module 3 exchange surfaces
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exchange surfaces
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what are limitations of the agar jelly experiment?
incosistency with SA ; impacts smallest cube most
subjective results
why do larger organisms need specialised exchanged surfaces?
smaller SA:V
long diffusion distance (oxygen cannot diffuse in quick enough to meet metabolic needs)
higher metabolic activity
what are the features of an efficient exchange surfaces?
large SA to increase rate of diffusion (root hair cells,alveoli)
thin diffusion pathway (alveoli)
good blood supply/ventilation to maintain concentration gradient (gills/alveolus)

label the structure of the mammalian gas exchange system
image
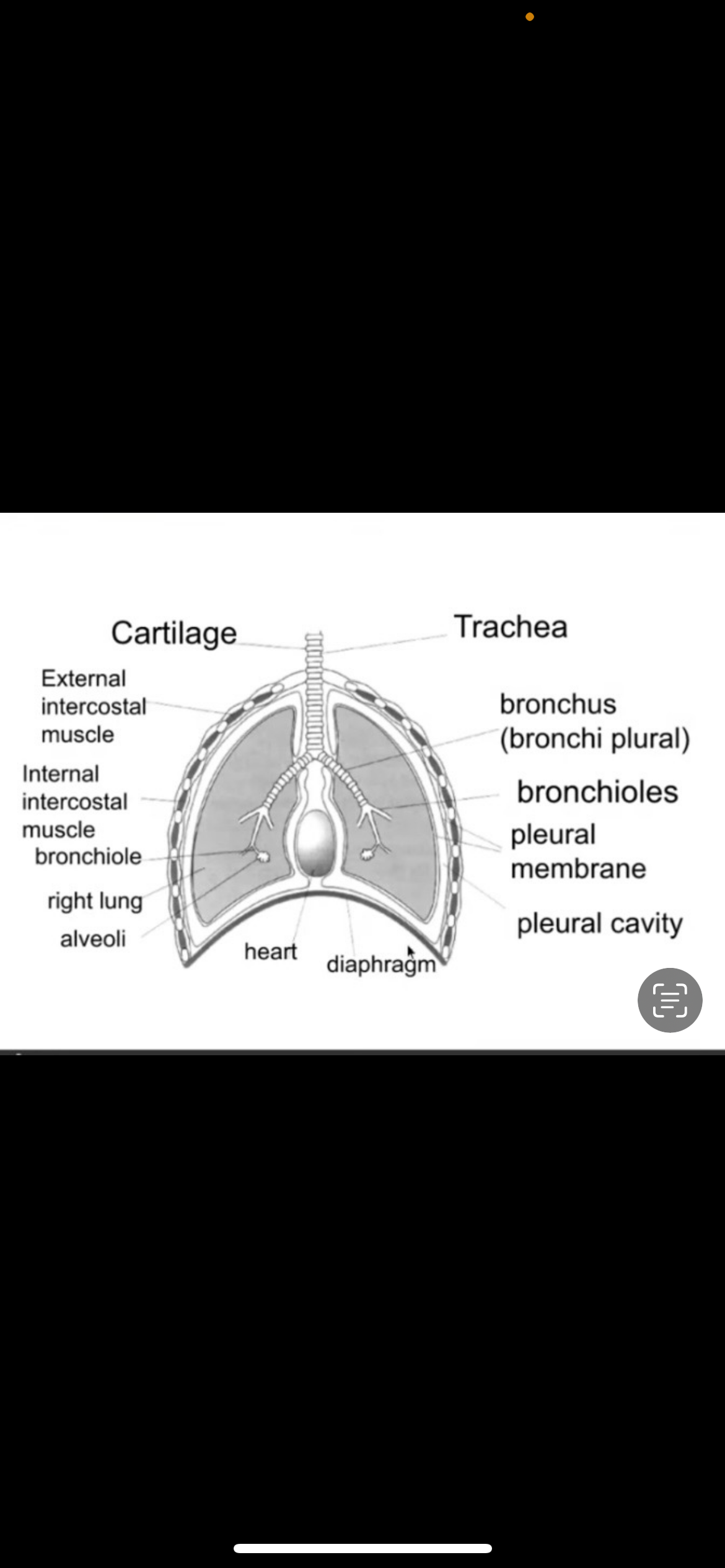
whats the function of goblet cells?
they secrete mucus which traps dust/bacteria that enters the lungs
whats the function of cilia?
they waft mucus to top of trachea/back of mouth where it is swallowed or coughed up
whats the function of elastic fibres?
they recoil to their original shape to expel air and prevent lungs from bursting
whats the function of smooth muscle?
they contract to restrict the airways
whats the function of cartilage?
it provides strength and support for trachea and bronchi and it helps prevent collapse during breathing in as chest volume increases there will be a lower/negative presssure in the trachea
whats the composition of trachea?
it has c shaped rings of cartilage ,smooth muscle and ciliated epithelial cells
whats the composition of bronchi?
it has pieces of cartilage , smooth muscle , elastic fibers and ciliated epithelial cells
whats the composition of bronchiole?
it has smooth muscle , elastic fibres , squamous epithelial cells
whats the composition of alveoli?
it has elastic fibres and squamous epithelial cells
whats the process of inspiration?
1) diaphragm contracts and flattens
2) ribs move up and out , external intercostal muscles contract , internal relax
3) volume of thorax increases
4) pressure in thorax decreases
5) air moves in lungs along pressure gradient
whats the process of expiration?
