Comprehensive Guide to Acids, Bases, Salts, and pH Concepts in Chemistry
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Arrhenius acid
Hydrogen-containing compound that produces H+ ions in solution
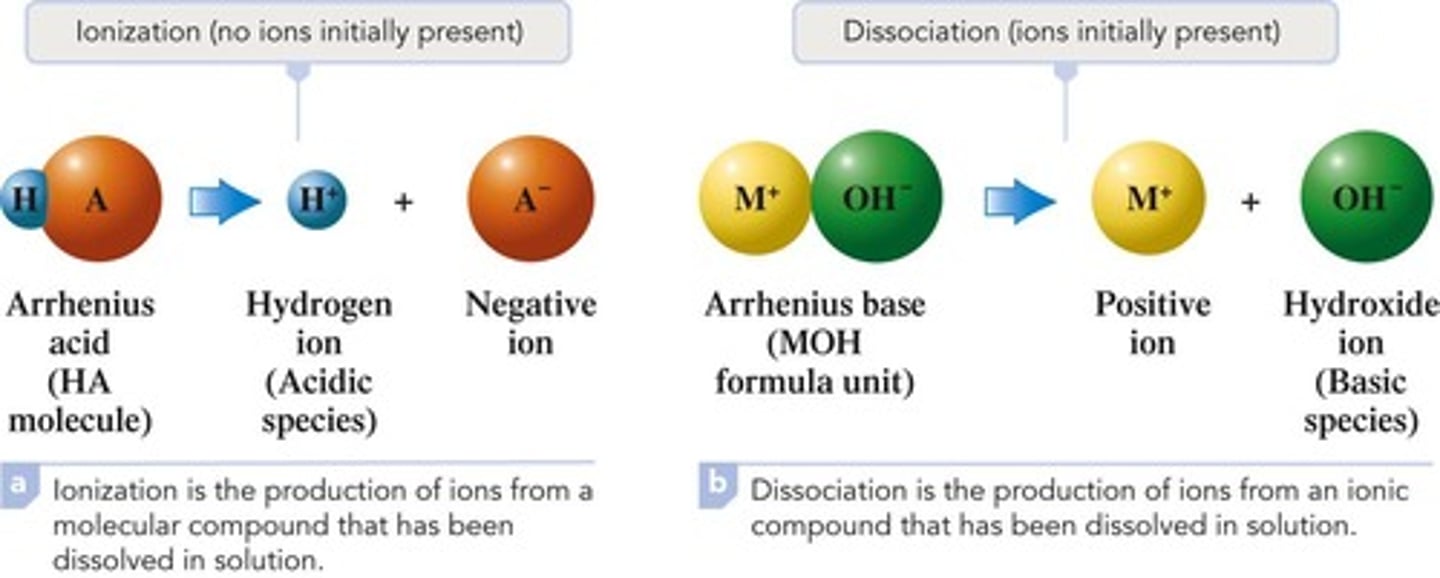
Arrhenius base
Hydroxide-containing compound that produces OH- ions in solution
Ionization
The process in which individual positive and negative ions are produced from a molecular compound that is dissolved in solution
Dissociation
The process in which individual positive and negative ions are released from an ionic compound that is dissolved in solution
Bronsted-Lowry acid
Substance that can donate a proton (H+ ion) to some other substance
Brønsted-Lowry base
Substance that can accept a proton (H+ ion) from some other substance
Acid
A substance that donates a hydrogen ion to another substance.
Base
A substance that accepts a hydroxide ion from another substance.
Acid in Water
A substance that produces hydrogen ions in water.
Base in Water
A substance that produces hydroxide ions in water.
Conjugate Acid-Base Pair
Two members that differ from one another by one H+.
Amphiprotic Substance
A substance that can either lose or accept a proton and thus can function as either a Brønsted-Lowry acid or a Brønsted-Lowry base.
Example of Amphiprotic Substance
H2O, H3O+, OH-.
