GEO 303 Exam 3 Shanahan
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
erosion
the grinding away and removal of the Earth's surface
deposition
the accumulation of transported sediment
mass movements
downslope motion of rock, regolith (soil, sediment, and debris), snow, and ice
creep
slow, gradual downslope movement of regolith on a slope
solifluction
the slow, downslope flow of soil saturated with water in areas surrounding glaciers at high elevations
landslide
a slide of a large mass of dirt and rock down a mountain or cliff

rock glacier
a slow-moving mixture of rock fragments and ice
slump
a type of mass movement that occurs when a mass of material moves down a curved slope
failure surface
a weak surface that forms the base of a landslide
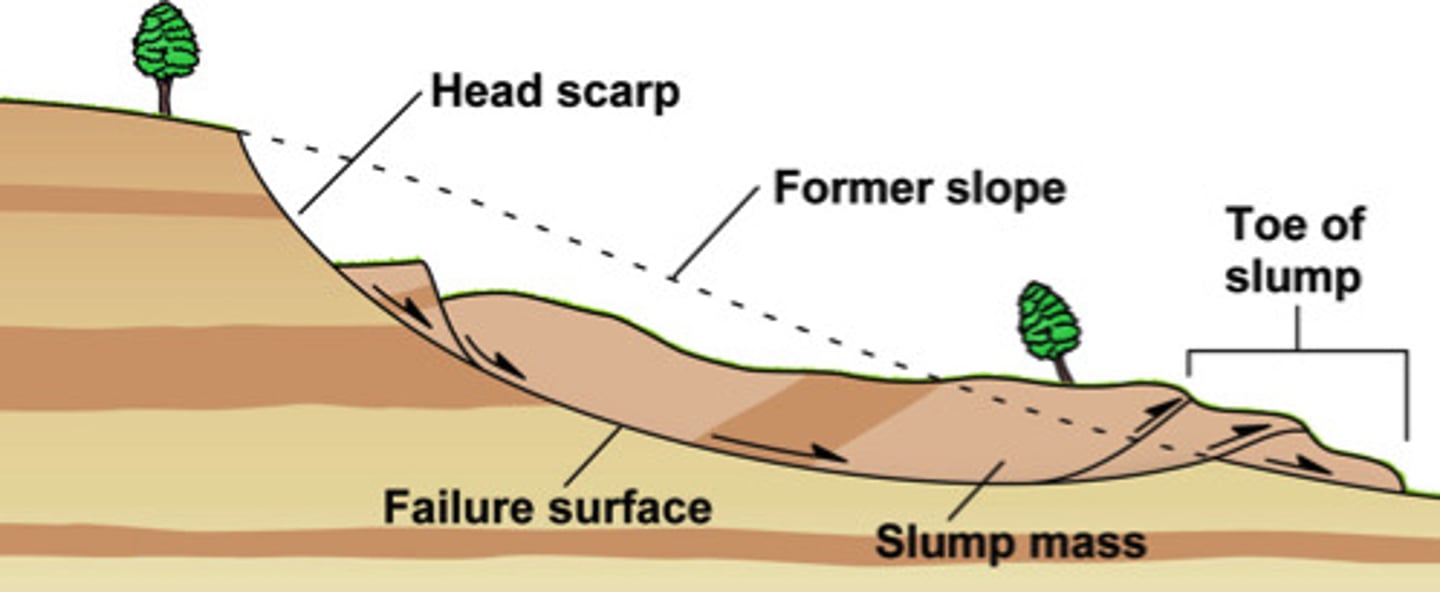
head scrap
the distinct step along the upslope edge of a slump where the regolith detached
mudflow
a downslope movement of mud at slow to moderate speed
debris flow
a mudflow with many large rocks
lahars
a thick slurry formed when volcanic ash and debris mix with water, either in rivers or from rain or melting snow and ice on the flank of a volcano
rockslide/debris slide
a sudden downslope movement of rock (or of regolith)
snow avalanche
rapid downslope movement of snow, ice, and rock, typically transforms snow into a turbulent cloud
rock falls and debris falls
a mass of rock that separates from a cliff and free falls downslope
talus
a sloping apron of fallen rock along the base of a cliff
submarine slumps
the underwater downslope movement of a semicoherent block of sediment along a weak mud detachment
turbidity current
a submarine avalanche of sediment and water that speeds down a submarine slope
liquefication
the process by which an earthquake's violent movement suddenly turns loose soil into liquid mud
identifying regions at risk
head scarp, swampy low area, dead trees, sinking foundations, tight power lines, tilted poles, cracked roads, etc.
