Anatomy lab final- digestive system
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
gastrointestinal tract
-continuous, hollow, muscular tube that runs from mouth to anus
-lined with specialized mucosae
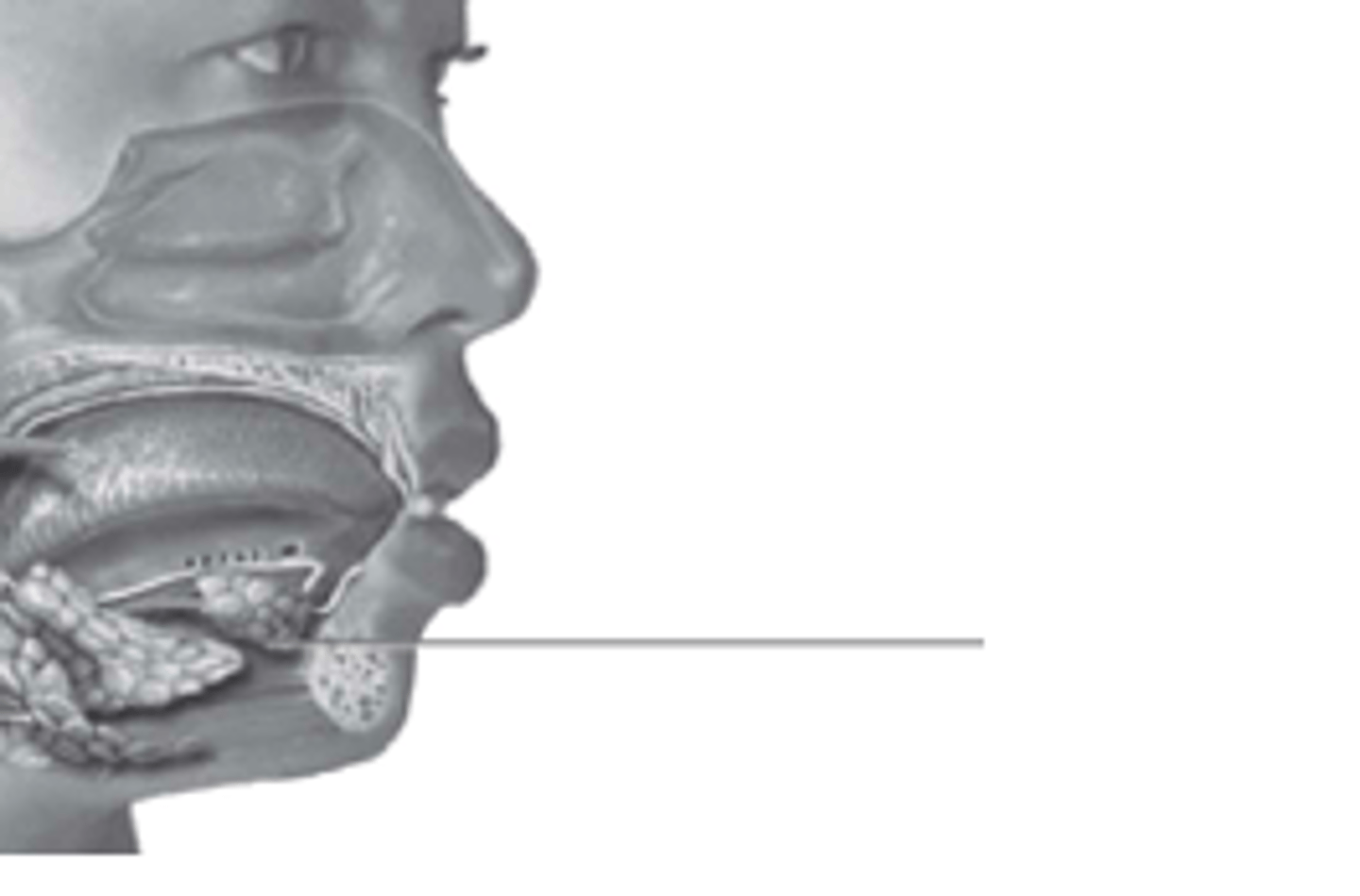
submandibular
what gland is this?
parotid
what gland is this?
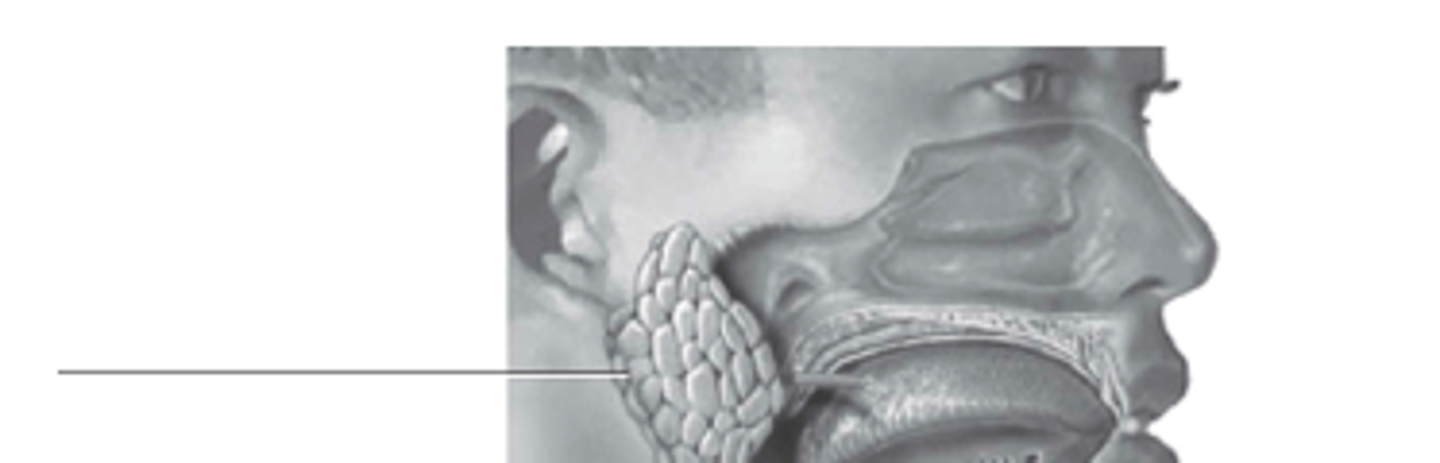
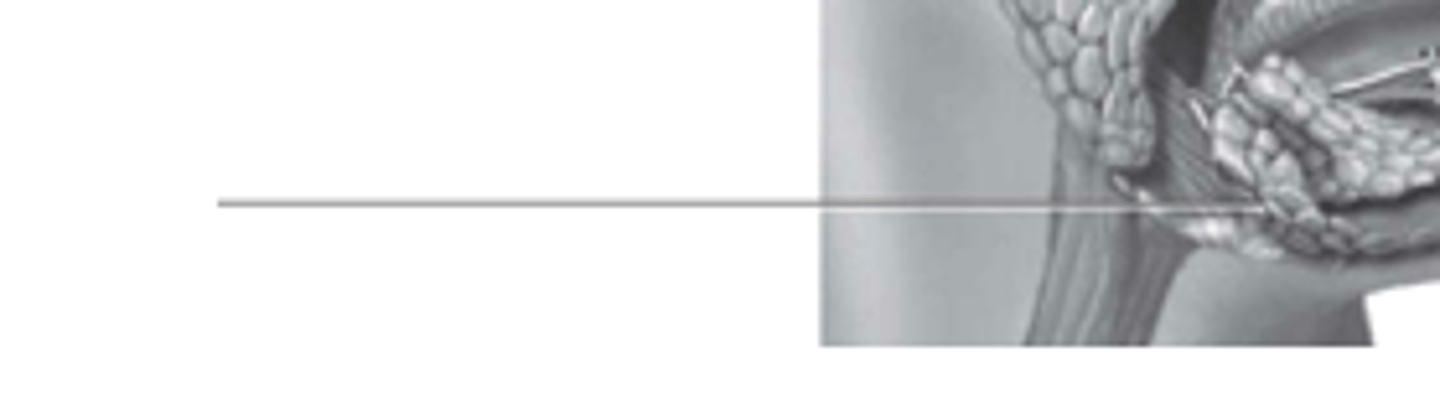
sublingual
what gland is this?

lymphatic nodule/Peyer's patch
what is this?
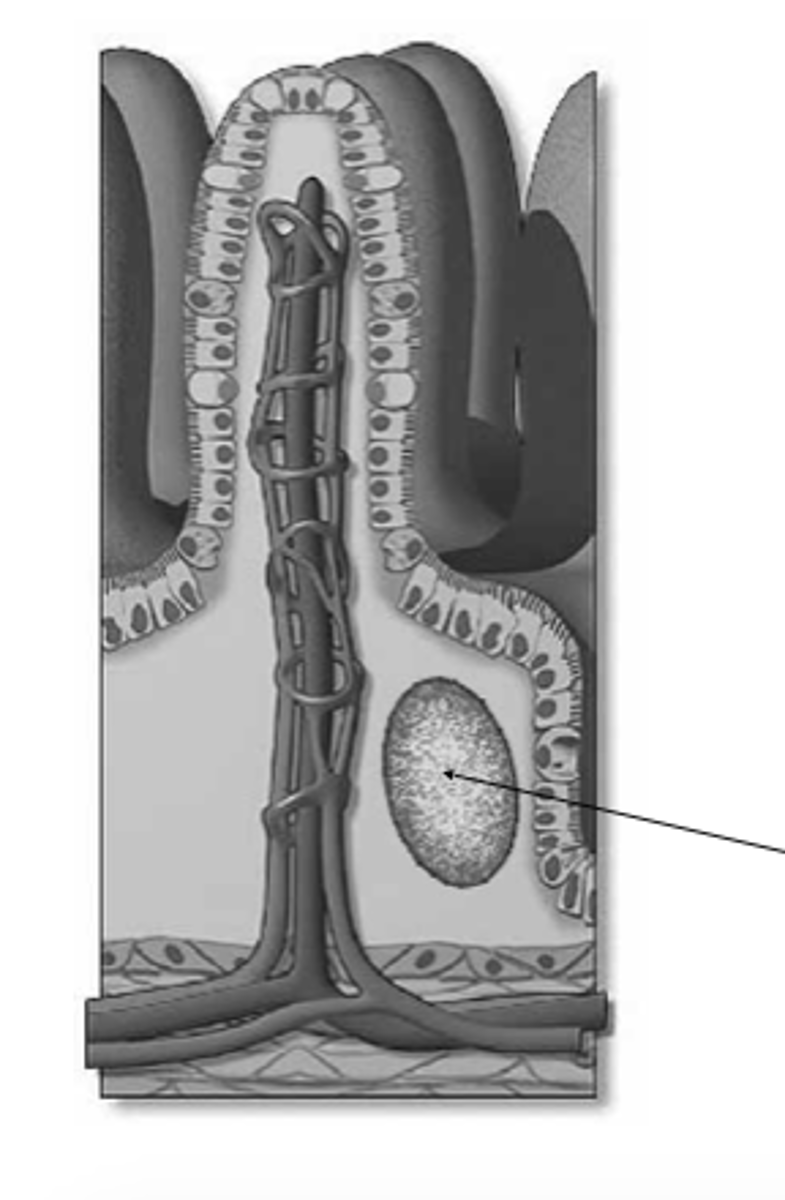
capillary
what is this?