Monoprotic Acid
An acid that supplies one proton (H+ ion) per molecule during an acid-base reaction.
Examples of Monoprotic Acid
HCl, HNO3, HBr.
Diprotic Acid
An acid that supplies two protons (H+ ions) per molecule during an acid-base reaction.
Examples of Diprotic Acid
H2CO3, H2SO4.
Triprotic Acid
An acid that supplies three protons (H+ ions) per molecule during an acid-base reaction.
Example of Triprotic Acid
H3PO4.
Polyprotic Acid
An acid that supplies two or more protons (H+ ions) during an acid-base reaction.
Difference between Monoprotic, Diprotic, and Triprotic Acid
A monoprotic acid supplies one proton per molecule; a diprotic acid supplies two protons per molecule; and a triprotic acid supplies three protons per molecule.
Acidic Hydrogen Atoms
Acidic hydrogen atoms are routinely listed at the beginning of the chemical formula.
Example of Acidic Hydrogen Atom
Acetic acid's formula is HC2H3O2.
Strong Acid
Transfers ~100% of its protons to water in an aqueous solution.
Weak Acid
Transfers only a small percent of its protons to water in an aqueous solution.
Equilibrium position of Strong Acid
Lies far to the right.
Equilibrium position of Weak Acid
Lies far to the left.
Strong Acids
Strong electrolytes.
Weak Acids
Weak electrolytes.
Strong Bases
Hydroxides of Groups IA and IIA.
Acid Ionization Constant (Ka)
An equilibrium constant for the reaction of a weak acid with water.
Acid Strength
Increases along with an increase in percent ionization.
Percent Ionization
Increases with an increase in the magnitude of Ka.
Base Ionization Constant (Kb)
The equilibrium constant for the reaction of a weak base with water.
Ionic Compounds
Contain a metal or polyatomic ion as the positive ion and a nonmetal or polyatomic ion (except hydroxide) as the negative ion.
Soluble Salts
All common soluble salts are completely dissociated into ions in solution.
Definition of a Salt
Ionic compound containing a metal or polyatomic ion as the positive ion and a nonmetal or polyatomic ion (except hydroxide) as the negative ion.
Neutralization Reaction
The chemical reaction between an acid and a hydroxide base in which a salt and water are the products.
Self-Ionization
An extremely small percentage of water molecules in pure water interact with one another to form ions.
Ion Product Constant for Water
At 24°C: Kw = [H3O+][OH-] = 1.00 × 10-14.
![<p>At 24°C: Kw = [H3O+][OH-] = 1.00 × 10-14.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2ce4ae15-3306-47d2-b167-2a277b868f81.jpg)
Three Possible Situations
[H3O+] = [OH-]; neutral solution, [H3O+] > [OH-]; acidic solution, [H3O+] < [OH-]; basic solution.
![<p>[H3O+] = [OH-]; neutral solution, [H3O+] > [OH-]; acidic solution, [H3O+] < [OH-]; basic solution.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/35bf315d-3d5f-44c8-a8d2-c24999fd3c6c.jpg)
Acidic Solution Definition
An aqueous solution in which the concentration of H3O+ ion is higher than that of OH- ion.
pH Formula
pH = -log[H3O+].
![<p>pH = -log[H3O+].</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0c831c6b-aa53-4f0e-9626-a68353b28bc6.jpg)
pH Range
pH range between 0 and 14 in aqueous solutions at 24°C.
Net Effect of Self-Ionization
The formation of equal amounts of hydronium and hydroxide ions.
Acidic Solution Characteristics
An aqueous solution in which the concentration of H3O+ ion is higher than that of OH- ion.
Basic Solution Characteristics
An aqueous solution in which the concentration of OH- ion is higher than that of H3O+ ion.
Neutral Solution Characteristics
An aqueous solution in which the concentration of H3O+ ion is equal to that of OH- ion.
pH
A measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, calculated as pH = -log [H3O+].
