Depression
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
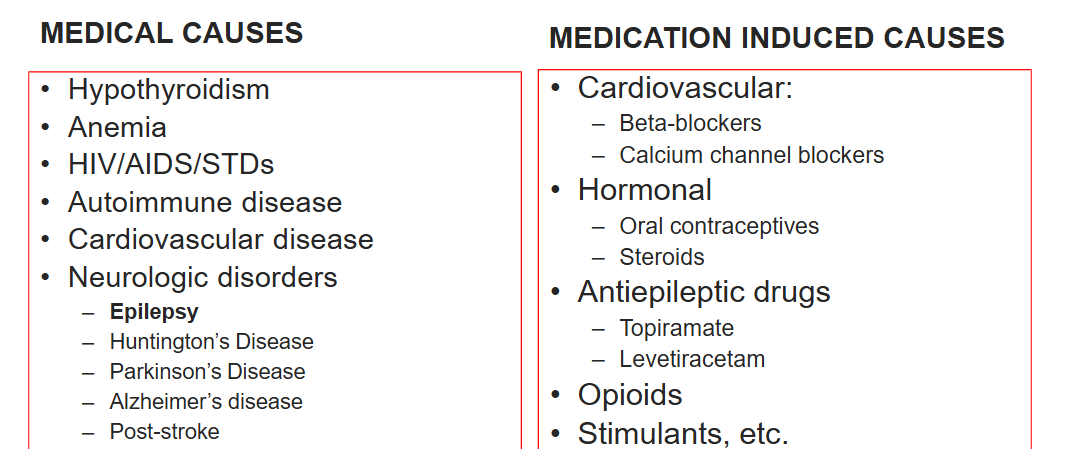
What can cause depression symptoms?
What is meant by uncomplicated and complicated depression?
Uncomplicated: no comorbidities
Complicated: comorbidities such as:
Catatonia
Psychotic depression
Severe suicidality
History of previous ECT success
Need for rapid response
Risks for other treatments
History of poor response to antidepressants
How to treat someone who just has depression by itself

How to treat someone who has depression with complications?
Treatment: Psychotherapy PLUS pharmacotherapy ECT with or without psychotherapy
What is the BBW for all antidepressants?
Increased risk of thoughts and behavior ages 24 and younger
Increased monitoring first 3 months (but can be anytime)
Risk decreases with advancing age
What is shared is between all antidepressants
Use of antidepressant monotherapy in patients with underlying bipolar disorder can precipitate a switch to mania
Formulations: do not crush or chew sustained/extended release, liquids may contain alcohol
Drug interactions: majority 2D6
How to navigate antidepressant side effects?
• If experience anxiety: lower doses and titrate slowly
• If insomnia or sedation: switch administration time
• If headache: can treat with OTC PRN for few days trial to resolve
• Gastrointestinal: give with food
• Weight gain: explore diet/exercise or switch agents if needed
• Sexual side effects: usually switch needed. Alternatives:
Bupropion, vortioxetine other off-label options
What drugs are SSRIs?
Citalopram
Escitalopram
Fluoxetine
Fluvoxamine
Paroxetine
Sertraline
Citalopram
SSRI
indicated only for MDD
ADRs: QT prolongation
Maximum dose for elderly over 60 years: 20mg/day
Escitalopram
SSRI
indicated for MDD (12-17 yrs), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
Risk of use in patients with concomitant illness
Maximum dose for elderly over 60 years: 10mg/day
Fluoxetine
SSRI
Indicated for: MDD (8-17 yrs), OCD (7-17 yrs), Panic, Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), bulimia nervosa
Reduced appetite and weight
Anxiety and insomnia
Long half-life (only SSRI with a once weekly dose option)
Fluvoxamine
SSRI
Indication: OCD (8-17 yo)
Many significant drug interactions
Not approved for MDD
Paroxetine
SSRI
Indication: MDD, GAD, OCD, Panic, PTSD, PMDD, and SAD
Risk for use in pregnancy
Risk of bone fractures
Akathisia
Short half-life and anticholinergic side effects
Sertraline
SSRI
Indication: MDD, OCD (6-12 yrs), Panic disorders, PTSD, PMDD, and SAD
What are universal things shared across SSRIs?
ADRs: Increased bleeding, hyponatremia, serotonin syndrome, sexual side effects, seizures, activation of mania, angle closure glaucoma, discontinuation syndrome.
First dose monitoring considerations: cognitive/motor impairment-use caution with first dose
Monitor for any potential allergic reaction with first dose
First few days/weeks: increased anxiety, GI symptoms, headache
What are the SNRIs?
