L73: stomach of polygastric animals
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
181 Terms
MCQ: which animal is a pseudoruminant?
camelids
MCQ: how many compartments are present in the ruminant stomach?
4
what are the compartments of the ruminant stomach?
rumen
reticulum
omasum
abomasum
what are the two types of feeding patterns in ruminants?
grazers
browsers
polygastric stomach
a complex stomach divided into multiple compartments that aids in digestion of plant materials mainly cellulose
what is another name for ruminants?
foregut fermenters as fermentation happens cranially in the gut
what do polygastric animals rely on for digestion?
microbial fermentation to break down tough plant fibers before digestion
list the animals that are considered ruminants
cow
sheep
goat
deer
buffalo
antelopes
what is another name for the rumen?
paunch
what is the location of the rumen?
on the left side of the abdominal cavity from the diaphragm to pelvis
what is the position of the rumen?
extends from the 7th rib to the pelvis
what is the clinical significance of the rumen?
palpable and surgically accessible at the paralumbar fossa
what is the largest compartment of the stomach in adult ruminants?
rumen
what part of the stomach produces and absorbs volatile fatty acids?
rumen
what are the functions of the rumen?
store and soften ingested food
fermentation and digestion of cellulose
microbial action
produce and absorb VFAs
generate gases
what part of the stomach generates methane and carbon dioxide which will be released via burping?
rumen
how do we access the rumen?
via parietal surface on the left side by paralumbar fossa
what view do we see the omasum?
right lateral view
what is the visceral/right surface of the rumen related to?
liver, instestines, omasum, and abomasum
ruminal grooves
external linear depressions follows by muscular internal folds
which longitudinal groove is considered incomplete?
right
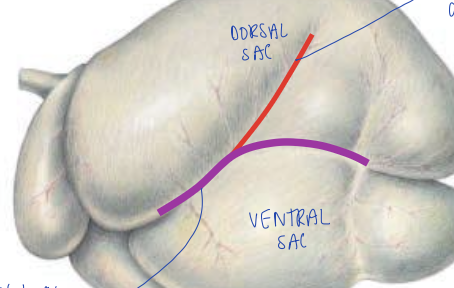
what groove is the red line?
left accessory
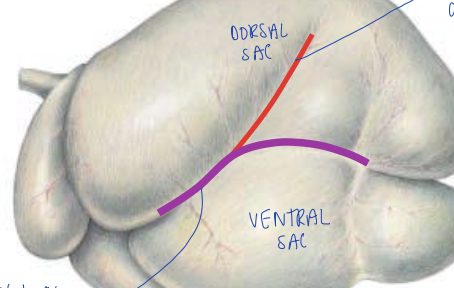
what groove is the purple line?
left longitudinal groove
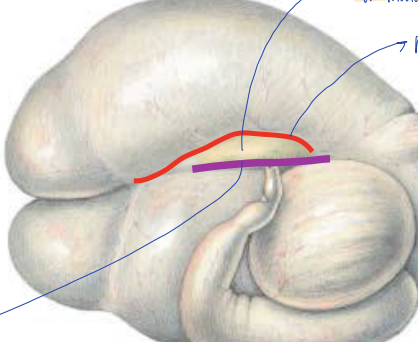
what groove is the red line?
right accessory groove
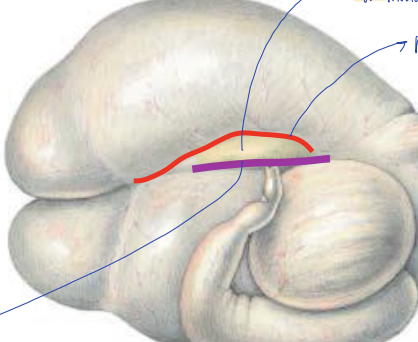
what groove is the purple line?
right longitudinal groove
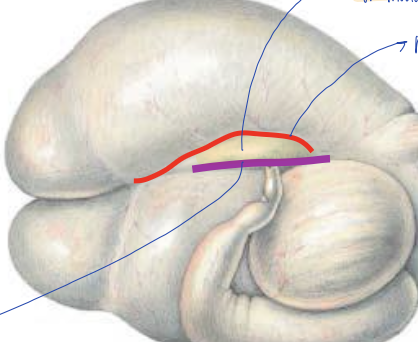
what is the space between the two grooves in the picture shown called?