slope stability
gravity - driving force for movement
steeper slopes create a larger force imbalance
angle of repose
slope strength - weathing, vegetation cover, water content
preventing mass movements
trees - roots stabilize potential failure plane
terrace steps - remove load and catch debris
drainage - potential failure plan dries and becomes stronger
reducing undercutting
engineering structures - traps debris
hydrologic cycle
the cycle through which water in the hydrosphere moves; includes such processes as evaporation, precipitation, and surface and groundwater runoff
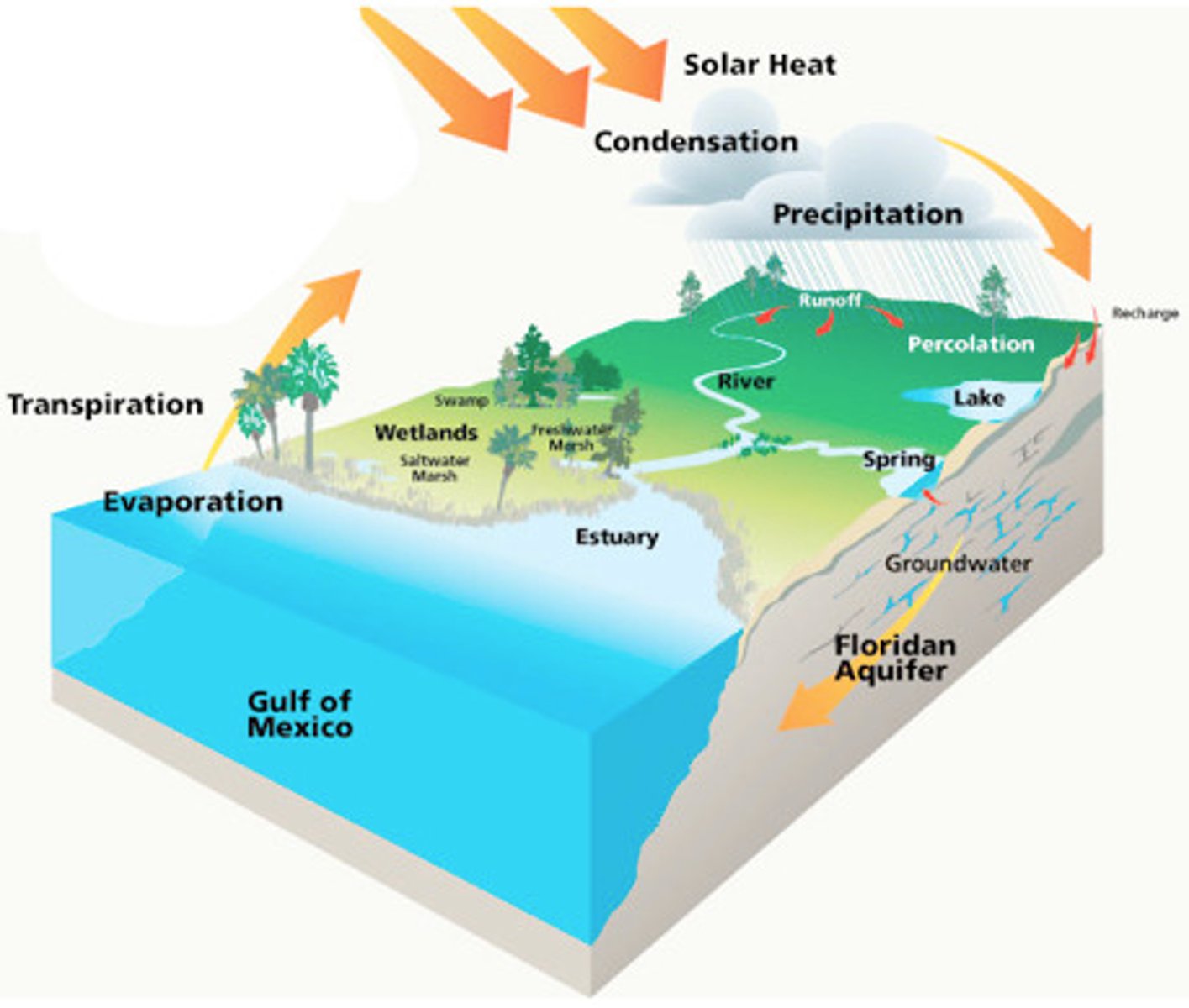
sheet wash
a film of water less than a few mm thick that covers the ground surface during heavy rains
runoff
water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground
downcutting
the process in which water flowing through a channel cuts into the substrate and deepens the channel relative to its surroundings
headward erosion
the process by which a stream channel lengthens up its slope as the flow of water increases
tributaries
smaller streams and rivers that flow into a main river (trunk stream)
drainage network
an array of interconnecting streams that together drain an area
drainage basin/watershed