Desvenlafaxine
Duloxetine
Venlafaxine
Levomilnacipran
Desvenlafaxine
SNRI
Indication: MDD
Duloxetine
SNRI
Indication: MDD, GAD (7-17 yo), Fibromyalgia, Neuropathic pain
Venlafaxine
SNRI
Indication: MDD, GAD, Panic disorder, social phobia (social
anxiety disorder)
Levomilnacipran
SNRI
Indication: MDD
What is shared amongst the SNRIs?
Same as SSRIS + increased risk of BP elevation (noradrenergic action)
What are the TCAs?
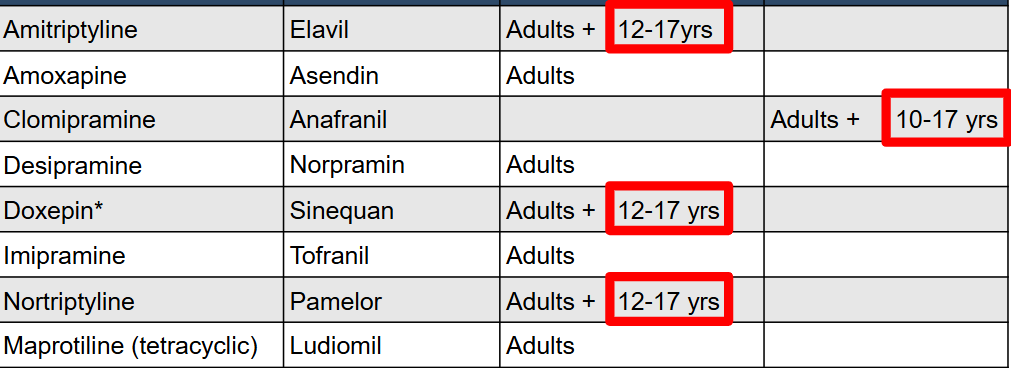
What are the indications for TCAs?
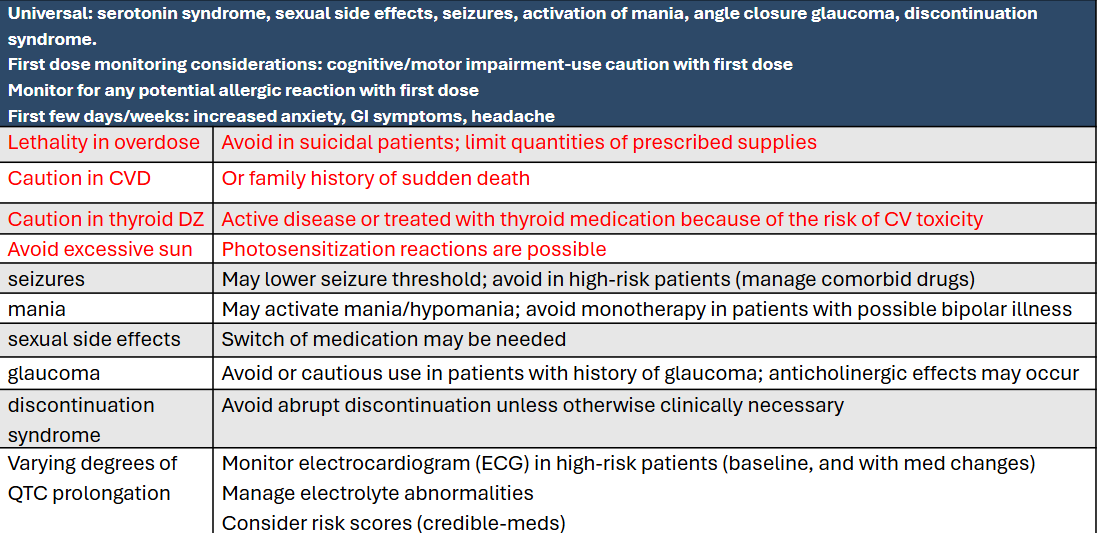
ADRs for TCAs:
Avoid tyramine containing foods, sympathomimetic agents; NO overlap switch other AD
nefazodone is contraindicated and general monitoring of liver function tests (every 3 to 6 months with discontinuation if LFT are 3x or greater upper limit
Esketamine causes increase in BP and sedation
Brexanolone induced sedation and LOC
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAO-I) names:
Isocarboxazid
Selegiline PATCH
Phenelzine
Tranylcypromine
Note: Phenelzine and tranylcypromine are nonselective MAO inhibitors
Isocarboxazid
Nonselective irreversible MAO inhibitor
Increase 5-HT, NE and DA in synapse
CI: CVD, HTN or treatment with BP meds, hepatic impairment,
severe renal impairment, history of headache, excessive caffeine intake
Selegiline
Irreversible selective MAO-B inhibitor (selectivity dose dependent)
MAO-B at clinical doses, MAO-A at higher doses
Phenelzine
Nonselective irreversible MAO inhibitor
CI: heart failure, hypertension or treatment with BP meds, hepatic impairment, severe renal impairment
Avoid in pregnancy
Peripheral neuropathy reported
Tranylcypromine
Nonselective irreversible MAO inhibitor
Has additional effects like amphetamines (increase DA release into the synapse and inhibits NE at higher doses)
CI: CVD, HTN or treatment with BP meds, hepatic impairment, history of headache
What is there to know about MAOIs?
when switching:
2 weeks wash out before starting another MAO!
