5.3 - thermoregulation
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
behavioural & physiological
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is the body’s core temp?
36.8 Celsius
define thermoregulation
the maintenance of body temperature at approximately 36.8°C by balancing heat loss and gain.
what is the purpose of thermoregulation? Why do we need to balance our heat loss & gain
to maintain a constant internal body temperature (keep body core temp within tolerance limits) independent of the environmental temperature
How does thermoregulation occur?
occurs by the control of heat exchange & metabolic activity through physiological & behavioural mechanisms
what causes body heat to increase?
increase in metabolism (e.g. due to exercise, stress, etc) or heat absorbed from our surroundings
conduction
convection
radiation
define metabolic rate
The rate at which energy is released by the breakdown of food
what is the temperature cycle?
our core body temp is the lowest in the morning, but the highest in the evening
what can a constant increased body temp cause?
nerve malfunction
change in structure of proteins
death
complete the following:
___ reactions in ___ are very ___ sensitive
chemical reactions in cells are very heat sensitive
complete the following:
most of the time ___ body temp is higher than ____ _____ temp
most of the time internal body temp is higher than surrounding environmental temp
what causes heat loss?
conduction, convection, radiation & evaporation
define radiation
The transfer of energy in the form of waves - no direct contact with source
define convection
The transfer of heat by the movement of liquids or gases e.g. when hot or cold air passes over a body
define conduction
The transfer of heat by direct contact between particles - direct contact
define evaporation
The process of a liquid forming a gas, which absorbs heat energy
identify, define & explain the 2 thermoreceptors
Peripheral thermoreceptors: A temperature receptor in the skin and in some mucous membrane
detect changes in external environment & send info to the hypothalamus
Central thermoreceptors: A thermoreceptor located in the hypothalamus, spinal cord & organs
detect changes in temp of internal environment, sends info to the hypothalamus
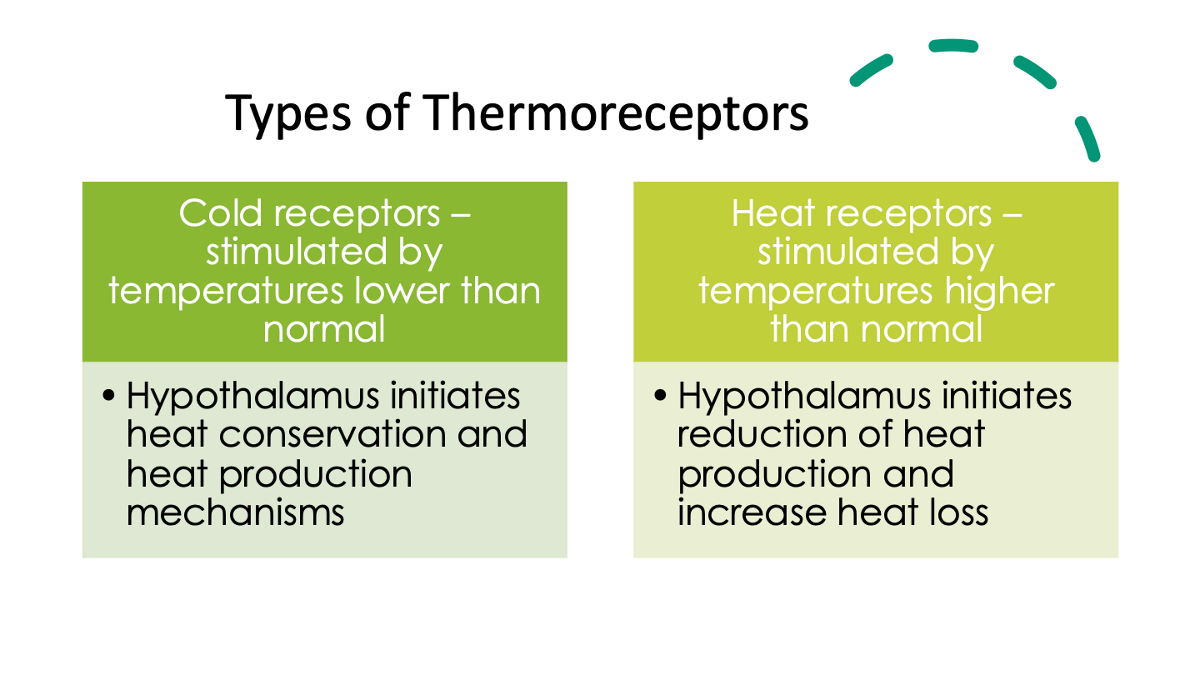
there are cold & heat receptors - how are they stimulated & what does the hypothalamus initiate due to the stimulation of these receptors?
name the 2 ways that the body does to prevent body temp from falling
increasing heat production
reducing heat loss
how does the body increase heat production to prevent body temp from falling?

