Anatomy Chap 7 & 8: Disorders of bone tissue and skeletal system
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
How Fractures are Classified
By Cause
By Structural Characteristics
By Cause
Stress Fracture
Pathological Fracture
Stress Fracture
Caused by abnormal trauma (sudden physical force)
Examples: Falling, sports injuries
Pathological Fracture
Caused by a disease that weakens the bone
Example: Bone cancer, osteoporosis
By Structural Characteristics
Non displaced
Displaced
Greenstick
Closed
Fracture
Open Fracture
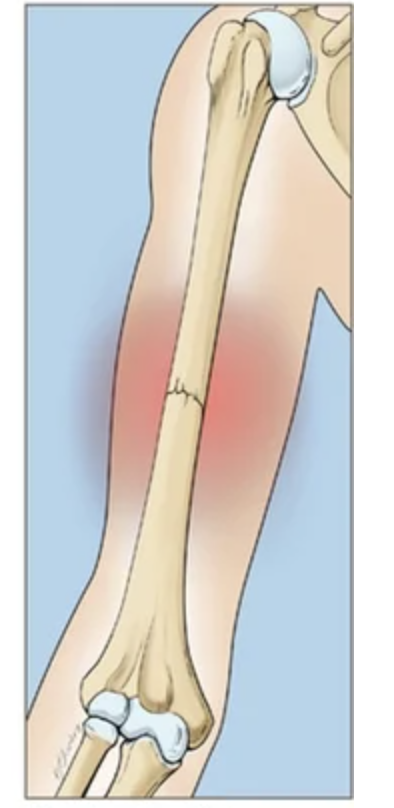
Non displaced
Bone breaks but stays aligned
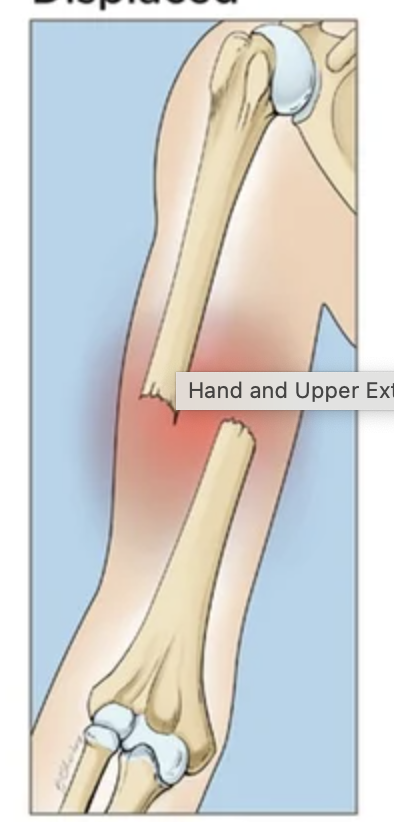
Displaced
