Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport in Eukaryotic Cells
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Eukaryotic Cells
Contain a Basic Set of Membrane-enclosed Organelles
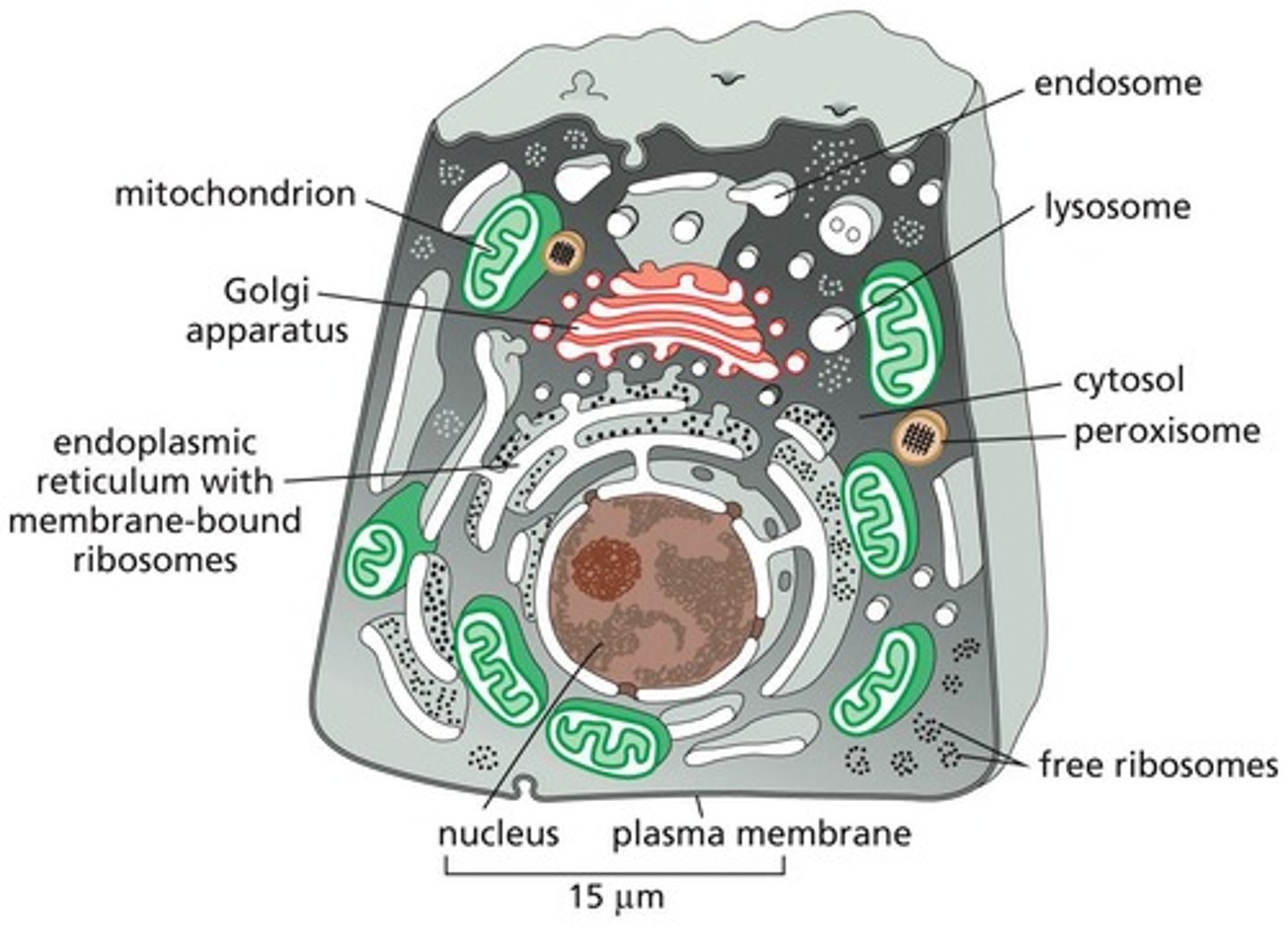
Cytosol
Contains many metabolic pathways; protein synthesis; the cytoskeleton
Nucleus
Contains main genome; DNA and RNA synthesis
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Synthesis of most lipids; synthesis of proteins for distribution to many organelles and to the plasma membrane
Golgi Apparatus
Modification, sorting, and packaging of proteins and lipids for either secretion or delivery to another organelle
Lysosomes
Intracellular degradation
Endosomes
Sorting of endocytosed material
Mitochondria
ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation
Chloroplasts
ATP synthesis and carbon fixation by photosynthesis
Peroxisomes
Oxidative breakdown of toxic molecules
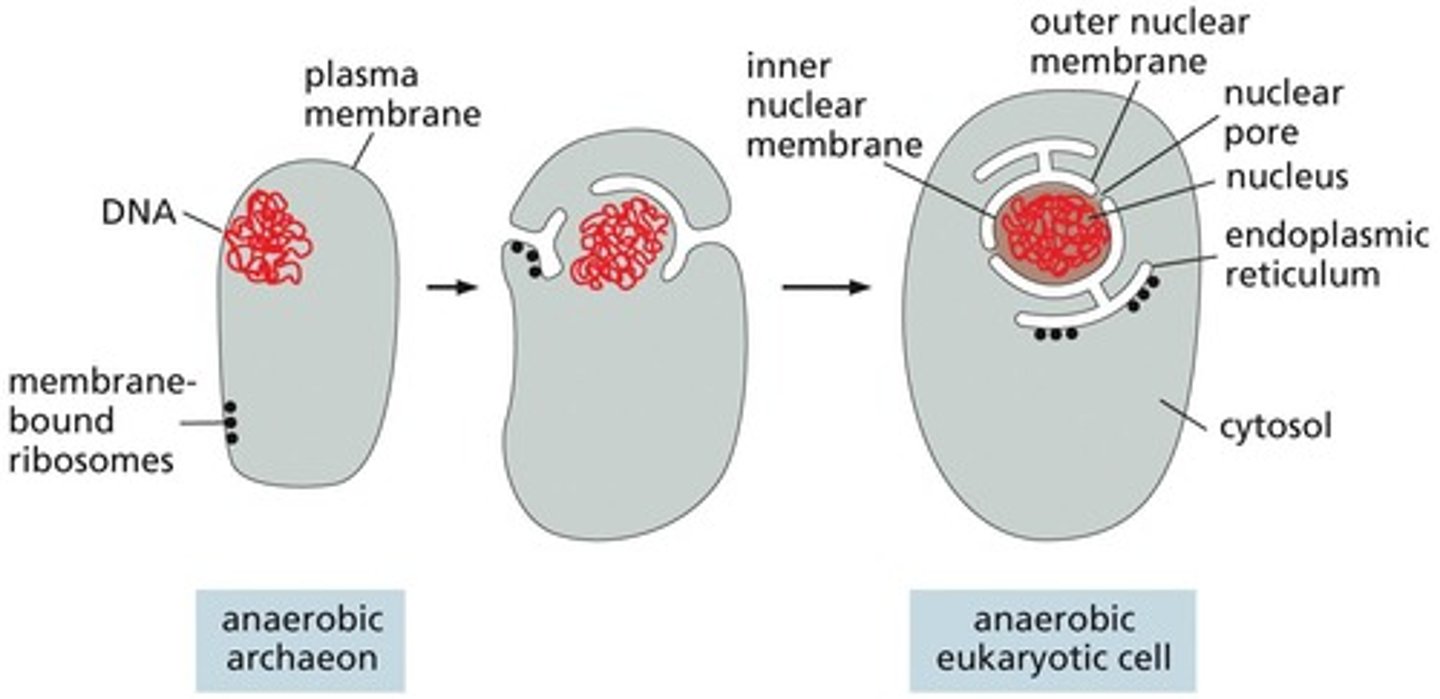
Nuclear Membranes and ER Evolution
May have evolved through invagination of the plasma membrane
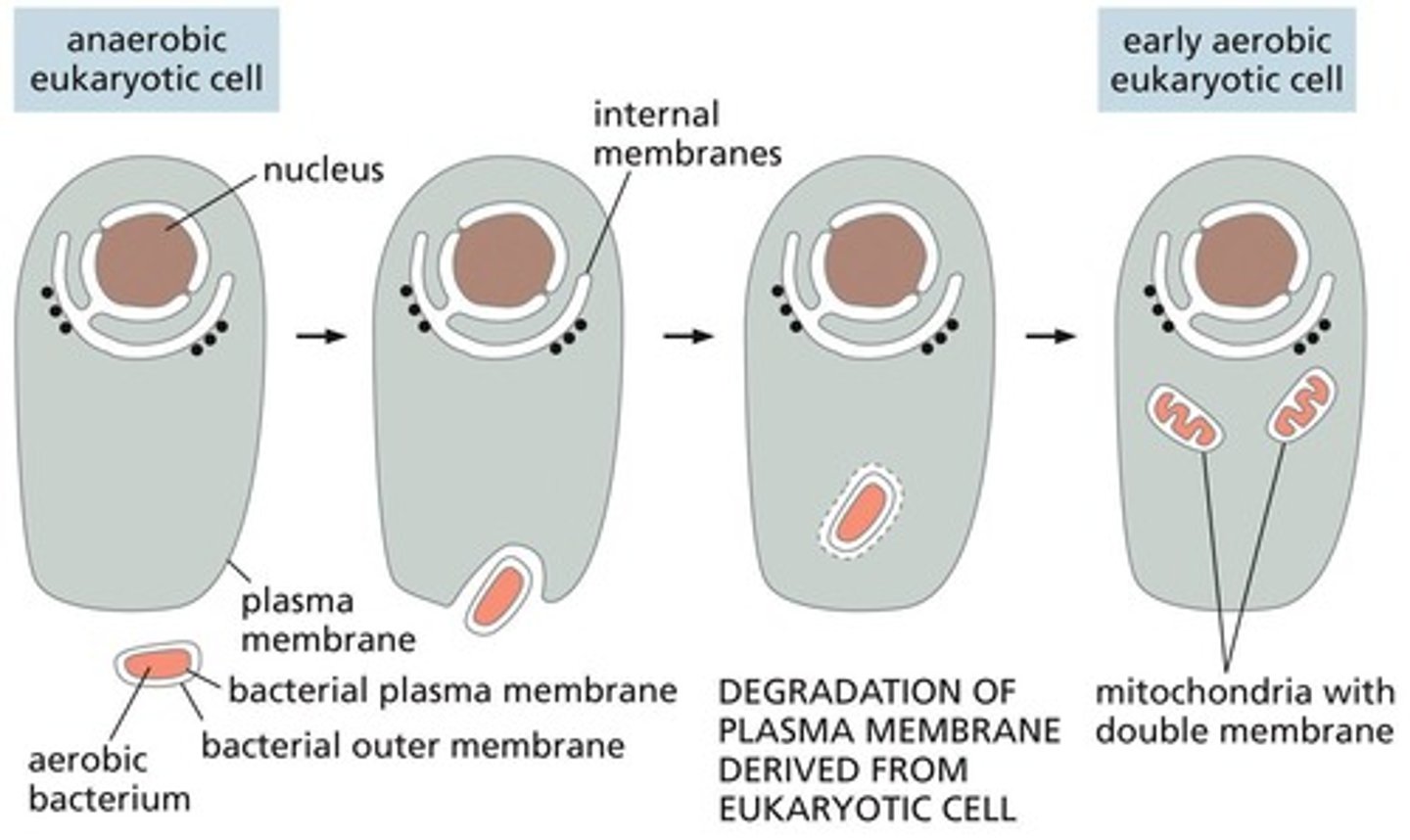
Mitochondria Origin
Thought to have originated when an aerobic bacterium was engulfed by a larger anaerobic eukaryotic cell
Chloroplasts Origin
Thought to have originated when a eukaryotic cell with mitochondria engulfed a photosynthetic bacterium
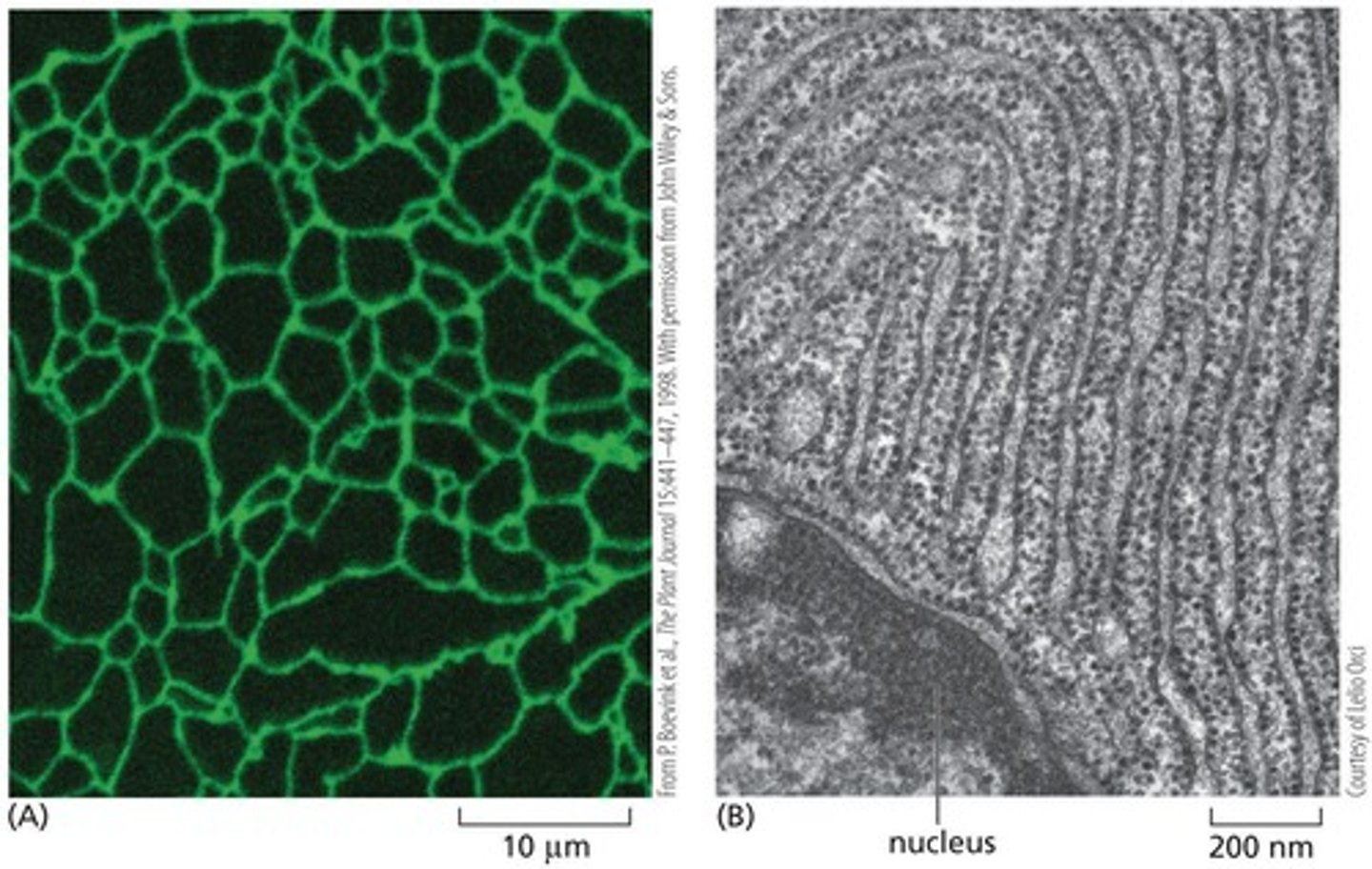
Rough ER
ER that has ribosomes bound to its cytosolic surface
Smooth ER
ER that lacks ribosomes
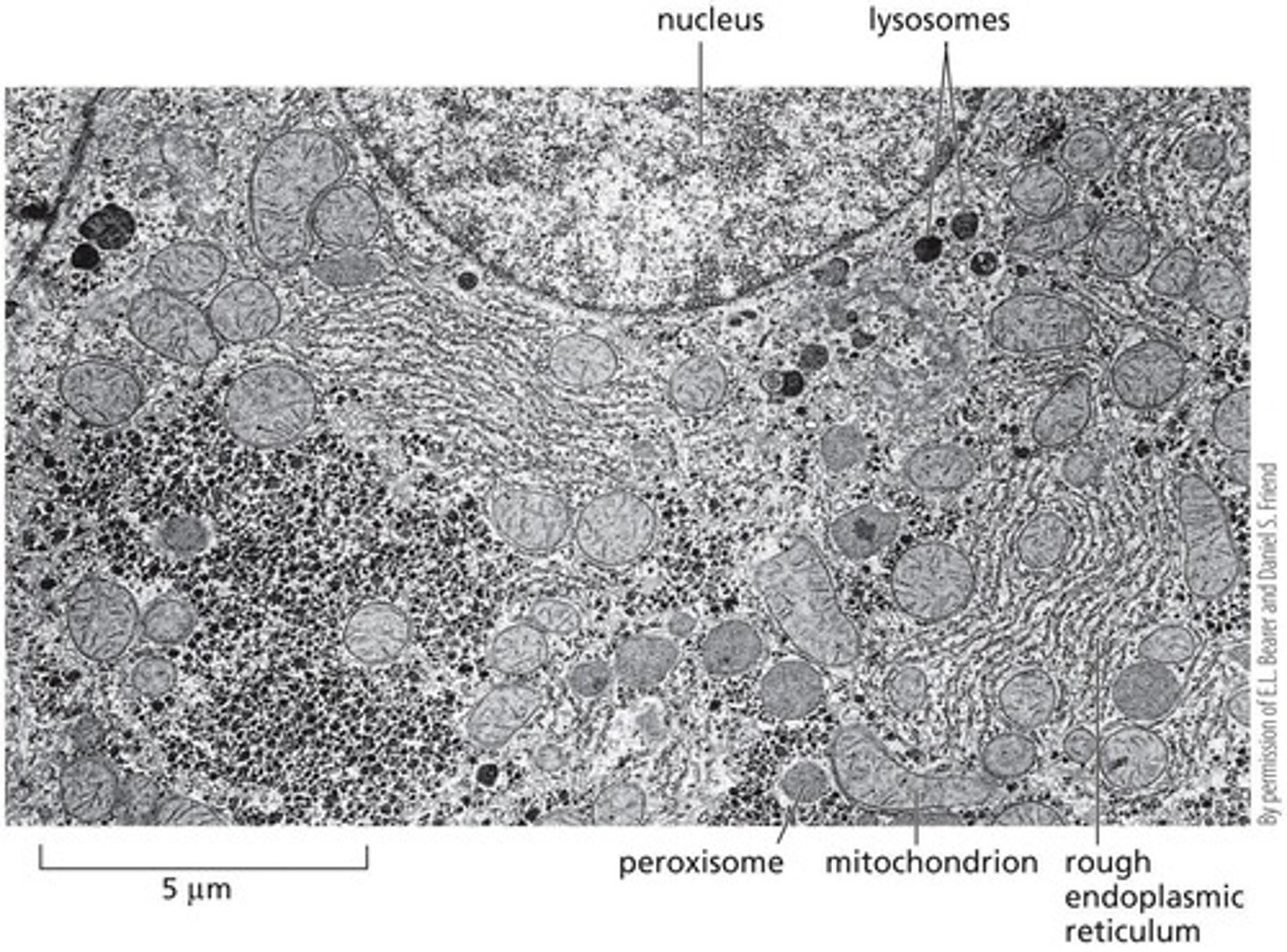
Electron Micrograph
