Population and Environment
Population
The amount of people in a defined area, e.g. the world's population is currently 8 billion (2024).
Density
Measurement of population per unit area, providing insight into population characteristics.
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Population
The amount of people in a defined area, e.g. the world's population is currently 8 billion (2024).
Density
Measurement of population per unit area, providing insight into population characteristics.
Distribution
How a population is spread globally or regionally, e.g. most of the UK's population is located in the South of England
Physical Environment
Factors like climate, soil, and natural resources that influence population well-being and support.
Climate
Affects health, agriculture, food availability, and disease incidence in a population.
Natural Resources
Essential for population support, including clean water supply, materials for shelter, and fuel.
Development Processes
Advancements in society that affect population growth, resources, and opportunities.
Neolithic Revolution
Transition from mobile hunter-gatherer populations to agricultural communities, impacting birth rates and food supply.
Green Revolution
Utilization of technology and efficient farming practices to maximize food yields, supporting larger populations.

Industrial Revolution
Transition to technology manufacturing processes, revolutionizing agriculture, goods production, and causing world population growth.
Urbanized Areas
Highly populated regions due to job prospects and opportunities, with 55% of the population currently living in urban areas.
Sparsely populated areas
Regions like Sahara, Central Australia, Canada with uninhabitable conditions
Densely populated areas
Regions capable of supporting a large population due to food production
Population change in Bangladesh
Bangladesh is overpopulated. It has a population of 173 million which is largely all on low lying river delta (prone to flooding). Bangladesh is just half the size of the UK, it is low lying, flat as well as hot and wet climate. Its fertile river delta floodplain are ideal for rice production.
Population change in Bangladesh Part 2
Declining fertility rate of 2.2 due to educated women starting careers as well as widespread use of contraception. However, improvements in healthcare mean life expectancy has increased to 73 years, from 50 years in 1970.
Social consequences of population change in Bangladesh
Slums as large as 200,000 people due to rural-urban migration. Poor-quality housing and lack of basic services lead to inequality gap. Sanitation systems haven't kept up with population growth, only 18% of Dhaka has a sewer system.
Economic consequences of population change in Bangladesh
Falling dependency ratio means Bangladesh is now experiencing the economic benefits of a demographic dividend. High level of emigration means Bangladesh gets $12 billion a year in remittance payments however some emigrants leave Bangladesh permanently which leads to lack of doctors, engineers etc
Environmental consequences of population change in Bangladesh