![<p>A measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, calculated as pH = -log [H3O+].</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b1cb6c06-06c2-4b11-ad83-92ee71187991.jpg)
Neutral pH
A pH of 7.00, indicating a neutral solution.
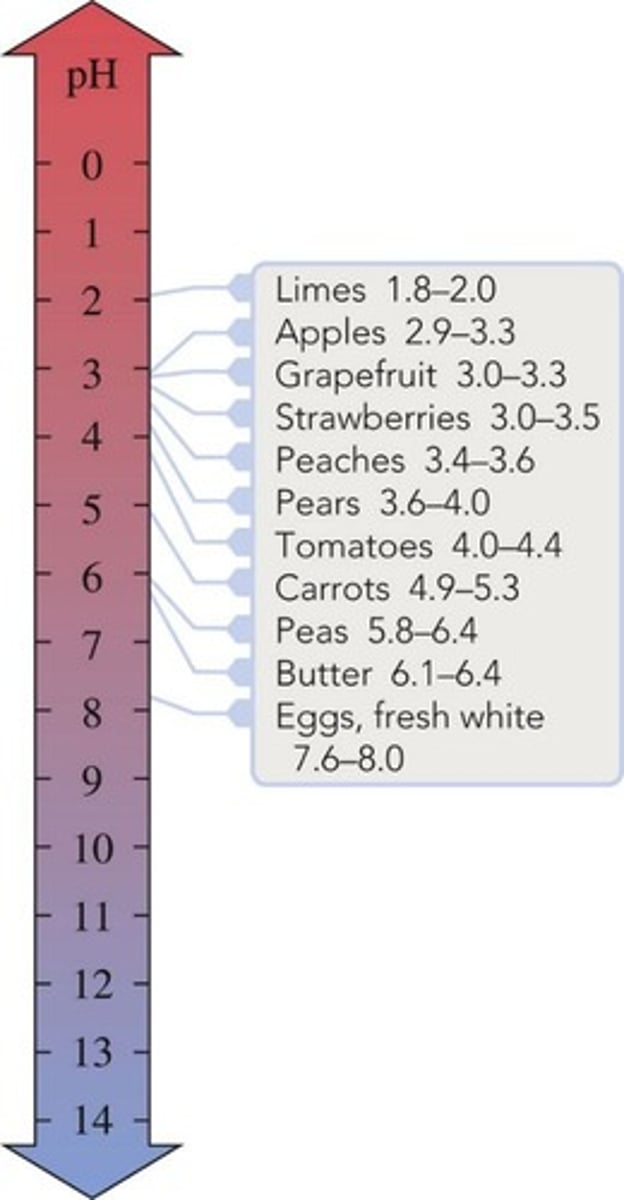
Basic pH
A pH greater than 7.00, indicating a basic solution.
Acidic pH
A pH less than 7.00, indicating an acidic solution.
pKa
A method of expressing the strength of acids, calculated as pKa = -log Ka.