the region that collects water that feeds into a given drainage network
drainage divide
a highland or ridge that separates one drainage basin from another
gaining stream
the volume of water increases in the downstream direction

losing stream
the volume of water decreases in the downstream direction

permanent vs ephemeral stream
flow all year or only part of the year
all ephemeral streams are losing streams
hyporheic zone
region of saturated sediment next to a stream and immediately beneath it
stream discharge
the volume of water that passes through an imaginary cross section across a stream, generally increases downstream, controls amount of material a river can carry
stream velocity
the rate of flow (not the amount of water)
discharge and velocity are not equivalent
thawleg
the deepest part of the channel (usually highest current velocity)
turbulence
the chaotic twisting and swirling motion in flowing fluid
sediment transport
the material moved by streams is the sediment load
erosion in streams
streamflow does work - material carried by stream abrades channel
maximized during floods - high discharge and velocity
longitudinal profile of a stream
graph of the change in the stream's elevation beginning in its headwaters and ending in its base level
toward the mouth of the stream the gradient flattens, discharge increases, sediment grain sizes are smaller and channels develop broad meander belts
bars
a sheet or elongate lens or mound of alluvium
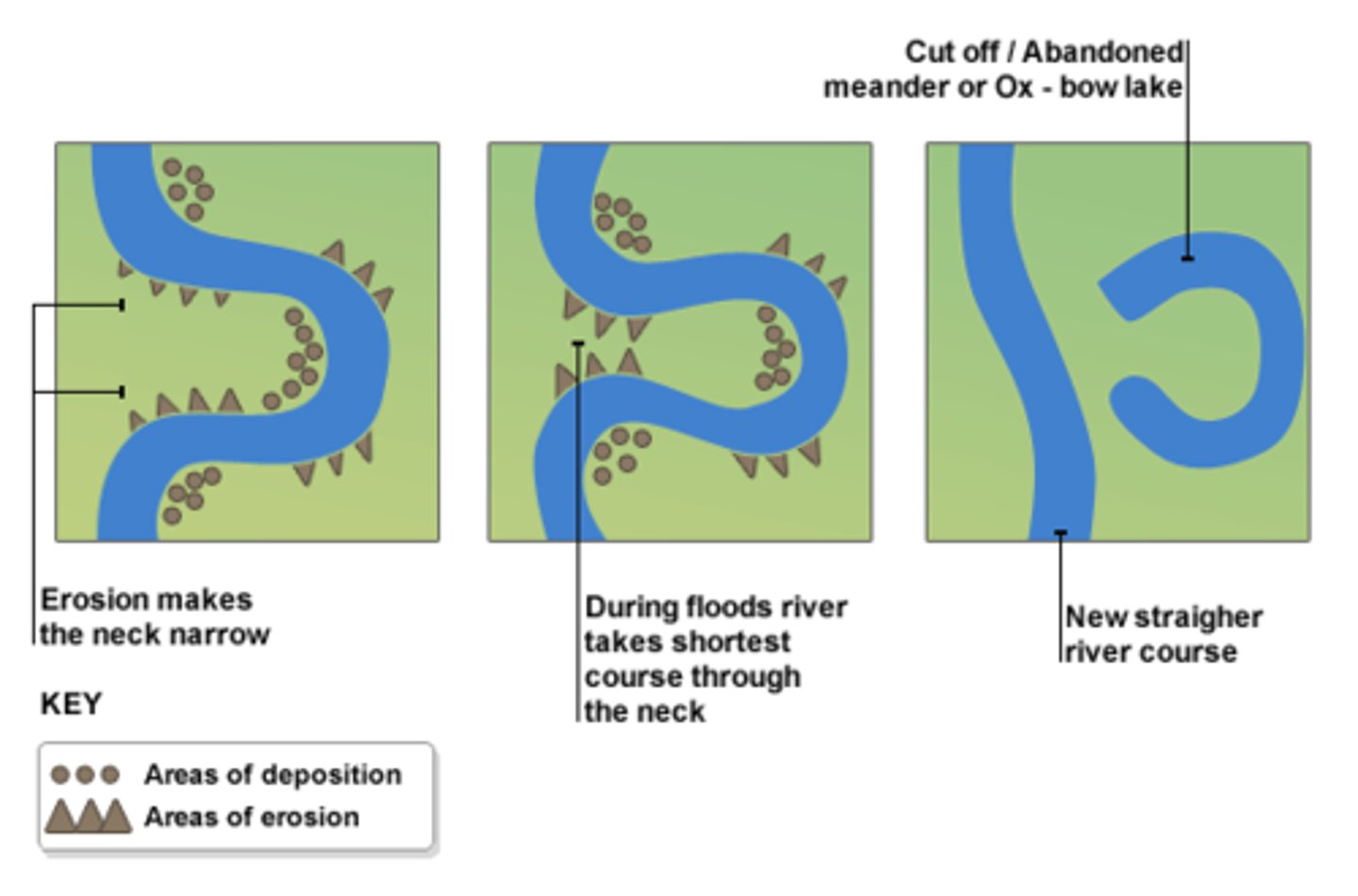
point bars
a wedge-shaped deposit of sediment on the inside bank of a meander
cut bank
the steep bank feature that forms on the outside of a river bank due to erosion
floodplain
flat land along a river that is prone to flooding
headwaters
high velocity = erosive = high competence
stream mouth
low velocity = depositional = low competence
base level
the lowest point to which a stream can erode
meandering streams
channels form intricately looping meanders along the lower gradient portion of the longitudinal profile
oxbow lake
a meander that has been cut off from the river
alluvial fan
a gently sloping apron of sediment dropped by an ephemeral stream at the base of a mountain in arid or semiarid regions
deltas
the triangle-shaped deposit of sand and sediment that occurs where a river flows into an ocean
delta classification
1. rivers - sediment delivery
2. waves - sediment redistribution
3. tides - sediment removal/erosion
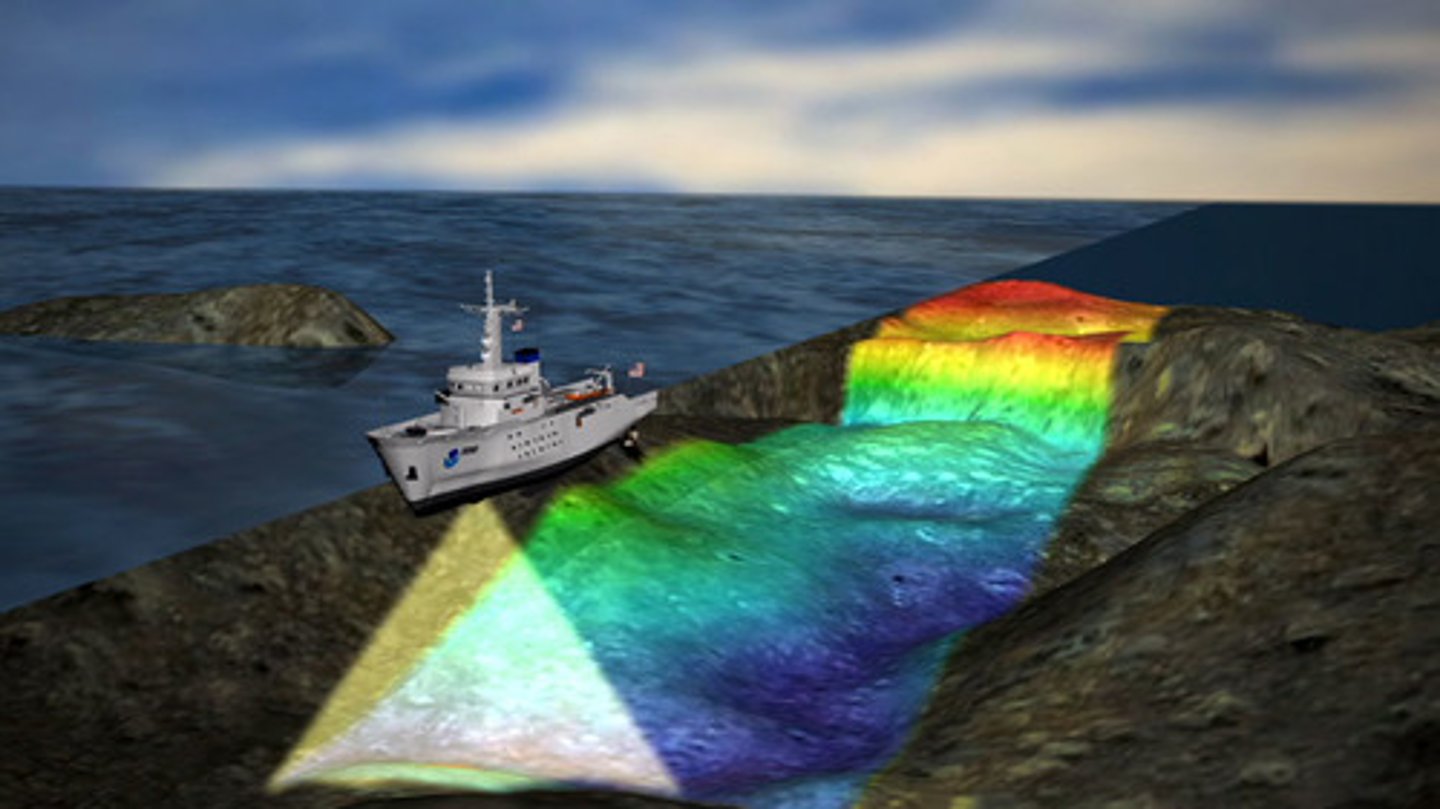
bathymetry
variation in depth
passive continental margin