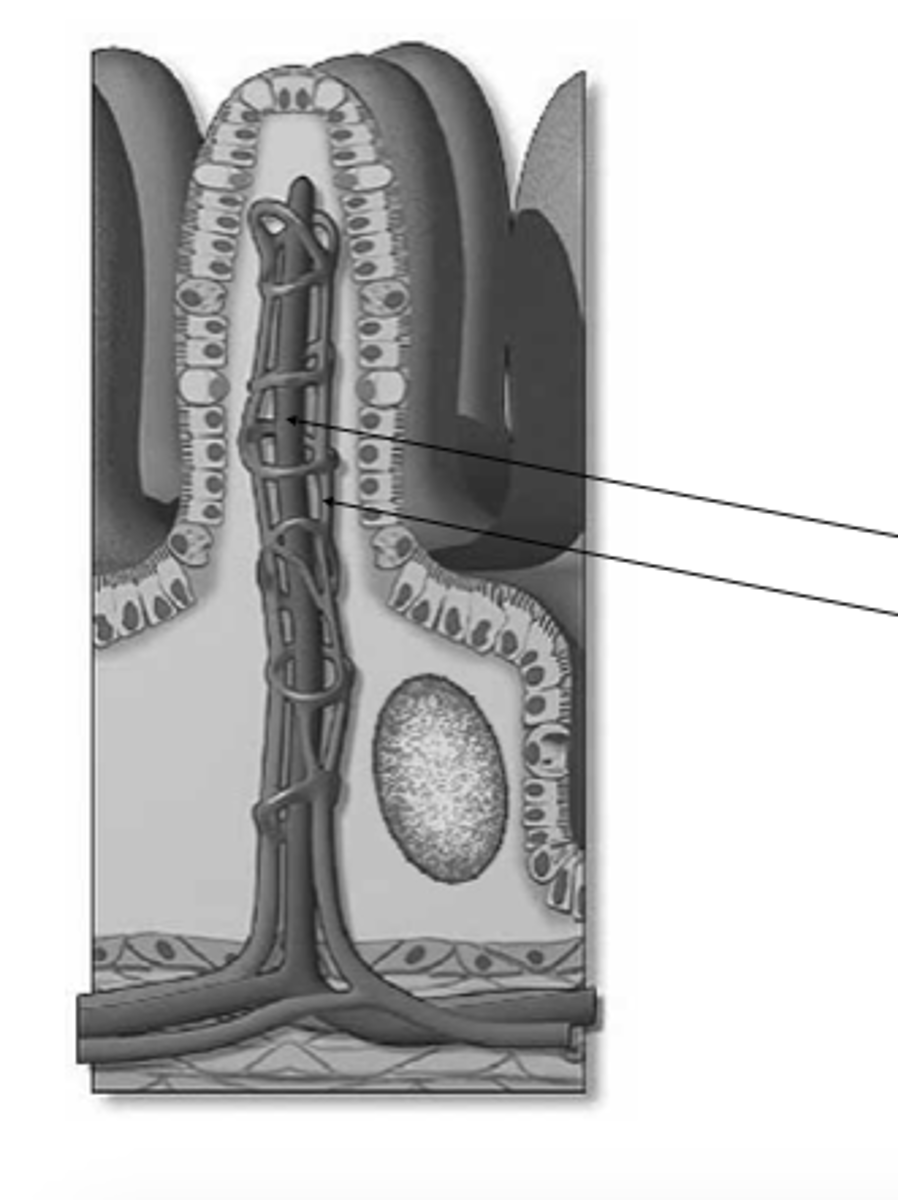
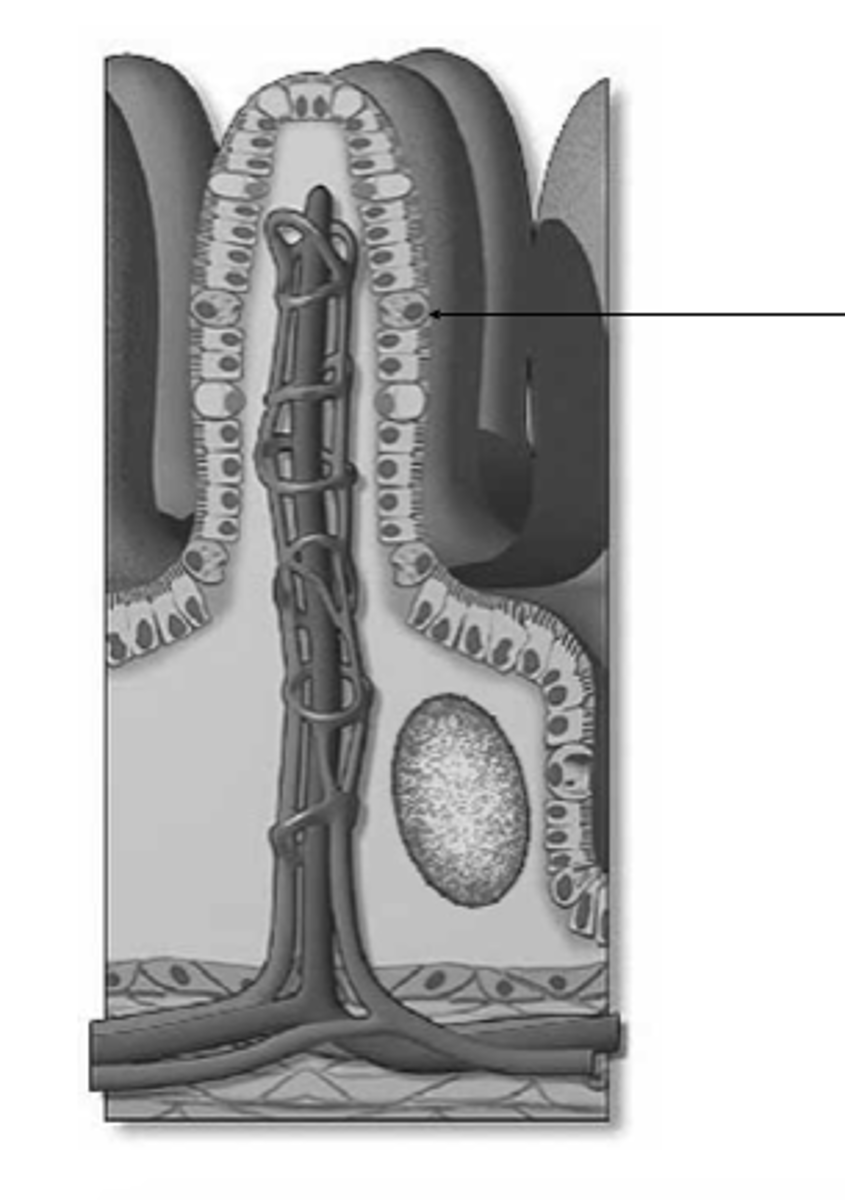
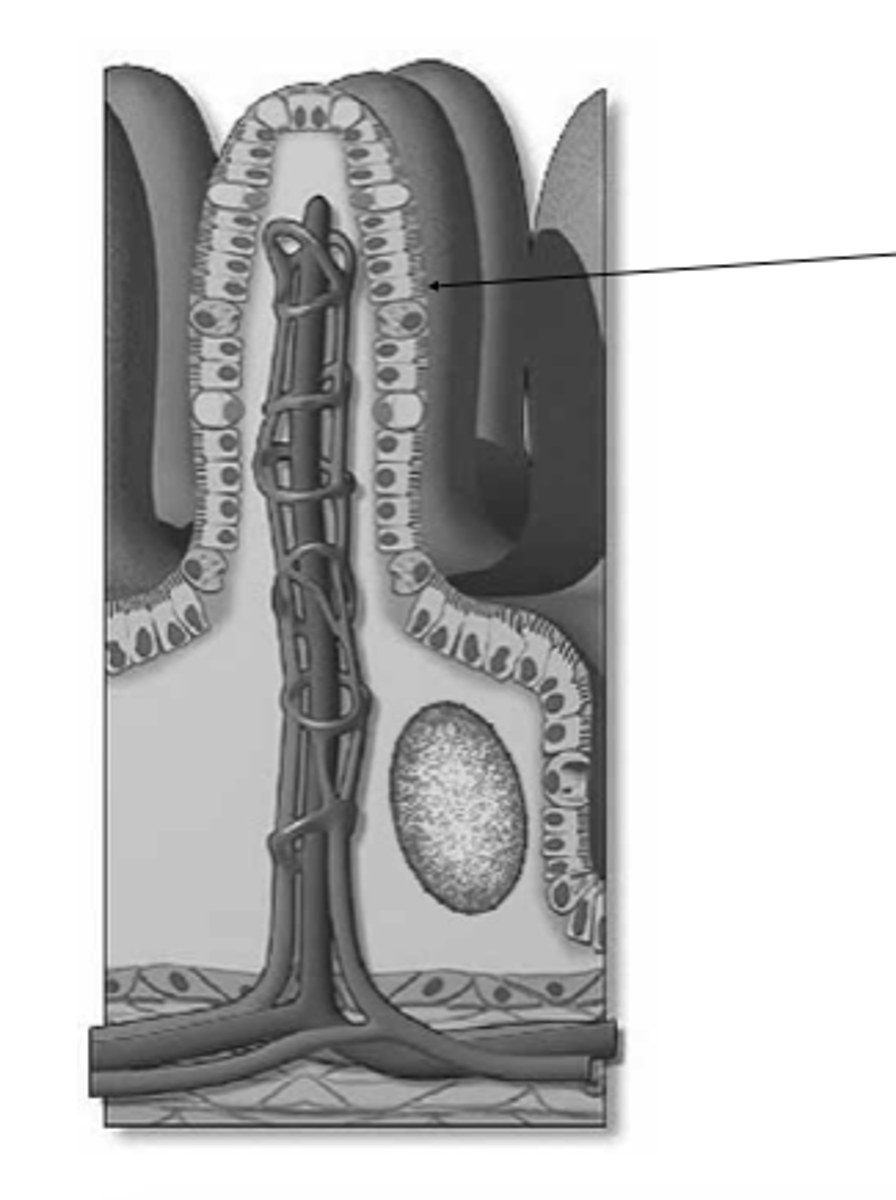
goblet cell
what is this?
microvilli
what is this?