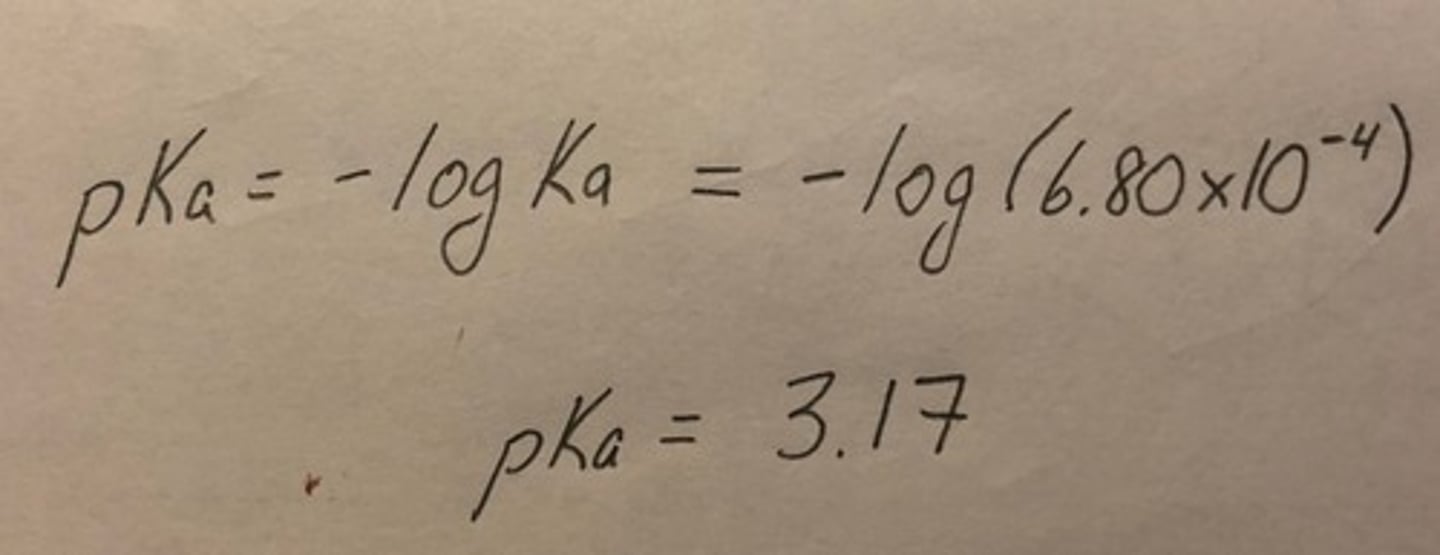
Ka
The acid dissociation constant, used to measure the strength of an acid.
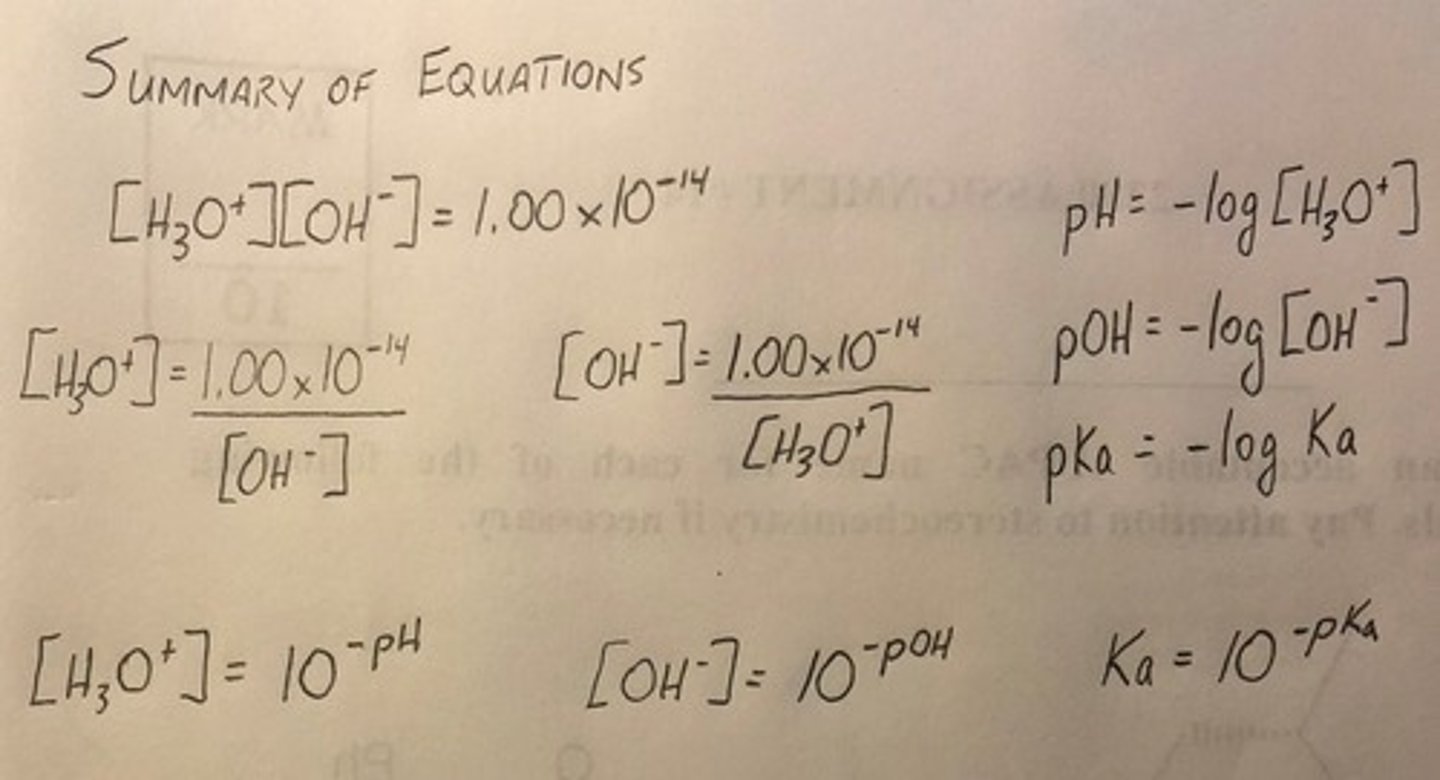
Hydrolysis
The reaction of a salt with water to produce hydronium ions and/or hydroxide ions.