a continental margin that does not occur along a plate boundary, does not display seismicity
older, higher sediment supply
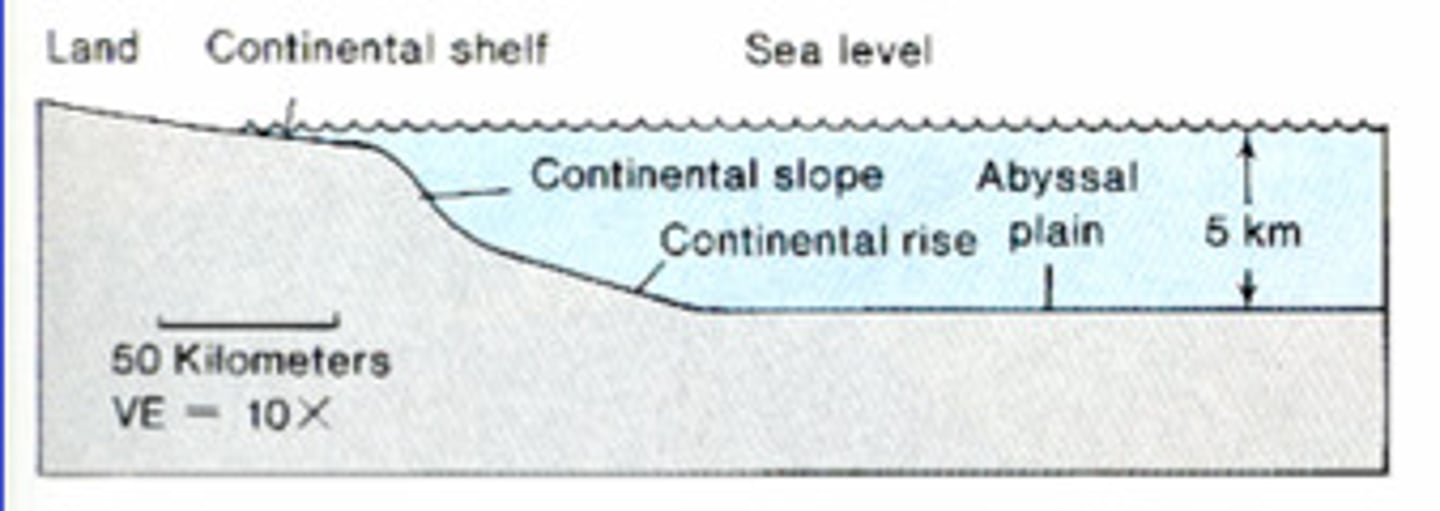
active continental margin
a continental margin that coincides with a plate boundary
younger, less sediment supply

abyssal plains
broad, relatively flat regions of the ocean that lie at a depth of about 4 to 5 km below sea level
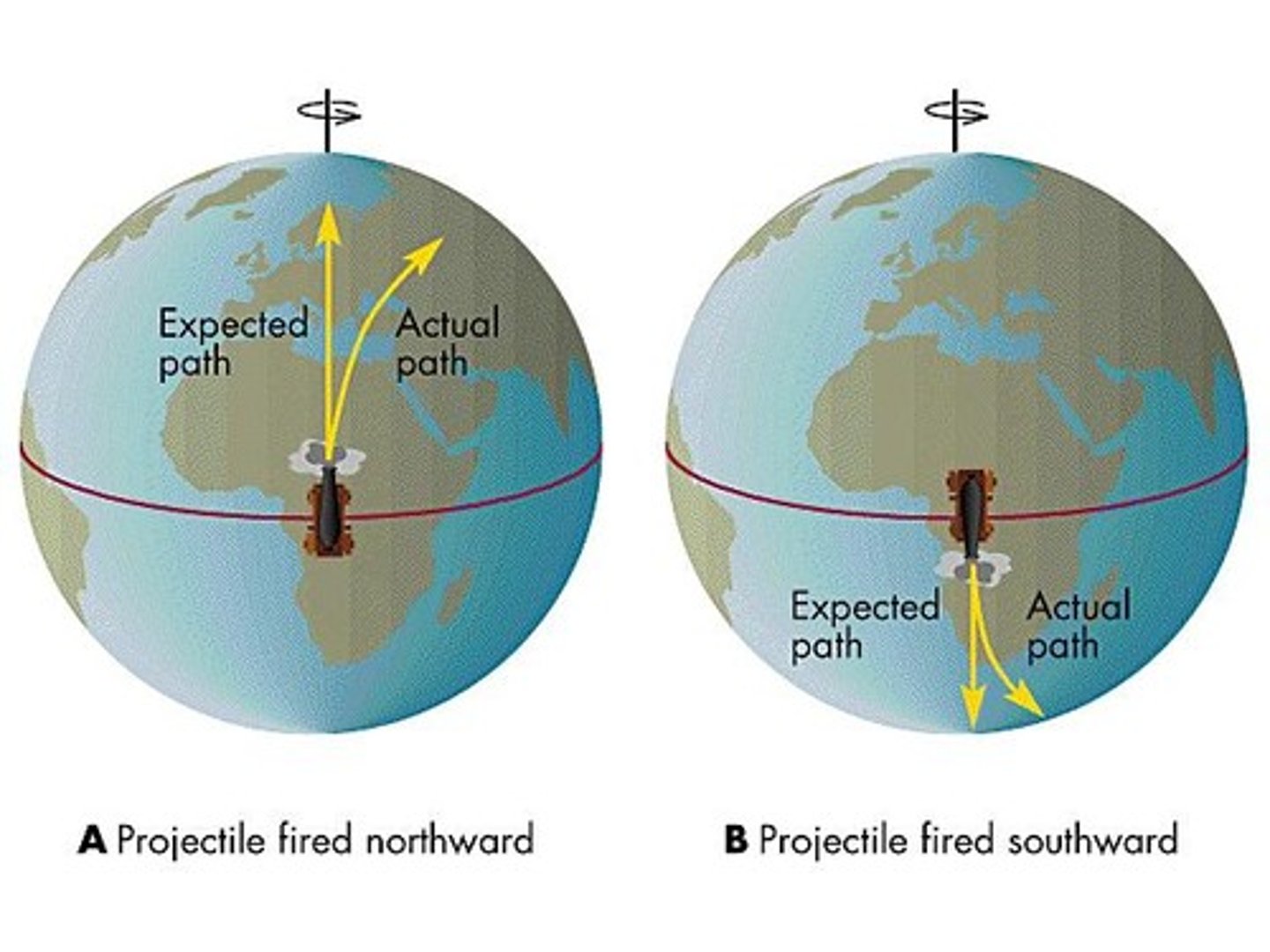
Coriolis effect
the deflection of an objects, winds, and currents path due to the rotation of Earth
Ekman
the overall movement of a mass of water resulting from the Ekman spiral, in a direction 90 degrees to the wind direction
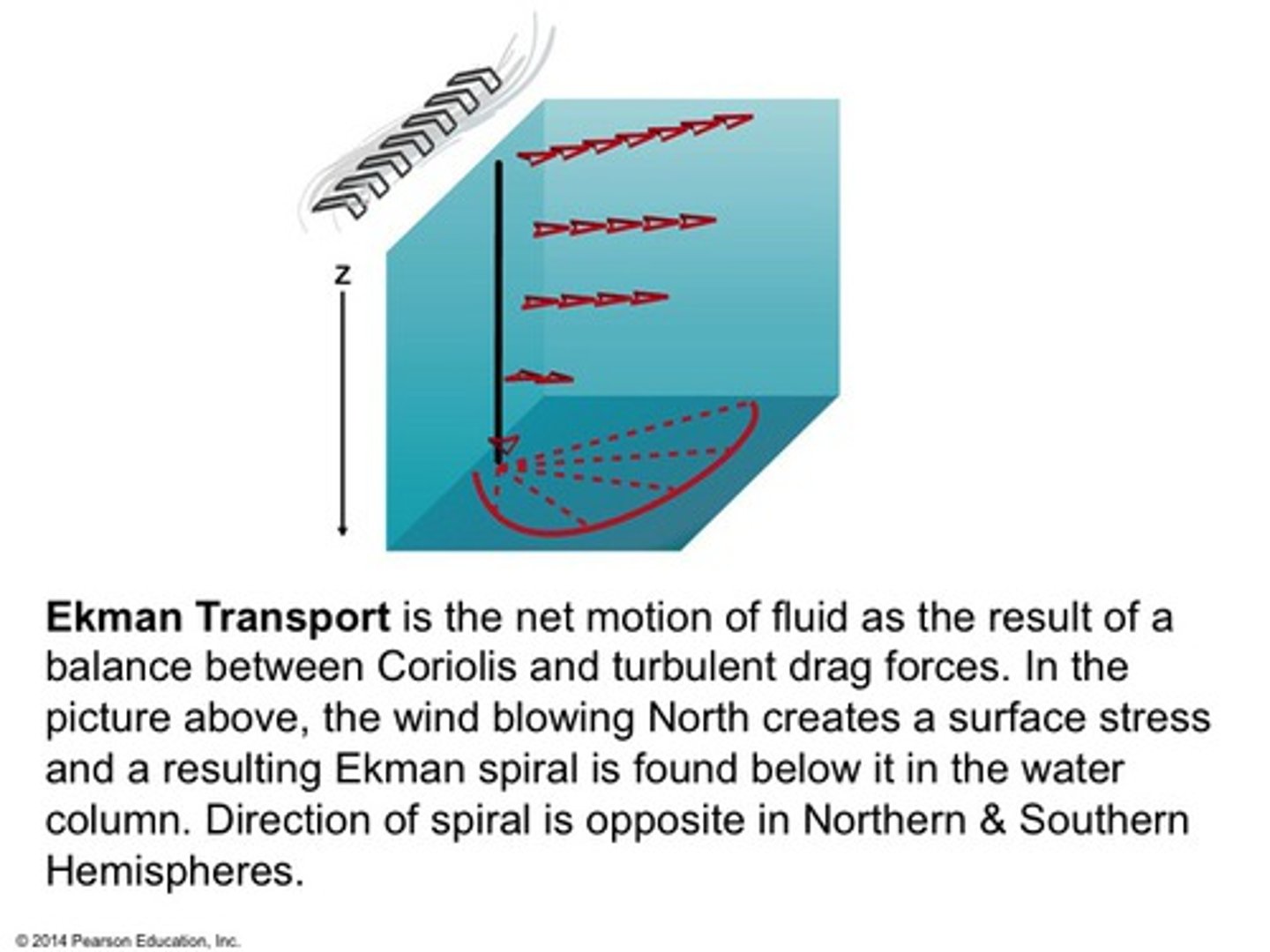
downwelling
places where near-surface water sinks

upwelling
places where deeper water rises

thermohaline circulation
an oceanic circulation pattern that drives the mixing of surface water and deep water
tides
the regular rise and fall of the ocean's surface influenced by the moon's gravity pulling on earth
water waves
driven by wind shear across the surface
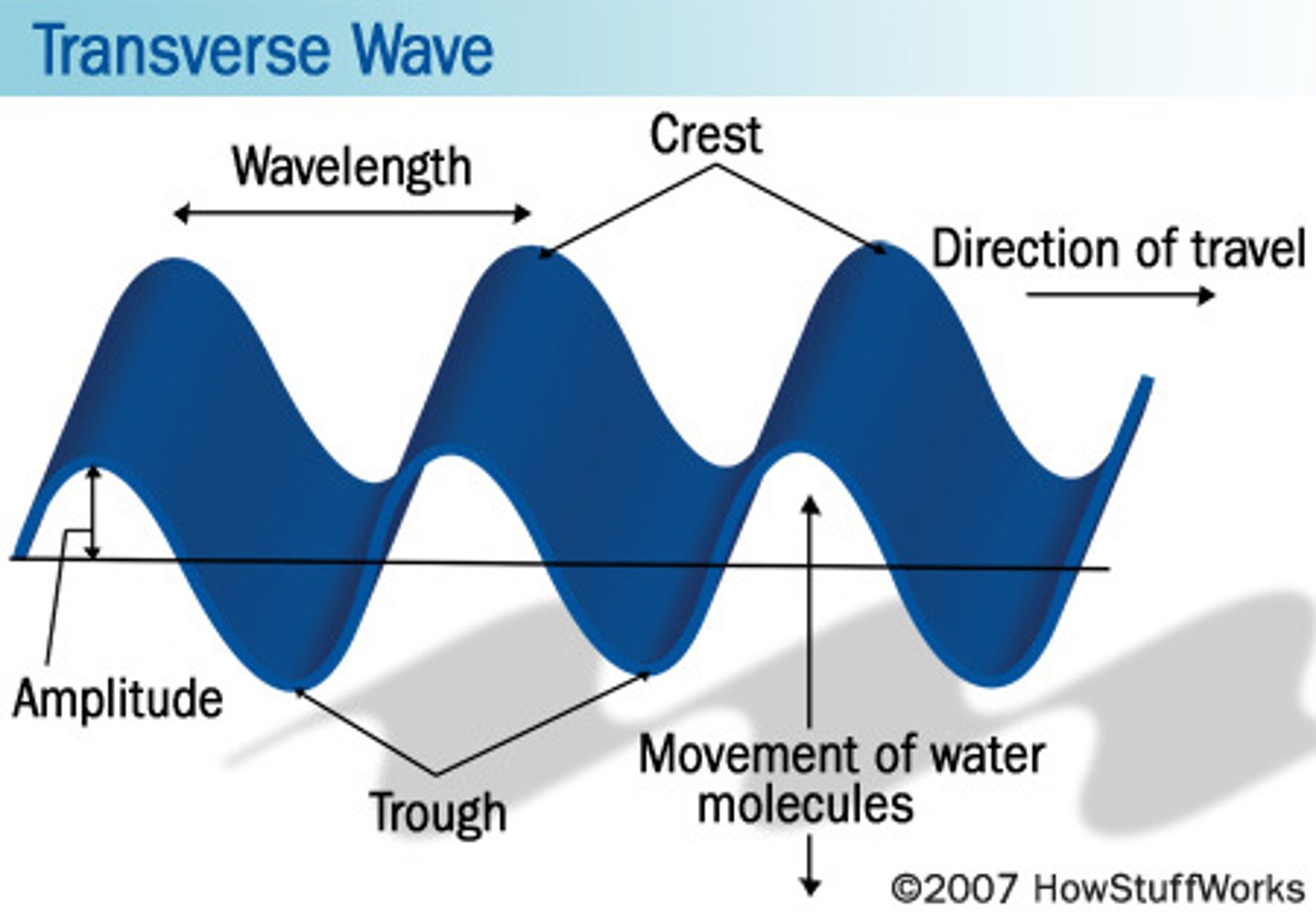
wave refraction
bends the waves parallel to the beach due to the increases in velocity as water shallows

headland erosion
wave energy erodes protrusions into the open water, erosion works to straighten out an irregular shoreline
