criminal courts & appeals
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the 3 categories criminal offences are put into
Summary - least serious tried in the magistrates court
E.g. assault, battery
Triable either way - middle range offences tried in the magistrates or crown court
E.g. ABH, theft
Indictable - most serious tried in the crown court
E.g. murder, manslaughter
What do the magistrates hear (jurisdiction)
Jurisdiction is set out in the Magistrates & court act 1980
All summary offences
Plea before venue & mode of trial hearings in triable either way offences, & trials of triable either way if they have the sentencing power
What can the magistrates do
Issue search & arrest warrants to police
Grant bail
Hears young offenders cases
Impose a max sentence of 6 months, or 12 months where D is charged with 2 triable either way offences
Max fines
What do the crow court hear (jurisdiction)
Triable either way where the magistrates do not have the sentencing power to deal with the case/D chooses crown
Plea & preparation for trial hearings, trials of indictable cases, & bail applications
Appeals from magistrates court against conviction/sentence
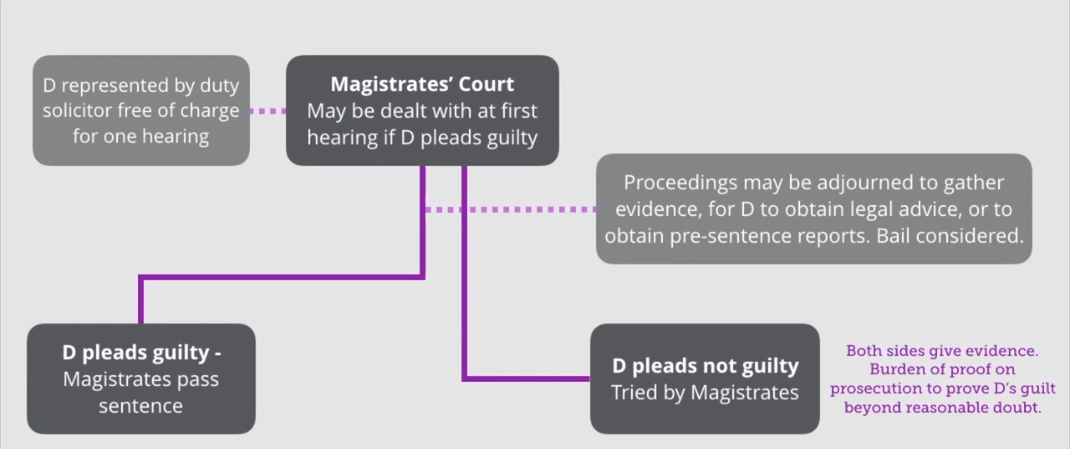
What is the procedure for summary offences
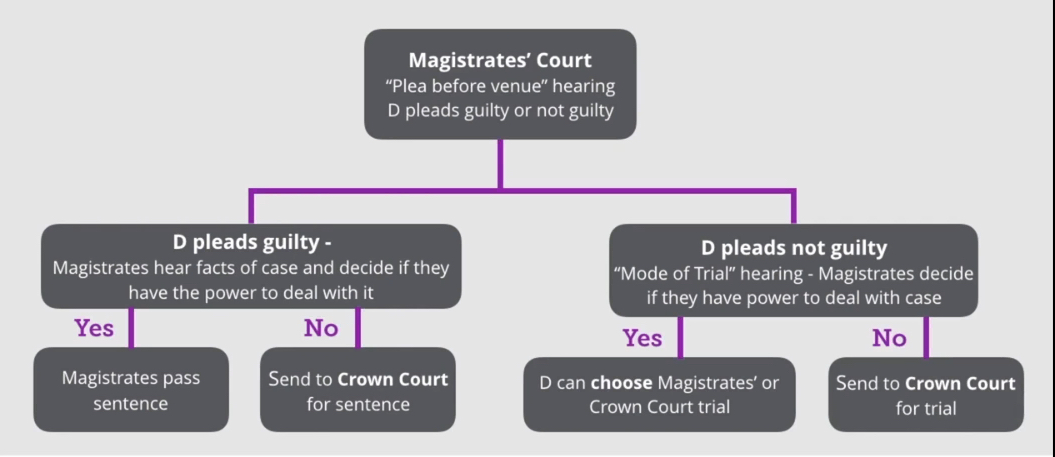