Salt of strong acid and strong base
Does not hydrolyze, resulting in a neutral solution (e.g., NaCl, KBr).
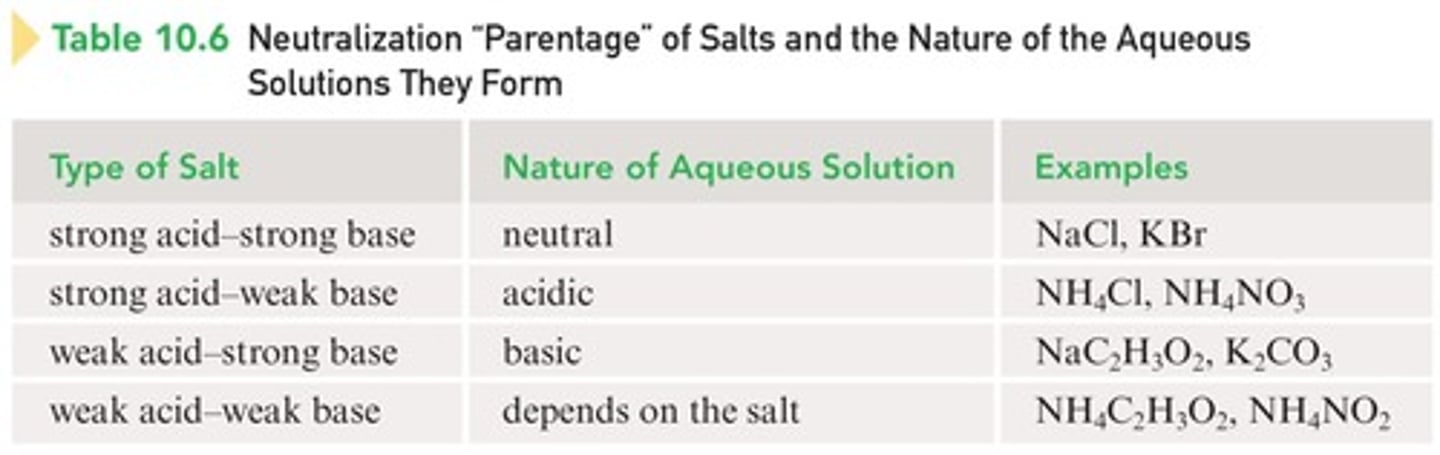
Salt of strong acid and weak base
Hydrolyzes to produce an acidic solution (e.g., NH4Cl).
