1.1: anatomy & physiology terminology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
regional anatomy
interrelationships of structures in the body; show structures work together
systemic anatomy
structures that make up part of the body; groups of structures working together
ex: muscular system consisting of muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
physiology
how parts of the body functions
integumentary system
encloses internal body structures
ex: hair, nails, skin
skeletal system
supports the body and movement
ex: bones, joints, cartilage
muscular system
supports movement along with skeletal system
nervous system
receives and processes sensory information
endocrine system
secretes hormones to regulates bodily processes
cardiovascular system
delivers oxygen & nutrients to tissue
anabolism
building bigger molecules with smaller ones
catabolism
breaking down bigger molecules into smaller ones
set point
value in which the normal range fluctuates
negative feedback
reverses changes to return to set point & reduces stimulus
parts of the negative feedback loop:
sensor (receives info), control (compare to set point and communicate with effector), effector (makes changes to return to homeostasis)
positive feedback loop
intensifies bodily responses to deviate more instead of reversing it to return to homeostasis and increases stimulus
how does negative feedback loop compare to positive feedback loop?
the external change is stopped by negative feedback loops internally, while positive feedback loops are stopped by use of external changes
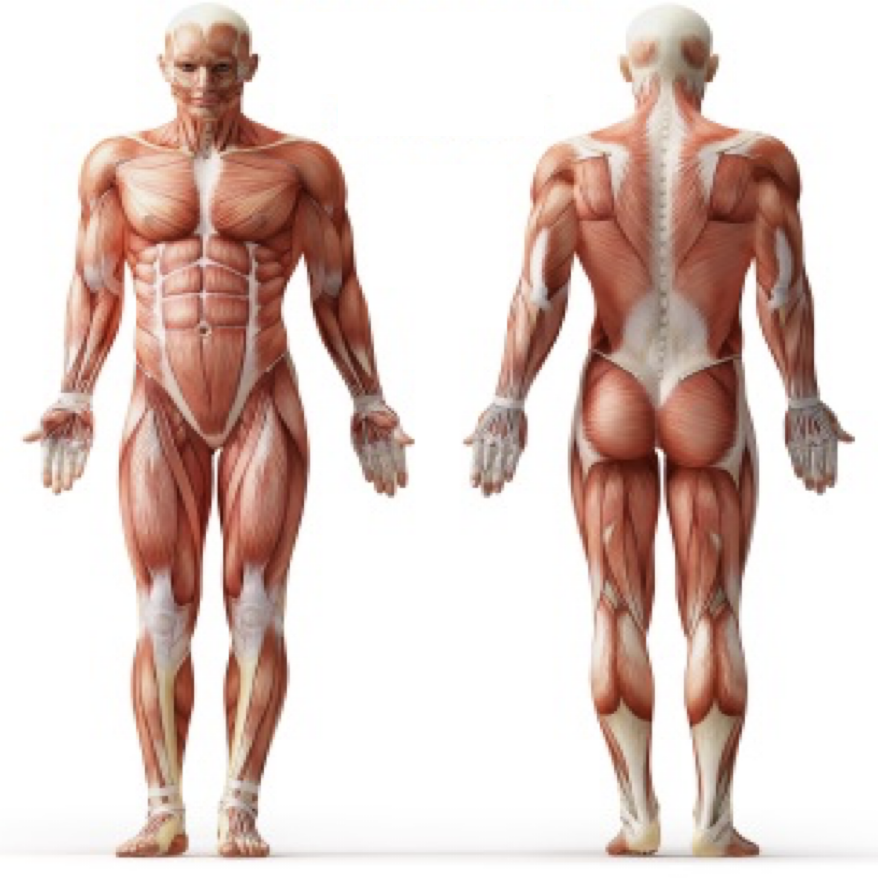
what’s the position on the left? right?
anterior/ ventral, posterior/ dorsal

what’s superior and what’s inferior?