ruminal island / insular ruminal
ruminal island
space between the right longitudinal and right accessory groove
right accessory groove
diverges away from longitudinal grooves to caudal aspect of rumen
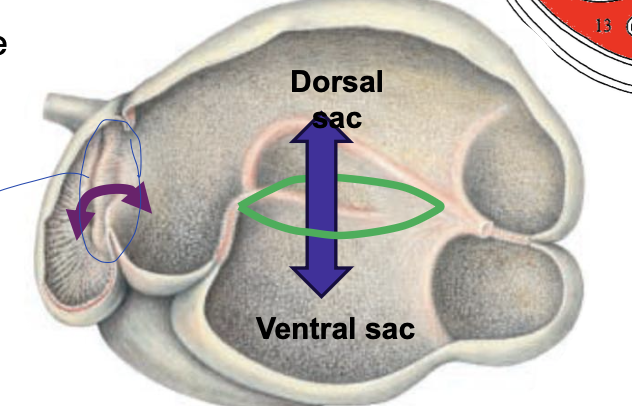
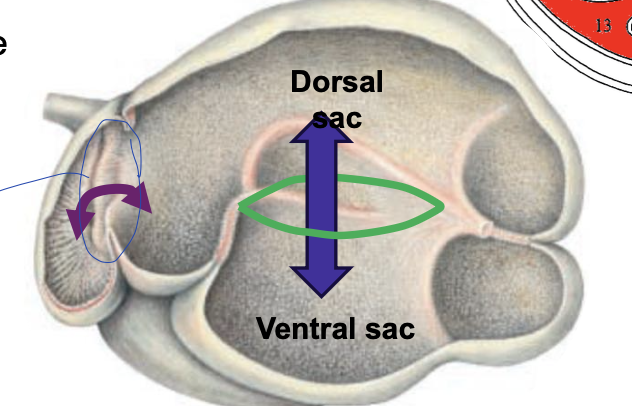
cranial and caudal transverse grooves
where grooves meet around the rumen to divide the rumen into a dorsal sac and ventral sac
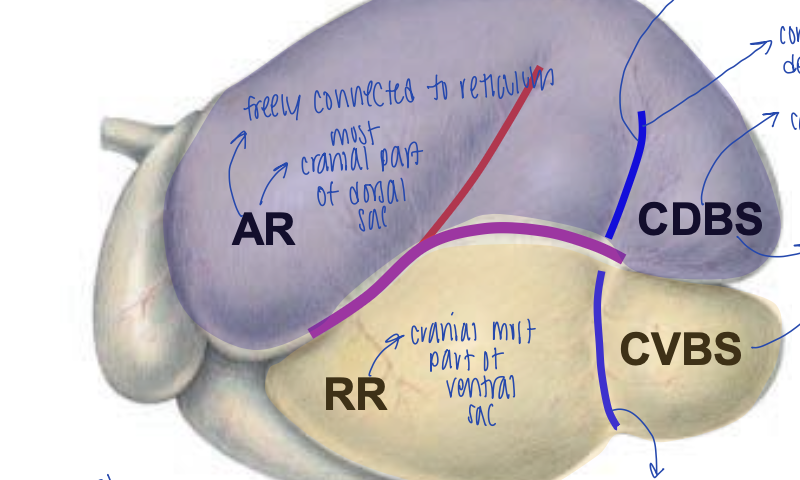
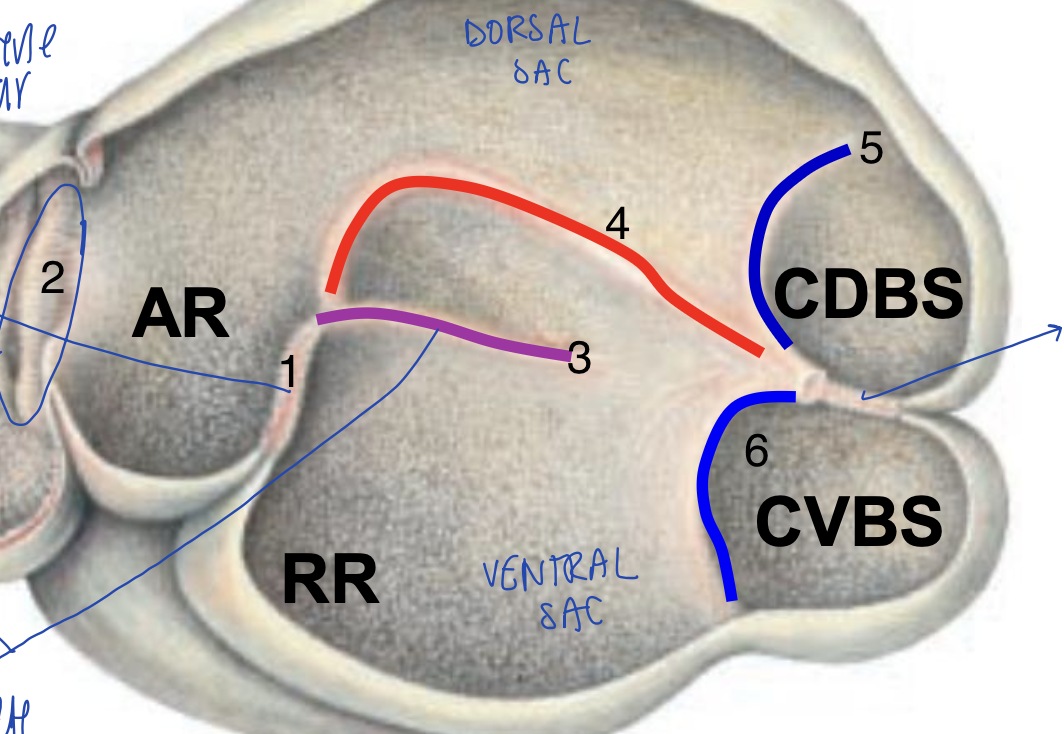
what is the cranial most dorsal sac of the rumen?