Bone breaks into 2 or more pieces and the pieces shift out of alignment
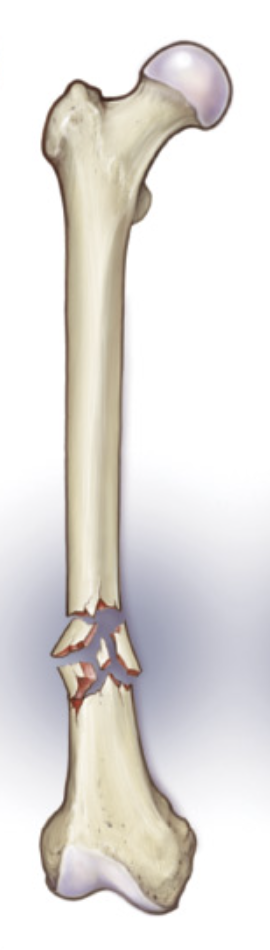
Comminuted
Bone breaks into 3 or more pieces
Pieces are misaligned
Greenstick
Incomplete break: One side cracks, the other side bends
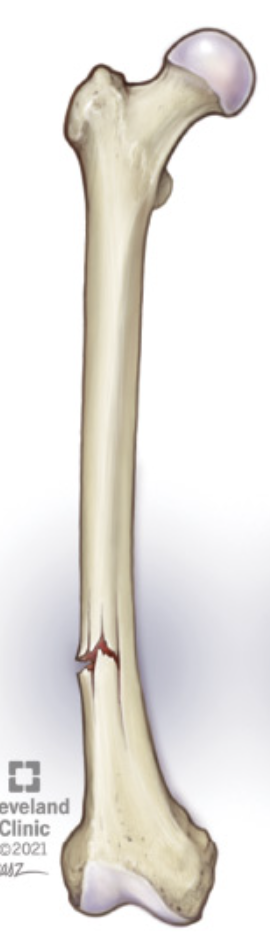
Closed Fracture
Bone breaks, but the skin is not pierced
Open Fracture
Bone breaks through the skin
High risk of deep bone infection
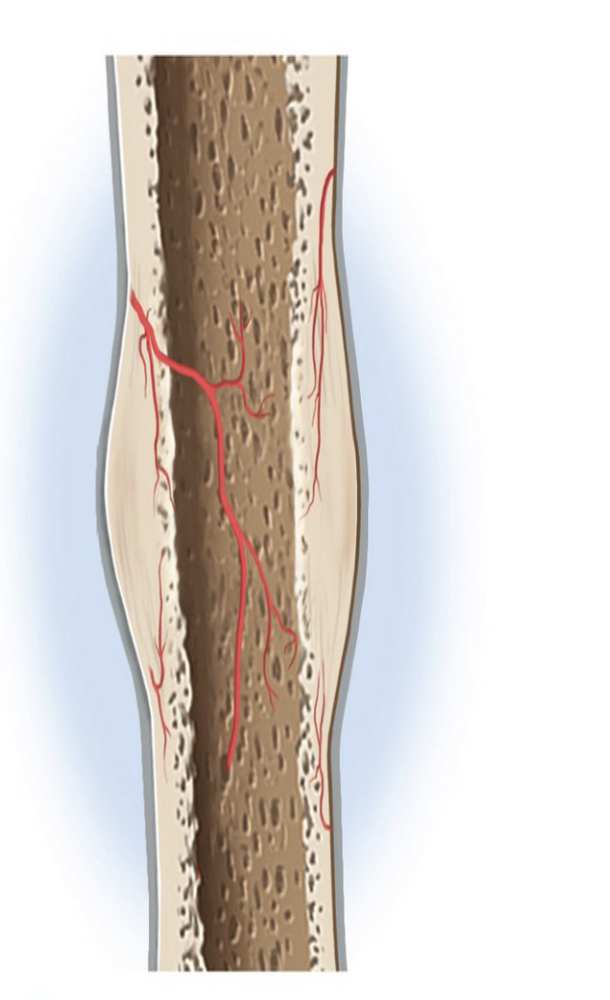
How Fractures Heal (8-12 weeks)
Hematoma Formation
Soft Callus Formation
Hard Callus Formation
Bone Remodeling
Hematoma Formation
Broken blood vessels cause bleeding, forming a fracture hematoma (blood clot)
Cells move into the area:
Fibroblasts
Macrophages
Osteoclasts