Only 11% of Bangladesh is forested, leading to increased soil erosion. Clearance of coastal mangroves leads to flooding and coastal erosion and soil salination. Intensive farming requiring fertilisers has increased water pollution due to agricultural runoff. Dhaka air pollution is over 8 times higher than recommended air quality, more than 120,000 deaths due to PM2.5 (air particulates)
Demographic Transition Model
Model explaining the shift in population growth rates globally
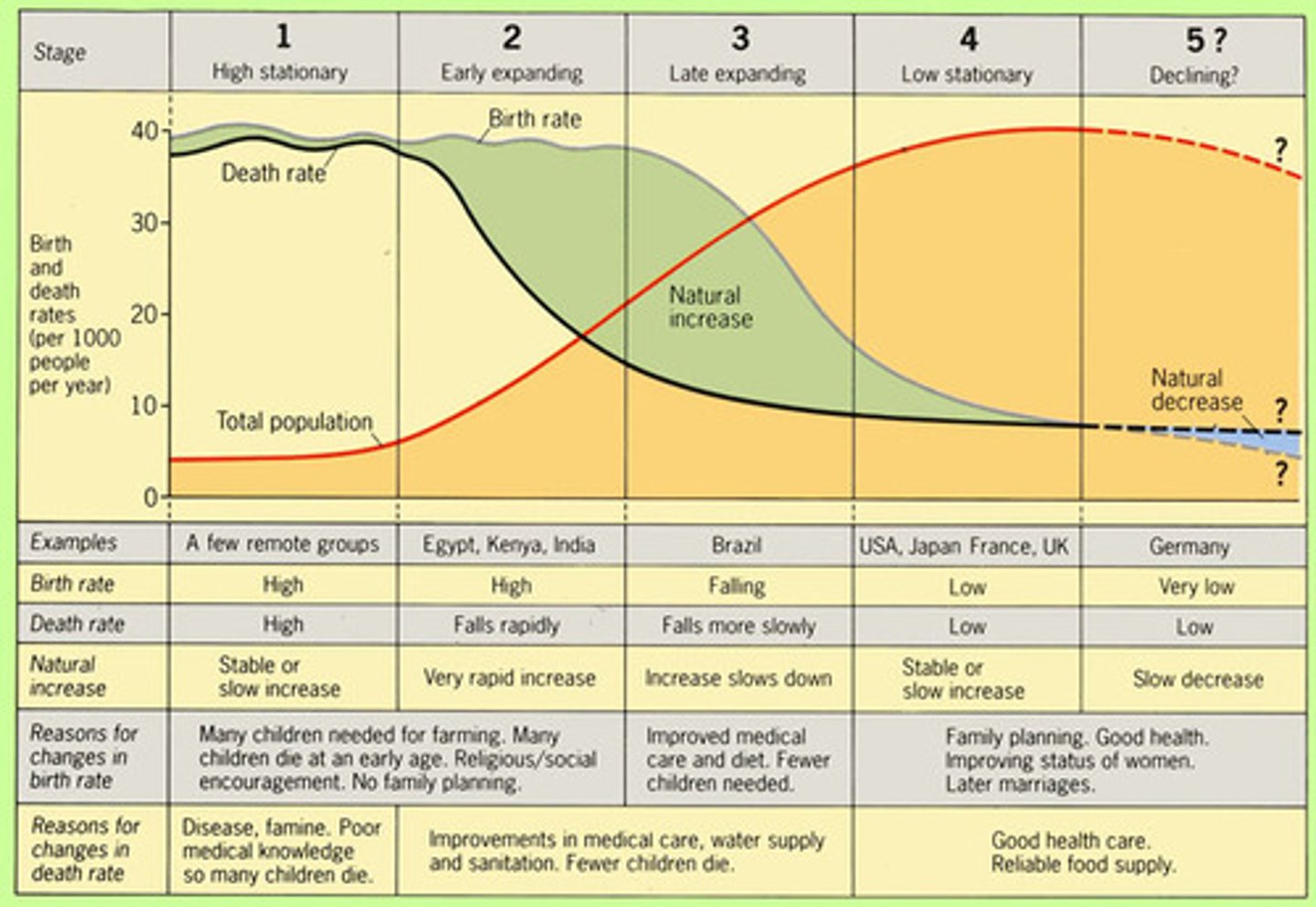
HICs
High-Income Countries with historically high population growth rates
LICs
Low-Income Countries experiencing high population growth rates
Urban areas
Regions with higher population growth rates compared to rural areas
Food production
Global increase in crop production due to various factors like machinery and resources
Malnourishment and Undernourishment
Malnourishment refers to a poor diet but can include over-eating. Undernourishment refers to a lack of nutrients.
Somalia and Haiti rank as the top countries by undernourishment rate.
Arable land
Land suitable for growing crops

Farming machinery
Equipment like combine harvesters increasing crop collection efficiency
Herbicides and pesticides
Substances used in farming to maximize crop yields
Food consumption
Global increase in food intake per person over time
Cereals
Major food source globally, especially in developing countries
Rice consumption
Highest in China and Eastern Asia, projected to decline
Wheat consumption
Increasing in developing countries
Coarse grains
Significant in Sub-Saharan Africa's cereal intake
Meats consumption
Higher in developed countries, with a variety of meat sources
Non-animal based protein
Common protein source in developing countries
Agriculture
The global population relies heavily on the products of agriculture for food and other purposes. Productivity affects how a population can be supported.
Livestock products
Products such as eggs and dairy. Developed countries dominate consumption, with some increase in egg consumption in developing countries.
Meats
Different meats are consumed in various regions, with developed countries eating the most meat. Meat consumption is increasing globally.
Agricultural Systems
Agriculture produces yields through the addition of resources and processes, functioning as a system with inputs, processes, and outputs.
Agricultural Productivity
The efficiency of a farm shown by the amount of useful outputs in proportion to inputs. High productivity farms achieve high yields with low inputs.
Factors Affecting Productivity
Includes the type of agricultural system, climate, and soils, which influence the inputs and outputs of agriculture.
Intensive farming
Agricultural system with high inputs to produce the highest possible output, often involving a lot of labor or high capital inputs.
Extensive farming
Agricultural system with low labor and capital inputs in relation to agricultural land, resulting in lower outputs.
Commercial farming
Agriculture intended for commercial sale to make a profit, often associated with intensive farming for higher profits.