1. segmentation
2. peristalsis
the two types of movements produced by contractions of the smooth muscle of the intestines
1. body
2. fundus
3. cardiac
4. pylorus
list four regions of stomach
1. HCL
2. pepsinogen
3. gastric lipase
4. intrinsic factor
the four main components of gastric juice
E
which of the following is a function of HCL in the stomach
a. activates pepsinogen
b. breaks down cell walls
c. kills most bacteria
d. denatures proteins in food
e. All of the above are functions of HCl.
intrinsic factor
without ___________ _______, vitamin B12 cannot be absorbed by the intestine
1. duodenum
2. jejunum
3. ileum
list three regions of small intestine
brush border
the microvilli of small intestine's epithelial cells form the ______ ________
1. water
2. salt
the large intestine absorbs which two things?
the main digestive enzyme producing organ
vagus
what nerve controls most of the smooth muscle contraction of digestion
1. pepsin
2. trypsin
3. chymotrypsin
4. carboxypeptidase
what are the four peptidases(enzymes that cleave proteins) of the GI tract
small intestine
list where in the GI tract the following nutrients are absorbed: monosaccharides, amino acids, fatty acids, nucleic acids
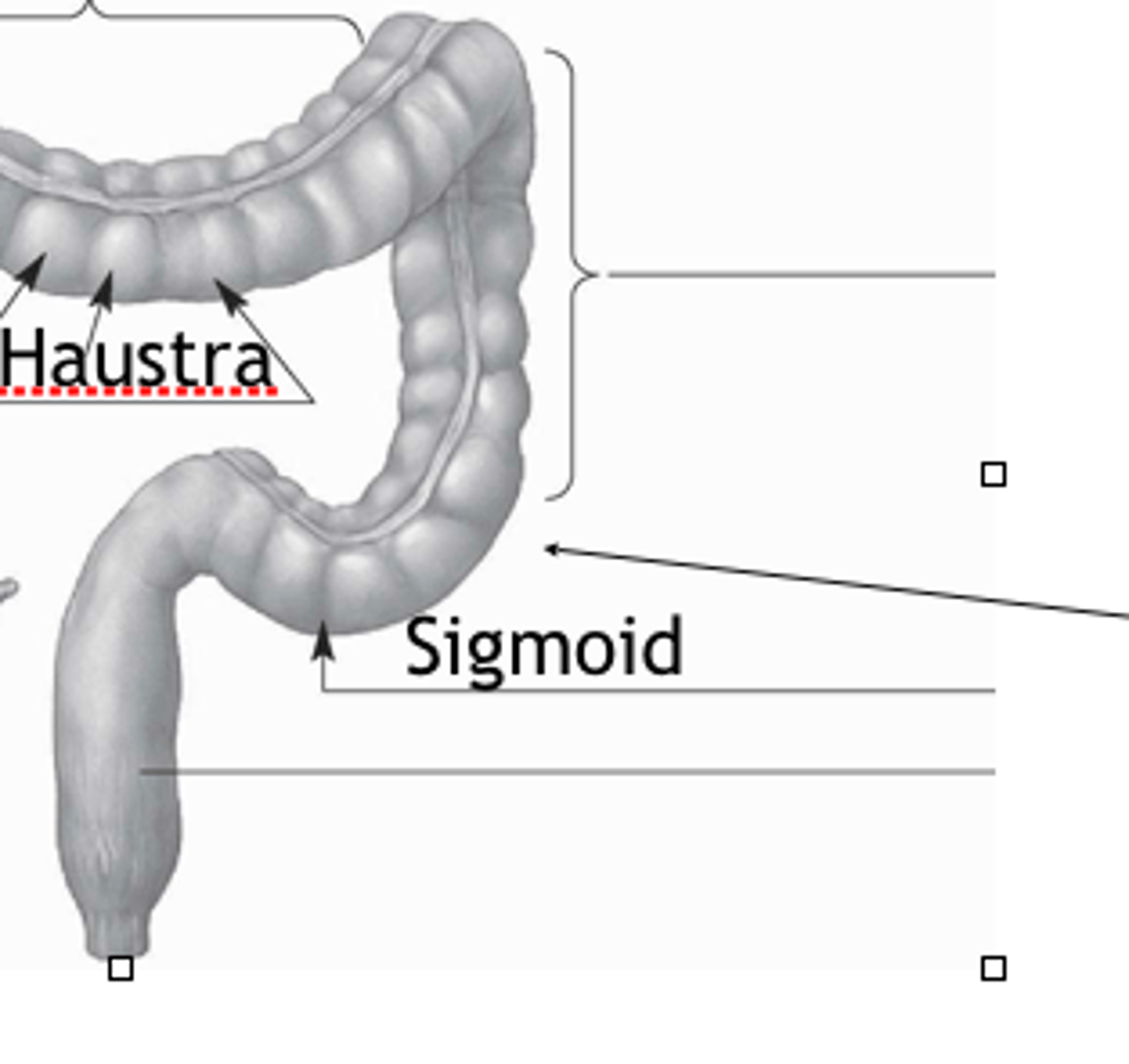
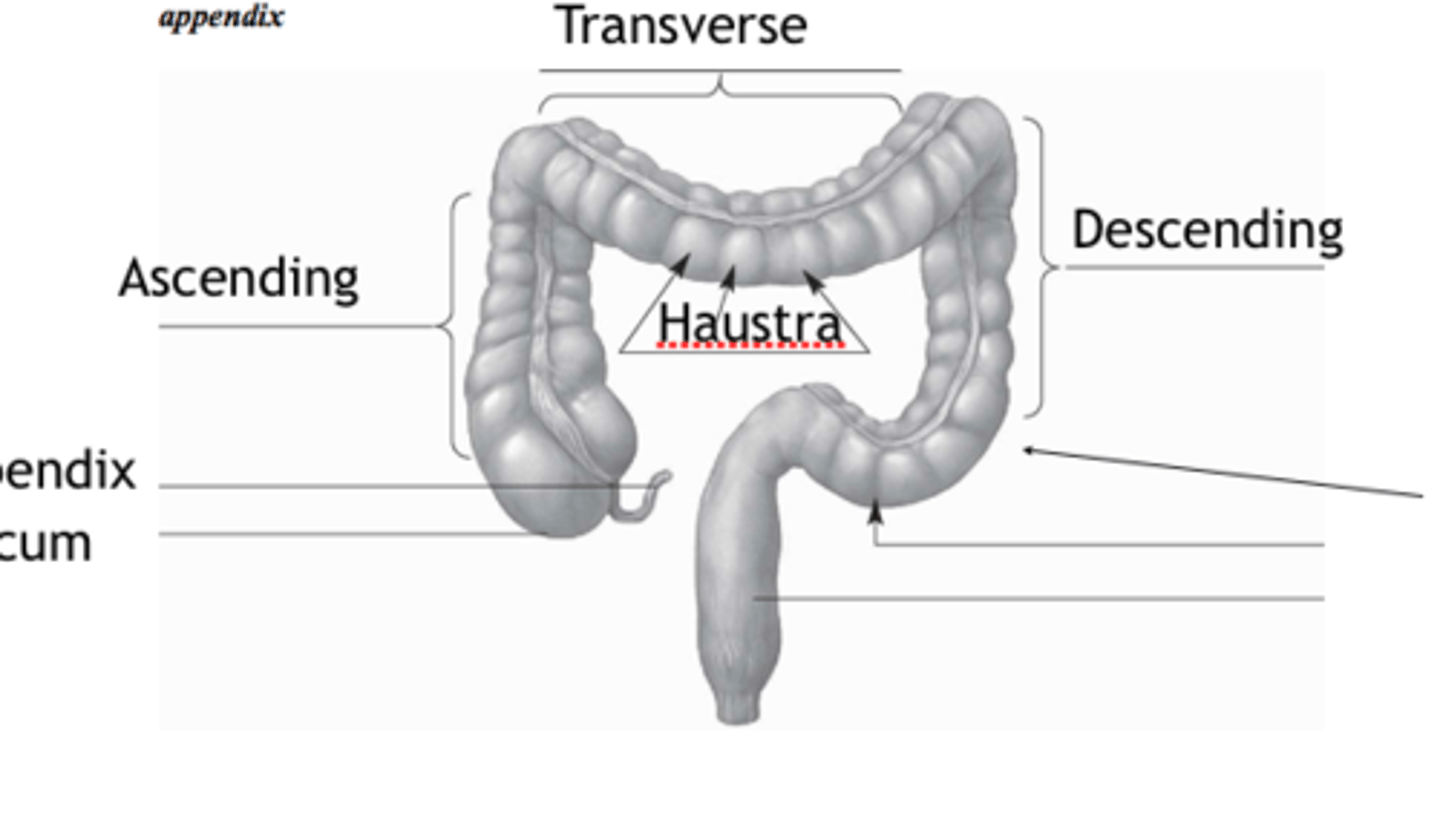
haustra
pockets or out touchings formed by contractions of taeniae coli musculature
micelles
bile salts that surround monoglycerides and free fatty acids to form tiny droplets
chylomicrons
Triglycerides combine with lipoproteins inside the intestinal epithelial cells to form
_________
lacteals