Salt of weak acid and strong base
Hydrolyzes to produce a basic solution (e.g., NaC2H3O2).
Salt of weak acid and weak base
Hydrolyzes to produce a slightly acidic, neutral, or slightly basic solution, depending on the relative strengths.
pH + pOH
The relationship that states pH + pOH = 14.00.
Calculation of [H3O+]
To calculate the concentration of H3O+, use the formula [H3O+] = 10^-pH.
Calculation of Ka
To calculate the Ka value of an acid, use the equation Ka = 10^-pKa.
Example of pKa calculation
Calculate the pKa for HF given that the Ka for this acid is 6.80 × 10^-4.
Neutral Solution
When the salts of a strong acid and strong base are placed in water, the resulting solution is neutral.
Buffer
An aqueous solution containing substances that prevent major changes in solution pH when small amounts of acid or base are added to it.
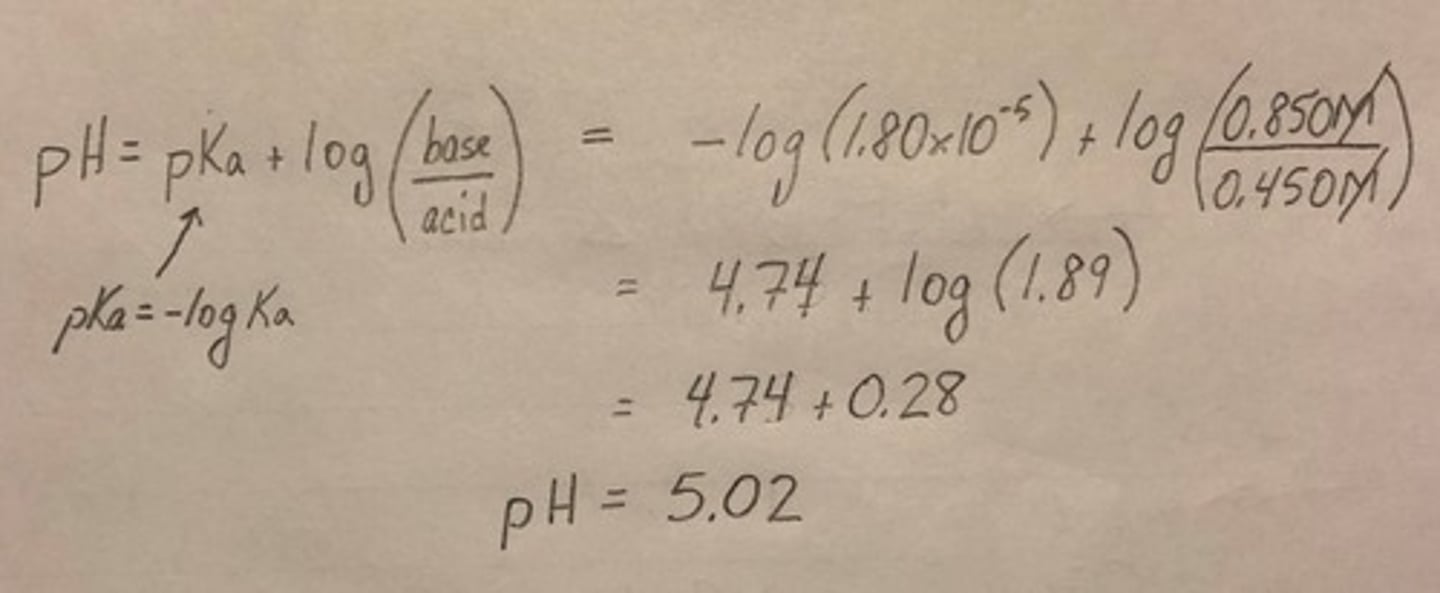
Buffer Components
Typically, a buffer system is composed of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
Active Chemical Species in Buffers
A substance to react with and remove added base and a substance to react with and remove added acid.