identify & define how the body reduces heat loss to prevent body temp from falling
vasoconstriction of cutaneous blood vessels (sympathetic nervous system): A decrease in the diameter of arterioles, restricting the flow of blood through them
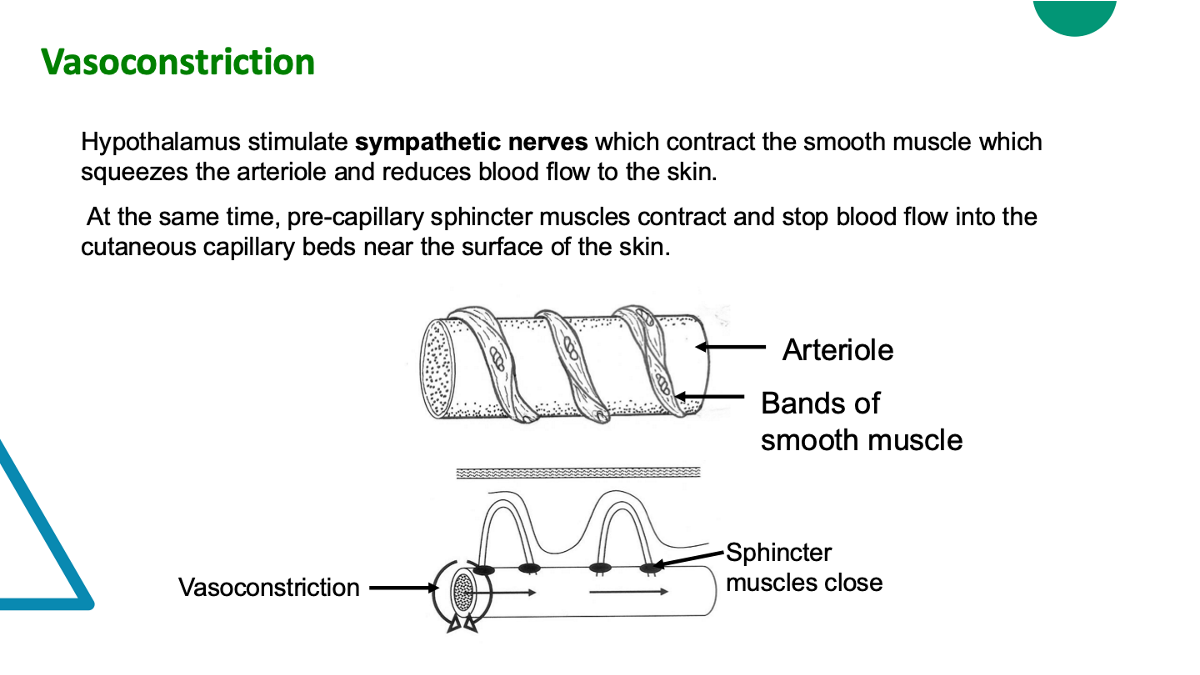
explain vasoconstriction
Blood vessels located in the dermis of the skin carry heat to the skin from the core of the body. The diameter of these arterioles is controlled by autonomic nerves. If the diameter of the arterioles is reduced by vasoconstriction, less blood is transported to the capillaries in the skin and the rate of heat loss decreases
name the 2 ways the body prevents body temp from rising?
reducing heat production
increasing heat loss
explain how the body reduces heat production

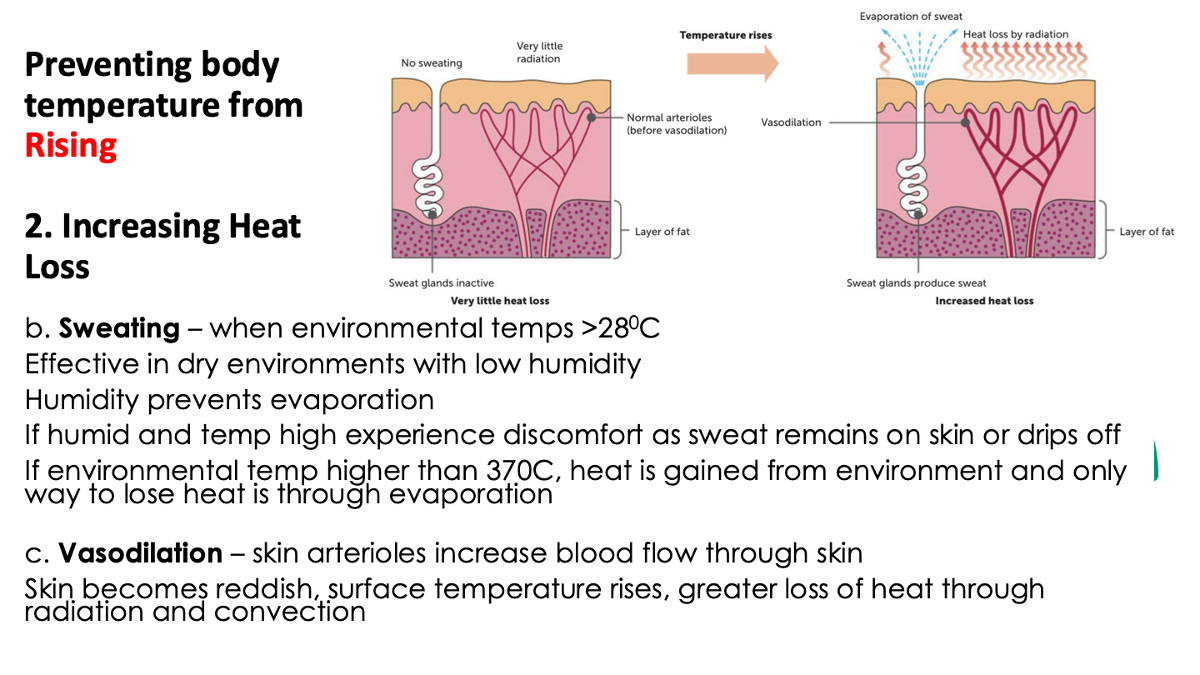
explain how the body increases heat loss
What body temp is considered dangerous & what body temp can cause death
temps around 42 Celsius is considered dangerous
death usually occurs around 45 Celsius
what causes high body temps?
fever & certain environmental conditions
define/explain heat stroke & include a treatment
Heat stroke: The failure of a person’s temperature-regulating mechanisms when exposed to excessive heat

define/explain heat exhaustion
Heat exhaustion: The collapse of a person after exposure to heat, during which their body’s heat-regulating mechanisms continue to function normally

define/explain hypothermia
Hypothermia: Abnormally low body temperature; the temperature drops below the level required to maintain normal body functions
