Exam 3 Human Growth and Development
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Happiest memories
when psychological needs rather than material needs were satisfied
Unhappiest memories
when basic psychological needs were left unfulfilled
Social clock
the culturally determined psychological timepiece providing a sense of whether we have reached the major benchmarks of life at the appropriate time in comparison to our peers
Women’s Social Clocks according to Ravenna Helson
People have several social clocks from which to choose.
The selection has implications for personality development during early and middle adulthood.
The particular clock is less important; it is more critical to invest in and focus on a trajectory.
Social clocks are culturally determined.
Intimacy-Versus-Isolation stage: Erikson
the period from postadolescence into the early 30s that focuses on developing close, intimate relationships with others
Emerging adulthood
the period from the late teenage years extending to the mid-20s in which people are still sorting out their options for the future
Five features of emerging adulthood
identity exploration
instability
self-focus
feeling in-between
optimism
Influences on friendship:
proximity, similarity, personal qualities
Passionate (or romantic) Love
a state of powerful absorption in someone
Companionate Love
the strong affection for those with whom our lives are deeply involved
Sternberg’s Triangular Theory: The Three Faces of Love
Intimacy
Passion
Decision/Commitment
Sternberg’s Intimacy Component
encompasses feelings of closeness, affection, and connectedness
Sternberg’s Passion Component
comprises the motivational drives relating to sex, physical closeness, and romance
Sternberg’s Decision/Commitment Component
embodies both the initial cognition that one loves another person and the longer-term determination to maintain that love
Types of love - Sternberg
nonlove
liking
infatuated love
empty love
romantic love
companionate love
fatuous love
consummate love
Nonlove
Intimacy: absent
Passion: absent
Decision/Commitment: absent
Example: the way you might feel about the person who tables your ticket at movies
Liking
Intimacy: present
Passion: absent
Decision/Commitment: absent
Example: good friends who have lunch together at least once or twice a week
Infatuated Love
Intimacy: absent
Passion: present
Decision/Commitment: absent
Example: a “fling” or short-term relationship based only on sexual attraction
Empty Love
Intimacy: absent
Passion: absent
Decision/Commitment: present
Example: an arranged marriage or a couple who have decided to sat married “for the sake of the children”
Romantic Love
Intimacy: present
Passion: present
Decision/Commitment: absent
Example: a couple who have been happily dating a few months but have not made any plans for a future together
Companionate Love
Intimacy: present
Passion: absent
Decision/Commitment: present
Example: a couple who enjoy each other’s company and their relationship, although they no longer feel much sexual interest in each other
Fatuous Love
Intimacy: absent
Passion: present
Decision/Commitment: present
Example: a couple who decides to move in together after knowing each other for only two weeks
Consummate Love
Intimacy: present
Passion: present
Decision/Commitment: present
Example: a loving, sexually vibrant, long-term relationship
Filter explanation
says that people seeking a mate screen potential candidates through successively finer-grained filters, starting with attractiveness
Homogamy
the tendency to marry someone who is similar in race, age, education, religion, and other basic demographic characteristics, its importance is declining
Marriage Gradient
the tendency of men to marry women who are slightly younger, smaller, and lower in status, and for women to marry men who are slightly older, larger, and higher in status
Process of Filtering Potential Marriage Partners
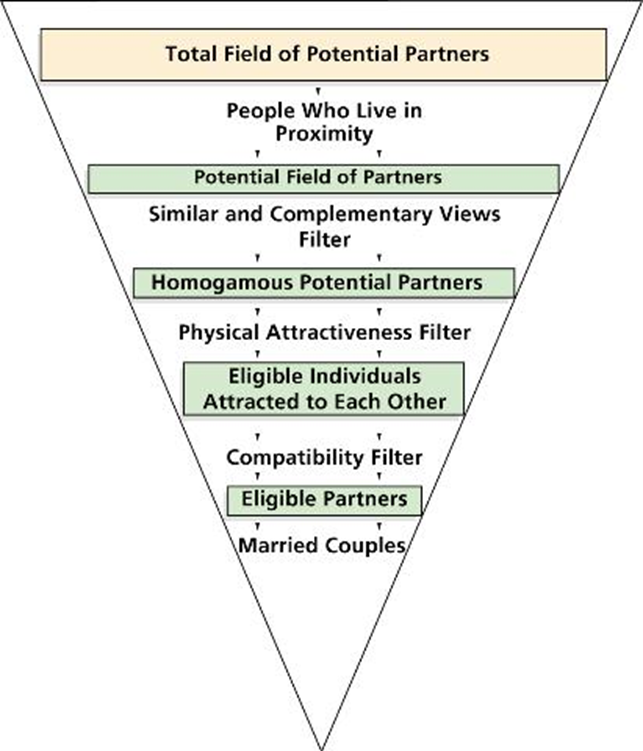
Cohabitation
couples living together without being married
Civil Union
a legal alternative to marriage for providing similar protections to marriage, but not federal benefits
Successful married partners
Show affection
Communicate relatively little negativity
Perceive themselves as part of an interdependent couple
Experience social homogamy, a similarity in leisure activity and role preferences
Divorce rates are _____, but they are still ______.
