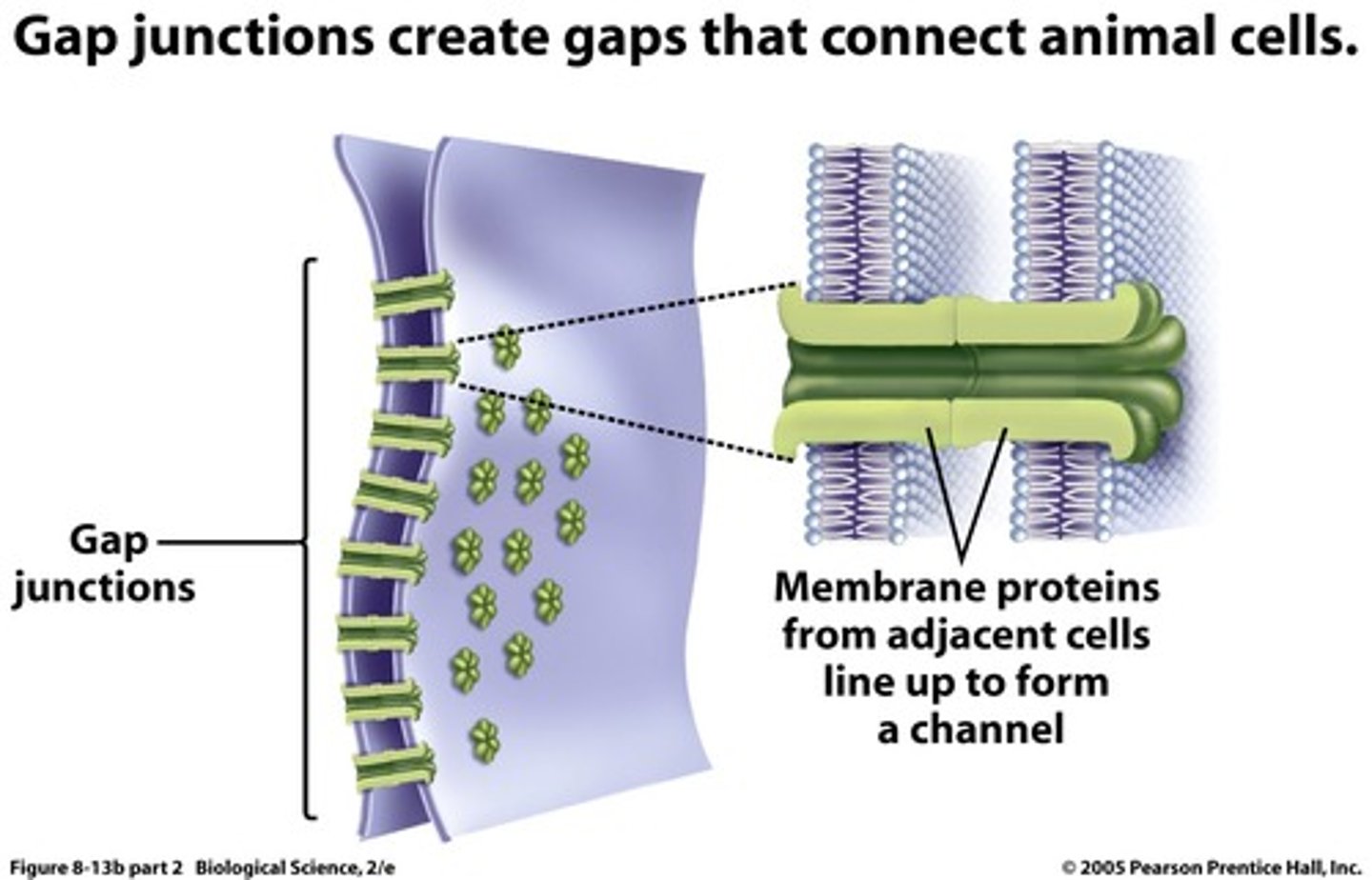
Gap junction
transmembrane proteins form pores (connexons) that allow small molecules to pass from cell to cell
ex: muscle for ion/signal transduction
Glycoprotein
Protein with polar sugar groups on outer membrane surface
Peripheral proteins
Proteins loosely attached to integral proteins
- filaments on intracellular surface
- function: enzymes
Receptors
Proteins that bind to specific molecules and initiate a cellular response
Cell-cell recognition
Process by which cells identify and interact with each other
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)
Proteins that anchor cells to the extracellular matrix or each other
Role of CAMs
- anchor to ECM
- assist in movement of cells
- attract WBCs to injury
Contact signaling
touching and recognition of cells
Chemical signaling
interactions between receptors and ligands that cause changes in cellular activities
Plasma membrane receptors
Proteins that bind to specific ligands and initiate a cellular response
Voltage-gated channel proteins
Proteins that open and close ion channels in response to changes in membrane voltage