superior is towards the head while inferior is towards the feet
ex: the pelvis is superior to the feet
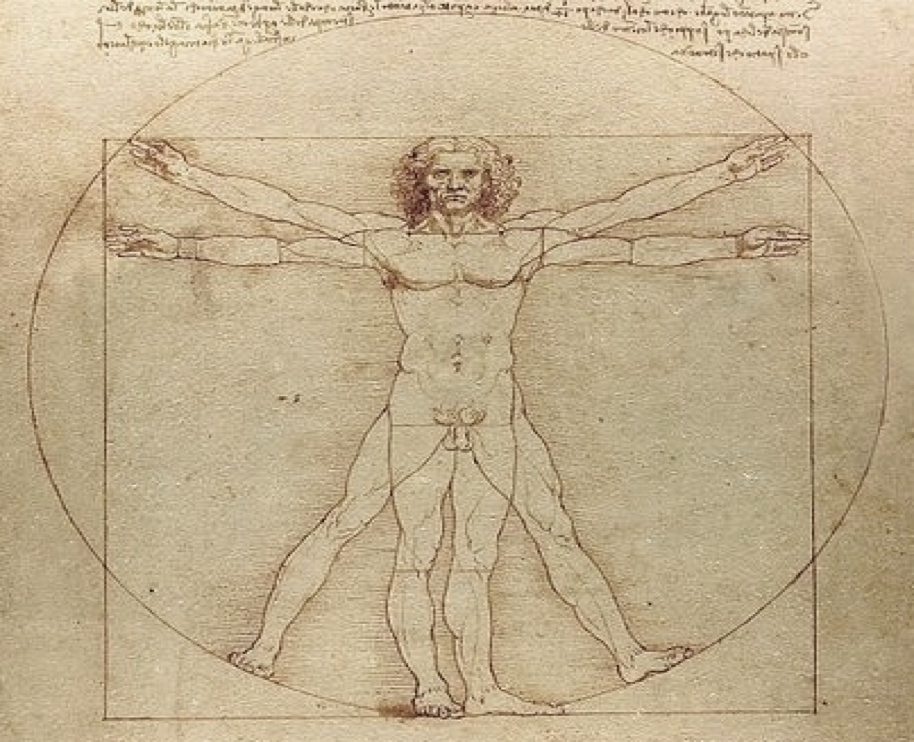
if a line were to run down the middle, with arrows pointing towards the middle, what would this position be called?
medial: towards the midline
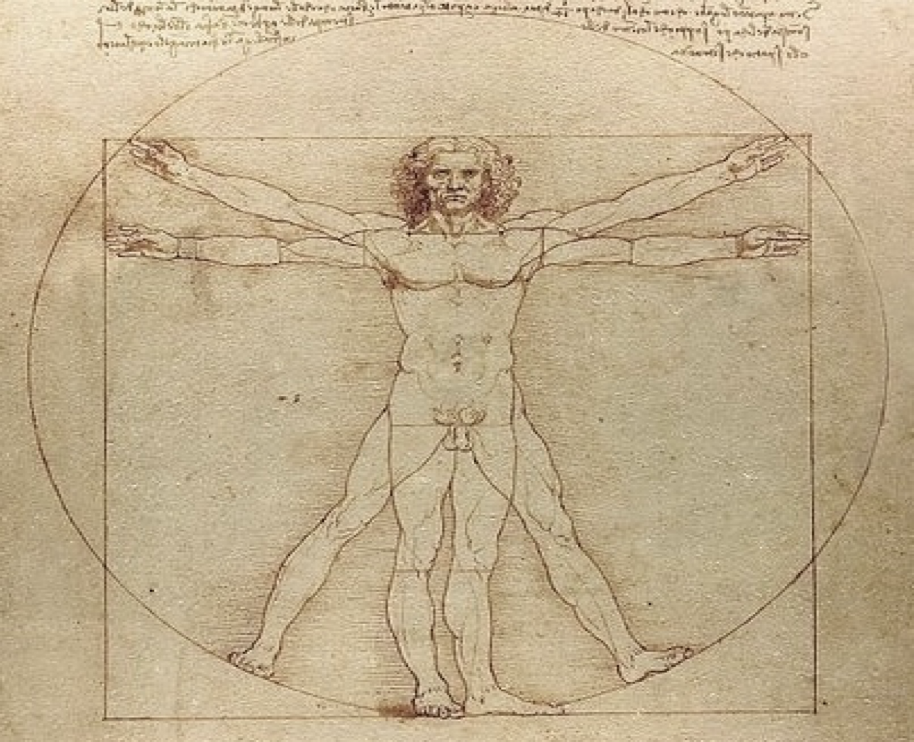
if a line were to run down the middle with arrows pointing away, what would the position be called?
