Endocrine Lecture Exam A&PII
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Target organs most often regulate the pituitary gland via _________.
negative feedback inhibition
The infundibulum is a ___________.
projection of the hypothalamus from which the pituitary gland hangs
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) targets the __________.
kidneys
The nervous system reacts to stimuli __________ compared to the endocrine system, adapts __________ compared to the endocrine system, and has __________ effects compared to the endocrine system.
quickly;quickly; specific
__________ secretion is controlled by neuroendocrine reflexes, whereas __________ secretion is controlled by negative feedback mechanisms.
ocytocin (OT); antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Which hormone stimulates glucocorticoid secretion?
ACTH
The zona fasciculata in the adrenal gland secretes ___________.
cortisol
The __________ secretes several hormones that stimulate the development of lymphatic organs and regulates development and activity of T cells (white blood cells).
thymus
Which of the following best describes a hormone?
a chemical messenger transported by the bloodstream that stimulates target cells in another organ often a good distance away.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events leading to the polyuria and dehydration associated with diabetes mellitus?
Hyperglycemia → glucose enters renal tubules → glucose transport maximum exceeded → glucose in urine raises osmolarity of tubular fluid → osmotic diuresis
The __________ secrete(s) a hormone as a response to hypocalcemia.
parathyroid glands
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone targets the __________.
anterior pituitary
Which of the following is not secreted by the pancreas?
somatotropin (growth hormone)
The hypophysial portal system connects the _________ with the _________.
anterior pituitary; hypothalmaus
Which of these hormones does not stimulate the release of another hormone by its target cells?
PRL
The anterior pituitary is __________ the posterior pituitary and has __________ connection to the hypothalamus.
larger; no neuronal
The posterior pituitary secretes _________.
oxytocin (OT)
Of the following hormones, which has more target cells in the body than the others?
growth hormone (GH)
Which of the following statements about diabetes mellitus is false?
both type I and type II DM are characterized by lack of, or low levels of insulin
The hormone called _________ plays an important role in synchronizing physiological function with the cycle of daylight and darkness.
melatonin
Many hours after a meal, alpha (α) cells in the pancreatic islets secrete _________, which _________ blood glucose.
glucagon; raises
Which of the following organs has both endocrine and exocrine functions?
the ovary
Growth hormone (GH) hypersecretion causes gigantism when it begins in childhood, but it is more likely to cause __________ when it begins in adulthood.
acromegaly
Any situation that upsets homeostasis and threatens one’s physical or emotional well-being is called __________.
stress
Which of the following is true regarding endocrine glands?
they release their secretions into the blood.
The absence of iodine in the diet leads to __________.
hypothyroidism
The ___________ can be found as part of the epithalamus, near the superior colliculi of the midbrain.
pineal gland
After eating a meal, blood sugar levels _________
increase
After a meal is eaten by a person who does not have diabetes, insulin is released and will cause blood sugar levels to _________.
return to about normal
In Type-I diabetes, blood sugar levels remain high after a meal because __________
no insulin is released
The treatment for Type-I diabetes always includes _________
insulin
The role of insulin is to _________
allow cells to take in glucose
Individuals with Type II diabetes _________
do not respond to insulin
Individuals with Type I diabetes __________
do not produce insulin
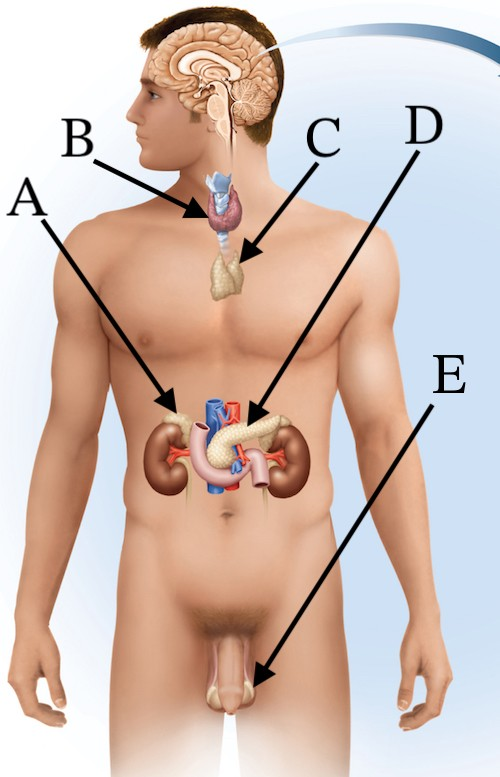
Hornones from which organ have the greatest effect on the basal metabolic rate (BMR)?
(B) Thyroid gland
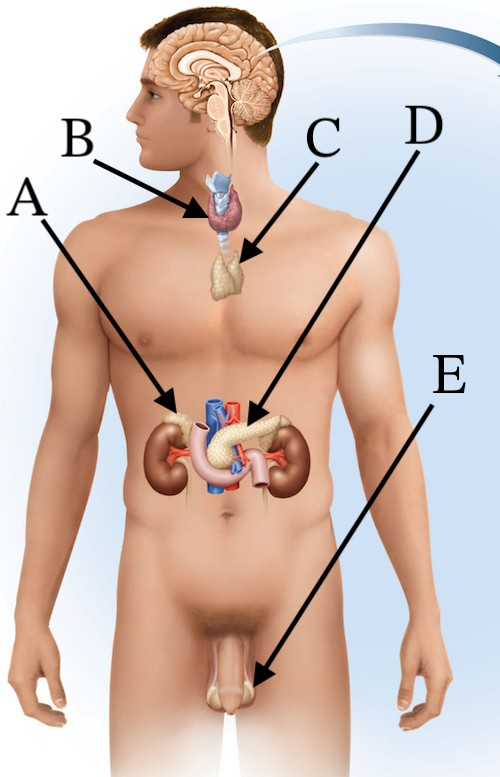
Follicle-stimulating hormone targets which of these organs?
E (ovarys and testes)
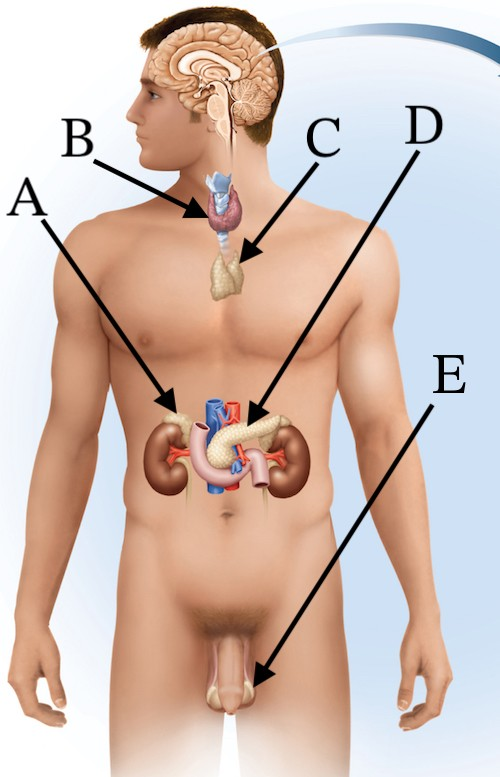
Which organ produces hormones that control blood electrolyte levels?
A (adrenal glands)
Dehydration is detected by osmoreceptors in the _________.
hypothalamus
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is released by the _________
posterior pituitary
ADH helps to conserve water during dehydration. T OR F
True
Which of the following is a function of ADH?
decrease urine volume output and cause blood-vessel constriction