Subsistence farming
Self-sufficient farming where crops are grown to support the family or community with little or no profit.
Soils
Quality of soil affects agricultural productivity, with different soils suited to different types of agriculture. Issues like erosion or flooding may decrease productivity.
How Climate Change Affects Agriculture
Climate change impacts agriculture productivity globally, affecting crop growth and food supply. Changes in climate can lead to yield declines in many regions.
Semi-arid (e.g. Sahel)
Between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. Savanna vegetation, tall grasses and woody trees. Unreliable crops due to climate, crops that are grown include millet, cowpea, cotton. Pastoral agriculture occurs, nomadic and rainfed due to lack of development in Sahel countries. Population growth is outstripping any increases in crop yields. Climate change is making rainfall less predictable and extreme temperatures to be more common

Mediterranean
Between 30 and 45 degrees north in latitude.
Small, drought resistant, vegetation (Thorny bushes, shrubs and small trees). Summers are warm/hot and dry. Winters are mild/cold and wet. 500mm rainfall per year. Intensive viticulture. Pastoral farming is rare due to sparse grass and shallow grass roots. Farming is currently reliable, and food security is good. High tourism pressures land and resources. Mediterranean Sea is warming due to climate change.

East Africa Temperatures
Temperature rise leading to decreased agricultural land due to desertification in East Africa.
Rice Yields
Predicted 20% decrease per 1°C temperature rise in Asia.
Severe Droughts in East Africa
Worsening due to global warming, affecting Kenya and Somalia.
Rainfall Changes
Becoming scarcer and unpredictable in East Africa.
Soil Problems
Erosion, desertification, and salinisation increasing due to higher temperatures.
Podsols
A type of soil found in the Scottish Highlands and Scandinavia. Most nutrients are found at the top of the soil due to a slow rate of decomposition as a result of the low temperature in these regions. Podsols are not suitable for crops due to low pH (acidic) and therefore is used as forestry. Soil depth is rarely over 1 meter
Soil Horizons
O Horizon (Organic Layer): Mainly decomposing plant and animal material, this layer is critical for nutrient recycling.
A Horizon (Topsoil): This layer is richest in organic material and is the primary zone for plant root activity and microbial life.
B Horizon (Subsoil): Characterized by mineral accumulation and signs of leaching, this layer has less organic matter than the A horizon.
C Horizon (Weathered Parent Material): Comprised of weathered parent rock, this layer indicates the geological and mineralogical history of the soil. The R horizon is bedrock/parent material
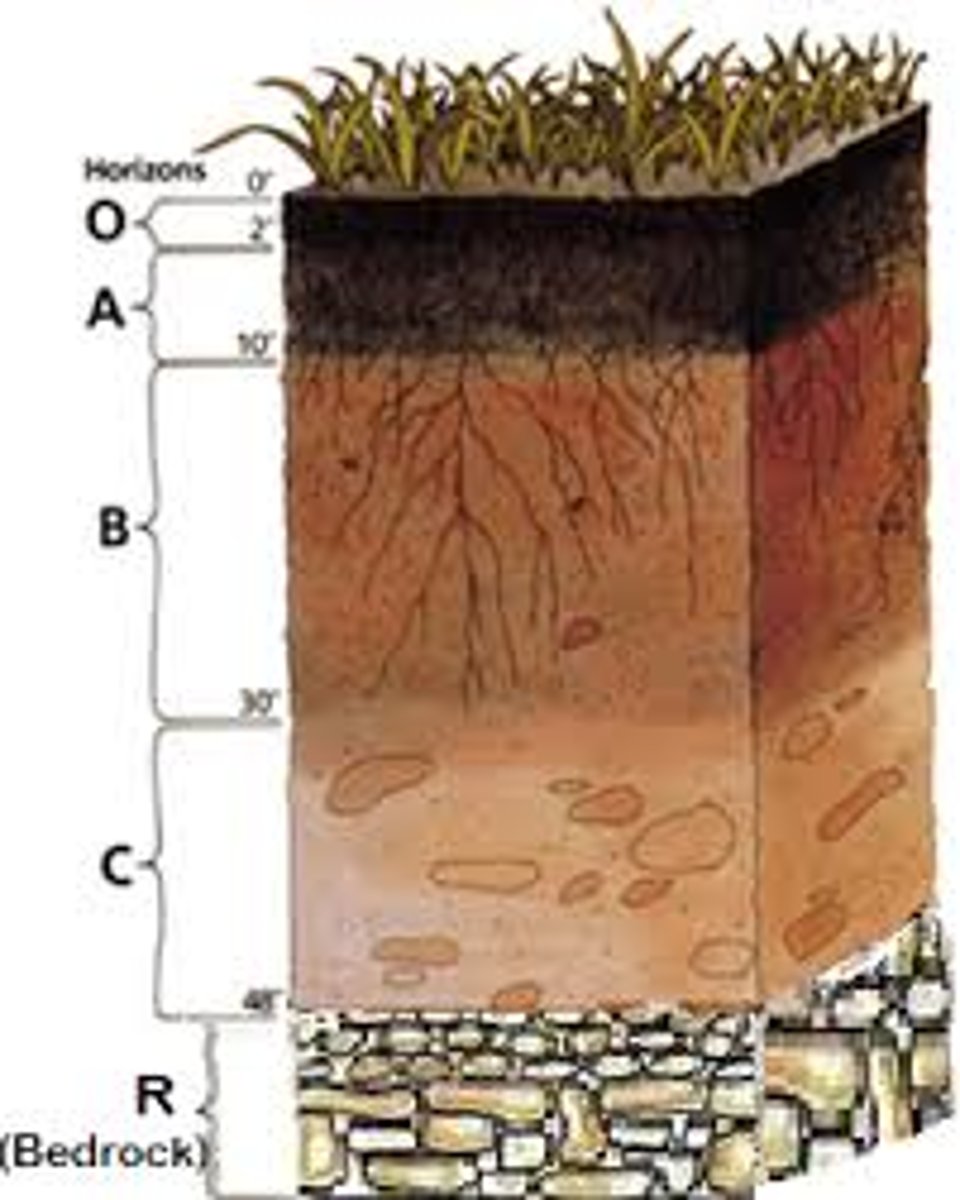
Ferralsols
