20. Conservation Biology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Humans Species. def.
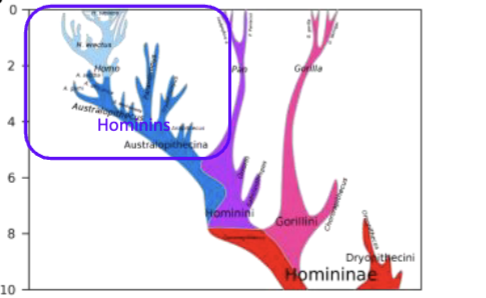
Hominins, the clase that includes Homo sapiens and extinct ‘humans’, arose arround 5.5. MYA

Age Phylogeny - of humans and chmpanzees
Fossil-calibrated molecular clock data suggest that the human & chimpanzee lineages split 5.5. to 7 million years ago (MYA)
When did Homo sapiens come to be
By ~ 0.2 million years ago (200,000) anatomically modern humans existed

Spread of humans came from where?
Africa

Humans are now…
everywhere

Modern humans now devide in mostly but some what?
Mostly sedentary societies, but a few nomadic groups

Human population growth map
Very slow increase up until after the Industrial Revolution

Human Population size now and projected
8,228,984,100
Projected 9.4 billion by 2050
What allowed such a huge population growth?
advances in food production, technology, sanitation, med, etc
increase max pop size that can be supported by the env.

Different human societies have different environmentl impacts due to
Lifestyle, agriculture, consturction, urban vs rural, food, etc.
What resources do humans needs?
O2, freshwater, and nutrients
Main crops in the world
corn (maize)
wheat
rice
potato
soybean
oat
cotton
sugar cane
canola
Main animal species consumed by humans
pig
caw (beef, veal)
Chicken (poultry)
sheet
Goat
Fish
Buffalo
Tuna, tilapia, slamon

Animals also consume what else on top of “food”
trees, and agriculutre aka deforsitation
Trend in areas used by humans
habitat transformation deforestation land clearing
air pollution of freshwater and marine ecosystems
disruption of biogeochecmical cycle soverharvesting of animals and plants
introduction of exotic species
climate change
Extinctions

Europeans exploration
European exploration really lead to the boom of the world and degradation of vast resources by the region colonized from the 1600s and onwards
(needs of the natives and traditional ways were largely disgraced)

European Origins
The elements of conservation developed in Europe (18th/19th centuries) based on experiences of scientific officers trained to make observations on biology, natrual history, geography, and anthropology of the colonial regions

Origins of Conservation in the U.S>
Opponents to a materialistic society
“People need far fewer possessions than they seek”
“Nature has intrinsic value apart from its value to humanity”
Role of American presidents in Conservation
Yellowstone National Park
First park establish by the U.S. in 1872 by Ulysses S. Gran
Theodore Roosevelt (1901-1909)
establish the first national wildlife refuge & expanded federal lands for conservation
What is Conservation Biology? (def)
Integrated, multidisciplinary scientific field that had developed in response to the challenge of preserving species & ecosystems
“the applied science of maintaining the earth’s biological diversity in response to human impacts”
“field that seeks to study and protect the living world and its biologically diveristy:
What does conservation biology do/merge?
Merges applied & theoretical biology & incorporates ideas & expertise from a broad range of fields towards the goal or preserving biodiveristy
Conservation Biology goals
To document the full range of biological diversity on Earth
To investigate human impacts on species, genetic variation, communities, & ecosystems
To develop practical approaches to prevent the extinction of species, and protect and restore biological communities and their associated ecosystems functions
Conservation Biology’s Ethical Principles
the diversity of species and ecosystems should be preserved
the untimely extinction of populations and species should be prevented
ecological complexity should be maintained
Evolution should continue
Biodiversity has intrinsic value