1) diaphragm relaxes and rises
2) ribs move down and in , external intercostal muscles relax , internal contract
3) volume of thorax decreases
4) pressure in thorax increases
5) air moves out of lungs along pressure gradient
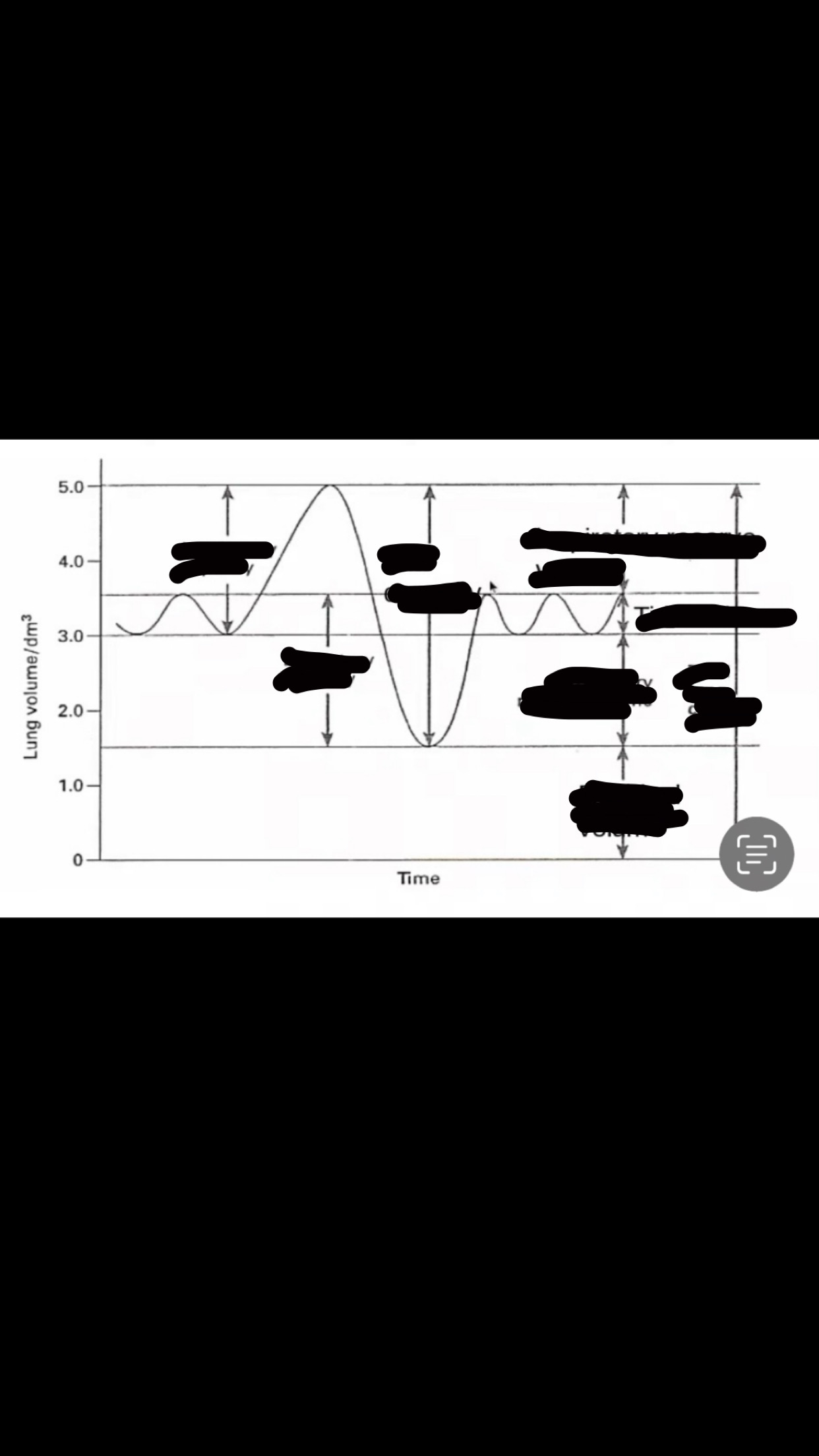
label the spirometer graph
image
define tidal volume
the volume of air breathed in and out in single breath at rest
define vital capacity
maximum volume of air that can be breathed in and out in single breath
how do you work out pulmonary ventilation?
pulmonary ventilation
tidal volume x breathing rate
whats oxygen uptake?
air breathed into spirometer once carbon dioxide has been removed by the soda lime
what are the four mechanisms of ventilation and gas exchange in fish?
many lamellae , large SA for gas exchange
presence of secondary lamellae on primary lamellae
short distance between blood and water
to maintain concentration gradient for faster diffusion
explain the steps of gas exchange in fish
1) fish opens mouth , increase in volume within buccal cavity
2) decrease in pressure
3) water is forced in through mouth and push along pressure gradient
4) fish closes mouth , decrease in volume within buccal cavity
5) increases pressure
6) forces water out over the gill filaments and out operculum
explain the tracheal system mechanism of ventilation and gas exchange in insects
spiracles=small openings on side of body , allow diffusion of oxygen into organism and carbon dioxide out
tracheoles=branches from trachea all over body taking oxygen to where needed mainly muscles for aerobic respiration to create ATP for muscle contraction
explain the tracheole fluid mechanism of ventilation and gas exchange in insects
muscle contracts-aerobic respiration-organism needs to switch to anaerobic because it will run out of oxygen availability
insect produces lactic acid which reduces the PH of cells in surrounding muscle tissue
as a result , fluid moves from tracheoles into surrounding muscle tissue via osmosis because of the lactic acid build up
tracheal fluid moved into muscle fibres surrounding tracheoles
more oxygen can diffuse further into muscle fibres so more oxygen available for aerobic respiration
explain the mechanism of ventilation and gas exchange in insects by how insects have air reserve
air can be stored incase organisms needs to close spiracles
when insects move it helps change volume of body cavity therefore causes changes in the pressure therefore helping to draw air in and out