wave-cut notches and bences
gradually undercut cliff face
barrier island
a long ridge of sand or narrow island that lies parallel to the shore

examples of different kinds of coasts
estuaries, uplifted terraces, swampy delta, coast plains and offshore sandbars, glacial fjords, coastal sand dunes, coral reefs off a mangrove swamp
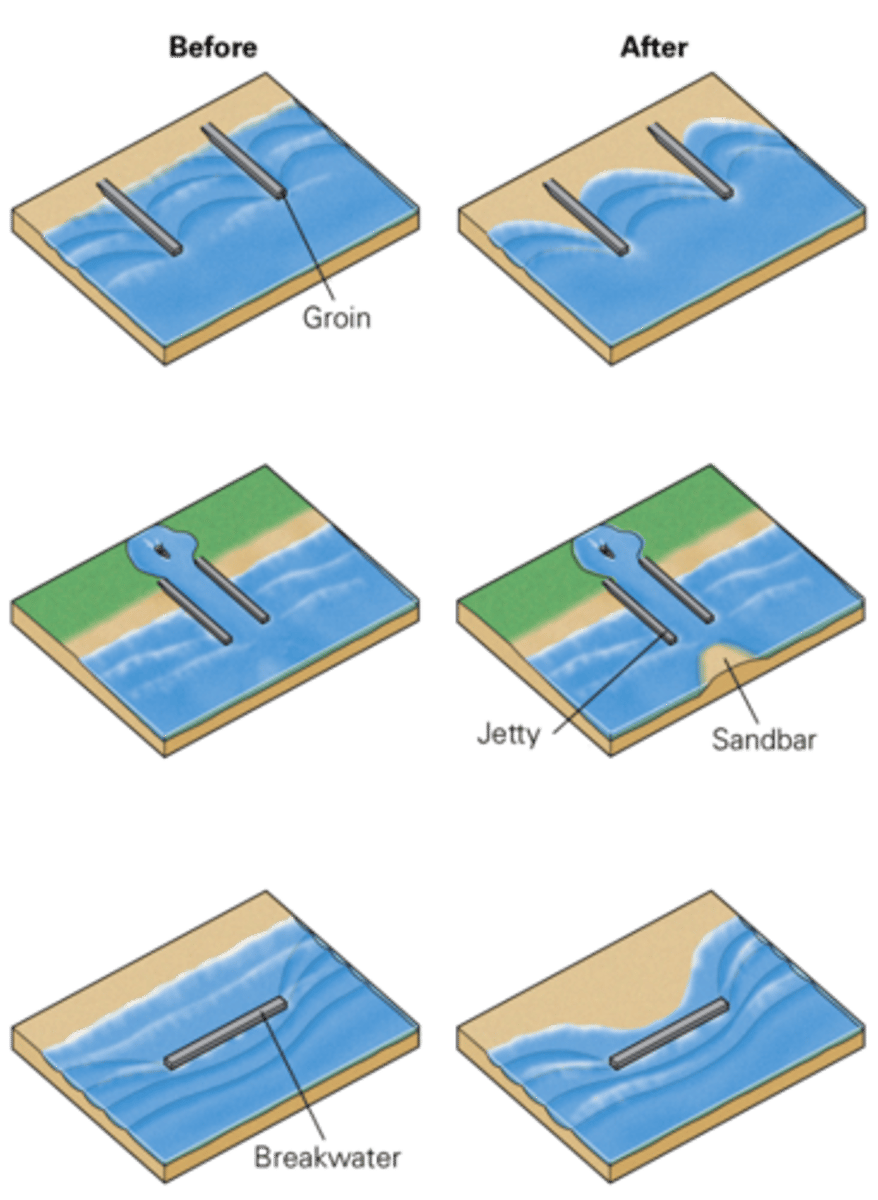
coastal stabilization techniques
groins - concrete walls protruding perpendicular to the shore
jetties - protect entrance to a harbor
breakwater - parallel to the beach to prevent full force waves reaching the harbor
groundwater
water in the Earth's subsurface filling the porous spaces in soils, sediments, and rocks
groundwater table
the depth at which all the pores in an interconnected geological unit are filled

primary vs secondary porosity
primary: consist of vesicles, relicts of air bubbles that were trapped during cooling
secondary: new pore space produced in rocks some time after the rock first formed
permeability
the degree to which a material allows fluids to pass through it via an interconnected network of pores and cracks
aquifers vs aquitards
sediments or rocks that have both high porosity and high permeability VS.