atrium ruminis (AR)
what do the ruminal grooves provide an attachment for>
attachment point for omentum and lodging area for nerves and blood vessels
what is the cranial most ventral sac of the rumen?
recessus ruminis (RR)
what is the caudal most part of the dorsal sac?
caudo-dorsal blind sac
what is the caudal most part of the ventral sac?
caudo-ventral blind sac
what structure within the rumen is freely connected to the reticulum?
atrium ruminus
what is the blue groove in the blue colored portion of the picture called?
left dorsal coronary groove

what is the blue groove in the yellow colored portion of hte picture called?
left caudoventral groove
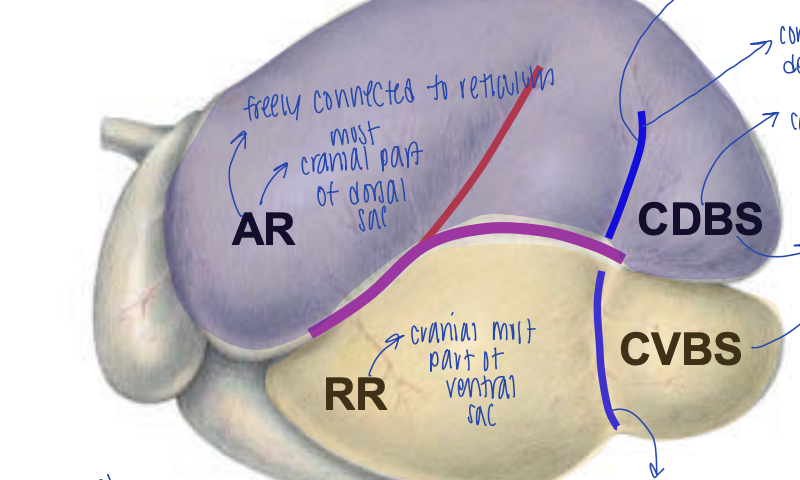
does this picture show the parietal or visceral surface of the rumen?
parietal
does this picture show the parietal or visceral surface of the rumen?
visceral

what is the blue groove in the blue portion called?
right dorsal coronary sac
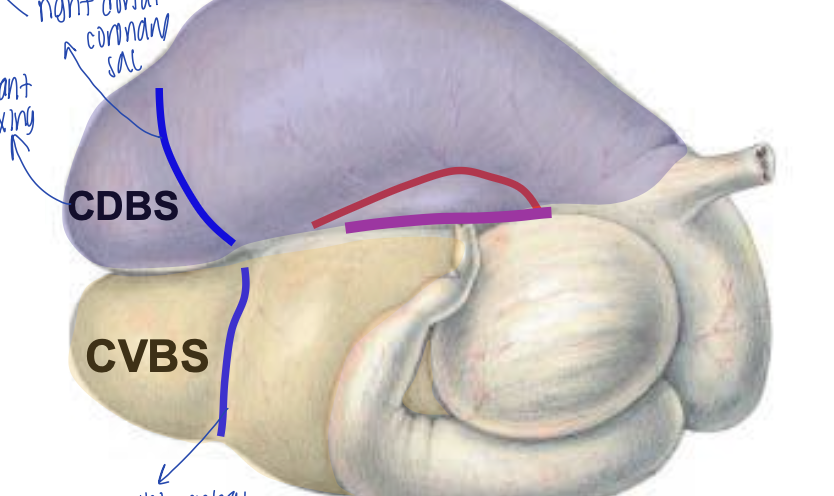
what is the blue groove in the yellow portion called?
right ventral coronary groove
what structure separates AR from RR in the rumen?
cranial pillar
what structure separates the caudodorsal blind sac from the caudoventral blind sac?
caudal pillar
what structure is the opening between the reticulum and AR of rumen?
ruminoreticular fold
what do the infoldings of the ruminal wall lack?
serosa, these are in the external surfaces of the rumen and reticulum
what structure accompanies ruminal grooves inside of the rumen?
pillers
what are pillars important for in the rumen?
proper fermentation of ingesta
what is 1?