lateral: away from midline
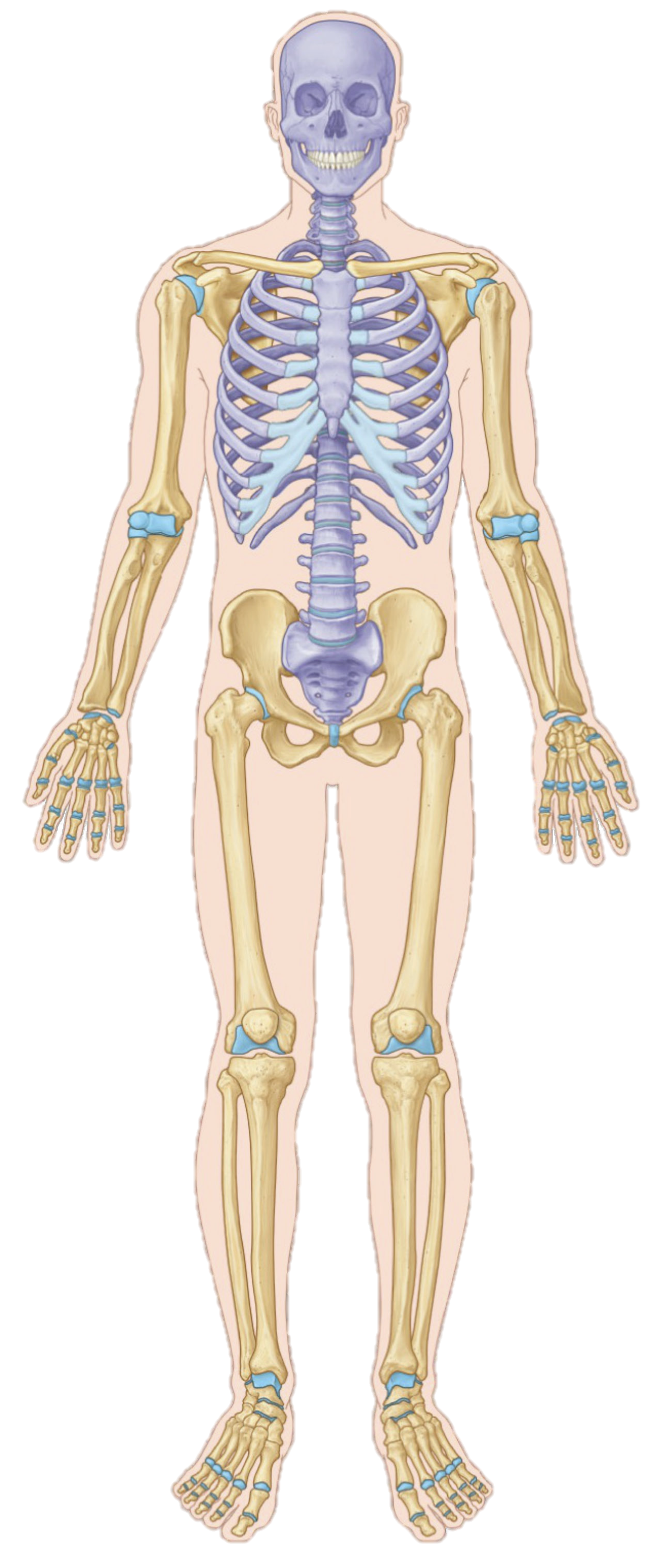
if an arrow pointed towards the trunk, what would this position be called
proximal
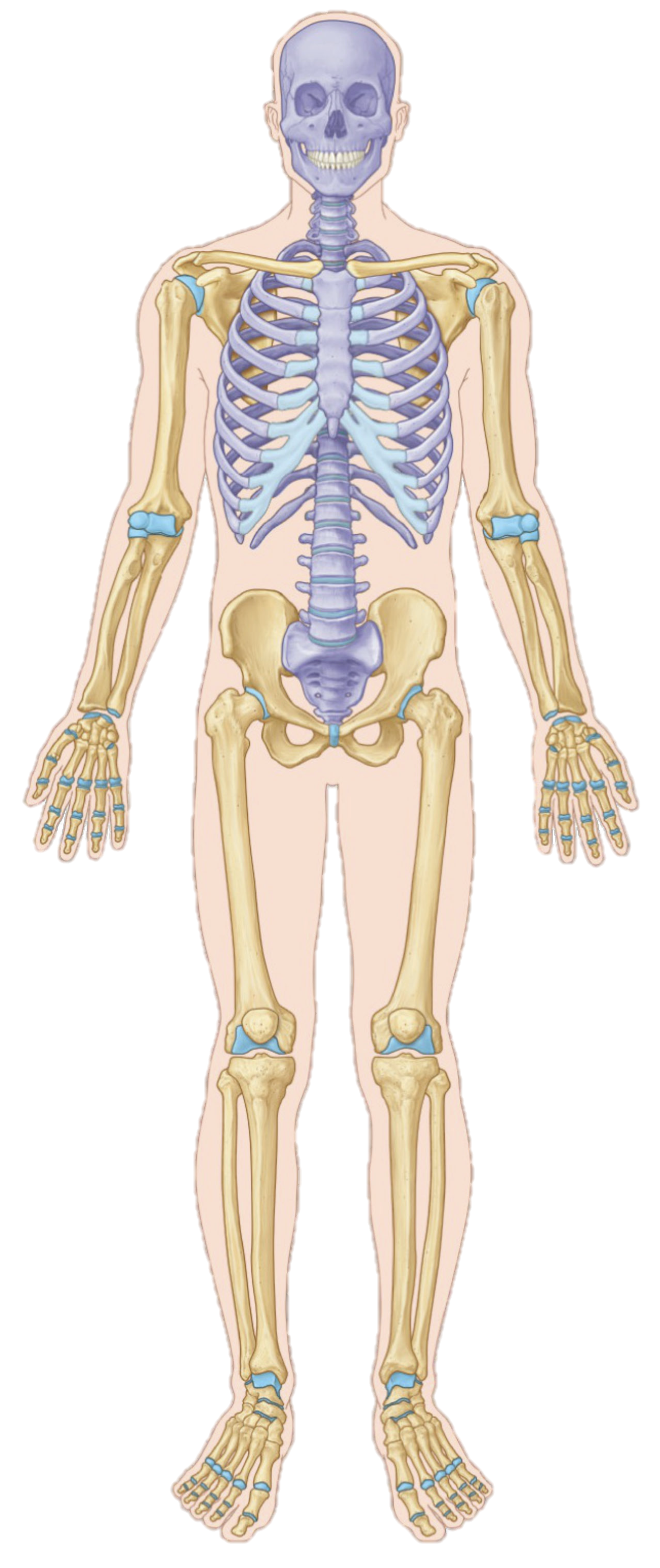