Shows major membrane-enclosed organelles in a liver cell
Glycogen
Aggregates of glycogen and the enzymes that control its synthesis and breakdown
Selectively Permeable Membrane
Separates organelles from the cytosol
Intracellular Compartments
Created by internal membranes in eukaryotic cells
Metabolic Processes
Different processes segregated by internal membranes
Protein Sorting
Process of directing proteins to their appropriate destinations
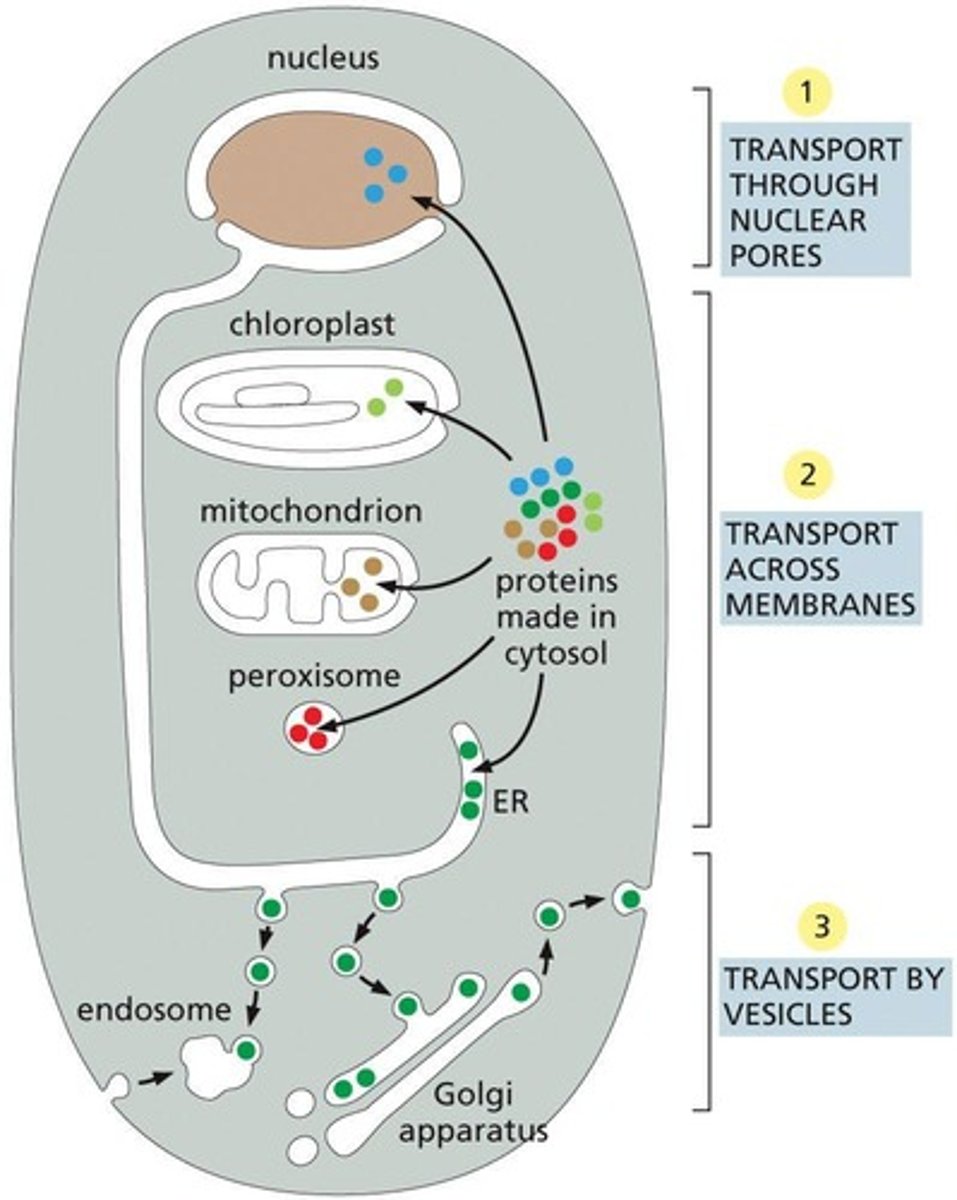
Vesicular Transport
Mechanism for transporting materials between organelles
Secretory Pathways
Pathways for the secretion of proteins and lipids
Endocytic Pathways
Pathways for the internalization of materials from the extracellular environment
Energy Requirement
All processes of protein sorting require energy.
