Allocation Concealment
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
allocation concealment
It is the process of keeping the randomization sequence hidden so that researchers cannot know which treatment a participant will receive before assigning them.
Why is allocation concealment important?
because if researchers know who is going to get which treatment, they might (even unintentionally) put “healthier” or “sicker” patients in one group, which would distort the results.
and to make sure the groups are as similar as possible at the start of the trial so that any differences at the end are due to the treatment — not pre-existing differences.
What happens if allocation concealment is NOT used?
The groups may start off different from each other, making it hard to know whether the treatment or the baseline differences caused the final outcome.
What happens if researchers KNOW which treatment a participant will receive?
They may (consciously or subconsciously) put healthier patients into one group and sicker patients into the other, making the groups unfair before the trial even starts.
problem because any difference at the end of the trial might be due to the groups being different at the beginning, not because the treatment actually worked.
What is selection bias in an RCT?
When people placed into each treatment group differ in ways that affect the outcome (e.g., one group starts healthier), causing inaccurate results.
How does allocation concealment prevent selection bias?
It hides the treatment assignment sequence so researchers can’t influence who goes into which group
How much can poor allocation concealment exaggerate treatment effects?
Studies show that the effect of a treatment can be exaggerated by 35–40% if allocation concealment is not properly used.
When does allocation concealment happen?
Before the participant is enrolled and receives treatment. It ensures that the person enrolling participants does not know in advance which group the next participant will be placed in.
What is the main difference between concealment and blinding?
Concealment = hiding group assignment before enrollment
Blinding = hiding the treatment after enrollment
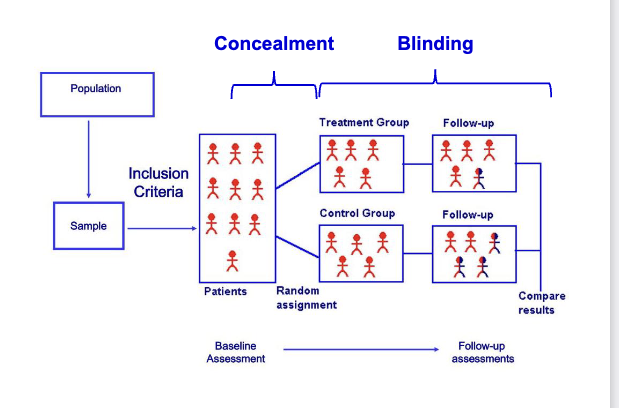
Who should do the allocation concelament
a third party should place participants in different groups that includes)

What is a centralized assignment system in an RCT?
It’s an online or phone-based system that automatically assigns participants to groups without the trial investigators seeing or influencing the process.
these centralized systems are all in one place solutions where participants can call in or log in to allocate remotely and without any action from trial investigators
What is one downside of centralized assignment?
It can have technological problems—like glitches, system crashes, or delays.
What is SNOSE?
SNOSE stands for Sequentially Numbered Opaque Sealed Envelopes — an older method used to hide group assignments in clinical trials before computer systems were available.
t’s used to help conceal allocation when a third party or computer system is not available. It is better than having no concealment at all.
What is a problem with SNOSE?
It can be tampered with—for example, envelopes can be held up to light or opened early—so it requires strict procedures to be effective.
If an RCT makes no mention of anything related to allocation concealment, it suggests _____
that thereserachers were not aware of the issue and the risk of bias is high
What is pharmacy-controlled assignment?
It’s when the hospital pharmacy (not the researchers) is in charge of giving out the treatment or placebo, which keeps the group assignments hidden from investigators.
They use numbered or barcoded containers and follow the protocol strictly so nobody can tell which container is real treatment vs placebo.
What type of trials is pharmacy controlled method especially useful for?
Drug trials, because pharmacies already handle medication storage, labeling, and distribution.
What is the main weakness of pharmacy-controlled assignment?
It only works well if the pharmacy staff are properly trained and follow the trial procedures exactly.
Assessing allocation concealment checklist

Allocation concealment RCT example

This is a bad example of allocation concealment.
Although the paper mentions the allocation ratio and the software used to generate the random sequence, it never explains how allocation was kept hidden from the person enrolling participants. Without describing who assigned participants to groups, or whether that person was blinded to the upcoming treatment, we cannot be sure the allocation was concealed.
Because the authors do not describe any method to prevent someone from predicting or influencing which group the next participant would enter, the study has a high risk of selection bias and fails CONSORT reporting standards for allocation concealment.
Allocation concealment RCT example 2
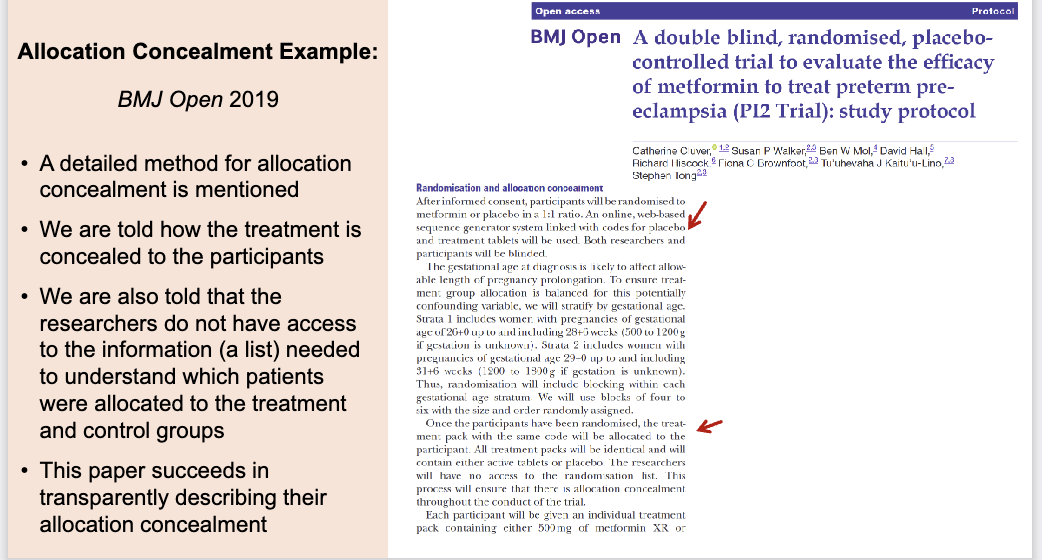
This is a good example of allocation concealment.
The authors provide a clear, detailed description of how allocation concealment was performed. They explain that:
A secure online, web-based system generated the random allocation sequence
Treatment packs were identical in appearance, preventing participants from knowing their assignment
Researchers did not have access to the allocation list, meaning they could not see or predict which treatment a participant was assigned
The process ensures that the person enrolling participants cannot influence or foresee group assignment
Because the paper clearly outlines how concealment was maintained and prevents selection bias, this study meets CONSORT standards and is considered a strong example of proper allocation concealment.