A type of soil found in the tropical regions of South America and parts of Africa. High rainfall leads to leaching of the soils nutrients. Rainforest vegetation sheds its leaves all year round which decomposes rapidly, supplying nutrients to support sustainable growth quickly
Rising Sea Levels
Caused by melting sea ice, leading to flooding in low-lying areas.
Pests and Plant Diseases
Projected increase due to climate change, reducing agricultural productivity.
Soil Erosion
Wearing away of soil, especially topsoil, crucial for agricultural activities.
Water Erosion
Degradation of soil due to water, influenced by climatic factors and agricultural practices.
Sheet Erosion
Uniform washing away of topsoil due to heavy rainfall and flooding.
Rills and Gullies
Erosional flowing water forming streams and ravines, washing away soil and nutrients.
Riverbank Erosion
Degradation of riverbank sides, causing loss of agricultural land.
Issues of Water Erosion on Agriculture
Includes soil and nutrient loss, weed spread, and obstruction of farming equipment.
Wind Erosion
Erosion due to high winds blowing away topsoil, prevalent in dry climates.
Structural Deterioration
Loss of soil structure, especially pores between particles, affecting air circulation.
Soil Compaction
Removal of air spaces in the ground due to livestock trampling or farming machinery.
Waterlogging
Soil oversaturation with water, leading to oxygen depletion and hindered plant respiration.
Salinisation
Increase in soil salt content, forming a salt crust on the topsoil.
Desertification
Transformation of fertile land into dry, unproductive desert-like conditions.
Food Security
Ensuring available, accessible, affordable, safe, and nutritious food for a healthy lifestyle. Food security is severely threatened by climate change as extreme weather events have become more frequent e.g. rainstorms, droughts
Ethiopia's food security
Ethiopia has 15.8 million people in need of food assistance in 2024. This is because of sustained soil erosion, conflict, monoculture, deforestation and droughts. NGOs and international aid is aiming to prevent this crisis from worsening.
Osmosis
Movement of water from high to low concentration, hindered by high salt content.
Mortality Rate
Number of deaths over time per unit of population, often measured per 1000.
Air pollution in China
Millions of people in China die from heart, lung and strokes related to air pollution. China still burns a lot of coal to heat homes (especially in the winter) and generate electricity, this causes dirty air build up. 38% of China's population live in an area with a long-term air quality labelled 'Unhealthy'.
Infant Mortality
Number of infant deaths per 1000 births, indicating mortality rates in a region.
Death Rate
Number of deaths in a year, per 1000
Causes of death in HICs
Cancer, CVD, cardiac arrest, heart attacks, stroke and Alzheimer's are major contributors to deaths in HICs
Causes of death in LICs
Malaria, HIV, respiratory infections and undernourishment are leading causes of death in LICs.