cranial transverse piller
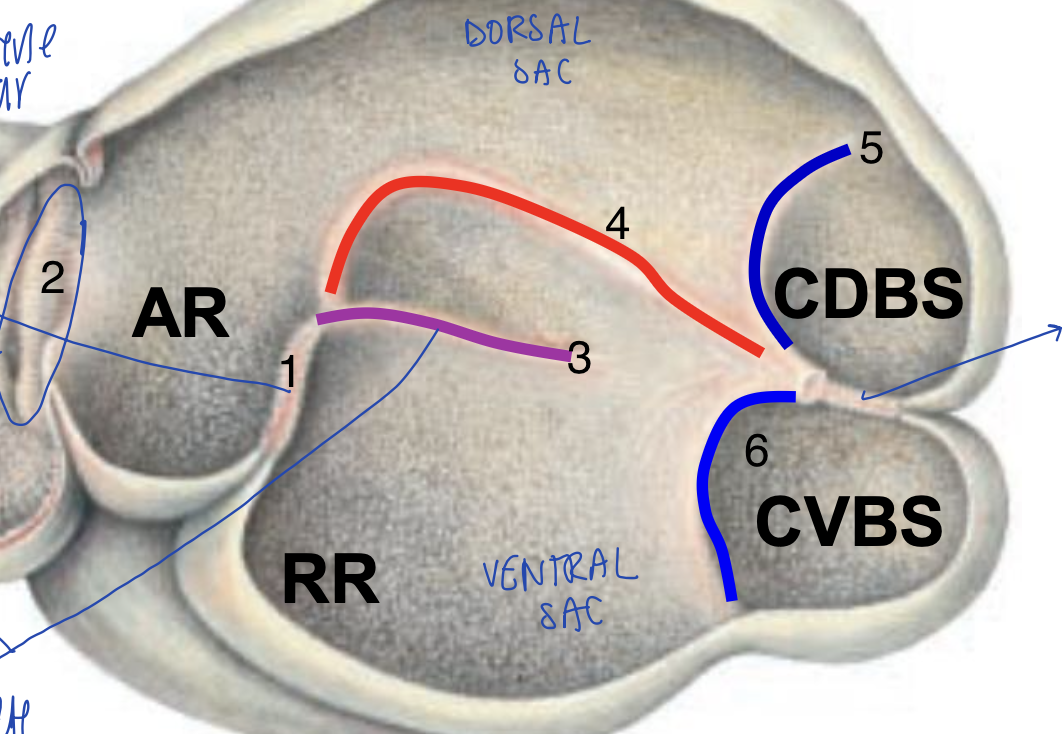
what is 2?
ruminoreticular fold

what is 3?
right longitudinal pillar
what is 4?
right accessory pillar
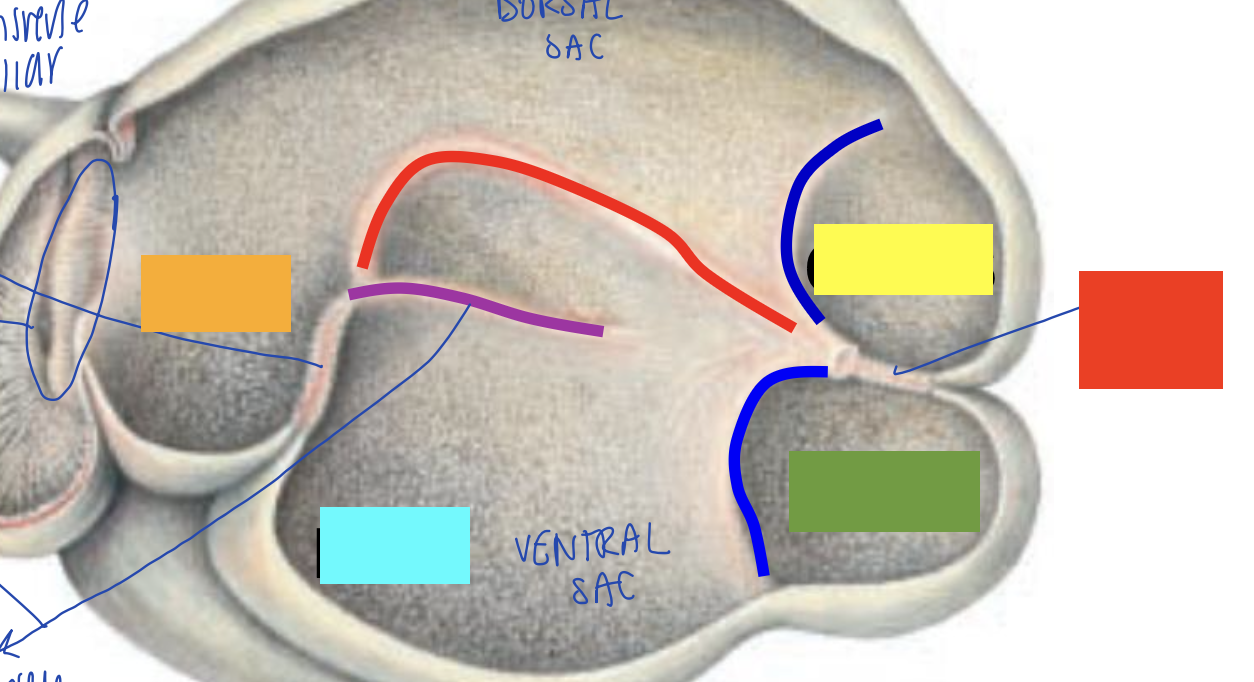
what is orange?