declining, high
The ______ is less than the ______.
fertility rate, placement level
Coparenting teamx
parents who work together, adopting common child-rearing goals
Singlehood
living alone without an intimate partner
increased significantly in the past several decades
about 20% will live their entire lives this way
Career consolidation
a stage entered between ages 20 and 40, when young adults become centered on their careers
Vaillant’s view
career focus supplanted personal intimacy and bridged Erikson’s intimacy-versus-isolation and generativity-versus-stagnation stages
Millennial Generation
those born after 1980 and who entered young adulthood around the millennium in 2000
Ginzberg’s Career choice theory
a series of three stages in choosing a career:
fantasy period
tentative period
realistic period
Fantasy period
until age 11; choices are made without regard to skills, abilities, or available jobs
Tentative period
adolescents begin to think about job requirements and their abilities and interests
Realistic period
young adults explore specific career options through experience or training
Holland’s Personality Type Theory
personality types are important in career choice
realistic
intellectual
social
conventional
enterprising
artistic
Communal Professions
occupations associated with relationships (traditionally for women)
Agentic professions
occupations associated with getting things accomplished (traditionally for men)
Glass ceiling
an invisible barrier that, because of discrimination, prevents promotions beyond a certain level
Extrinsic motivation
drives people to obtain tangible rewards, such as money and prestige
Intrinsic motivation
causes people to work for their own enjoyment, not just for the rewards work may bring
Status
the evaluation by society of the role a person plays
Senescence
naturally occurring declines related to age
Osteoporosis
women are more prone to a decline in height because this condition causes bones to become brittle, fragile, and thin
Visual Acuity
the ability to discern fine spatial detail in both close and distant objects; begins to decline around age 40
Glaucoma
pressure in the fluid of the eye increases
Presbycusis
loss of the ability to hear sounds of high frequency
Sound localization
problems identifying the direction and origin of a sound
metabolism
holds steady during middle adulthood
Sex challenges for men in middle adulthood
they typically need more time to get an erection
the volume of fluid that is ejaculated declines
the production of testosterone also declines
sex challenges for women in middle adulthood
the walls of the vagina become thinner and less elastic
the vagina begins to shrink, potentially making intercourse painful
Female climacteric
the transition from being able to bear children to being unable to do so; begins around age 45 and lasts 15 to 20 years
Menopause
the cessation of menstruation
hormone production changes and symptoms can include “hot flashes”, headaches, dizziness, heart palpitations, and aching joints
Perimenopause
the period beginning around 10 years prior to menopause when hormone production starts to change
Hormone Therapy (HT)
estrogen and progesterone are given to alleviate menopause symptoms
can reduce some problems, like hot flashes, the thinning of bones, and risks of stroke and colon cancer
may also lead to a greater sex drive
can increase risks of breast cancer, blood clots, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease
Male Climacteric
the period of physical and psychological change relating to the male reproductive system that occurs during late middle age
the production of testosterone and sperm decreases, but men can still father children
the prostate gland often enlarges, leading to problems with urination
erectile dysfunction, the inability to achieve an erection, becomes more common
Chronic diseases that appear during middle adulthood:
Arthritis (after age 40)
Type 2 diabetes (between 50 and 60)
Hypertension (high blood pressure) (middle age)
Psychoneuroimmunologists note three main consequences of stress
it has direct physiological outcomes
it leads people to engage in unhealthy behaviors
it has indirect effects on health-related behavior
Direct Physiological effects of stress
elevated blood pressure
decrease in immune system functioning
increased hormonal activity
psychophysiological conditions
Harmful behaviors from stress
increased use of nicotine, alcohol, and other drugs
decreased nutrition
decreased sleep
Indirect health-related behaviors from stress
decreased compliance with medical advice
increased delays in seeking medical care
decreased likelihood of seeking medical advice
Risk factors of heart disease
some people are genetically predisposed
men are more likely to have it, risk rises with age
environmental and behavioral factors like cigarette smoking, diet high in fat and cholesterol, lack of exercise, psychological factors like stress
Type A behavior pattern
includes competitiveness, impatience, frustration, and hostility
links between this type and heart disease are correlational; no evidence supports causation
Type B behavior pattern
includes non competitiveness, patience, and lack of aggression
this type men have half the risk of heart disease
Type D behavior
“distressed” includes insecurity, anxiety, related to risk for heart attacks
Cancer is the ______ leading cause of death in the US
second
Treatment options for cancer
radiation therapy
chemotherapy
gene therapy
surgery