Addition of Base to Buffer
The added OH- ion reacts with H3O+ ion, producing water (neutralization), shifting the equilibrium to produce more H3O+ ion.
Addition of Acid to Buffer
The added H3O+ ion increases the overall amount of H3O+ ion present, shifting the equilibrium to consume excess H3O+ ion.
Electrolyte
Substance whose aqueous solution conducts electricity.
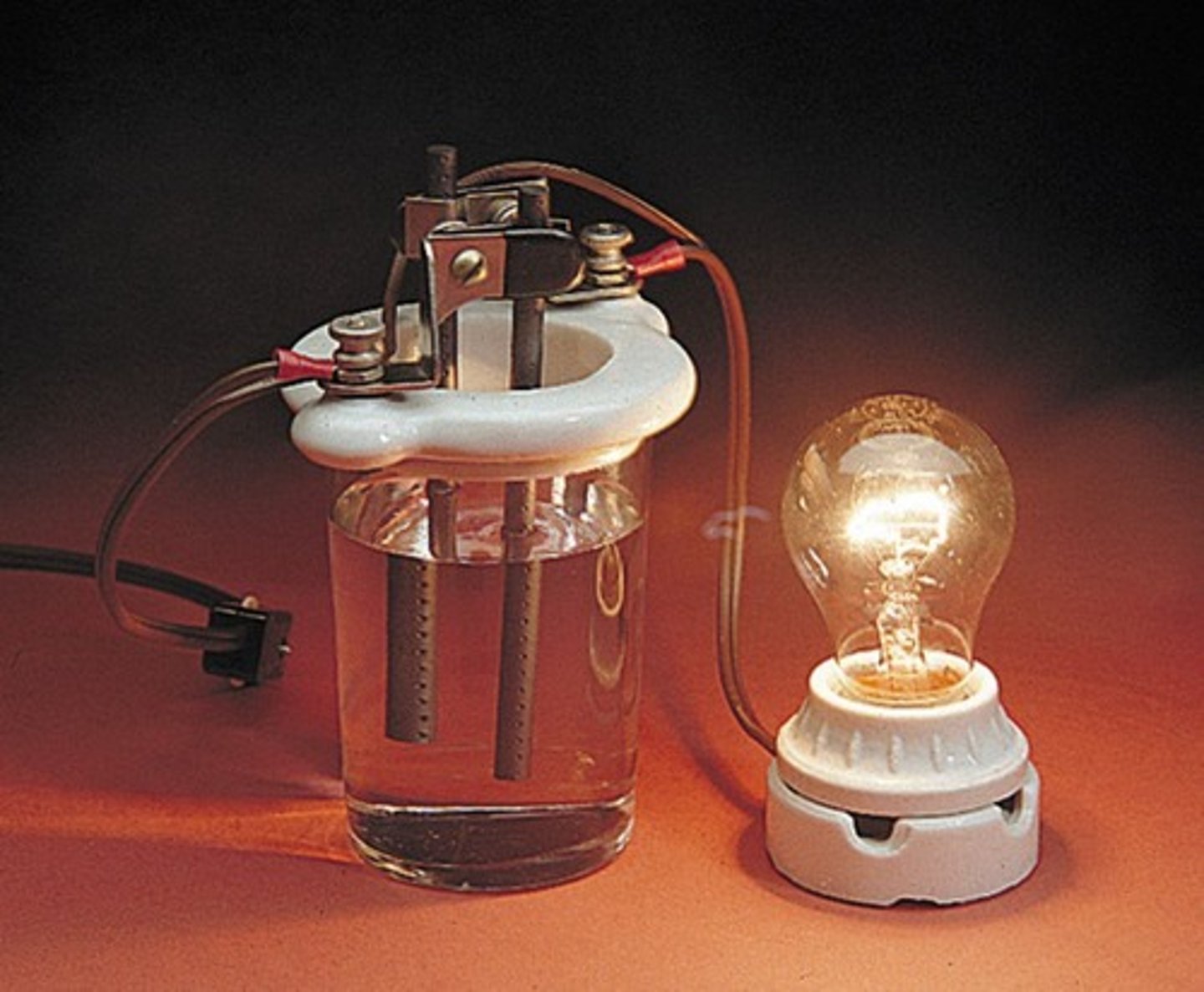

Nonelectrolytes
They do not conduct electricity because there are no ions when dissolved. Example - Table sugar (sucrose) and glucose.