atrium ruminis
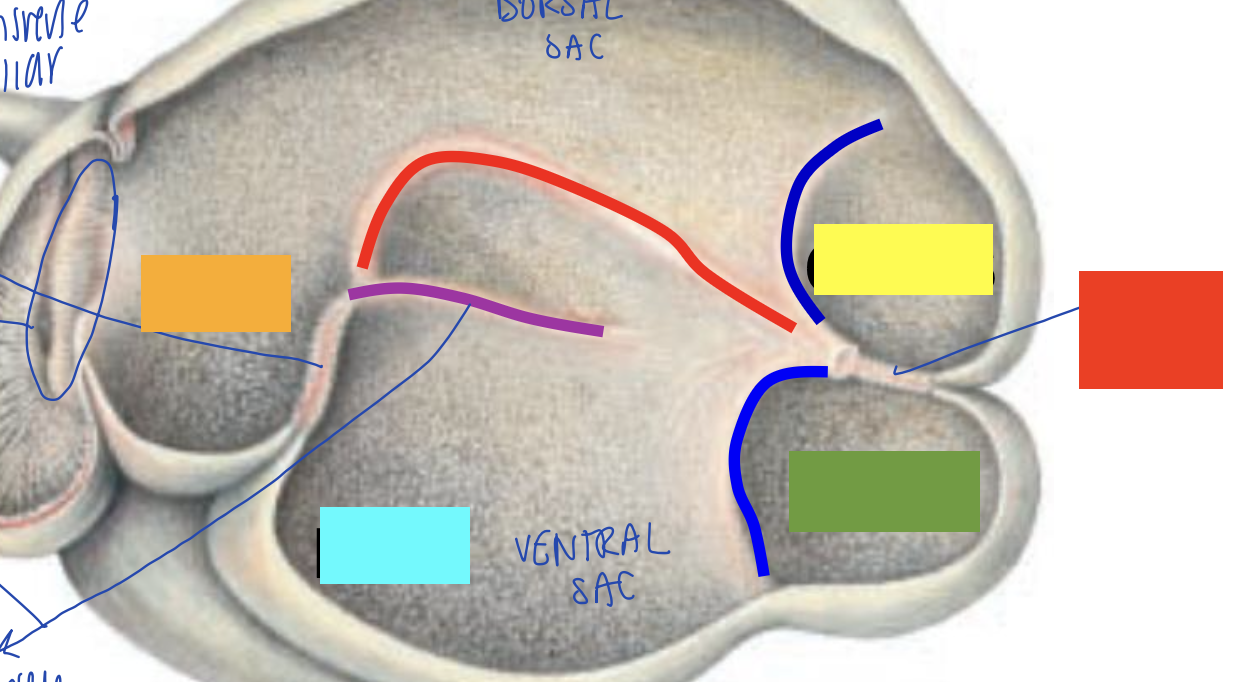
what is blue?
recessus ruminis
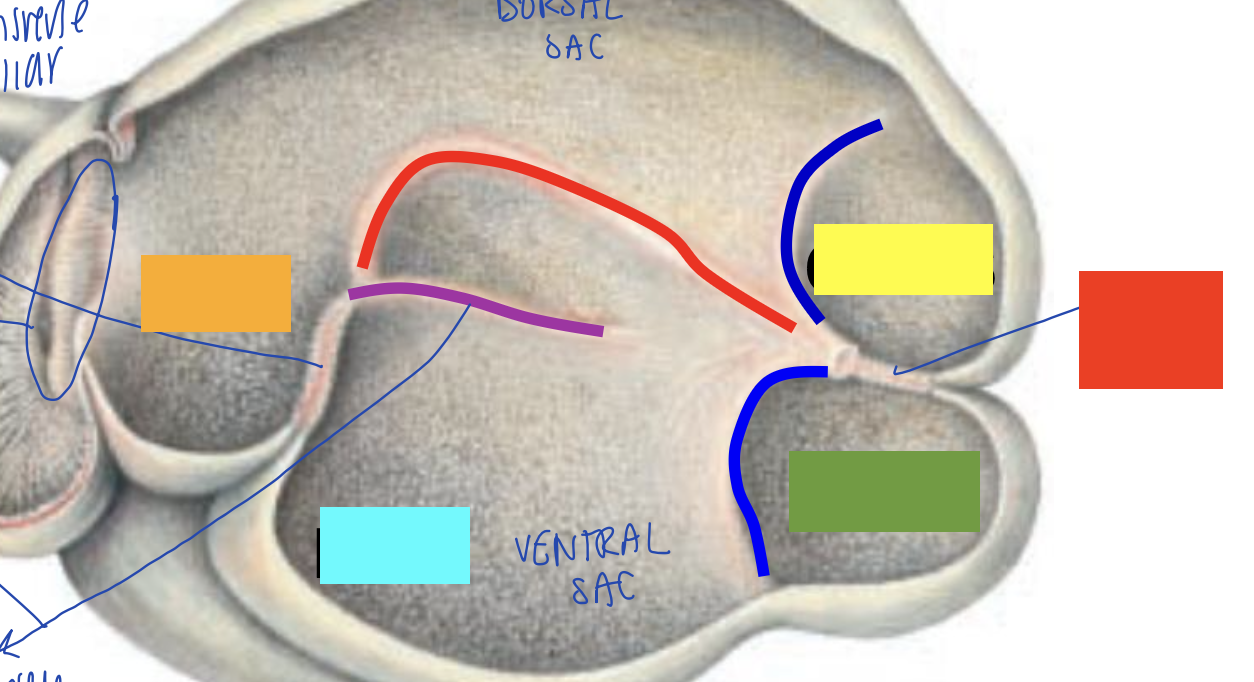
what is yellow?
