1: intraoral radiographic techniques
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
types of intraoral radiographs
periapical, bitewing, occlusal
periapical radiography
- more emphasis on the tooth apex and area around tooth apex
- generally, must record entire crown, root, and 2-3mm of periapical area
Bitewing radiography
- used to examine the crowns of both maxillary and mandibular teeth using one image
- ideal for evaluation of alveolar bone loss
- ideal for evaluation of inter-proximal surfaces of teeth for caries (especially in posterior teeth)
Full mouth series
provides a thorough examination of all the teeth and supporting structures
- FMX generally consists of 14-16 PAs and 4BWX
when to do vertical bitewings
for periodontal evaluation if bone loss is significant
types of image receptors
films
sensors
phosphor plates
projection techniques used for periapical radiographs
paralleling technique
bisecting technique
benefits of paralleling technique
minimal distortion
parallel technique
1) Long axis of tooth and film are parallel to eachother
2) The central ray is directed perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth and film
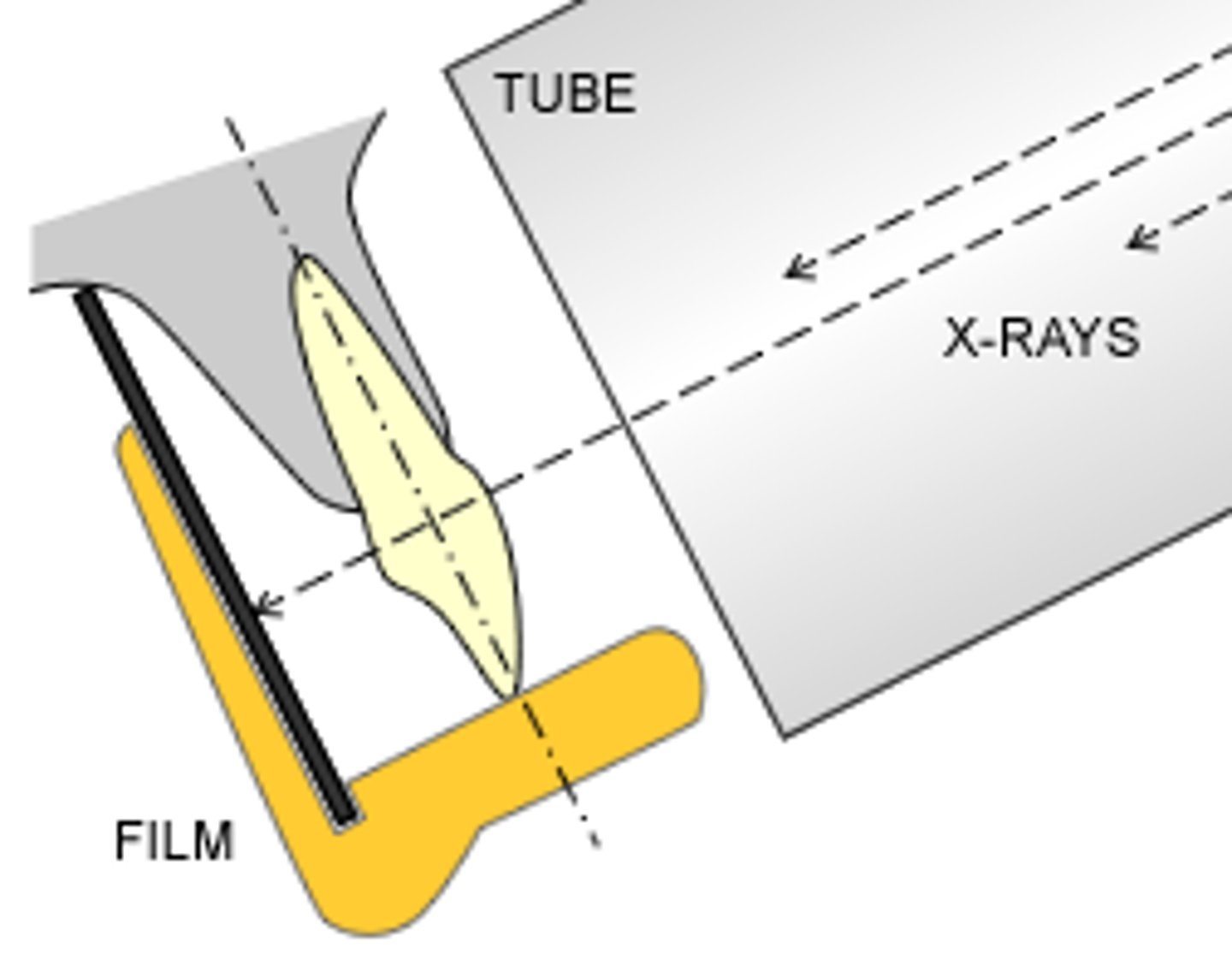
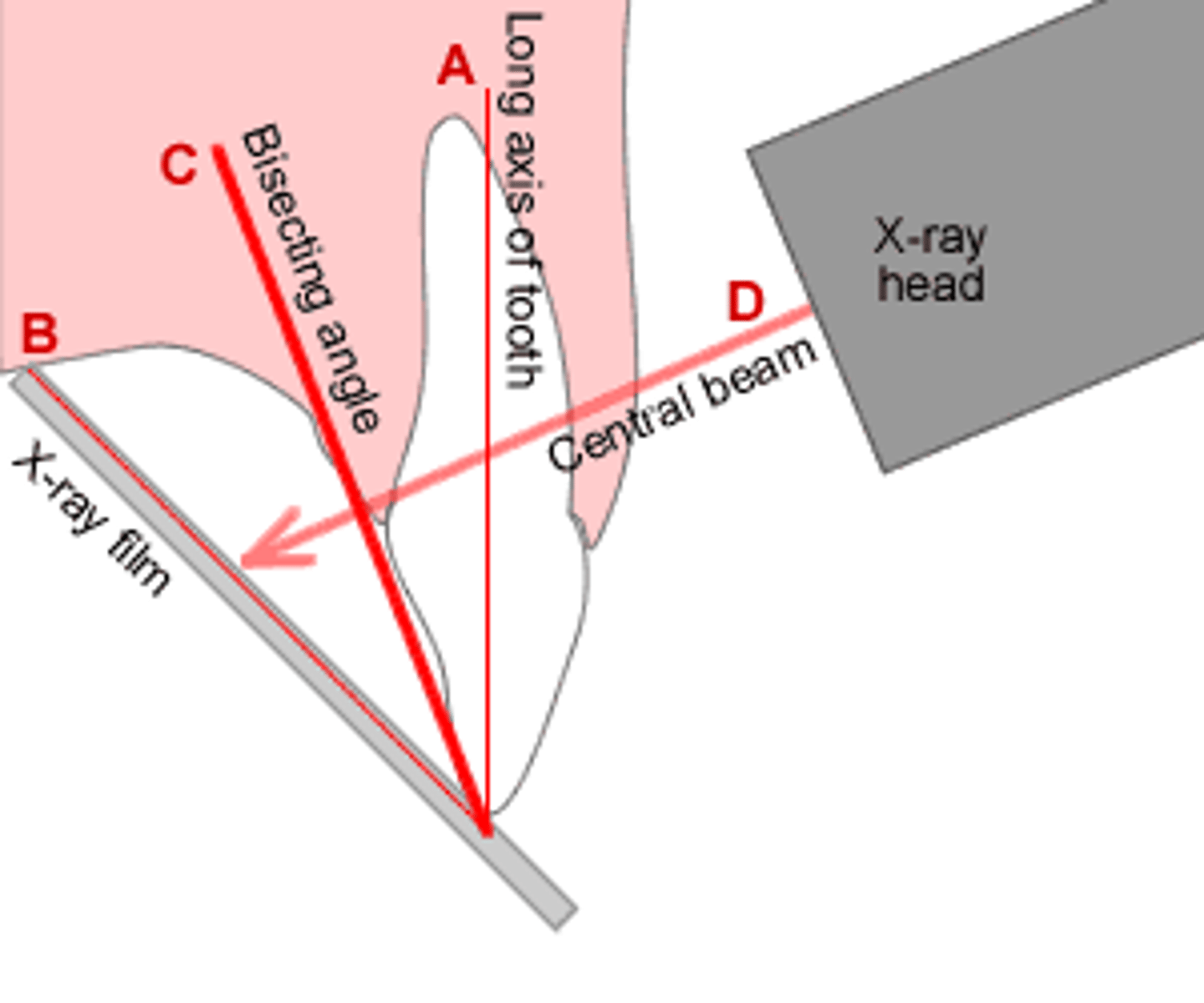
Bisecting angle technique
x rays are directed perpendicular to the imaginary line bisecting the angle formed by the long axis of the tooth and the image receptor
correct vertical angulation results in...
an image identical to the tooth in dimension
indications for use of bisecting angle technique
- difficulty in positioning receptor parallel to teeth
- difficult anatomy
- shallow palate
- edentulous patients
- pediatric patients
- palatal tori/anatomical variations
- shallow floor of mouth
- severe gag reflex