Strong Electrolytes
They completely ionize/dissociate into ions, resulting in high conductivity in solution. Example - Strong acids, bases, and soluble salts.
Weak Electrolytes
They incompletely ionize/dissociate into ions, resulting in low conductivity in solution. Example - Weak acids and bases.
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
A formula used to calculate the pH of a buffer solution.
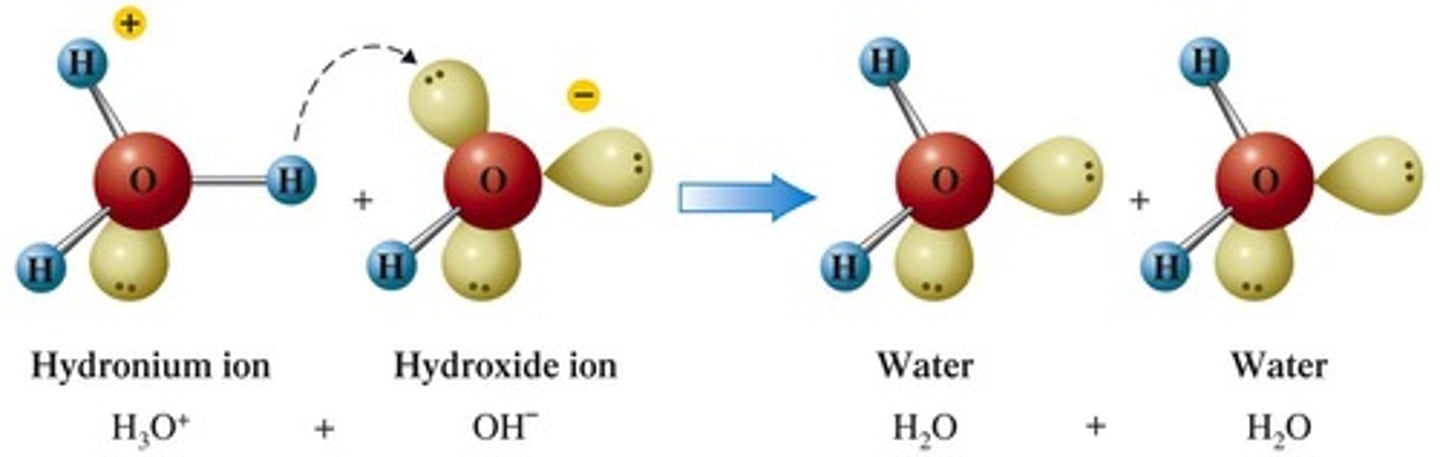
Hydronium Ion
An ion formed when an acid donates a proton to water.
Hydroxide Ion
An ion formed when a base accepts a proton from water.
Conjugate Base
The species that remains after an acid donates a proton.
Conjugate Acid
The species that is formed when a base accepts a proton.
Acidic Solution
A solution with a pH less than 7.
Basic Solution
A solution with a pH greater than 7.
Equilibrium Shift
The change in the position of equilibrium in a chemical reaction in response to a change in concentration, temperature, or pressure.
Stress on Buffer System
The addition of acid or base that disrupts the equilibrium of the buffer solution.