Transport Mechanism 1
The protein remains folded during transport.
Transport Mechanism 2
The protein usually has to be unfolded during transport.
Transport Mechanism 3
The protein remains folded during transport.
Signal Sequences
Signal sequences direct proteins to the correct compartment.
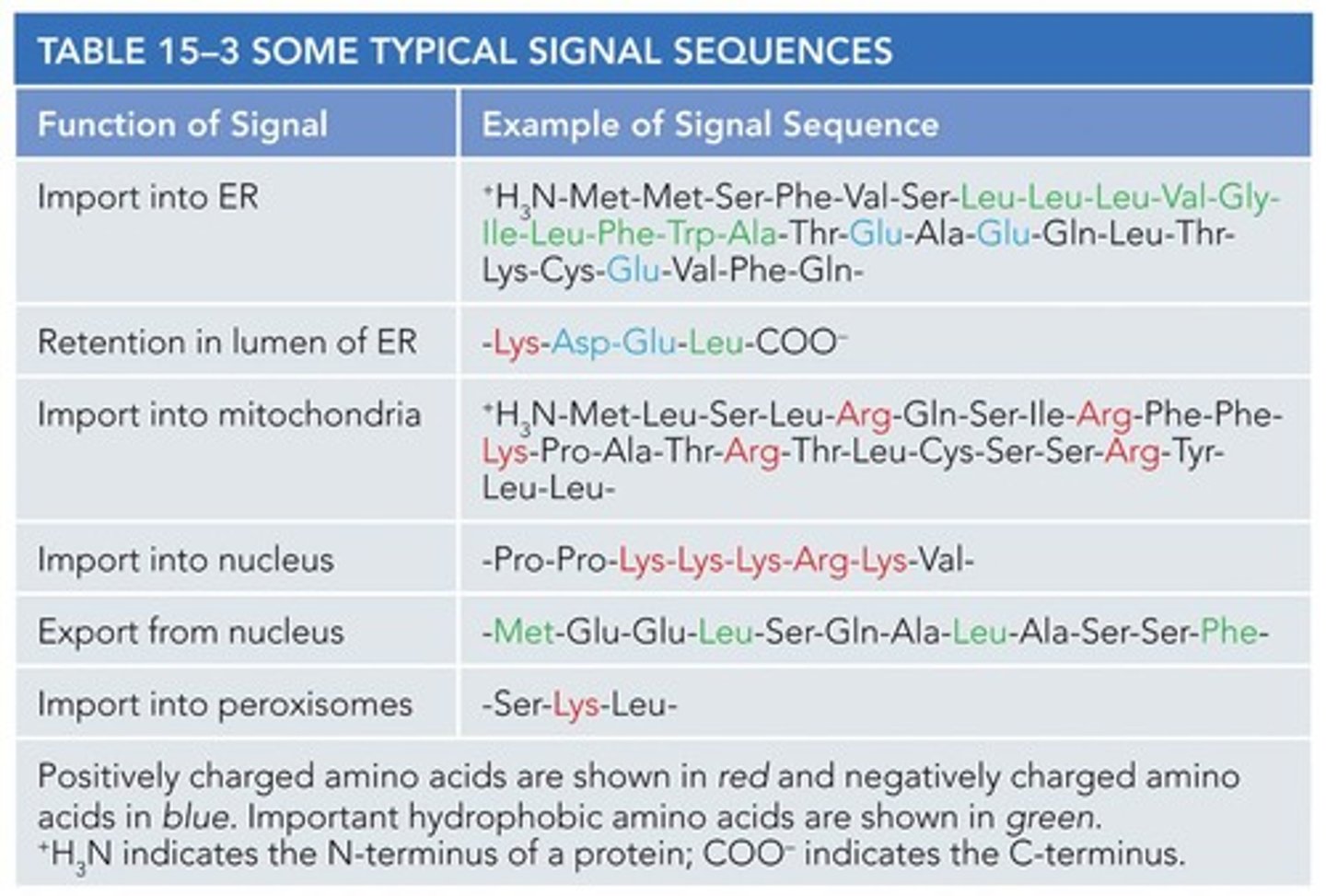
Example of Signal Sequence for ER
+H3N-Met-Met-Ser-Phe-Val-Ser-Leu-Leu-Leu-Val-Gly-Ile-Leu-Phe-Trp-Ala-Thr-Glu-Ala-Glu-Gln-Leu-Thr-Lys-Cys-Glu-Val-Phe-Gln-
Function of Signal for ER
Import into ER.
Example of Signal Sequence for Mitochondria
+H3N-Met-Leu-Ser-Leu-Arg-Gln-Ser-Ile-Arg-Phe-Phe-Lys-Pro-Ala-Thr-Arg-Thr-Leu-Cys-Ser-Ser-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Leu-
Function of Signal for Mitochondria
Import into mitochondria.
Example of Signal Sequence for Nucleus
-Pro-Pro-Lys-Lys-Lys-Arg-Lys-Val-
Function of Signal for Nucleus
Import into nucleus.
Example of Signal Sequence for Nuclear Export
-Met-Glu-Glu-Leu-Ser-Gln-Ala-Leu-Ala-Ser-Ser-Phe-
Function of Signal for Nuclear Export
Export from nucleus.
Example of Signal Sequence for Peroxisomes
-Ser-Lys-Leu-
Function of Signal for Peroxisomes
Import into peroxisomes.