Chylomicrons exit the intestinal epithelial cells and then enter the _______ due to their large size
transverse
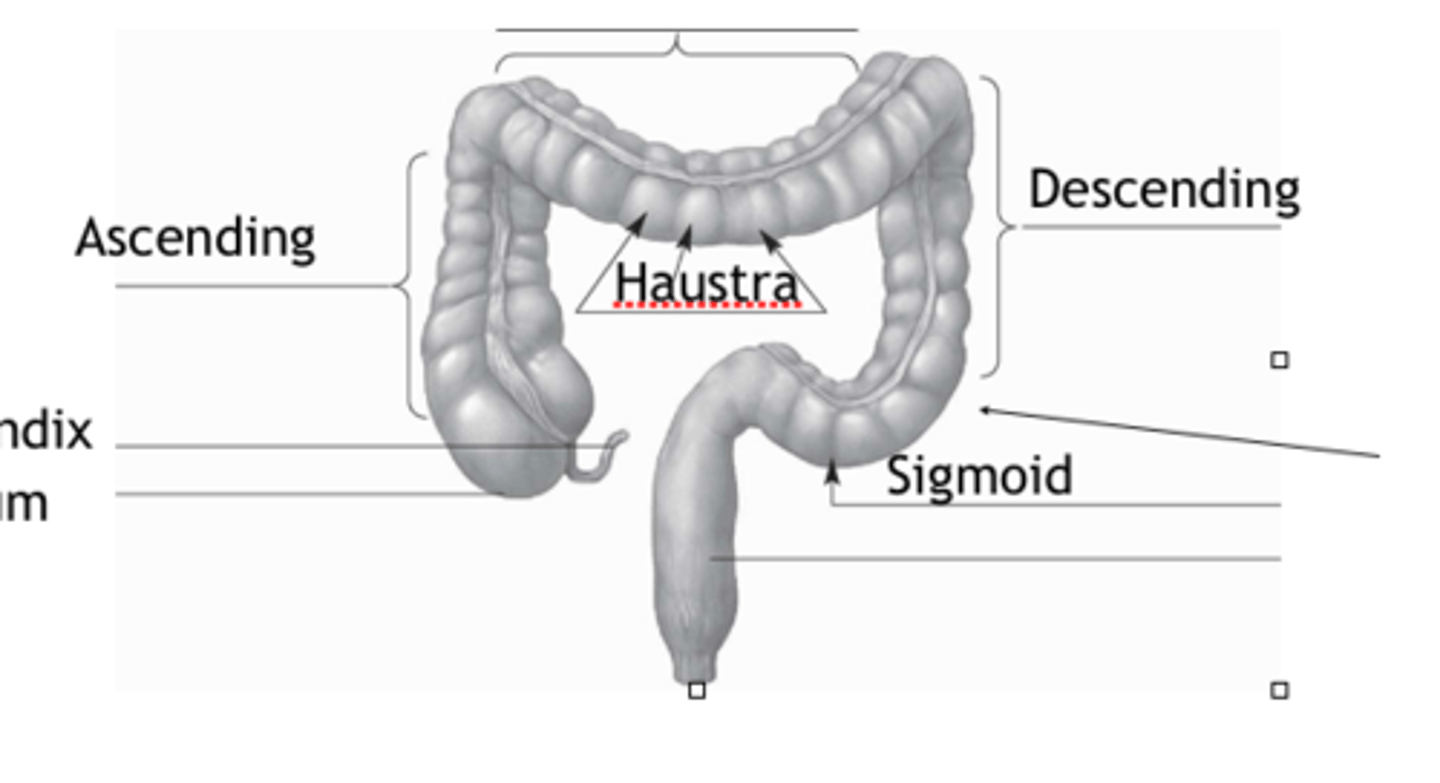
haustra
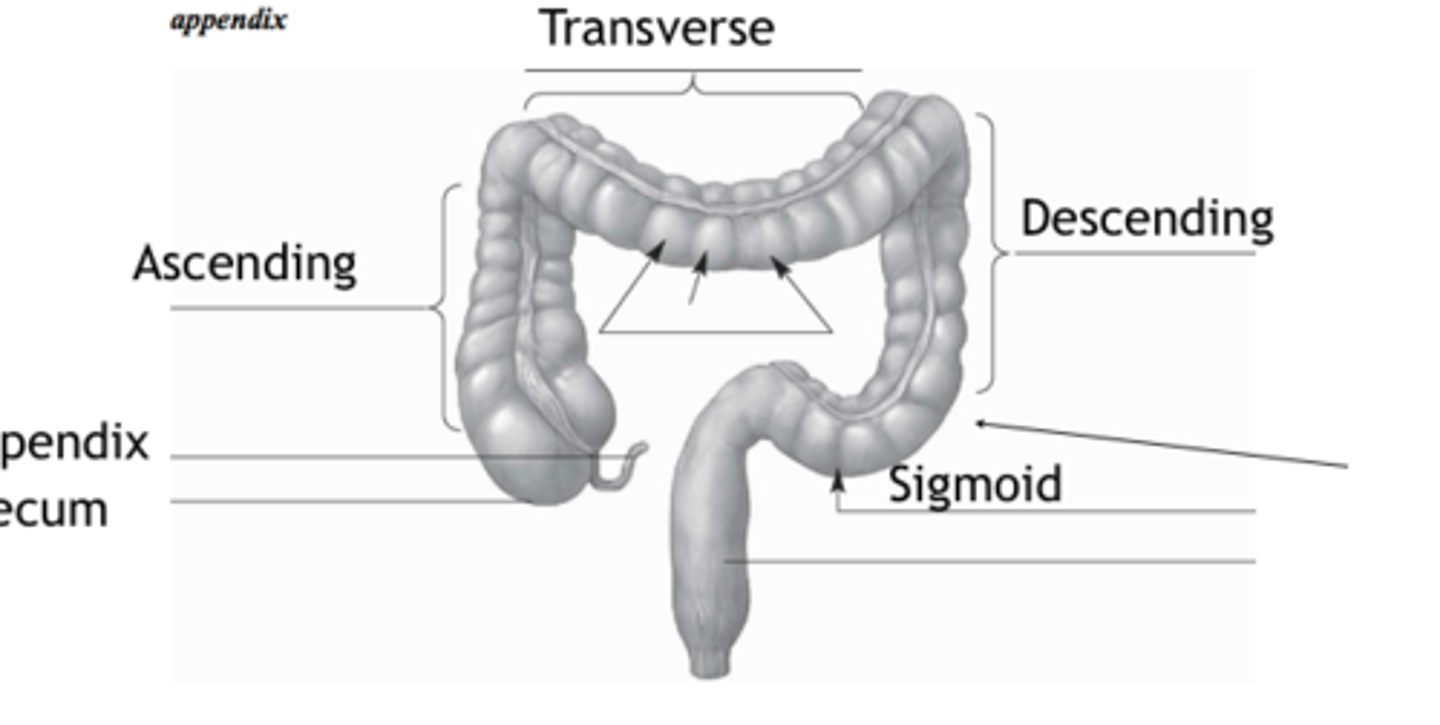
ascending
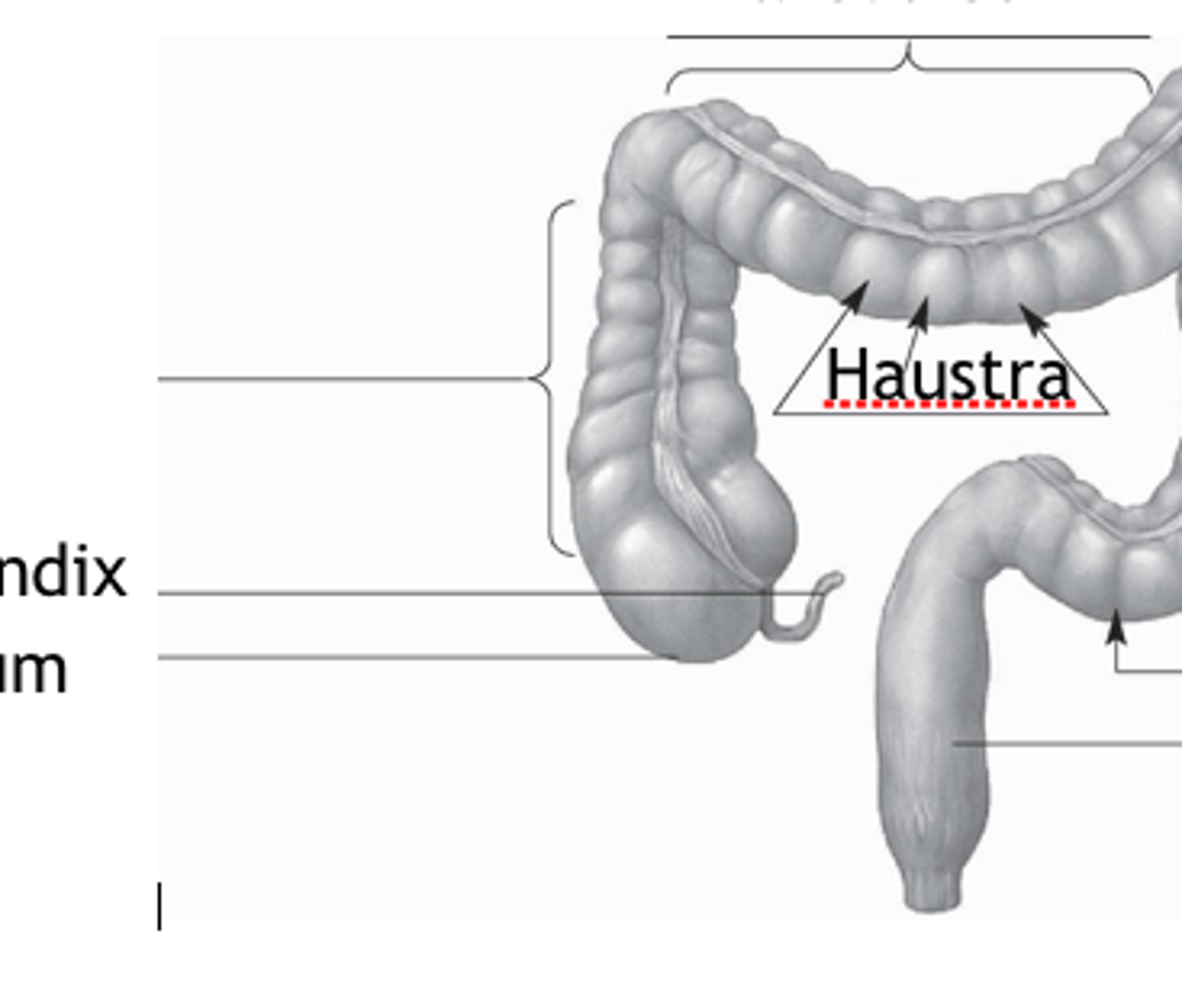
descending
appendix
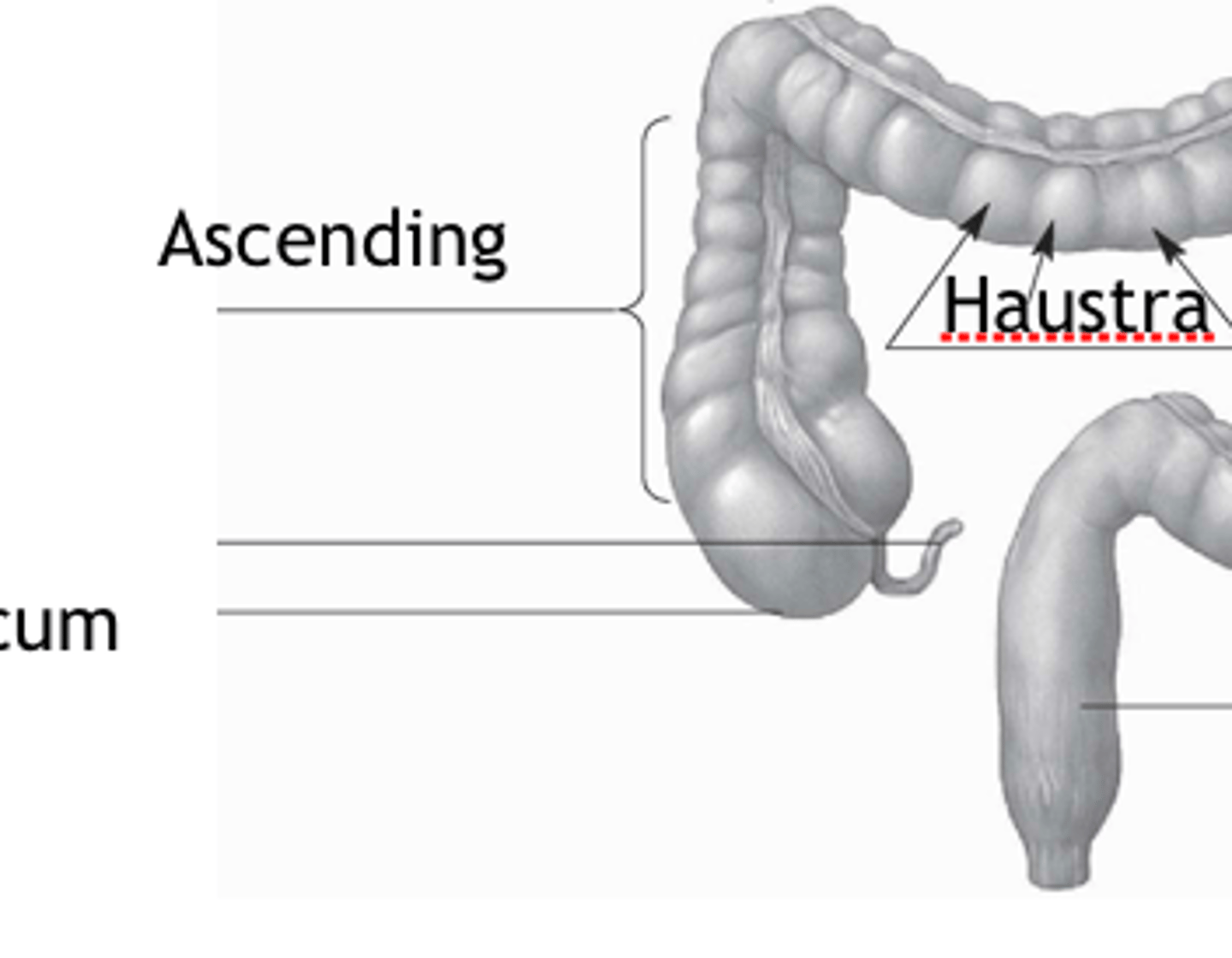
cecum
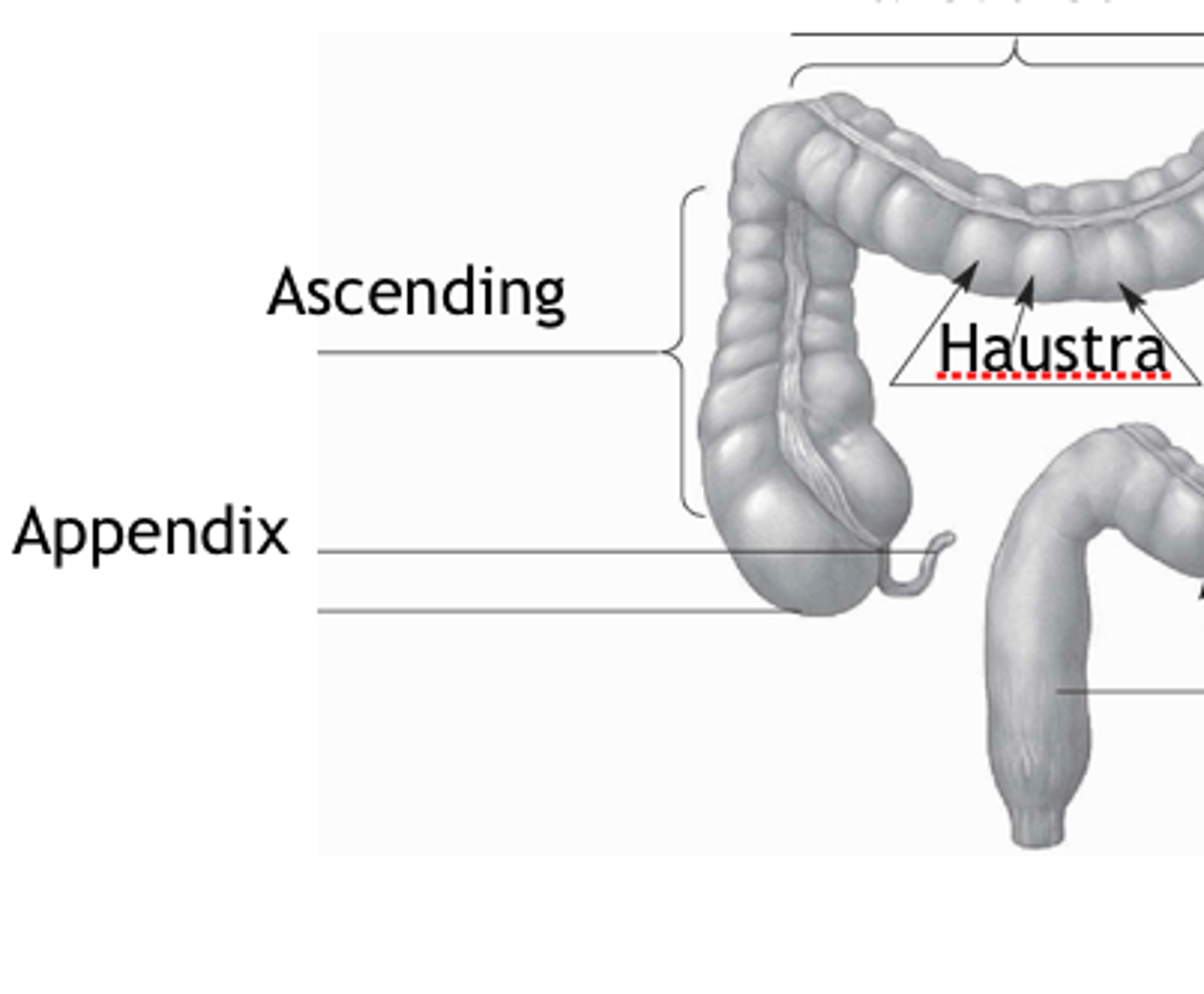
sigmoid
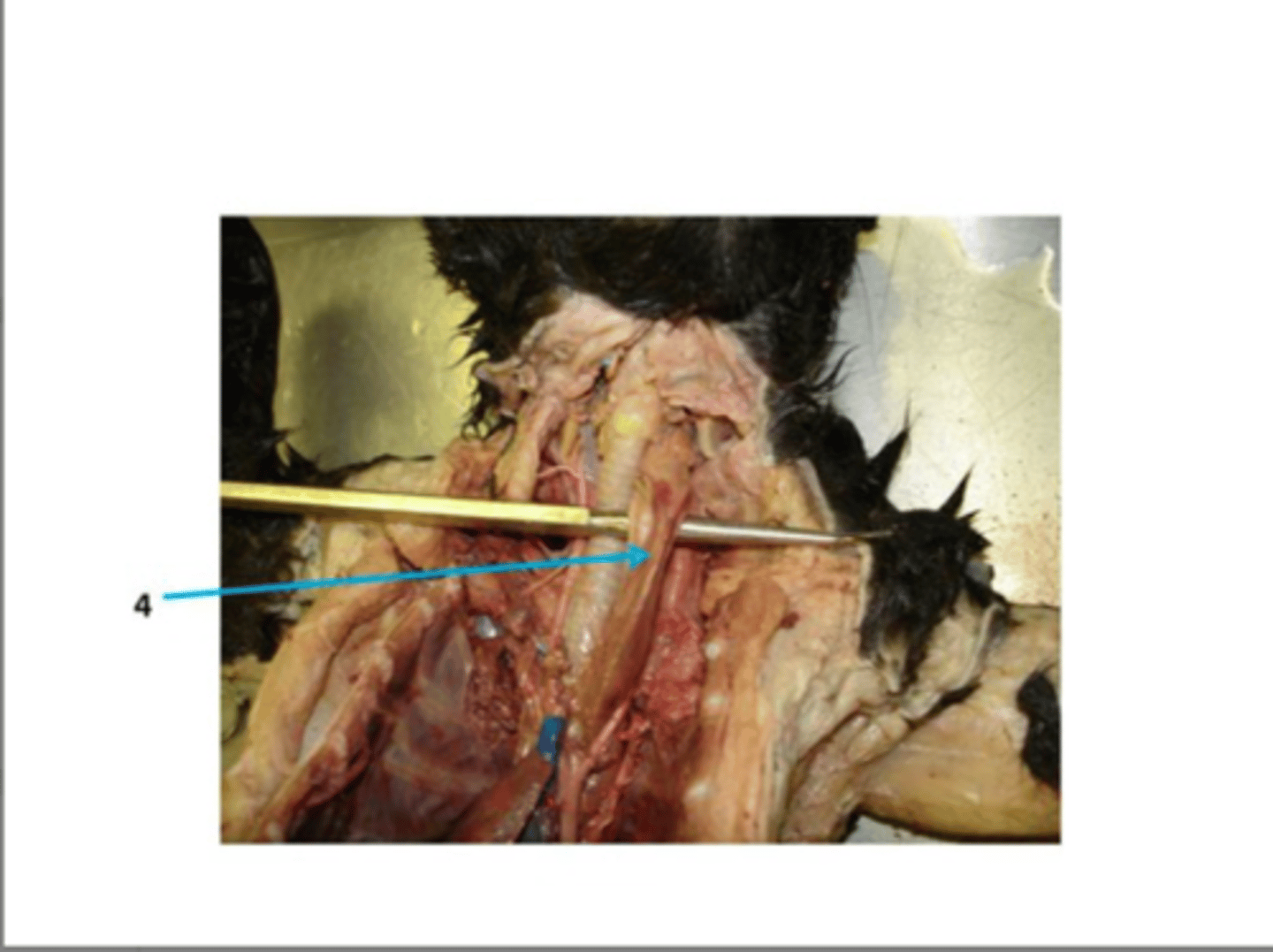
esophagus
greater omentum
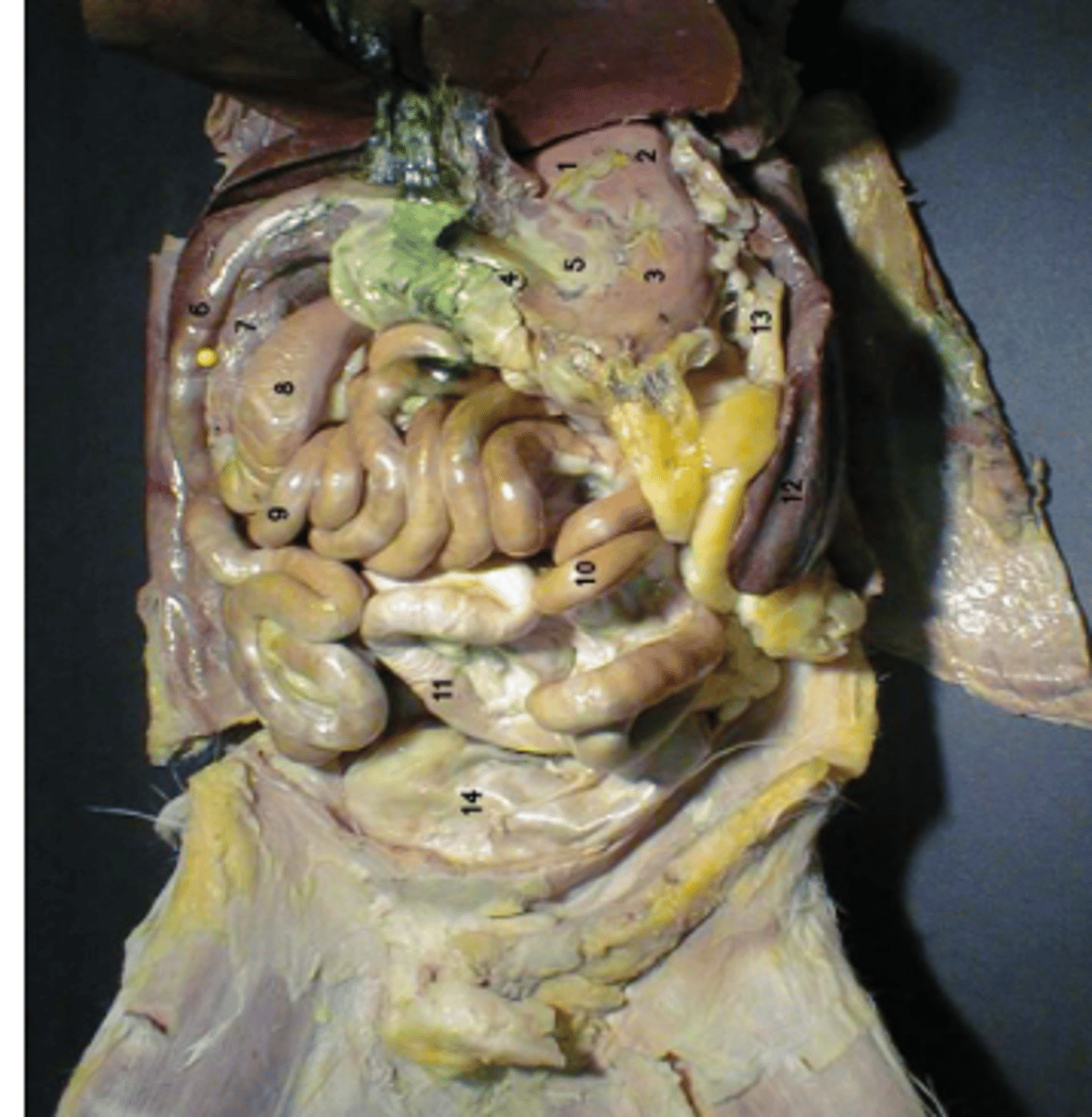
identify 1
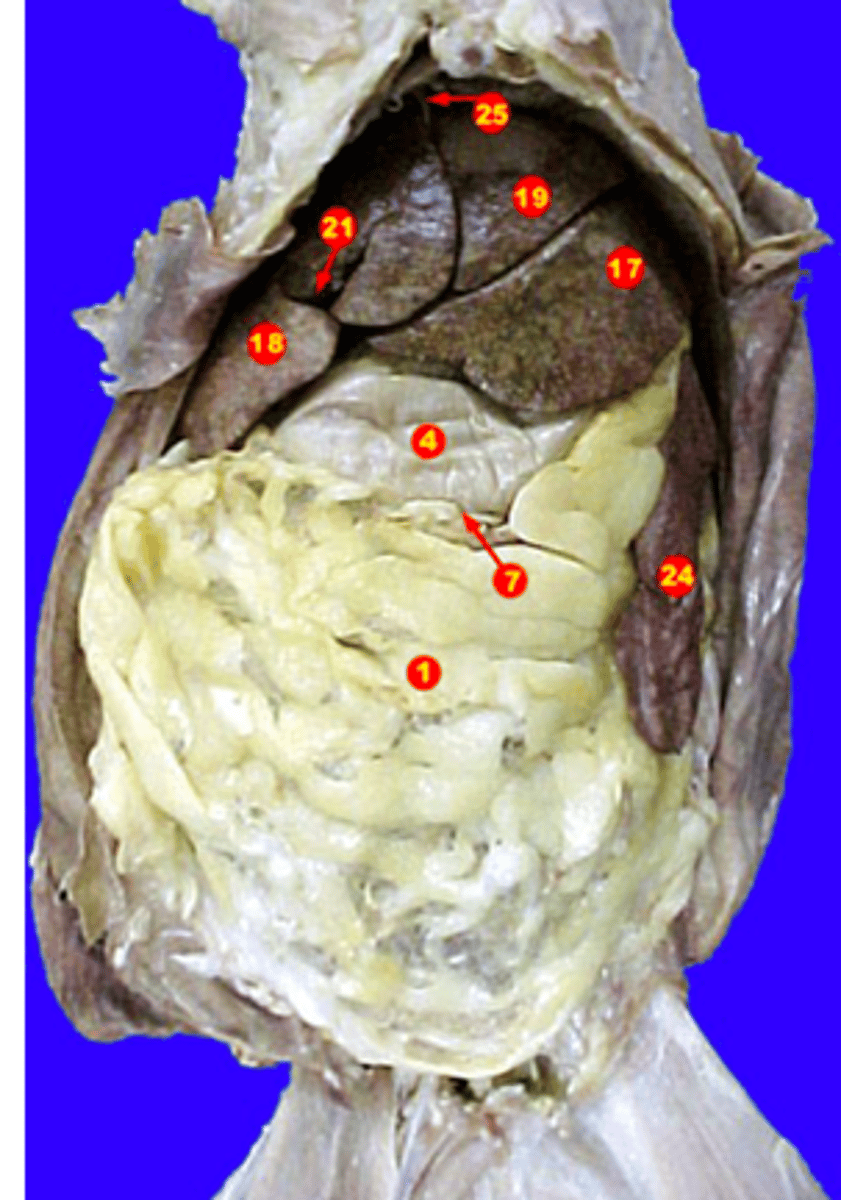
lesser omentum
label 7

fundus
identify 2

cardia
Identify 1.