Osteogenic cells
These convert the clot into granulation tissue (soft fibrous mass)

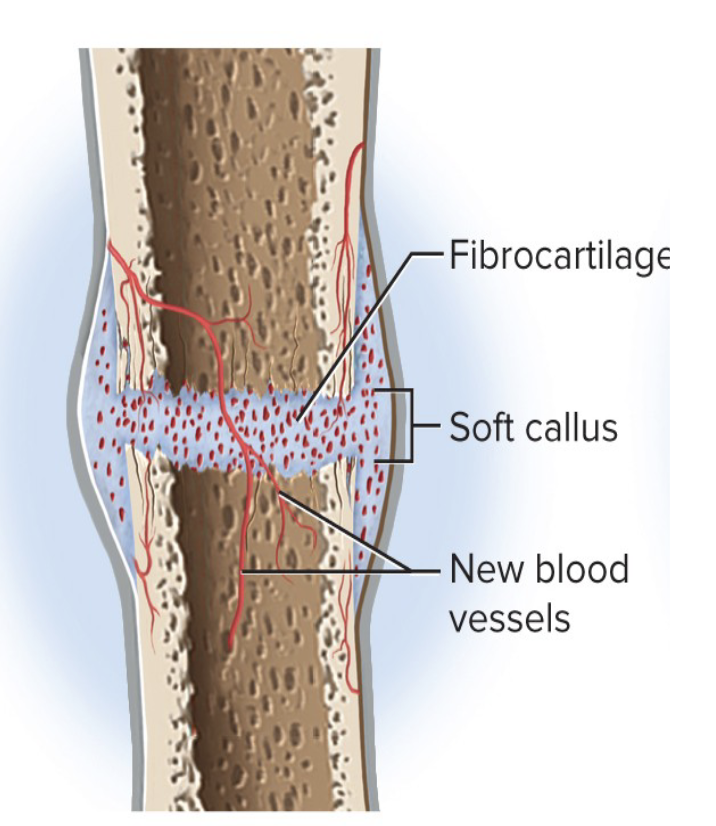
Soft Callus Formation
Fibroblasts deposit collagen
Osteogenic cells turn into chondroblasts, which make fibrocartilage
Collagen + fibrocartilage = soft callus
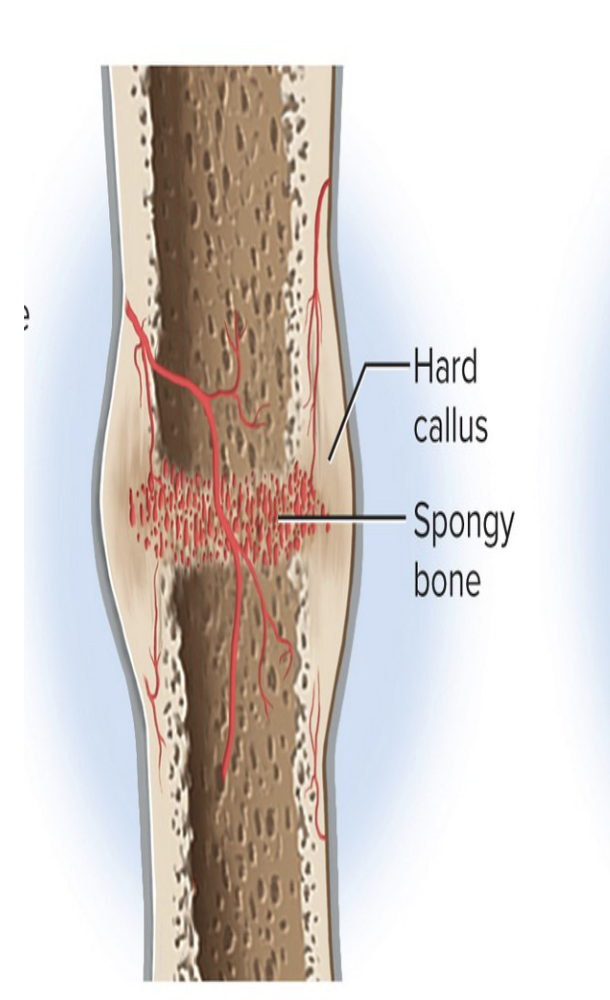
Hard Callus Formation
Osteoblasts build a hard bony collar (hard callus) around the fracture
Acts as a temporary splint
Must keep the bone immobilized so it doesn’t break again
Bone Remodeling
Osteoclasts remove small bone fragments
Osteoblasts lay down spongy bone filling gaps and preventing the bone from healing shorter
Over time, spongy bone becomes compact bone again