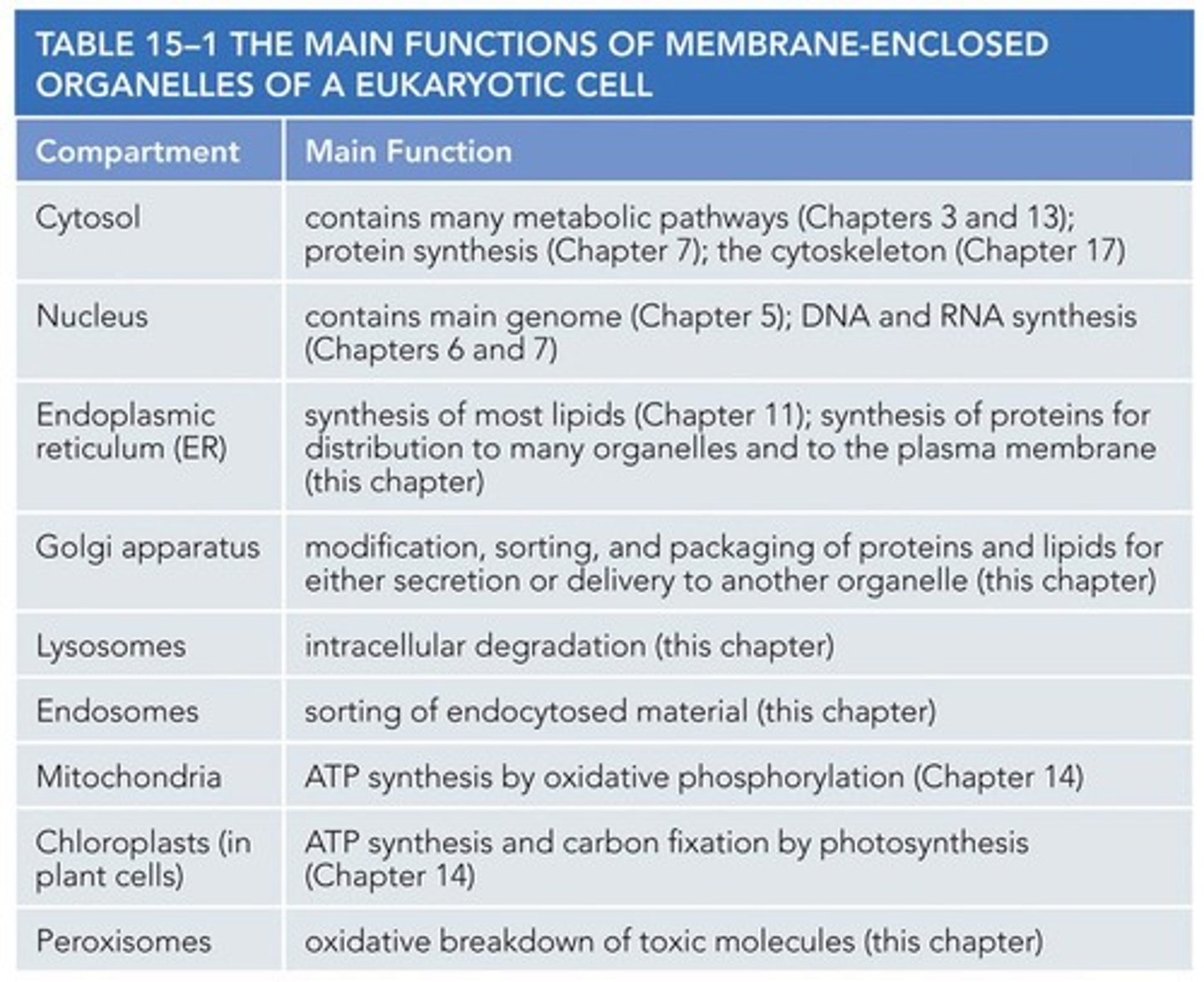
Nuclear Pores
Proteins enter the nucleus through nuclear pores.
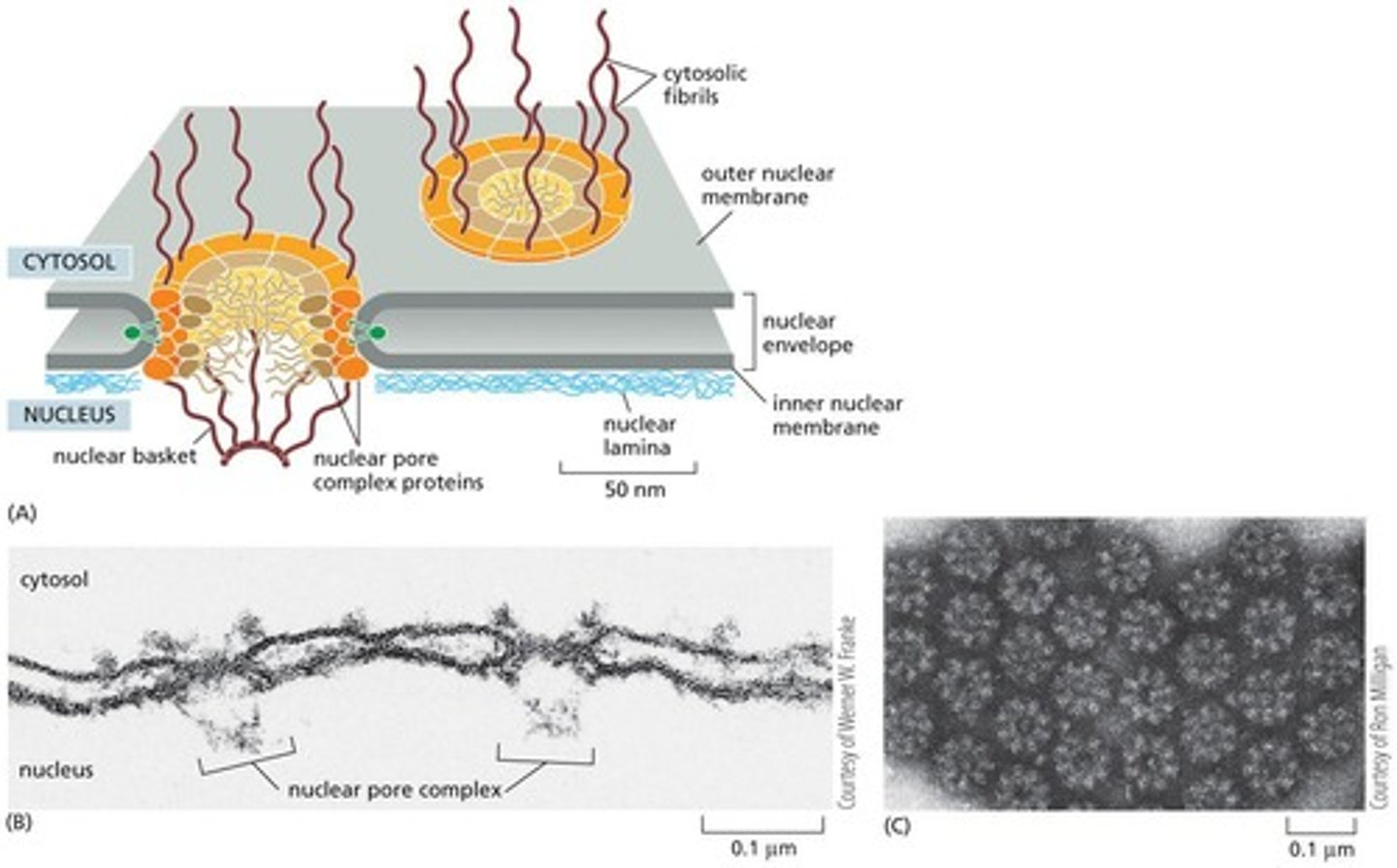
Nuclear Envelope
The double membrane of the nuclear envelope is penetrated by nuclear pores.
Nuclear Pore Complex
Forms a gate through which selected macromolecules and larger complexes enter or exit the nucleus.
Nuclear Localization Signal
Prospective nuclear proteins contain a nuclear localization signal recognized by nuclear import receptors.