5 weeks when switch from fluoxetine
Bupropion
MOA: Inhibits NE and DA transporters, increasing their concentrations in the synapse.
Contraindications in addition to “universal”
Seizure disorder or any other condition predisposing risk (such as abrupt discontinuation of alcohol, BZD, AED -will lower threshold)
Current or prior diagnosis of bulimia or anorexia nervosa
ADRs:
• May increase blood pressure
• Wakefulness/Activation and insomnia
• Associated with less sexual side effects compared to other AD
Bupropion with Dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan: NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor antagonist
Contraindications in addition to “universal”
Seizure disorder or any other condition predisposing risk (such as abrupt discontinuation of alcohol, BZD, AED -will lower threshold)
Current or prior diagnosis of bulimia or anorexia nervosa
ADRs:
risk of serotonin syndrome is greater, embryo-fetal toxicity,
may cause hyperhidrosis
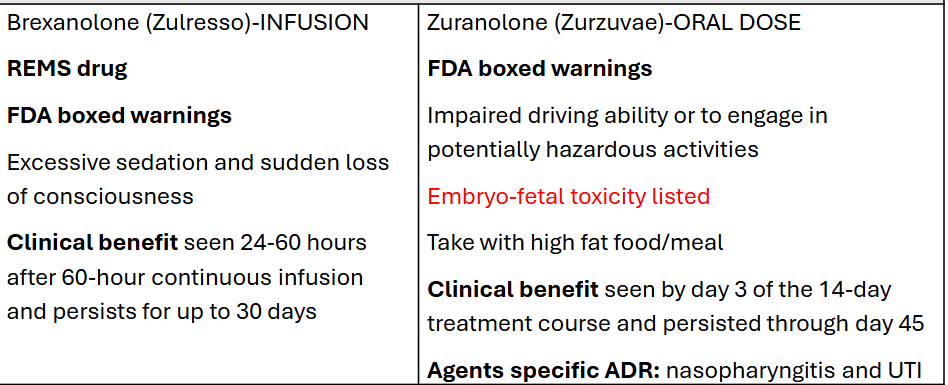
Brexanolone, Zuranolone
MOA: Positive allosteric modulation of GABAA receptors
Indication: approved for post-partum depression (after birth!
Esketamine
Mechanism of action: NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor antagonist
Indicated for Adults only: Treatment Resistant Depression (TRD) monotherapy or in combination with an oral AD
TRD=Failure of at least two other drugs
Contraindications: in addition to “universal”
History of intracerebral hemorrhage
Aneurysmal vascular disease or arteriovenous malformation (AVM
Mirtazapine
• Increased appetite and weight gain
• Drowsiness that generally continues
• Elevated cholesterol and triglycerides
Gepirone
Contraindications
Prolonged QTc interval at baseline (greater than 450msec)
Congenital long QTc syndrome
Severe hepatic impairment
Serotonin modulators names
Vortioxetine
Vilazodone
Trazodone
Nefazodone
Vortioxetine
serotonin modulator
Adverse effects unique difference:
Sexual side effects (drug holiday to mitigate not effective due to long T1/2)
Discontinuation syndrome (not as significant due to T1/2
Vilazodone
serotonin modulator
Take with food to increase effectiveness (absorption) and reduce GI ADR
Trazodone
serotonin modulator
MOA: Weak inhibition of 5-HT, alpha-1 receptor antagonism, 5-HT2 receptor antagonism
Considerations/warnings/cautions
Hyponatremia
Arrhythmogenic potential in those with underlying CVD
Abnormal bleeding
Priapism
Nefazodone
serotonin modulator
MOA:
Weak inhibition of 5-HT, alpha-1 receptor antagonism, 5-HT2 receptor antagonism
also inhibits NE
Contraindications in addition to universal: Previous (or current) liver injury
How to treat depression in children?
FDA approved pediatric AD: escitalopram and fluoxetine are
the only approved for pediatric depression
How to treat depression in elderly?
• Monotherapy preferred, least complicated regimens
• SSRI preferred (avoid paroxetine)
• TCA and MAO-I not recommended unless no other option