caudo-dorsal blind sac
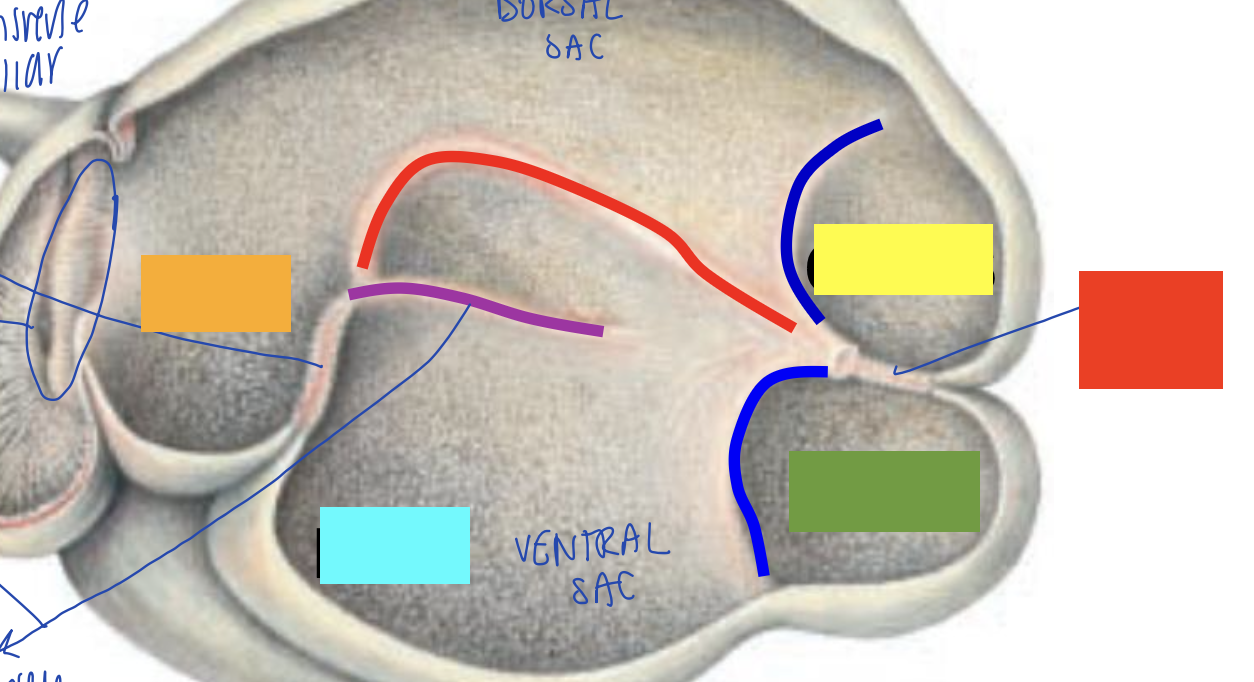
what is green?
caudo-ventral blind sac
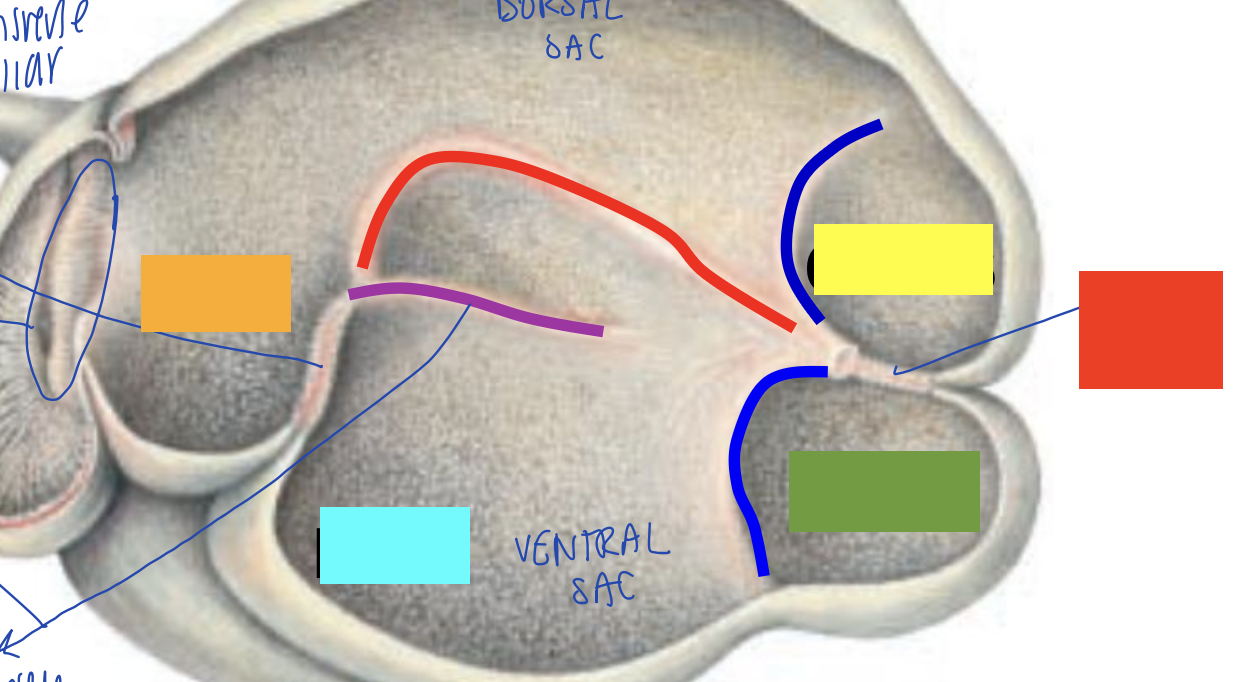
what is red?