if an arrow pointed away from the trunk, what would this position be called
distal
the brain is ____ to the skull
deep
the skull is ___ to the brain
superficial
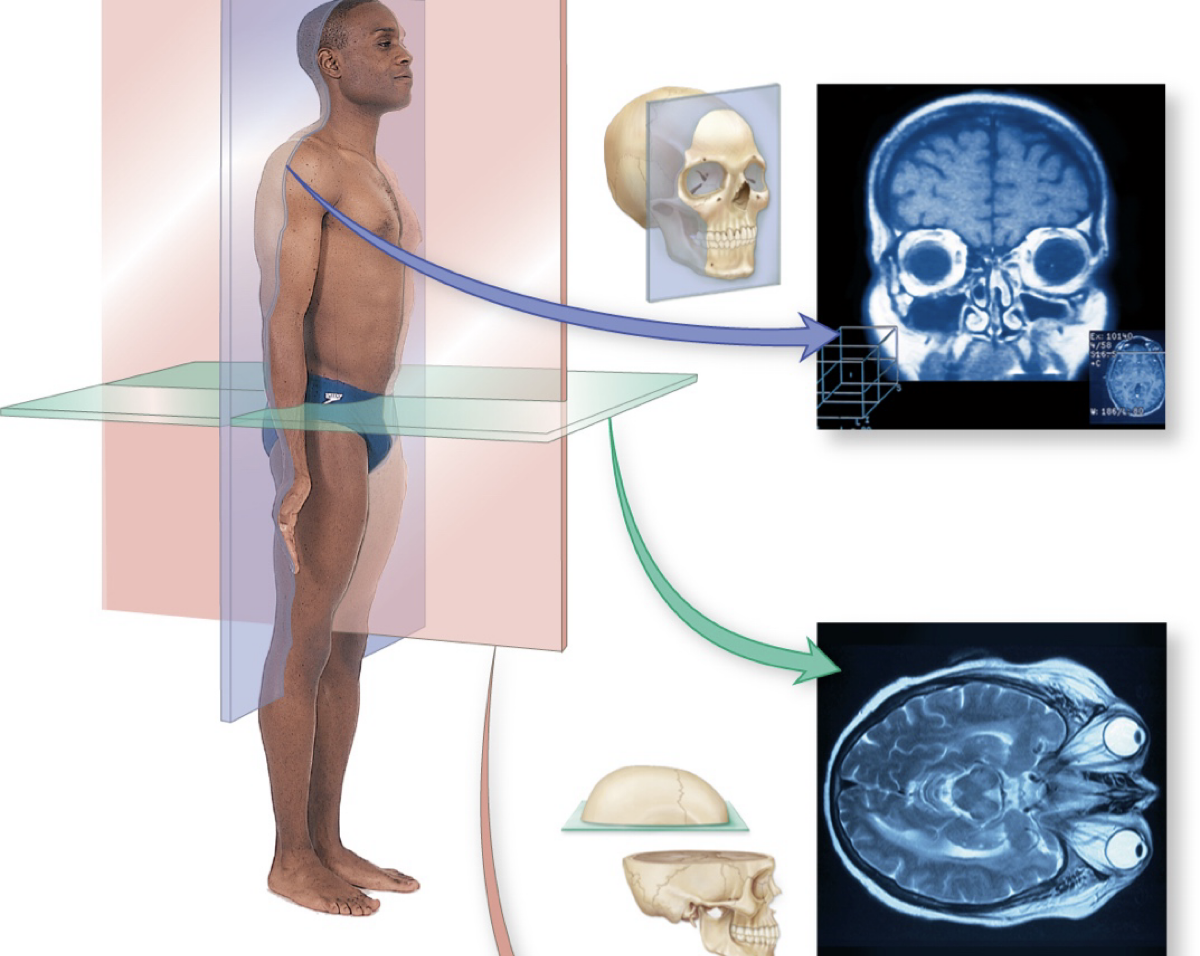