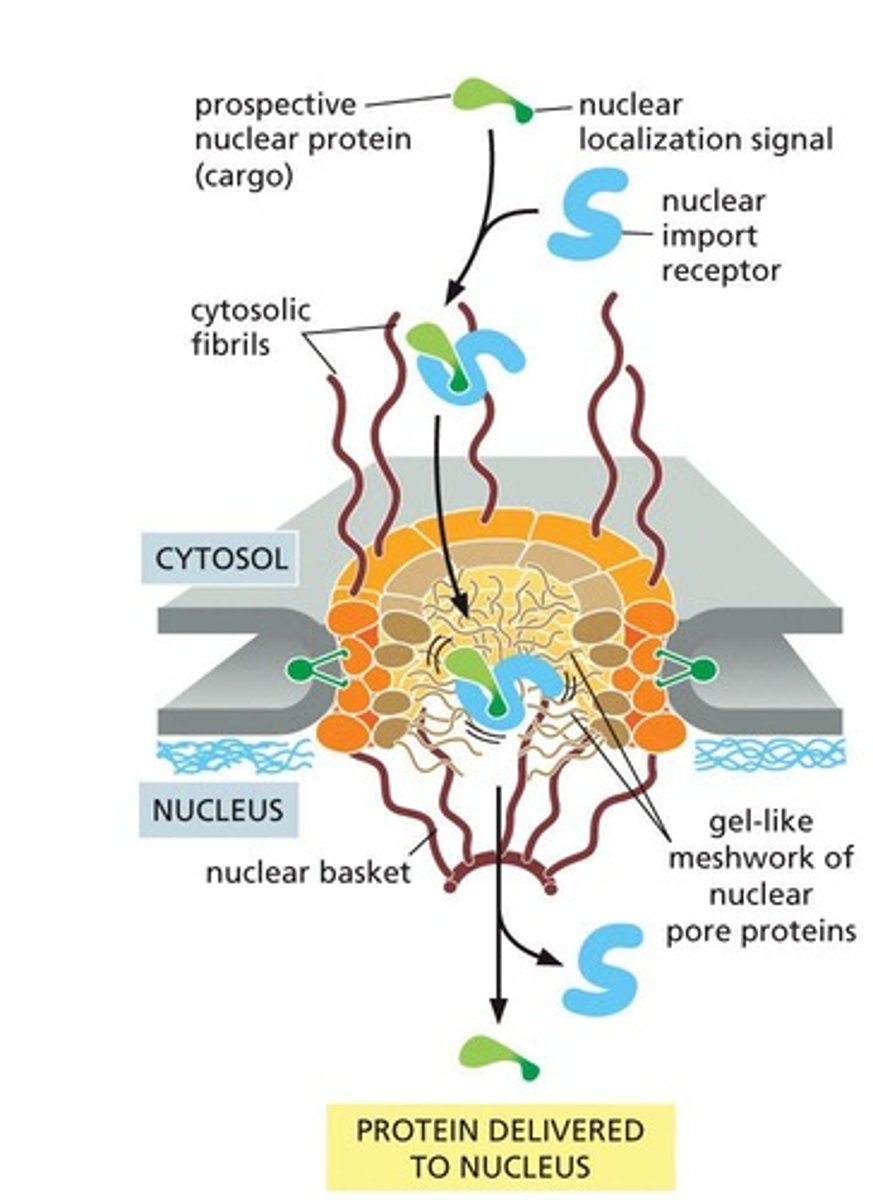
Nuclear Import Receptors
Interact with cytosolic fibrils that extend from the rim of the pore.
Cargo Release
Nuclear entry triggers cargo release.
Receptor Reuse
After cargo delivery, receptors return to the cytosol via nuclear pores for reuse.
Export of mRNAs
Similar types of transport receptors export mRNAs from the nucleus.
Ran
A small monomeric GTPase that exists in two conformations—one carrying GTP and the other GDP.
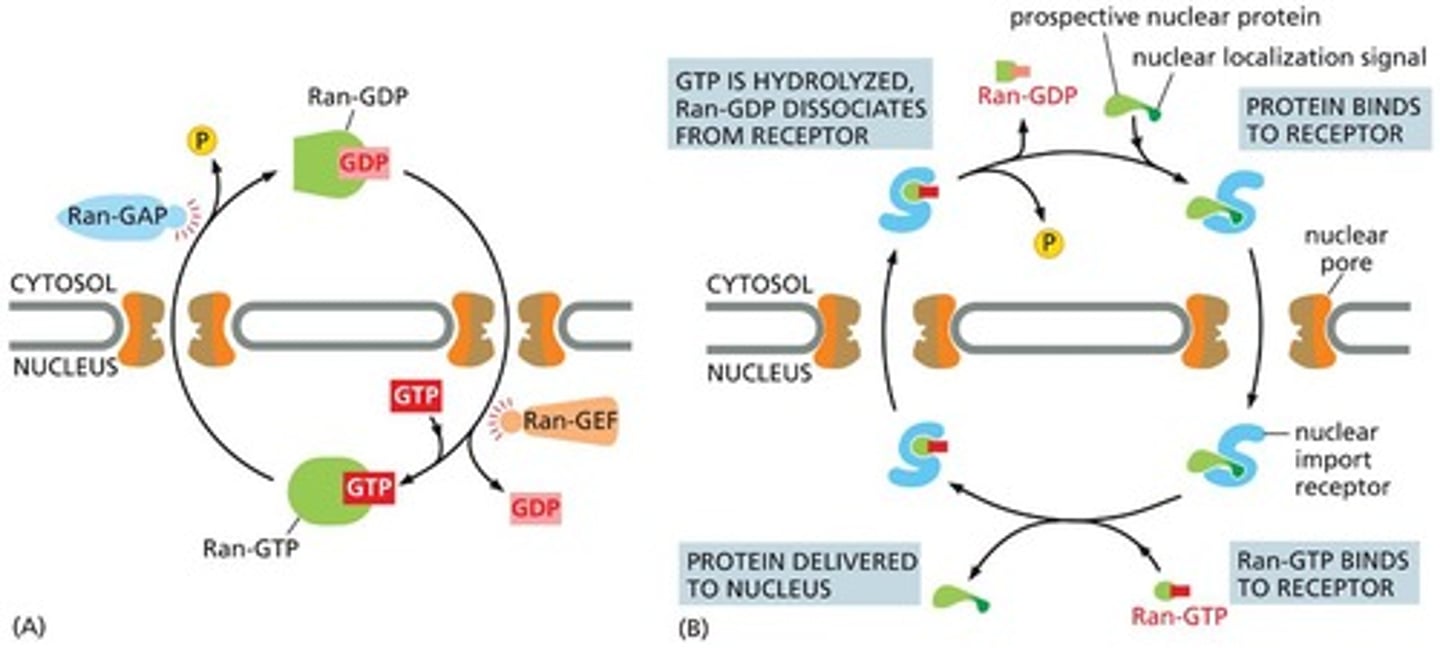
Ran-GAP
GTPase-activating protein that triggers GTP hydrolysis and is found exclusively in the cytosol.
Ran-GDP
The form of Ran after GTP hydrolysis, which falls off the import receptor after being transported back to the cytosol.
Ran-GEF
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor that causes Ran-GDP to release its GDP and take up GTP, found exclusively in the nucleus.
Nuclear import receptor
A receptor that picks up a prospective nuclear protein in the cytosol and enters the nucleus.
Mitochondrial precursor proteins
Proteins that must unfold to enter mitochondria and are recognized by receptors in the outer mitochondrial membrane.
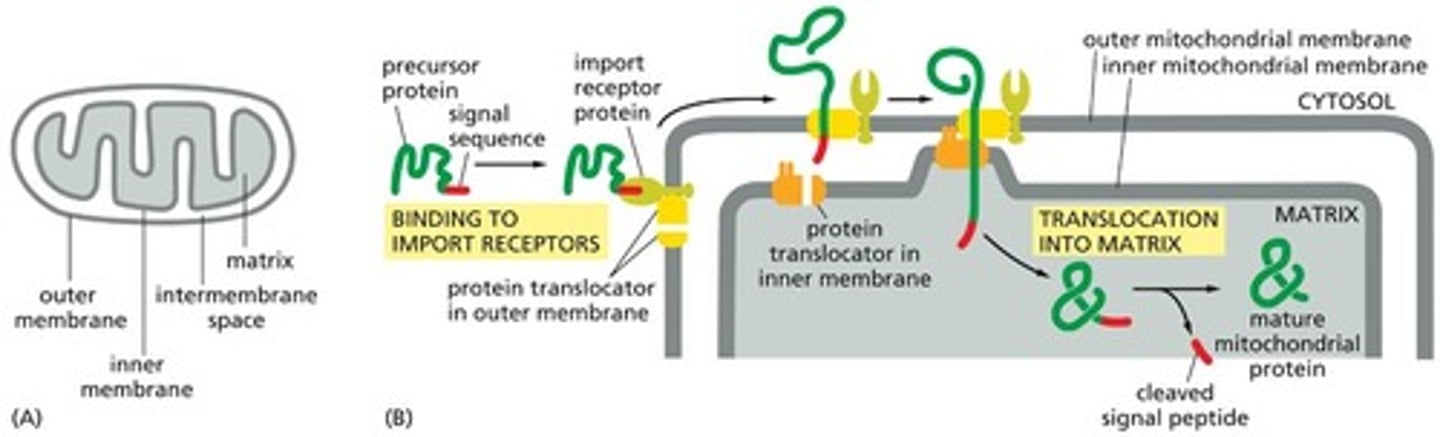
Mitochondrial signal sequence
A sequence on a mitochondrial precursor protein that is recognized by a receptor in the outer mitochondrial membrane.