What is the process for triable either way offences
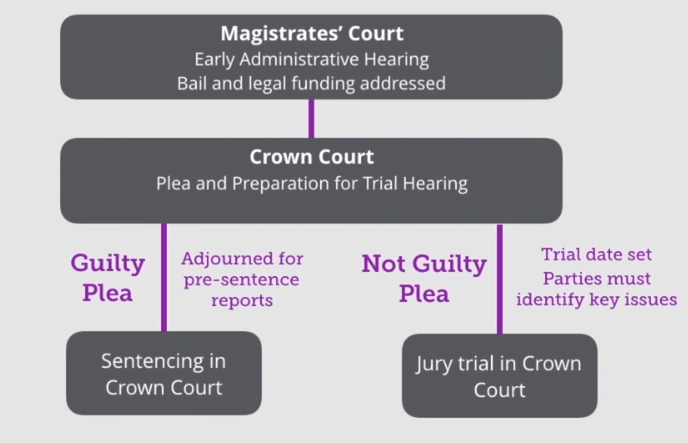
What is the process for indictable offences
Why would the defendant or prosecution appeal
If either are unhappy with the outcome of a case they can appeal, this could be due to perceived errors of law, fact, or procedure
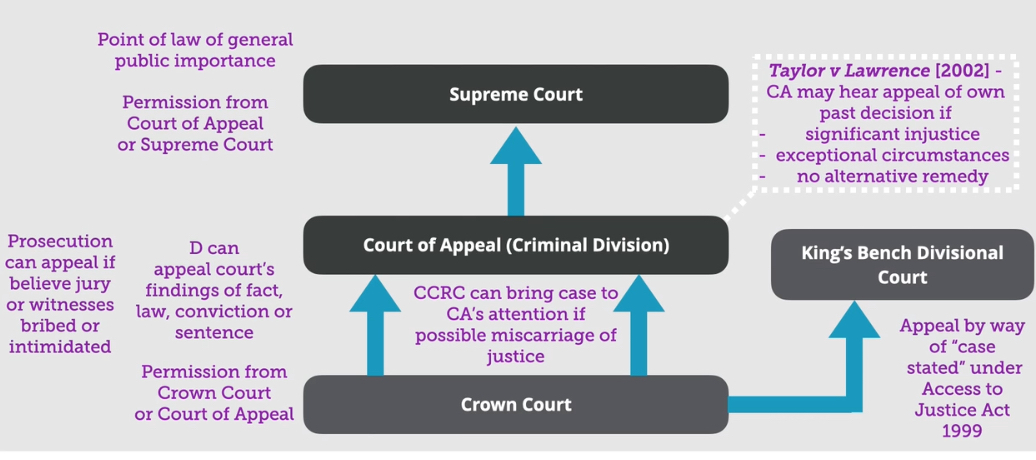
What are appeals governed by
Criminal Appeals Act 1995
When can appeals be made from the magistrates court
D has an automatic right to appeal when pleaded not guilty to the crown court with a circuit judge & 2-4 magistrates
There can be a rehearing to correct the error in the magistrates heard by a different bench
If either appeal because of a point of law it will be heard by the kings bench division
Or appeal on a point of law of general importance it can be heard by the Supreme Court with their permission
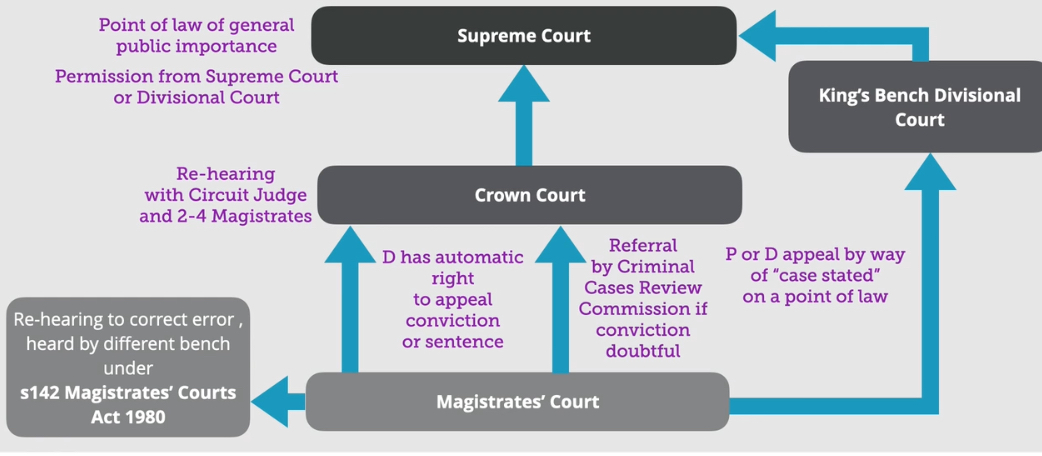
What are the 3 possible appeal routes
Court of appeal - D against courts findings of fact, la, conviction/sentence with permission from crown/appeal court
P against witness intimidation/bribes
Supreme court - against point of law of general importance with permission from appeal or Supreme court
Kings bench division - appeal by way of case stated