visual fields
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
describe the normal visual field
inferiors 75 degrees
superiorly 60 degrees
nasally 60 degrees
temporal 100 degrees
monocular fields overall to give 120 degree stereoscopic zone
what types of perimetry are there
static and kinetic
what is static perimetry
uses a stimulus of increasing intensity to determine threshold at a particular location on the retina generating sensitivity plot
what is kinetic perimetry
constant sized target brought towards central fixation and where just noticed used as a threshold relating to size
what types of static perimetry are there
full threshold, screening, estermann, ambler is gross static method
name types kinetic perimetry
gross perimetry
when should you conduct visual field assessment
px new to practise
drivers
risk factors eg FHG
signs and symptoms
what testing distance is the Henson 9000 at
25cm
what output results do visual fields include
total deviation
pattern deviation
what is total deviation
deviation individual points vs age matched normal
what is pattern deviation
modified plot showing localised defects by removing the effect of overall shifts in sensitivity
what reliability indices are there
false positives
false negatives
fixation losses
hemifield test
what percentages of these indices makes these percentages unreliable
false positives>15%
false negatives>30%
fixation losses>20%
describe how to do estermann fields
both eyes opening driving glasses
advise px that fixation light mat move and to follow the light if so
what counts as acceptable loss for estermann
scattered single missed points
single cluster of up to 3 adjoining points
what counts as unacceptable visual field loss
cluster of 4 or more adjoining missed points up to and including 20 degrees form fixation and any sep missed points within central 20 degrees area
any central loss that is an extension hemianopia and quadrantanopia size greater than 3 missed points
describe the amsler chart and how to use it
10cm by 10cm at 28cm. each square is 5mm wide corresponding to 1 degree
monocularly with reading glasses in good light
what amsler chart is used if someone has optic neuritis
red variant
what amsler is used if someone cannot see the fixation target
use amsler 2, with diagonal lines included
what is the red amsler useful for
detecting early adverse drug reactions at the macula eg hydorxycholoruqine maculoapthy
draw and label the visual pathway
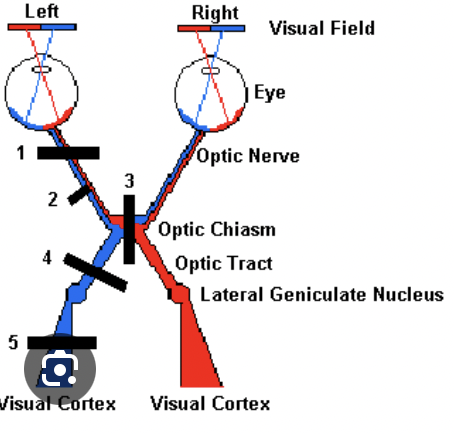
what lesion causes left homonymous hemianopia
lesion in right optic tract or LGN
what causes pie in the sky defect
lesion in Meyers loop of the optic radiation
what is a bitemporal hemianopia caused by
lesion at optic chiasm, pituitary adenoma
what can cause left homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing
lesiosn in occipital lobe. dual blood supply by MCA and PCA spared macula
what causes left inferior homonymous hemianopia
damage t superior fibres of optic radiations in parietal lobe
what causes monocle defect
retinal or optic centre problems