caudal pillar
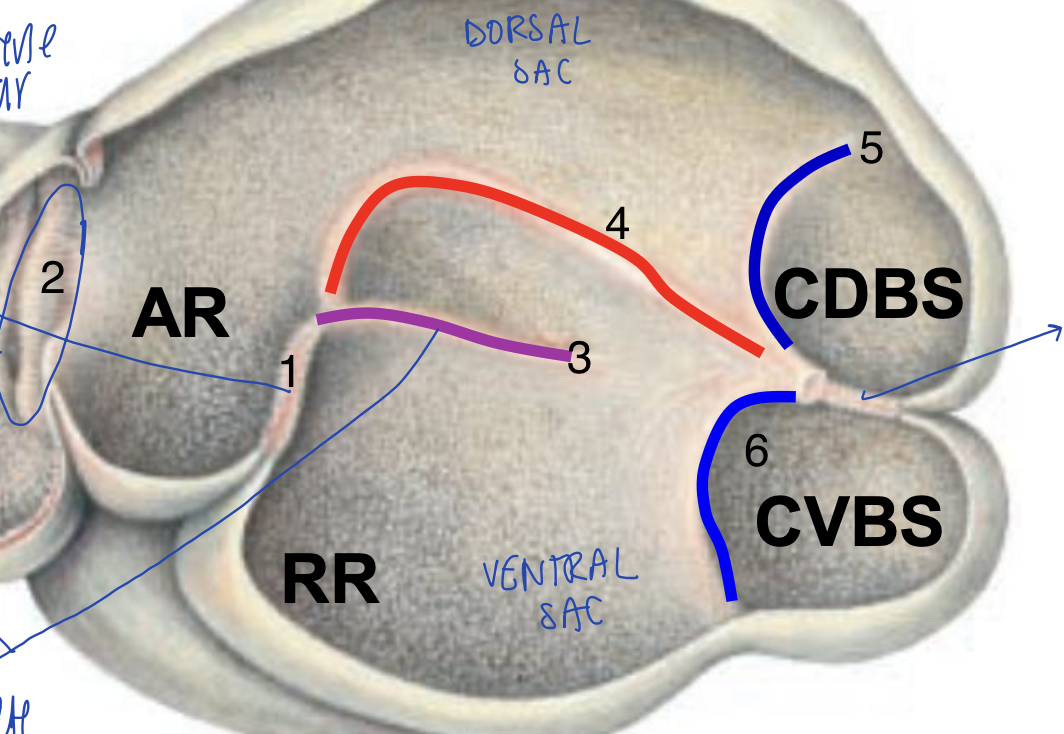
intraruminal ostium or opening
large opening encircled by pillars between dorsal and ventral sacs of the rumen
ruminoreticular ostium
opening between the rumen and the reticulum
what is the green circle?
intraruminal ostium
what is the purple arrow showing?
ruminoreticular ostium
what guards the ruminoreticular ostium?
ruminoreticular fold
what type of epithelium is in the mucosa of the rumen?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what does the mucosa layer of the rumen lack?
muscularis mucosae
what structures are present in the submucosa of the rumen?
connective tissue
blood vessels
nerves
what is not present in the submucosa layer of the rumen?
glands meaning that there will not be a secretory function
what layers are the ruminal papillae present in the rumen?
mucosa and submucosa
where will there not be ruminal papillae in the rumen?
ruminal pillars
where in the rumen will papillae be short and less in quantity?
at the dorsal aspect of the rumen
what do the ruminal papillae do in the ventral aspect of the rumen?
absorption of volatile fatty acids and gases
MCQ: where is the rumen located in the abdominal cavity?
on the left side
what else can the reticulum be called?
honeycomb
what is the location of the reticulum?
cranial to the rumen near the diaphragm
what is the position of the reticulum?
between the 6th and 8th ribs close to the heart
which part of the stomach in polygastric animals has a predisposition to Hardware disease?
