explanations for forgetting- interference
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What does forgetting mean ?
when learnt info can’t be retrieved
In the STM , why would forgetting occur ?
due to availability problem , either displaced or faded away
In the LTM , why would forgetting occur?
either decay (availability problem)
or because it’s hard to retrieve (accessibility problem )
or the information is confused (interference problem)
what is proactive interference ?
old memory interfering with a new mermory
what is retro active memory ?
new memory interfering with old memory
when is interference more likely ?
if info is similar
give one study where interference as an explanation for forgetting was investigated ?
Henk Schmidt (2000)
give one study that investors the effect of similarity on interference ?
McGeoch and McDonald (1931)
In short , give evaluative points for interference on forgetting .
strength - research support
strength - practical applications
weakness - supporting studies use artificial settings and tasks
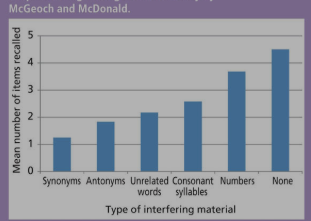
Describe Mcgeoch and McDonald’s procedure and findings ?
procedure
> studied retroactive interference by changing the amount of similarity between two sets of materials.
> p’s learnt list of 10 words until 100% recall accuracy
> 6 groups learnt different new lists
synonyms
antonyms
words unrelated to the original list
consonant syllables
three digit numbers
no new list - control condition
findings
> recal of original list was less accurate when new list was most similar to the original .
interference is strongest when memories are similar