Protein translocator
A protein complex that transports the mitochondrial signal sequence across the outer mitochondrial membrane.
Chloroplast import mechanism
A process similar to mitochondrial import, where proteins are imported into chloroplasts.
Chaperone proteins
Proteins that help pull the protein across membranes and assist in refolding after import.
Signal peptidase
An enzyme that cleaves the mitochondrial signal sequence off the precursor protein in the mitochondrial matrix.
ATP hydrolysis
A process that provides energy needed for protein translocation across membranes.
Nuclear import cycle
The process driven by the concentration of Ran-GTP in the nucleus, facilitating the transport of nuclear proteins.
Intermembrane space
The space between the outer and inner membranes of the mitochondrion where precursor proteins are transported.
Fluorescence micrograph
A type of imaging that shows the endoplasmic reticulum as a complex network of tubes in a living plant cell.
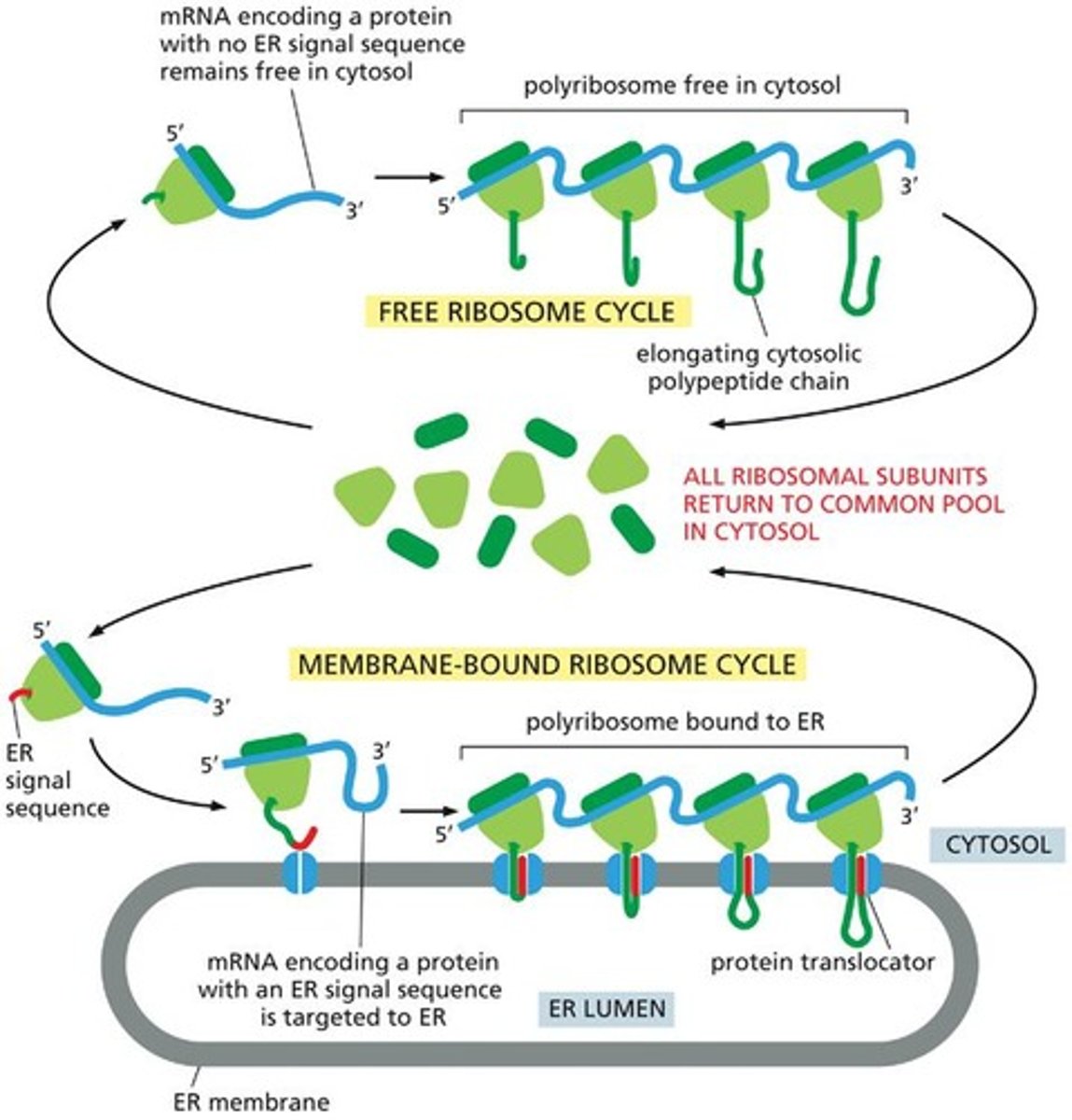
Ribosomes
Cellular structures that are studded on the rough ER and are involved in protein synthesis.
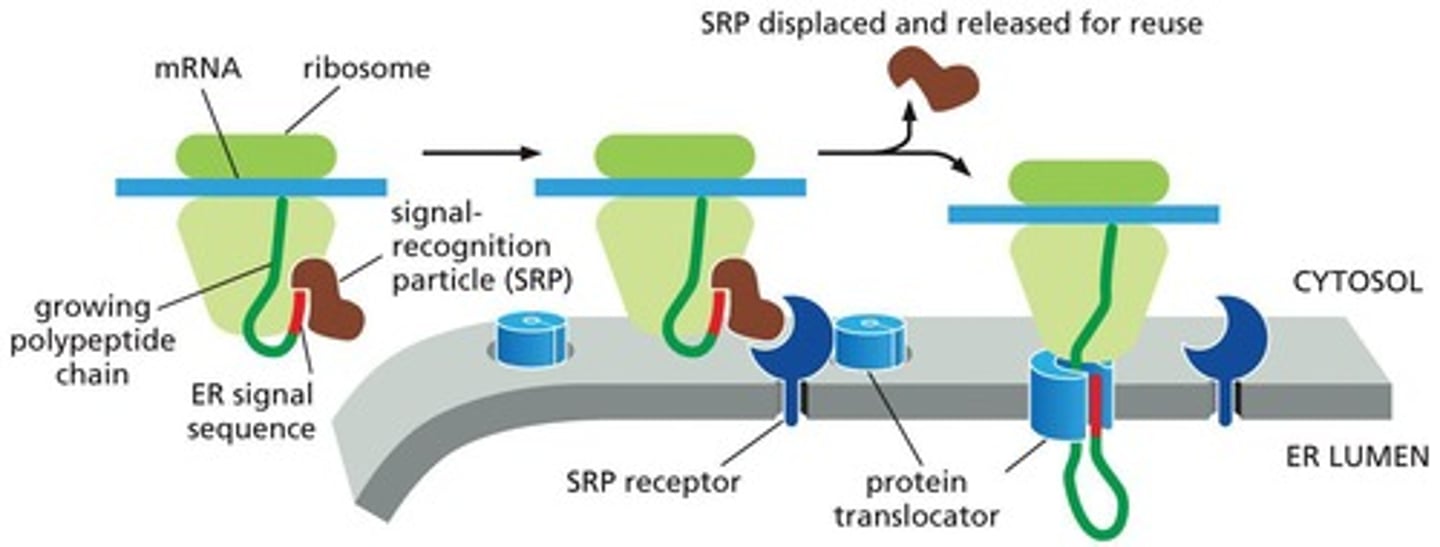
ER signal sequence
A peptide sequence that directs the ribosome to the ER membrane for protein translocation.