plane divided between left & right
midsagittal plane
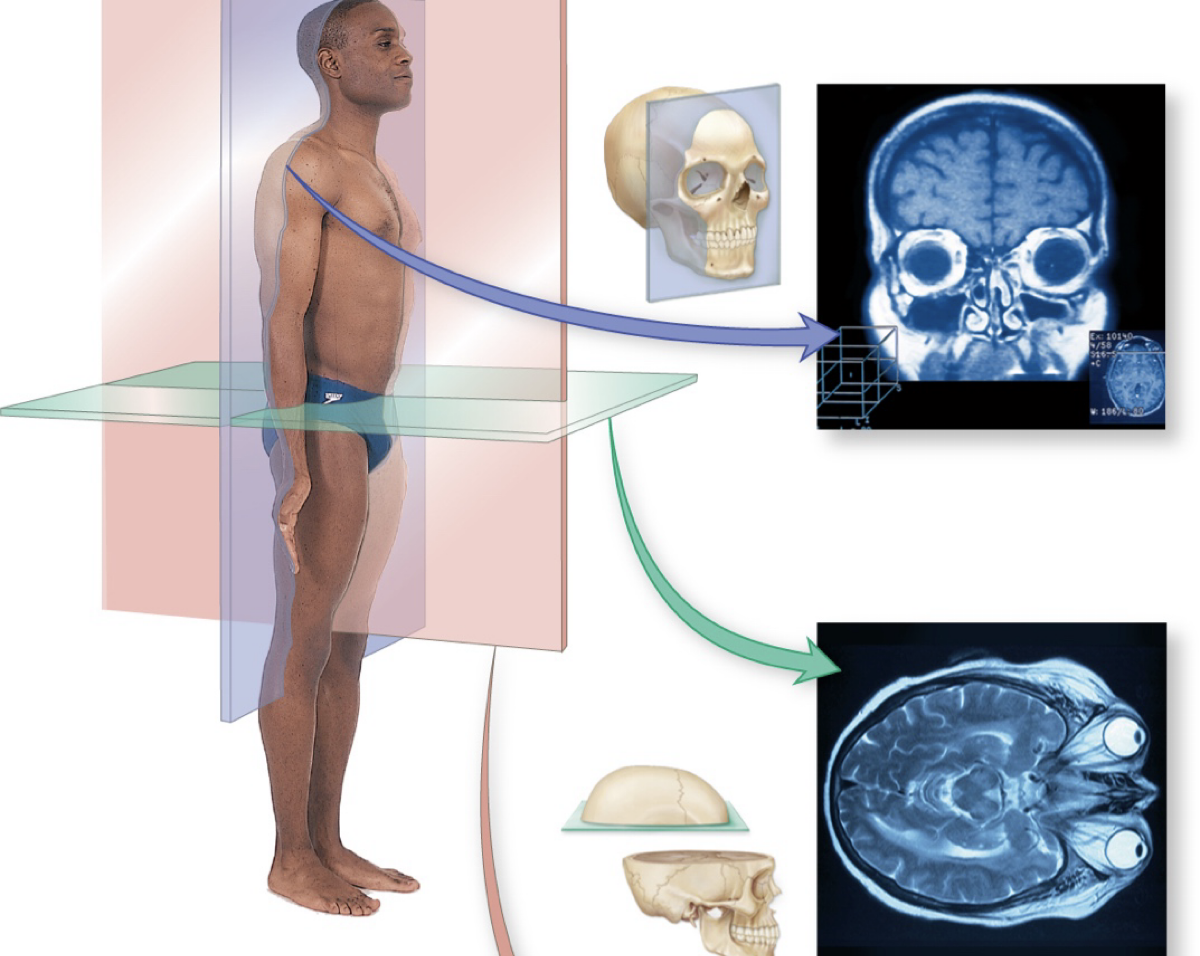
plane divided between front & back
coronal plane
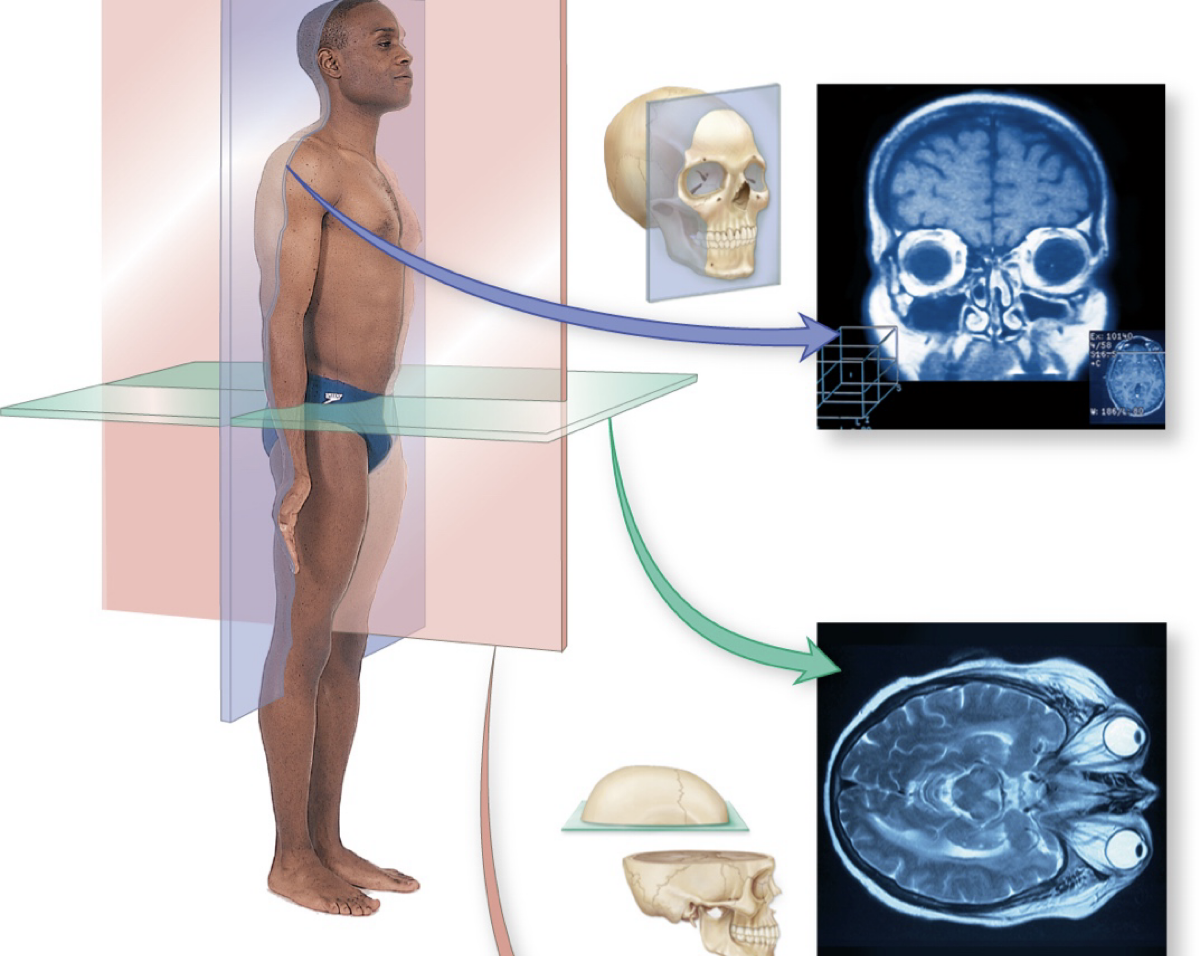
pane divided between top & bottom
transverse
body cavity
internal regions of the body
what’s so important to note about the anatomical pictures in textbooks?
everyone’s anatomy is unique and can therefore look different from examples shown, and still be normal
what planes does the coronal plane divide into?
anterior & posterior
what plane does the transverse plane divide into?
superior & inferior