reticulum
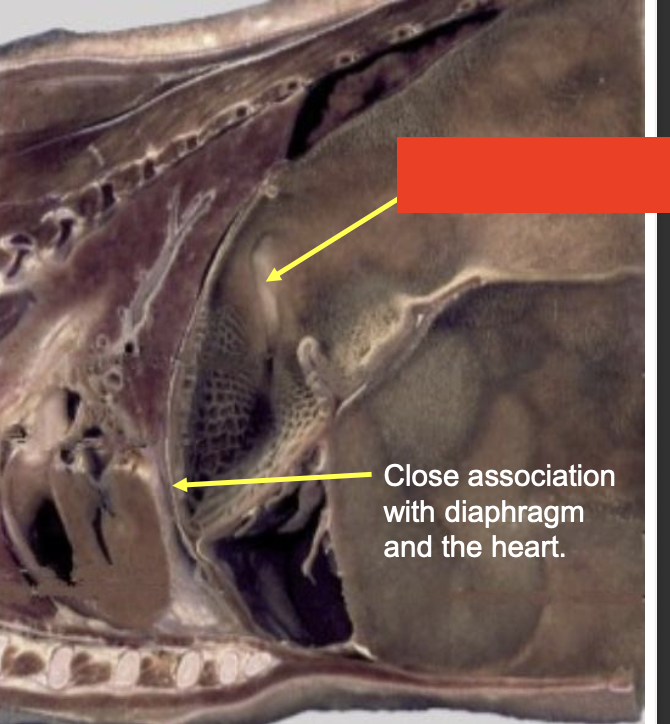
what is the yellow arrow pointing to (covered by red box)?
reticular groove

what portion of the stomach is this?
reticulum
what are the functions of the reticulum?
delay transit of ingesta to increase time of VFAs
sort and filter ingested material
aid in cud regurgitation
what structure of the stomach has a honeycomb appearance?
reticulum
what is the epithelium of the mucosa in the reticulum?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what structure is present in the mucosa of the reticulum?
muscularis mucosae present
what does the submucosa of the reticulum lack?
glands
what layers of the reticulum have reticular crests with conical papillae?
mucosa and submucosa
what is another name for the omasum?
many piles or book stomach
what is the location of the omasum
right side of the abdomen between the reticulum and abomasum
what is the position of the omasum?
lies between the 7th and 11th rib, in contact with the liver
what structure of the stomach will make an impression on the liver?
omasum
interlaminar recesses
spaces between the sickle-shaped omasal laminae
what is the function of the omasal laminae?
prevent dilution of content going into the abomasum
increase surface area to better absorb water
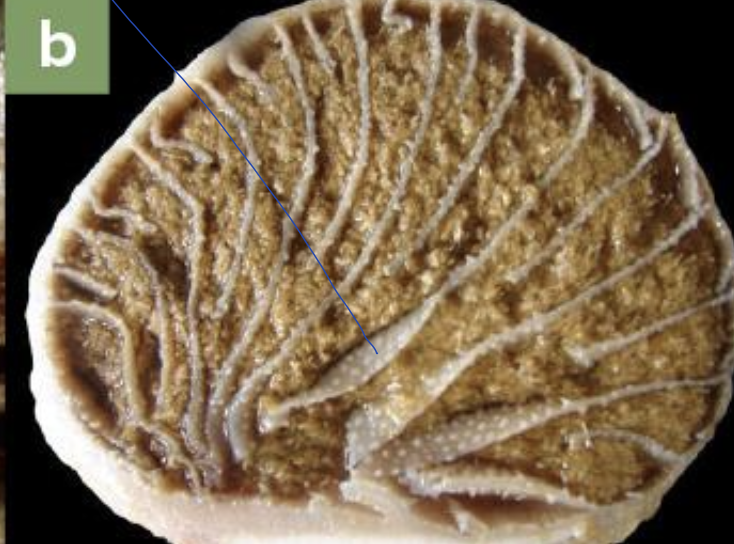

what does the image show?
wall of omasum
what is the location of the omasal groove?
at the base of the omasum; it joins the reticulo-omasal ostium to the omaso-abomasal ostium
what is the function of the omasum?
absorb water
reduce particle size
filtrate incoming food particles

what is 1?
omasabomasal opening
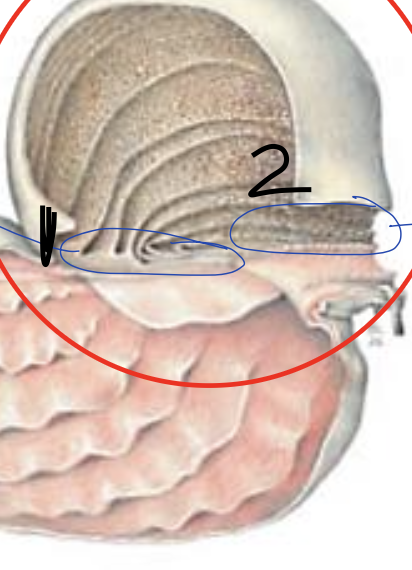
what is 2?
reticulomasal opening
what is the epithelium present in the mucosa of the omasum?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what is the only structure of the stomach that will have glands in the submucosa?
abomasum
where are omasal laminae with papillae present in the omasum?
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
what is another name for the abomasum?
true stomach
what is the location of the abomasum?
ventral (lower) abdomen mainly on the right side
what is the position of the abomasum?
from the 9th-12th rib partially into the lower abdomen