Polyribosome
A complex of multiple ribosomes bound to a single mRNA molecule, simultaneously translating it.
SRP (Signal Recognition Particle)
A protein-RNA complex that recognizes and binds to the ER signal sequence and ribosome.
SRP receptor
A protein in the ER membrane that binds the SRP-ribosome complex.
Lipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that forms the basic structure of cell membranes.
Transmembrane protein
A protein that spans the lipid bilayer, with parts exposed on both sides of the membrane.
N-terminal ER signal sequence
The initial ER signal sequence located at the N-terminus of a polypeptide that initiates its transfer to the ER.
Stop-transfer sequence
A hydrophobic sequence that halts the translocation of a polypeptide chain into the ER membrane.
Double-pass transmembrane protein
A protein that spans the membrane twice, containing both start-transfer and stop-transfer sequences.
Internal ER signal sequence
A sequence within a polypeptide that serves as a start-transfer signal for translocation.
Hydrophobic sequence
A sequence of amino acids that is non-polar and typically anchors proteins within the lipid bilayer.
Translocation process
The mechanism by which a polypeptide is moved across the ER membrane.
Soluble protein
A protein that is released into the ER lumen after translocation.
Cytosolic side
The side of the ER membrane that faces the cytoplasm.
Membrane-bound ribosome
A ribosome that is attached to the ER membrane and synthesizes proteins destined for the ER.
Protein synthesis
The process of translating mRNA into a polypeptide chain.
Cleavage of signal sequence
The process where the signal peptide is removed from the growing polypeptide by signal peptidase.
Anchored protein
A protein that is embedded in the membrane and remains attached after synthesis.
Start-transfer signal
A sequence that initiates the transfer of a polypeptide into the ER membrane.
Exocytosis
A process where a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, releasing its content to the cell's surroundings.
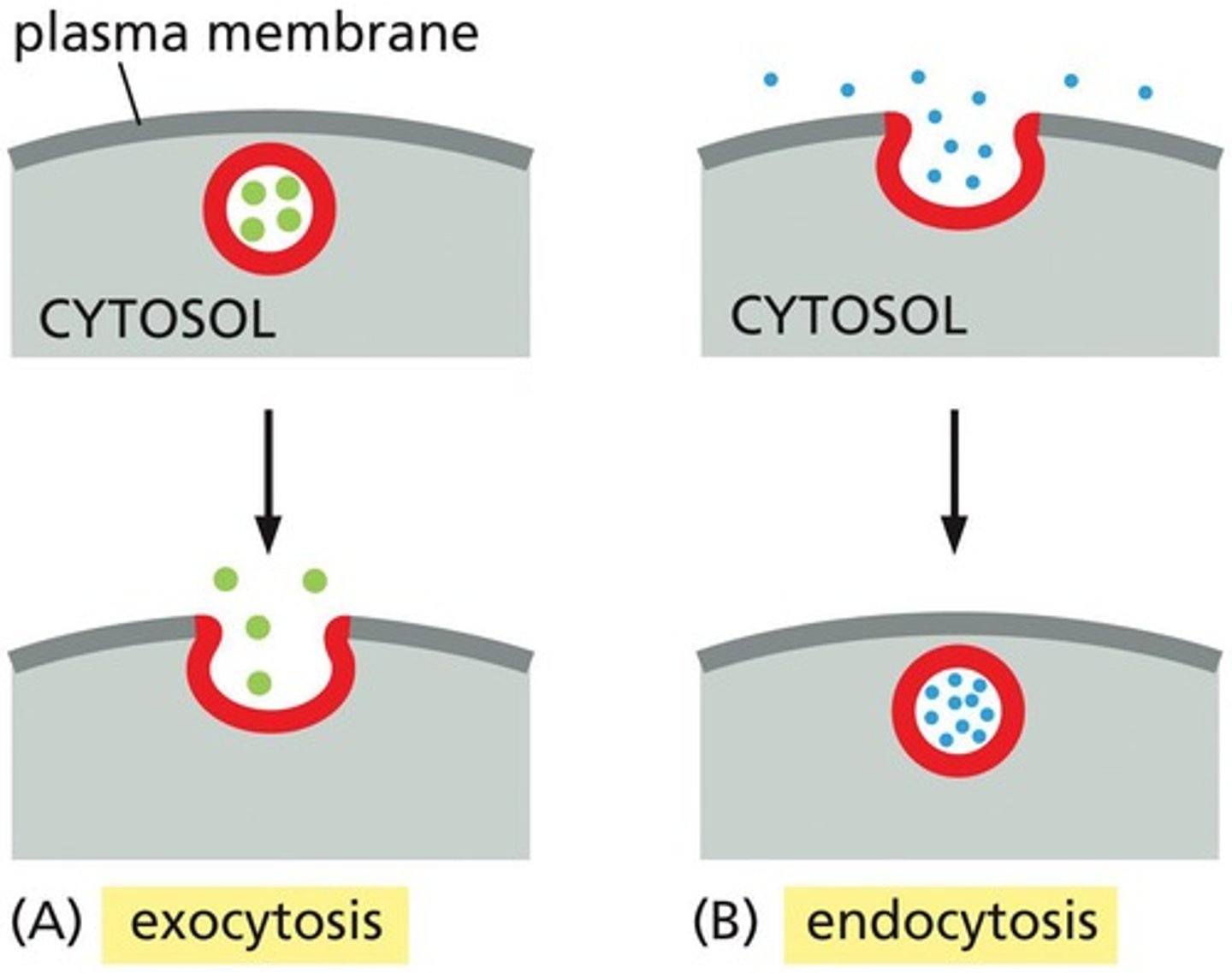
Endocytosis
A process where extracellular materials are captured by vesicles that bud inward from the plasma membrane and are carried into the cell.
Transport Vesicles
Carry soluble proteins and membrane between compartments.
Endomembrane System
A system that includes the plasma membrane and various membrane-enclosed compartments that communicate via transport vesicles.
Noncytosolic Side
The side of a membrane or vesicle that faces the lumen of the compartment or the outside of the cell.
Inward Endocytic Pathway
Pathway where extracellular molecules are ingested in vesicles derived from the plasma membrane and delivered to early endosomes and lysosomes.
Outward Secretory Pathway
Pathway where protein molecules are transported from the ER, through the Golgi apparatus, to the plasma membrane or lysosomes.
Vesicle Budding
A process driven by the assembly of a protein coat.
Clathrin
Molecules that form basketlike cages that help shape membranes into vesicles.
Clathrin-coated Vesicles
Transport selected cargo molecules and are formed from clathrin-coated pits.
Cargo Receptors
Proteins that capture cargo molecules and are bound by adaptins in clathrin-coated vesicles.
Adaptins
Proteins that bind cargo receptors and clathrin molecules to the cytosolic surface of budding vesicles.
Dynamin
Proteins that assemble around the neck of budding vesicles and pinch off the vesicle after hydrolyzing GTP.
Naked Vesicle
A vesicle that has had its coat proteins removed and is ready to fuse with its target membrane.
Coat Proteins
Proteins that are involved in the formation of coated vesicles.
COPII-coated vesicles
Vesicles that transport materials from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi cisterna, composed of COPII proteins.
COPI-coated vesicles
Vesicles that transport materials from the Golgi cisterna back to the ER, composed of COPI proteins.
Vesicle docking
The process by which vesicles attach to their target membranes, facilitated by tethers and SNAREs.