sediments or rocks that have low permeability
recharge area
a location where water enters the ground and infiltrates down to the water table
discharge area
a location where groundwater flows back up to the surface and may emerge at springs
hydraulic head
the potential energy available to drive the flow of a given volume of groundwater at a location
Darcy's Law
a mathematical equation stating that a volume of water, passing through a specified area of material at a given time, depends on the material's permeability and hydraulic gradient
springs
occur when the aquifer intersects the surface
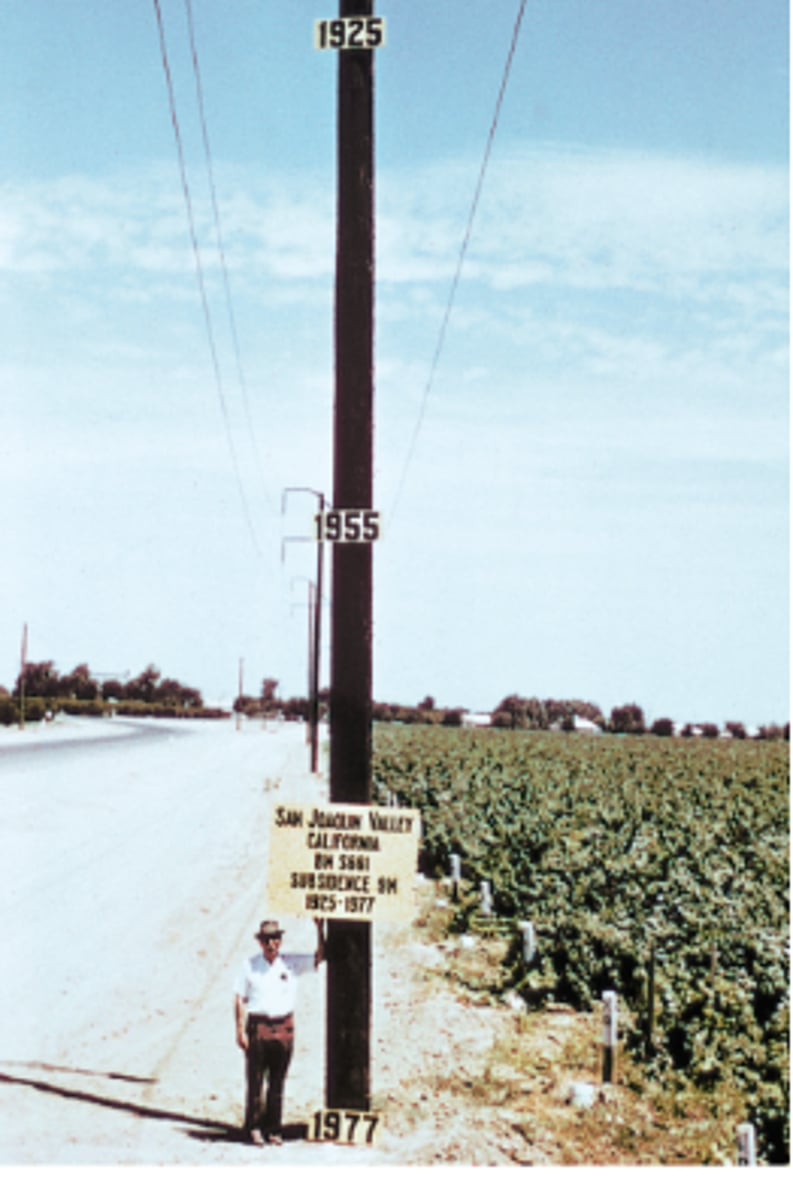
land subsidence
the sinking or settling of land to a lower level in response to various natural and human-caused factors, wells

groundwater contamination
addition of chemicals or microbes to the groundwater supply
karst landscapes
a region underlain by caves in limestone bedrock; the collapse of the caves creates a landscape of sinkholes separated by higher topography, or of limestone spires separated by low areas

sink holes
a cavity in the ground in limestone bedrock, caused by water erosion and providing a route for surface water to disappear underground
hydrocarbons
a chain-like or ring-like molecule made of hydrogen and carbon atoms; petroleum and natural gas are hydrocarbons
crude oil
petroleum that has not been processed
diversity of hydrocarbon products
as the length of the molecule increases the viscosity increases
source of oil