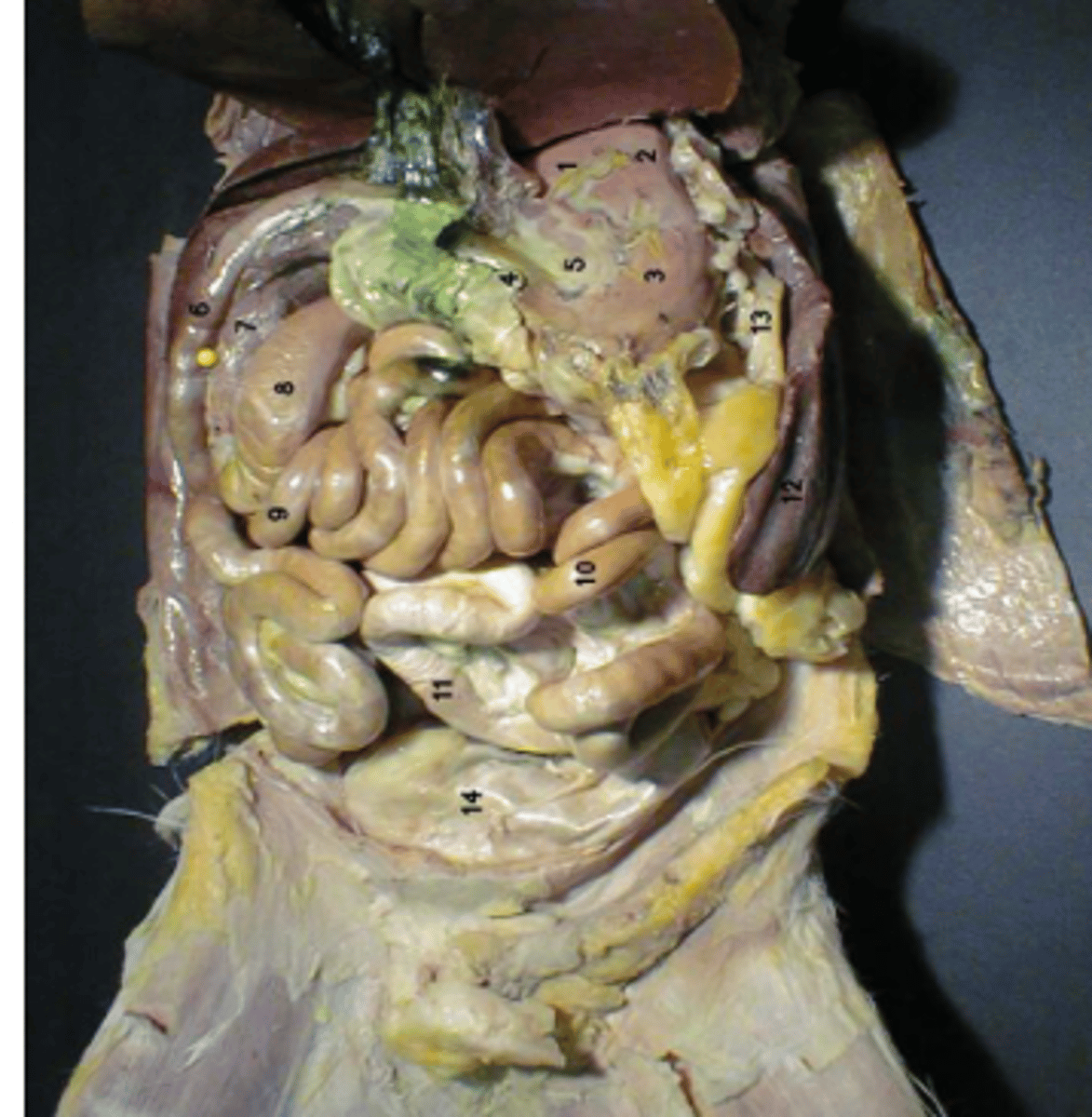
body
identify 3
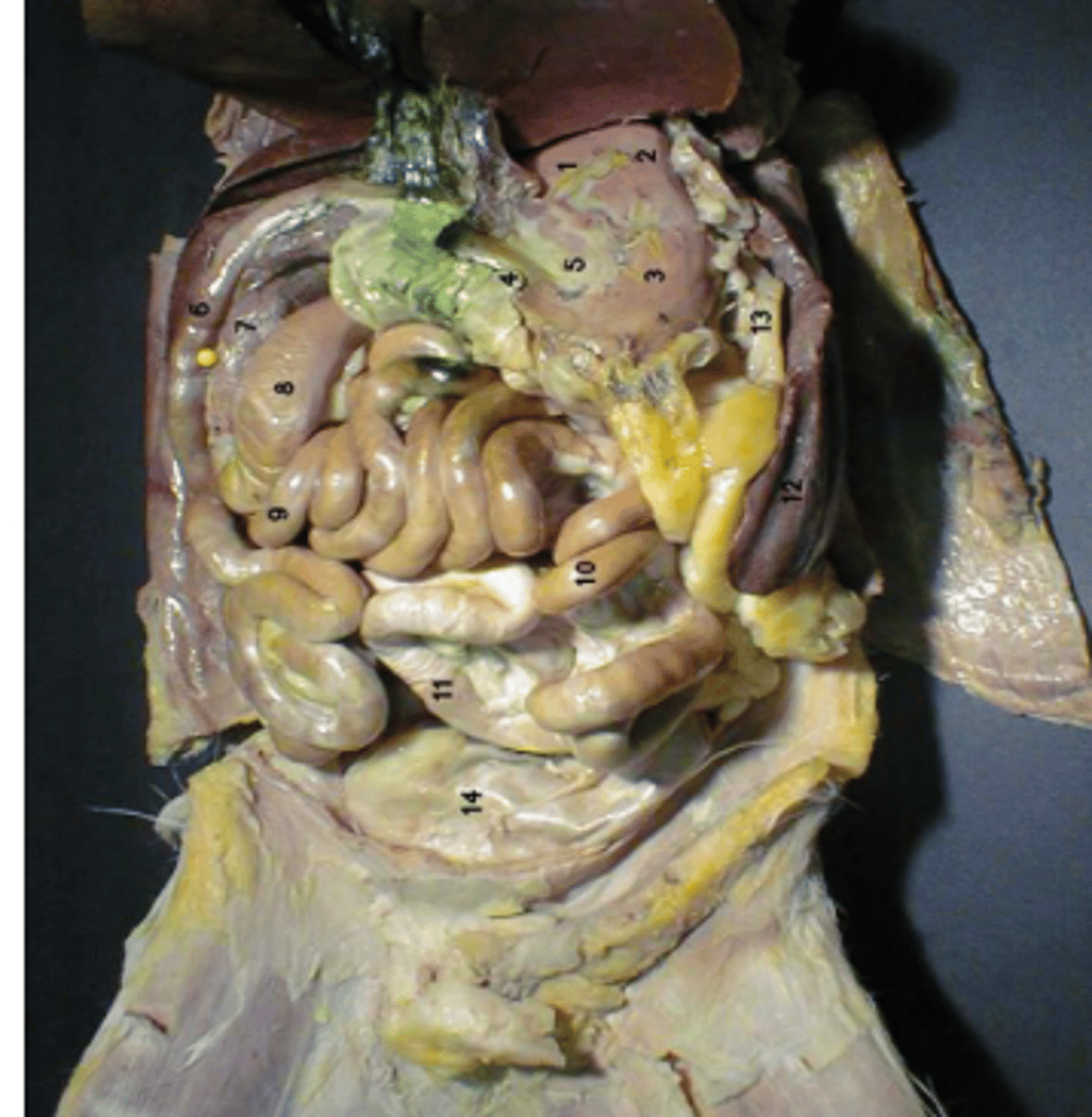
pylorus
identify 4
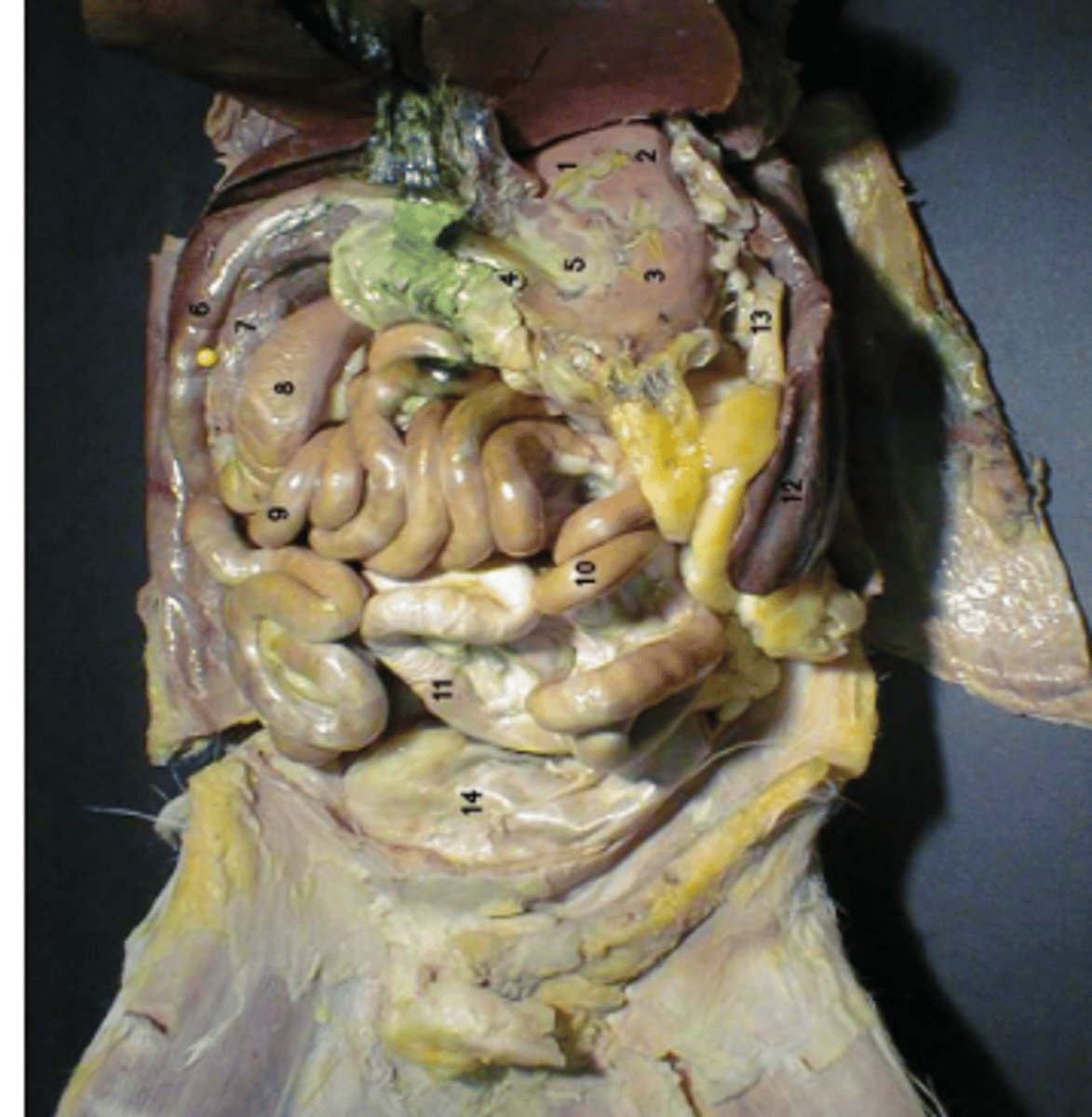
greater curvature
identify 7
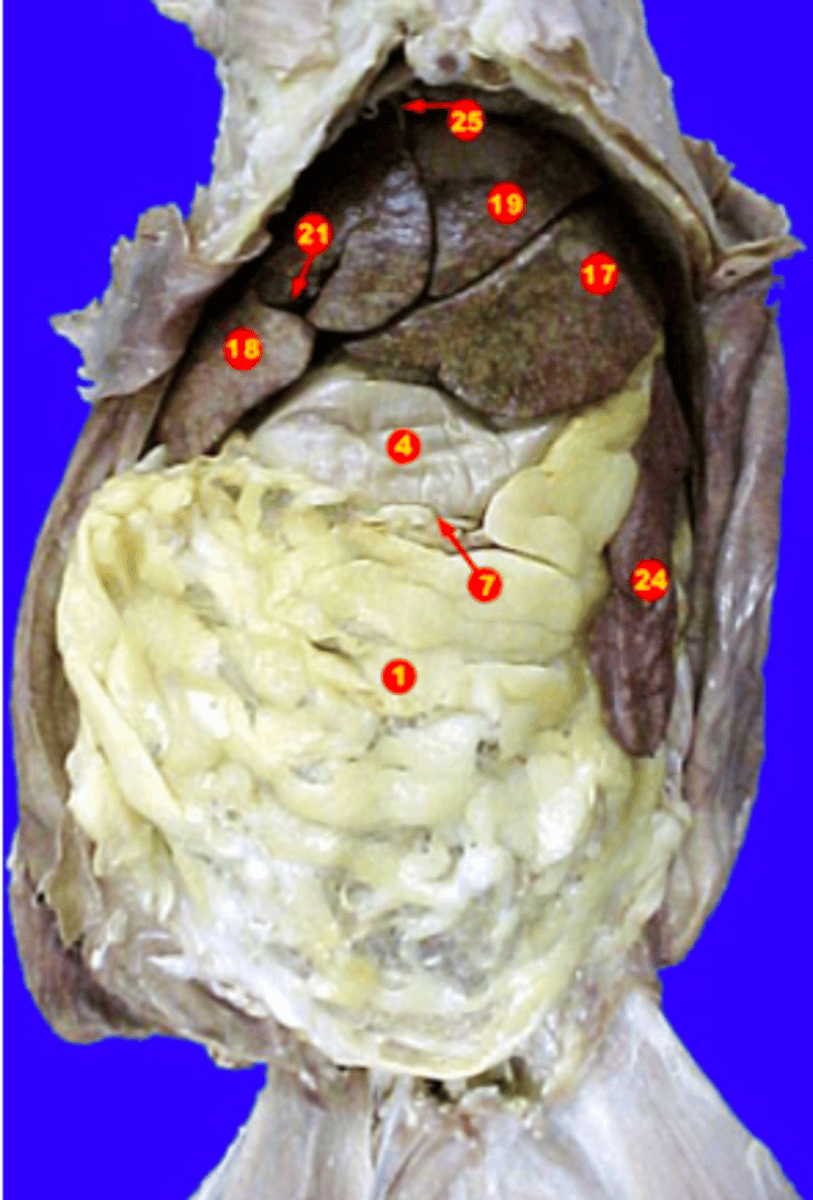