- no sensor holder available
vertical angulation - paralleling technique
central ray is directed perpendicular to receptor and long axis of tooth
horizontal angulation - paralleling technique
central x ray beam must be directed through the interproximal contact areas
Maxillary central incisor PA should include
both central incisors
their periapical areas
open interproximal contacts
Maxillary lateral incisor PA should include
lateral incisor centered over the sensor
Maxillary canine PA should include
entire canine and its perapical area and open interproximal contacts
Maxillary premolar PA should include
distal third of canine, two premolars, and first molar
maxillary molar PA should include
all three molars and part of tuberosity
Mandibular central/lateral PA should include
all central and lateral incisors and their periapical view
mandibular canine PA should include
entire canine centered over the receptor and its periapical area
- open the interproximal contacts
mandibular premolar PA should include
distal third of the canine, two premolars, and first molar
mandibular molar PA should include
all three molars and its periapical area
what should you capture in premolar bitewings?
distal third of canine, premolars, first molar
in vertical angulation, what is acceptable?
positive angulation of 7-10 degrees
"A" error code
missing area due to incorrect sensor position - missing apex, periapical bone, part of the tooth and root, bone level
"B" error code
Beam angulation - incorrect horizontal beam leads to overlap of the interproximal contacts. Incorrect vertical angulation leads to elongation or foreshortening and missing anatomy
"C" error code
Cone cut - incorrect horizontal, vertical angulation. PID is not aligned with XCP ring