electricity gcse physics aqa
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
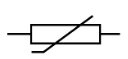
what is this circuit symbol
thermistor
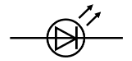
what is this circuit symbol
light emitting diode
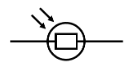
what is this circuit symbol
light dependent resistor
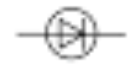
what is this circuit symbol
diode

what is this circuit symbol
fuse
which line of a battery represents positive
longer line
what way does electrons flow
negative to postive
what way does convectional current travel?
positive to negative
what is a short circuit
where there is a path in the circuit that doesn’t go through a component.
ohm’s law
the current of a component is directly proportional to the potential difference across it if the temperature is constant
what is an ohmic conductor
a component that follows ohm’s law
2 examples of ohmic conductors
wire, fixed resistor
2 examples of components that aren’t ohmic
diodes, filament lamps
what are i-v characteristics
current-potential difference graphs
what are linear components?
components with constant resistance that have straight line graphs
what is the relationship between resistance and current in a filament lamp?
the more current that flows through the lamp, the more the resistance increases
what is the relationship between resistance and current in a diode?
current only flows one way so resistance is initially high but drops as the potential difference increases letting current flow
what happens to resistance in a LDR
it decreases in bright light and increases in darkness
what happens to resistance in a thermistor
it decreases in hot conditions and increases in cool conditions
one example where are themistors useful
thermostats
why does the movement of a charge transfer energy?
the charge does work against the resistance of the circuit and work done is the same as energy transferred