liver
produces bile
gallbladder
identify 21

hepatic duct
cystic duct
common bile duct
duodenum
identify 6
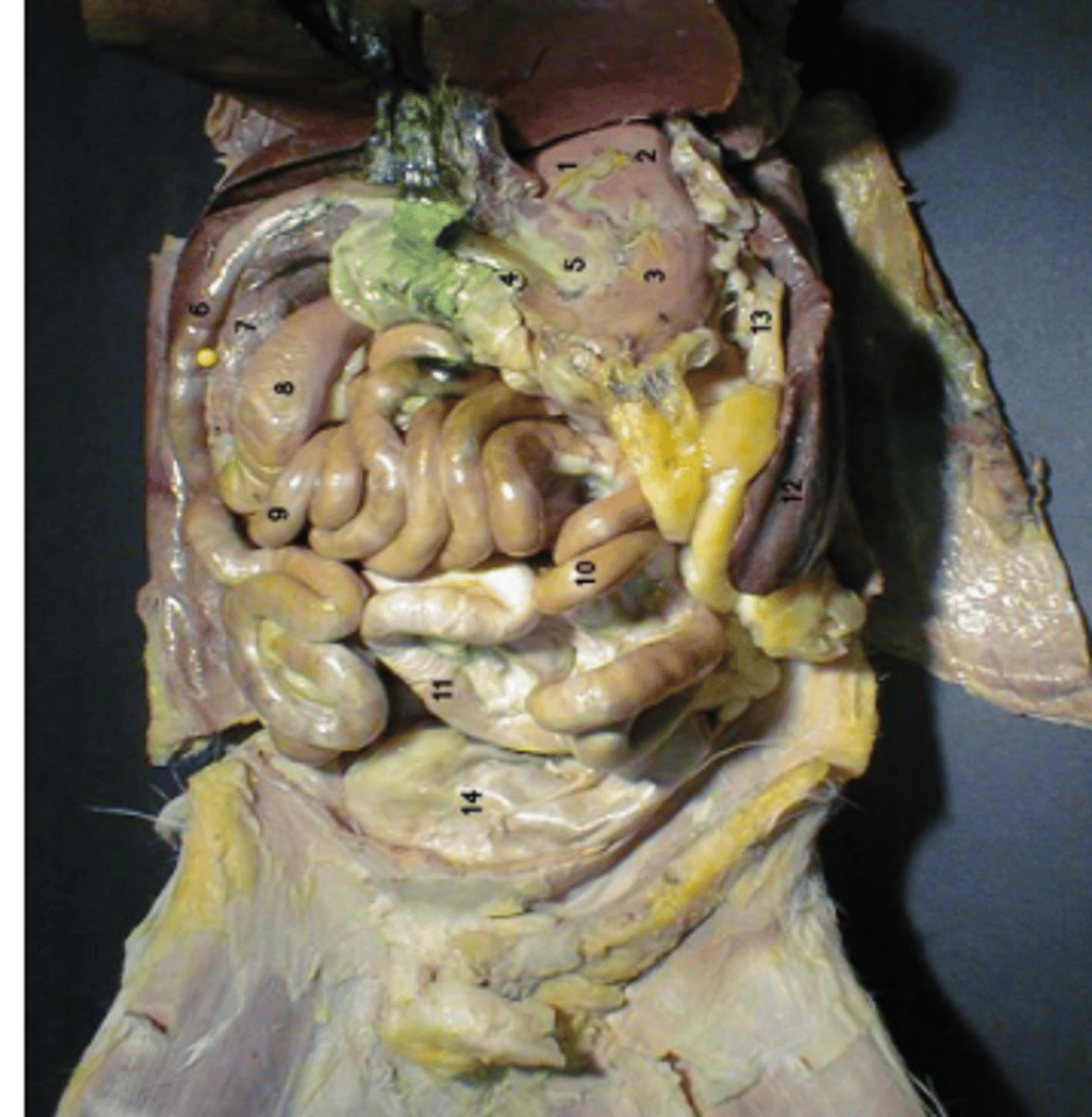
jejunum
identify 10
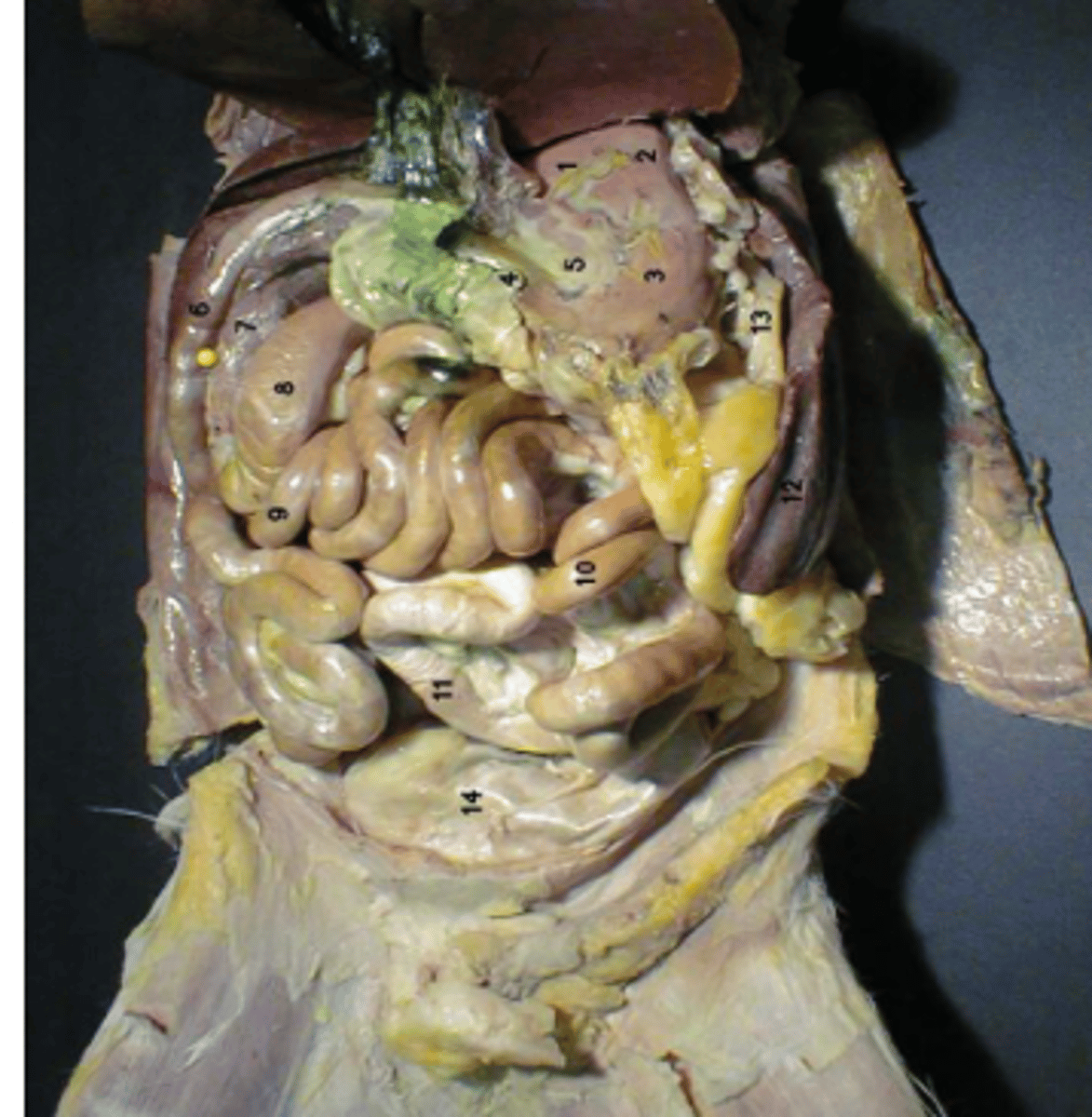
ileum
identify 9