Malaria
Malaria is spread by infected female mosquitos when they bite humans, the human gets a liver infection and infected blood cells, when the next mosquito bites this human, the mosquito gets these infected blood cells, the next human to be bitten by this mosquito then gets these infected blood cells. This causes the human to have a high temperature, sweats and chills, headaches, tiredness, diarrhoea, aches. If left untreated malaria can be fatal. Malaria is prevalent in Africa, SE Asia.
Malaria part 2
90% of 200m cases worldwide were in Africa, mainly in the Congo basin and West Africa.
Education, bed nets and faster diagnosis are steps taken to reduce its spread
Asthma
"Chronic disease characterized by recurrent attacks of breathlessness and wheezing"-WHO
Child asthma rates are highest in the USA, UK, Australia and Latin America.
WHO noted that "most asthma-related deaths occured in low and middle-income countries"
Asthma's triggers
The overall risk of developing asthma comes from environmental factors:
Air pollution, Smoking, Obesity, Indoor allergens, Pollen, Cold air. Family history also dictates the risk of developing asthma
Asthma in the USA
1 in 14 Americans suffer with asthma. Since the 1980s, Asthma has increased in all age, sex and racial groups. African Americans have a 3x chance of hospital stay because of asthma and 3x higher death rate due to asthma. This can be explained by the inequality between racial groups as African Africans on average have poor urban air quality, inadequate medical care and poverty
Asthma prevention
Avoiding triggers, taking medication (inhalers contain asthma drug Salbutamol). NGOs and Intl agencies, such as WHO and Global Asthma Network, are researching the cause of asthma and factors affecting its triggers.
Birth rate
Number of births in a year, expressed as a rate of 1000
Trade Blocs
Trading agreements benefiting countries struggling to provide enough food.
Aid and Relief
Providing assistance after crises or disasters to increase food security. Provided by NGOs and governments
NGOs and international governmental aid departments
World Health Organisation (WHO)- provided leadership, research and support on global health and disease
The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation- richest charity in the world, promotes eradicating poverty, improving health by using research and disease prevention
NGOs and international governmental aid departments .Part 2
Governmental aid departments- most countries (HICs in particular) have aid departments which send aid to countries in need.
Red Cross (Red crescent in Muslim countries)- Deals with humanitarian crisis, e.g. Gaza conflict
Oxfam- Aims to eridicate poverty, provided sanitation and water to crisis victims
Genetically Modified Crops
New technology increasing food production and potentially improving food quality.
High Yielding Varieties (HYVs)
Varieties of crops that produce higher yields, increasing food supplies.
Disease Incidence
Rate of new cases of a disease in a population over a specific time period.
Disease Prevalence
Proportion of individuals affected by a disease at a specific time.
Health in Knowsley/Liverpool City Region
Knowsley is part of the Liverpool City Region in the North-West of England. Over 27% of homes failed to meet the Decent Homes Standard in 2011 leading to premature deaths from poor insulation leading to cold and damp conditions. Few people use the open spaces in Knowsley for exercise, instead 30% of population smoke (20% UK avg.) This further leads to obesity and subsequently working age people out of work (7.7% compared to 5.3% UK avg.). Income in Knowsley (£475) is lower than UK avg (£539) partly due to lack of qualifications (25% of 16-64s don't have any qualifications compared to 15% UK avg)
Population change
Africa is projected to double in population from 2010 to 2050 (to 2 billion).
Asia's population doubled from 1975 to 2025 (to 4.8 billion)
Europe's population has remained constant at roughly 700 million.
World population is still increasing (currently 8b, projected 9.1b by 2050) but at a slower rate than from 1950-2000 (from 2.5b to 6.2b)
Population theories
The Malthusian theory on population is the idea that the rapid population growth that comes with industrialising (e.g. industrial revolution in 1800s) will outstrip the world's resources and war and famine will inevitably occur as a result.
Boserup theorised that as population increases, human's will innovate and invent and thus relieve the pressure on resources.
Club of Rome suggests that the world cannot support current economic and population growth after 2100, we need to change growth rates to prevent famine etc.
Population Pyramids
A population pyramid is a pyramid split into two halves with the left half being for the male population and the right half for the female population. Each horizontal bar represents a certain age group, often with a class width of 5 years. The width of the bar represents the proportion of the total population that group makes up e.g. the 0-5 years old group makes up 5% of the total population of the country.
