Life Sciences - Ecosystem Energetics and Nutrient Cycling
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Energy
the ability to do work or the process of doing work
Potential Energy
stored energy. For our purposes this will usually be energy stored in complex organic molecules.
Kinetic Energy
energy being used or released. This includes movement of mass, light, heat, solar radiation, and other forms.
The First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed. Account for the energy on both sides of the transformation
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
No transformation is 100% efficient. Without the addition of energy, disorder in a system increases.
Photosynthesis
This process involves the absorption of carbon dioxide by plants, which combined with water and sunlight produces glucose and oxygen.
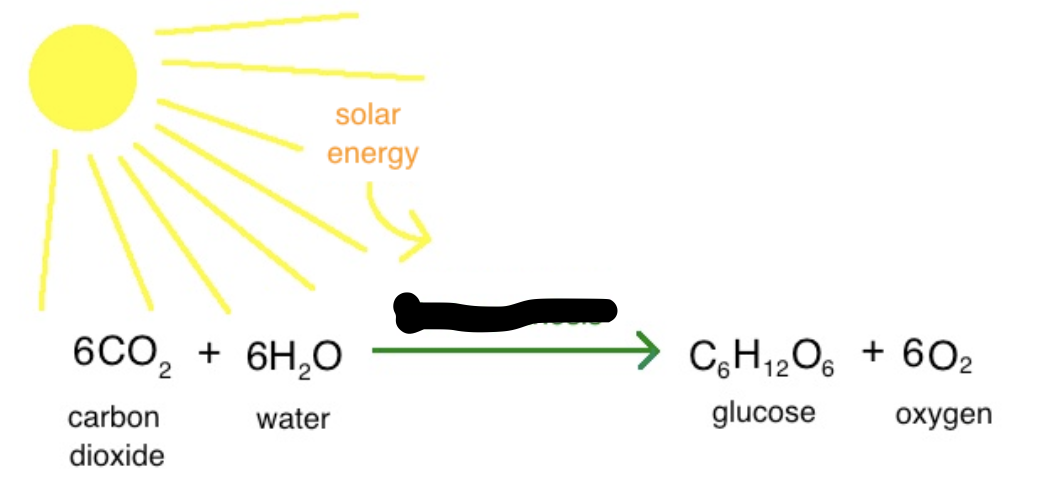
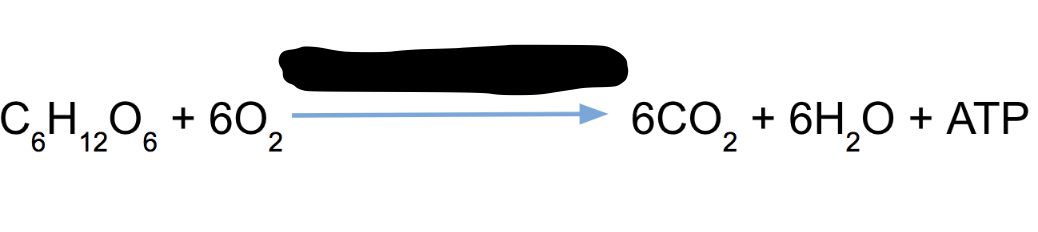
Cellular Respiration
This process converts oxygen and glucose into water, carbon dioxide and energy (ATP - used to power bodily functions)
1st Trophic Level
Source of Energy: producer
Trophic Name: autotroph
Feeding Pattern: green plant
2nd Trophic Level
Source of Energy: primary consumer
Trophic Name: heterotroph
Feeding Pattern: herbivore
3rd Trophic Level
Source of Energy: secondary consumer
Trophic Name: heterotroph
Feeding Pattern: carnivore
4th Trophic Level
Source of Energy: third level consumer
Trophic Name: heterotroph
Feeding Pattern: carnivore
Food Chain
description of the flow of energy through the populations in a community
Food Web
Representation of all possible transfers of energy in a community
Apex Predator
the predator not eaten by others in the food web
Pyramid of Energy/Biomass
necessary consequence of the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - visual representation of only 10% energy from one trophic level moving to the next.
Pyramid of Size
animals at higher trophic levels tend to be larger than their prey
Pyramid of Numbers
animals at higher trophic levels tend to be fewer than their prey
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
mass of carbon fixed through photosynthesis
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
mass of carbon fixed through photosynthesis minus that emitted by plants during respiration
Inverted Pyramid of Biomass
In certain marine ecosystems, there appears to be less biomass in a snapshot of the lower trophic levels than the higher ones because of the efficiency of phytoplankton(producers) and zooplankton(primary consumers)
Carbon
element found in biological tissues and atmospheric, geological, and fossil fuel reservoirs
Nitrogen
element found biologically in proteins, DNA, RNA, and tissues. It is also found in atmospheric reservoirs and it is a limiting nutrient used in fertilizers
Phosphorus
element found biologically in tissues and ATP/ADP. It is also found in geological reservoirs, and it is the other nutrient used in fertilizers.
Sulfur
element with a similar cycle to other mineral cycles, except that coal combustion produces an atmospheric version of it
Macronutrients
nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K)
Micronutrients
iron (Fe), calcium (Ca), manganese (Mn), magnesium (Mg)
Combustion
the process of burning something (fossil fuels or trees) - responsible for recycling carbon back into the atmosphere as CO2
Fixation
the process of transforming N2 gas (triple bonded) into NH4 and NH3 (ammonium/ammonia) done by nitrogen fixing bacteria (free living or mutualistic), lightning, or industrial fixation (to produce fertilizer)
Nitrification
the process of transforming ammonium/ammonia (NH4/NH3) into nitrites/nitrates (NO2/NO3), which is usable by plants. This is done by nitrifying bacteria.
Assimilation
plants do this by absorbing the NO2/NO3 (nitrites/nitrates) and converting them into proteins, DNA, and RNA, allowing nitrogen to enter the food chain. This can also apply to the mineral cycles because it means “the process by which living organisms take up and convert inorganic mineral nutrients from the environment into organic compounds necessary for their growth and survival.”
Ammonification
the process of transforming the proteins/DNA/RNA created by plant assimilation into ammonium/ammonia (NH3/NH4). This is done by ammonifying bacteria.
Denitrification
the process of transforming nitrites/nitrates (NO2/NO3) into nitrogen gas (N2). This is done by denitrifying bacteria.
Decomposition
the process of breaking down a substance into simpler components through natural or chemical means
Weathering
the process of breaking down rocks, soil, and minerals into smaller pieces through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, water, and living organisms
Erosion
the natural process where wind, water, or ice wears away land and moves it to another location
Lithification
the process by which unconsolidated sediments, like sand, clay, and gravel, are converted into solid rock through compaction and cementation
Sedimentation
the process where solid particles settle out of a liquid, typically due to gravity, leading to the formation of sediment
Geologic Reservoir
natural underground formations, typically porous and permeable rock layers, that can store fluids or gases like water, oil, natural gas, or carbon dioxide
Tectonic Processes
the movements and interactions of Earth's lithospheric plates, driven by heat from the planet's core, which cause landforms to be created, altered, and destroyed
Leaching
when nutrients are dissolved in water and carried away, either in the groundwater or as surface runoff
Eutrophication
the process where a body of water becomes enriched with excess nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, leading to harmful algal blooms and oxygen depletion