plankton (microscopic plants and animals that live in the ocean)
mid-Mesozoic times
migration
liquid oil and gas will buoyantly migrate upwards
primary migration: movement out of the source rock to a more porous rock
secondary migration: movement through the carrier rock to a trap
reservoir rocks
ock with high porosity and permeability, so it can contain an abundant amount of easily accessible oil
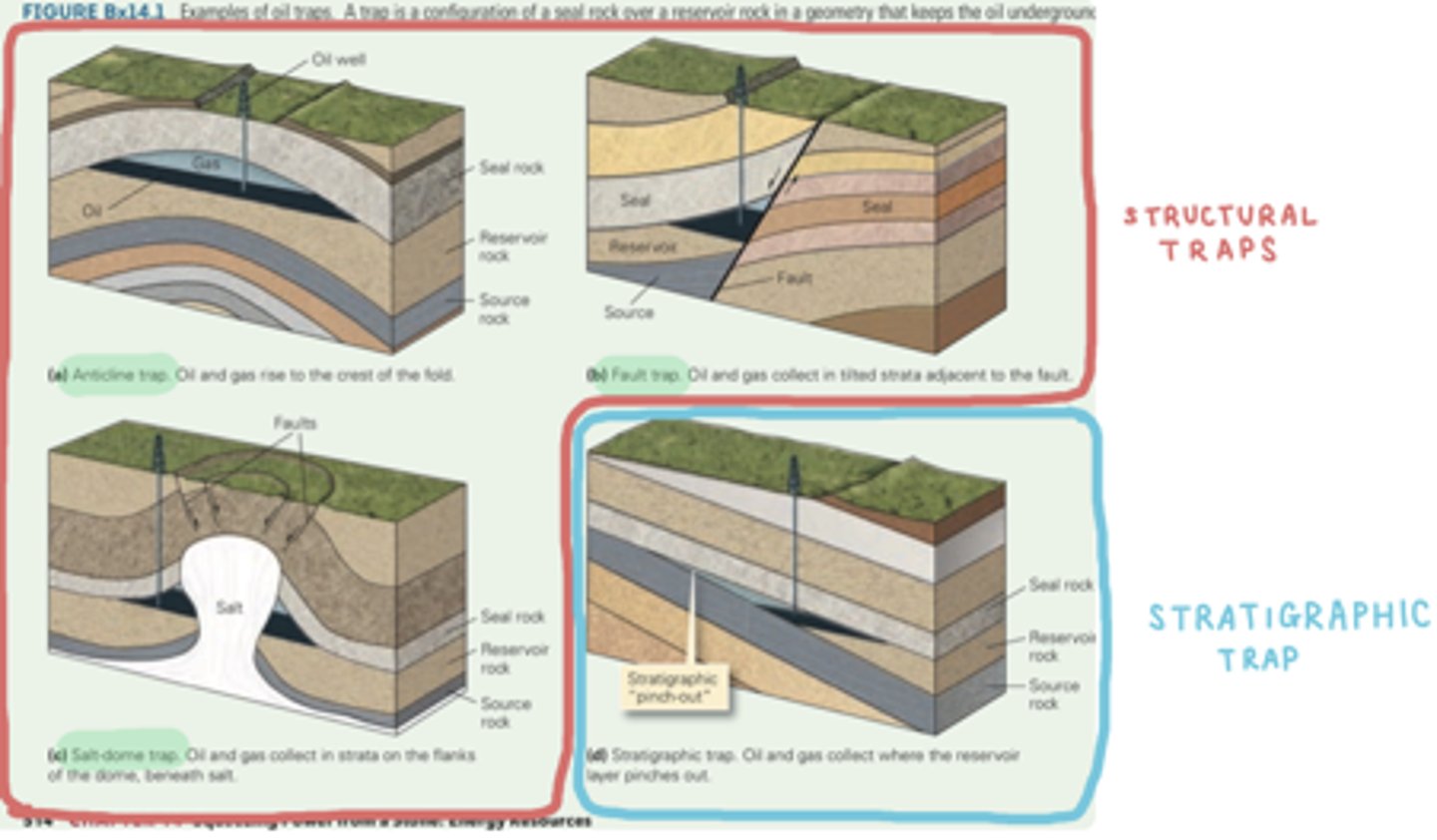
hydrocarbon traps
a subsurface configuration of seal rocks and structures that keep oil or gas underground so it doesn't seep out of the surface
directional drilling
the process of controlling the trajectory of a drill bit to make sure that the drill hole goes exactly where desired
fracking
a process by which drillers generate new fractures or open preexisting ones underground
time scales of climate variation
climate varies on all timescales ranging from annual to tectonic
Snowball Earth
the hypothesis that glaciers covered the planet's land masses from pole to pole 750 to 570 million years ago
Earth's energy budget
the balance between the amount of energy coming in from the Sun and going back out into space
feedback loops (positive and negative)
positive feedback: a change causes a process to continue (amplify)
negative feedback: a change causes a process to stop (supress)
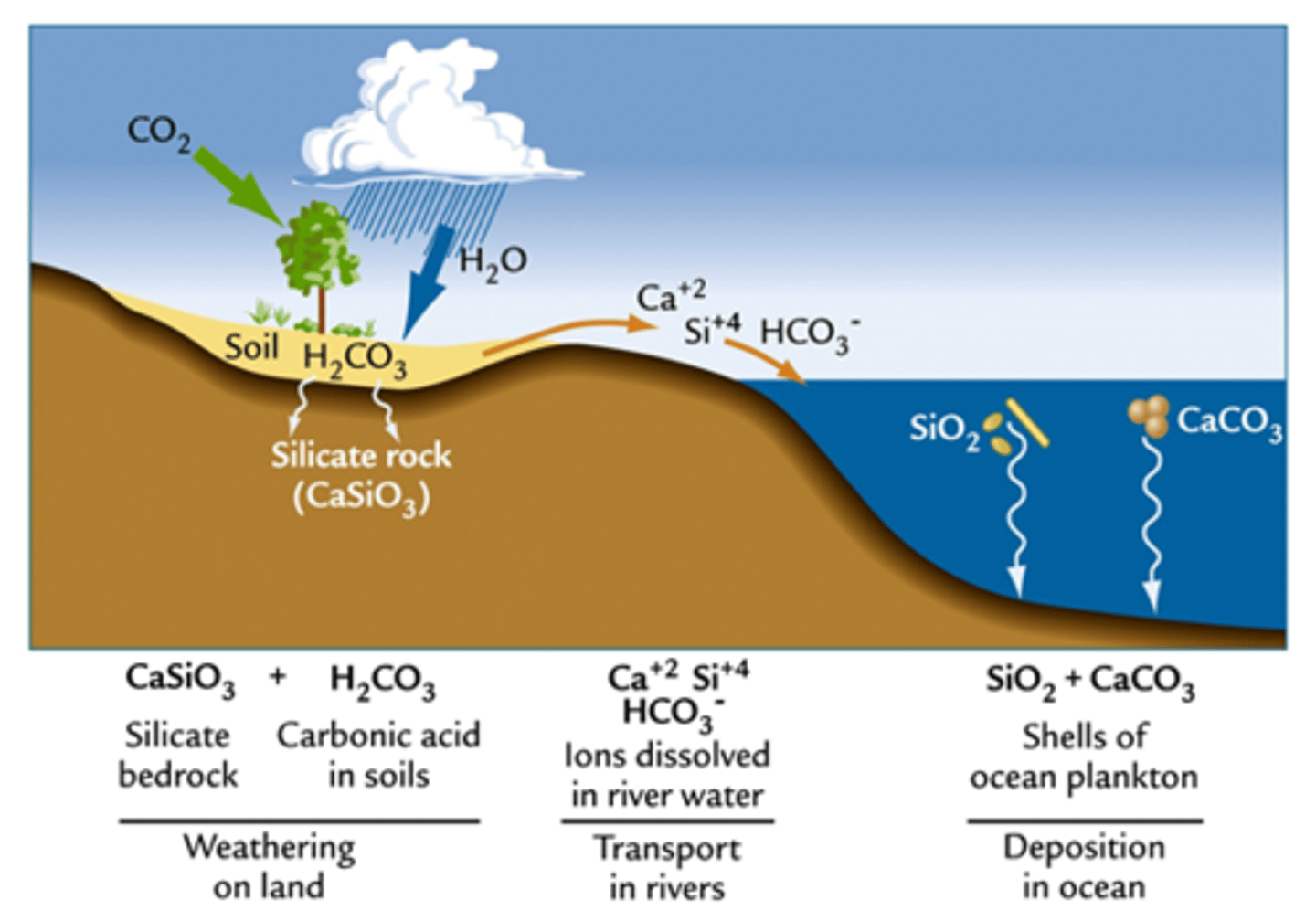
rock CO2 cycle
on tectonic timescales geology controls climate through changes in atmospheric CO2
weathering increases CO2 - supplies nutrients to oceans to stimulate productivity