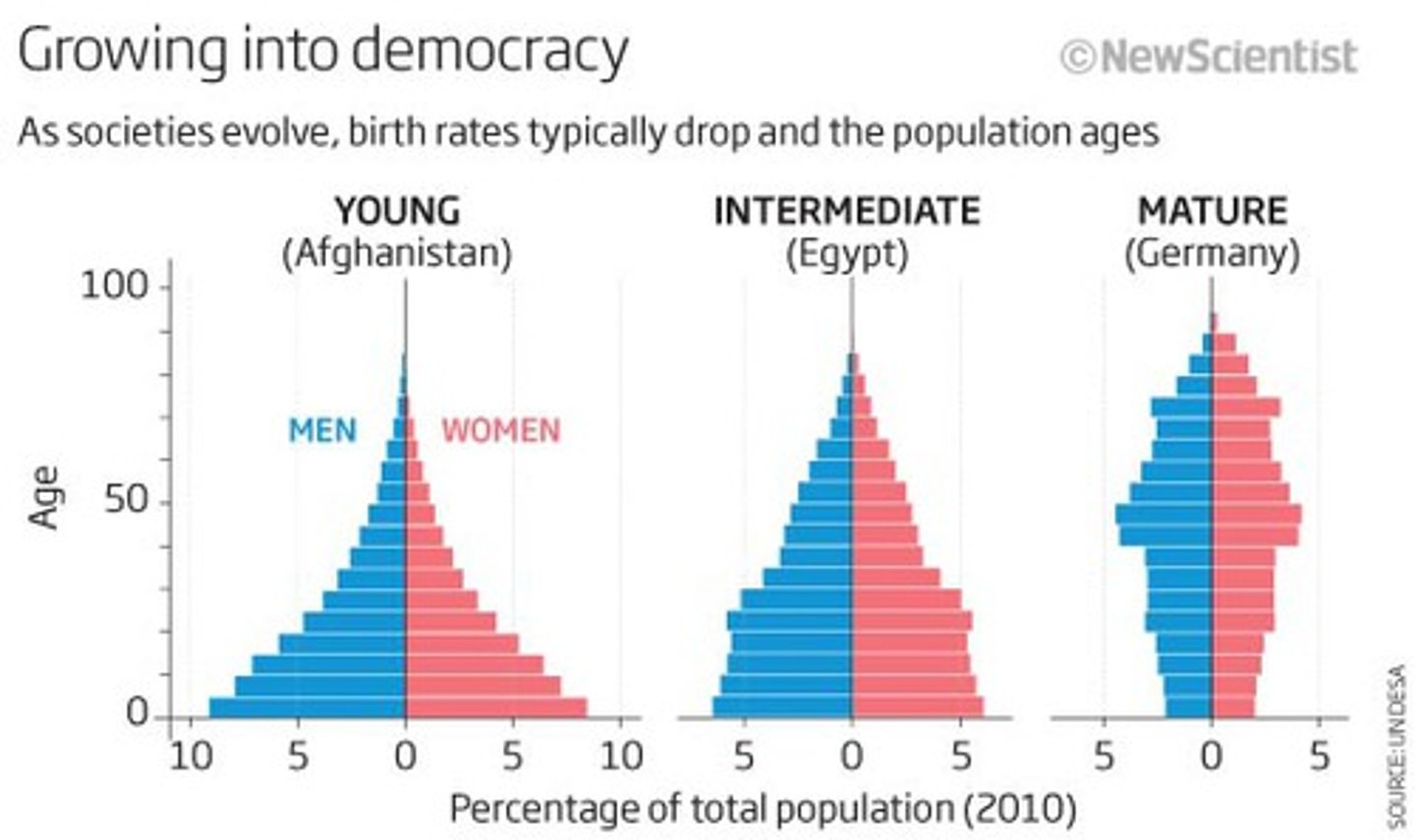
Fertility rate
If the average fertility rate in a country is 2.1, then the population is thought to remain as 2 children will replace their parents and the 0.1 accounts for child mortality.
Countries such as Niger have a fertility rate of 6.8 while South Korea has a fertility rate of 0.72.
Demographic dividend
Economic growth brought on by a change in the age structure of a country's population. The first demographic dividend is when fertility rate falls when a country develops from a rural economy, this fall in fertility rate means that the labour force grows faster than the population depending on it therefore GDP/capita increases