Chapter 6 - DNA Replication, Repair, and Recombination
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur?
S phase of interphase
How fast does DNA replication occur in bacteria?
1000 nucleotides per second
What are common causes of DNA damage?
Chemicals, radiation, accidents, reactive molecules in the cell
What is the purpose of DNA repair?
To keep mutations to a minimum
What is a mutation?
A change in DNA
What does semiconservative replication mean?
Each strand of DNA serves as a template for a new complementary strand
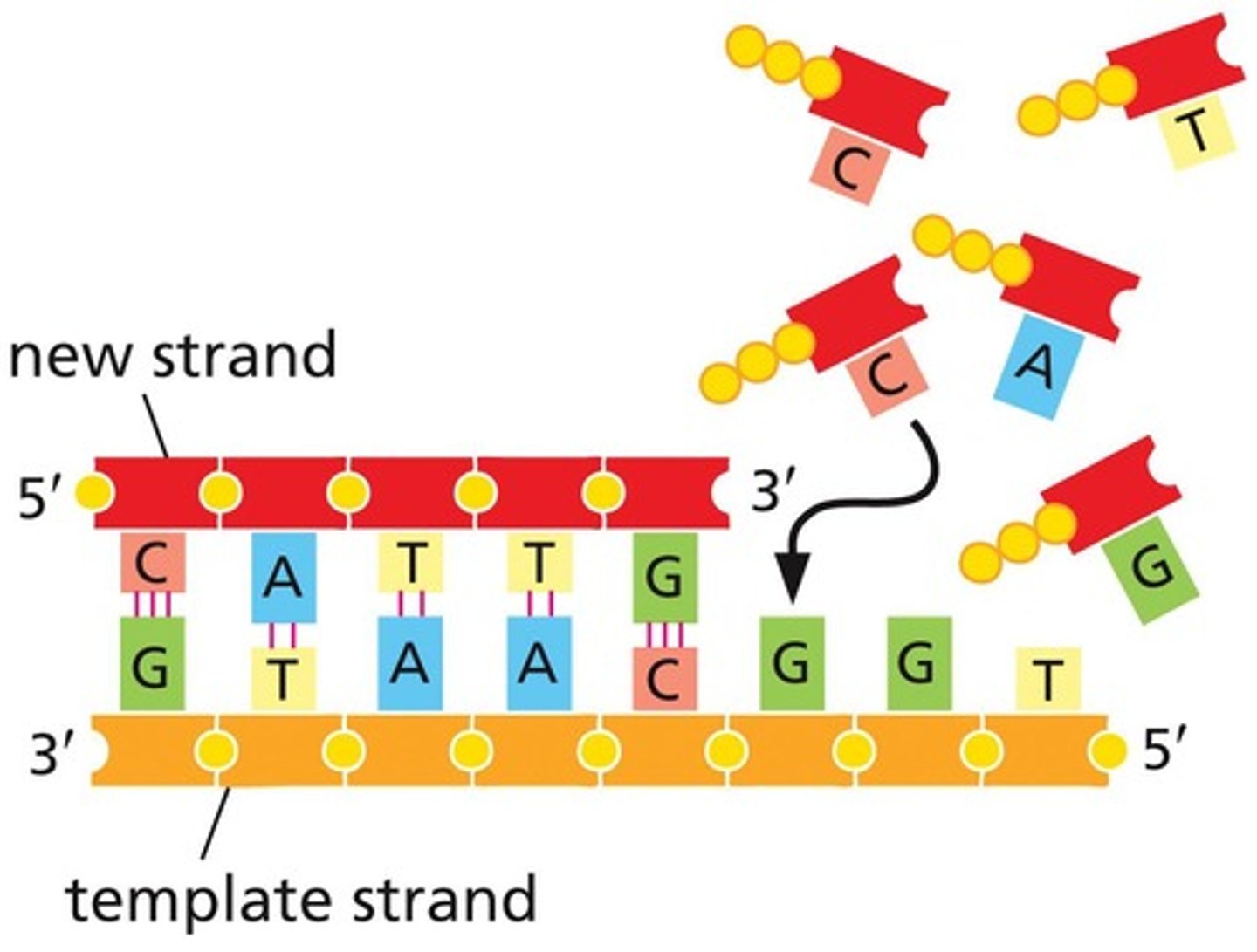
What keeps the two strands of the DNA double helix together?
Hydrogen bonding
What are origins of replication?
DNA sequences that attract initiator proteins, typically rich in A:T
How many origins of replication are there in the human genome?
Approximately 10,000
What is the role of primase in DNA replication?
To start a new polynucleotide chain in the 5' to 3' direction
What direction does DNA polymerase synthesize DNA?
5' to 3' direction
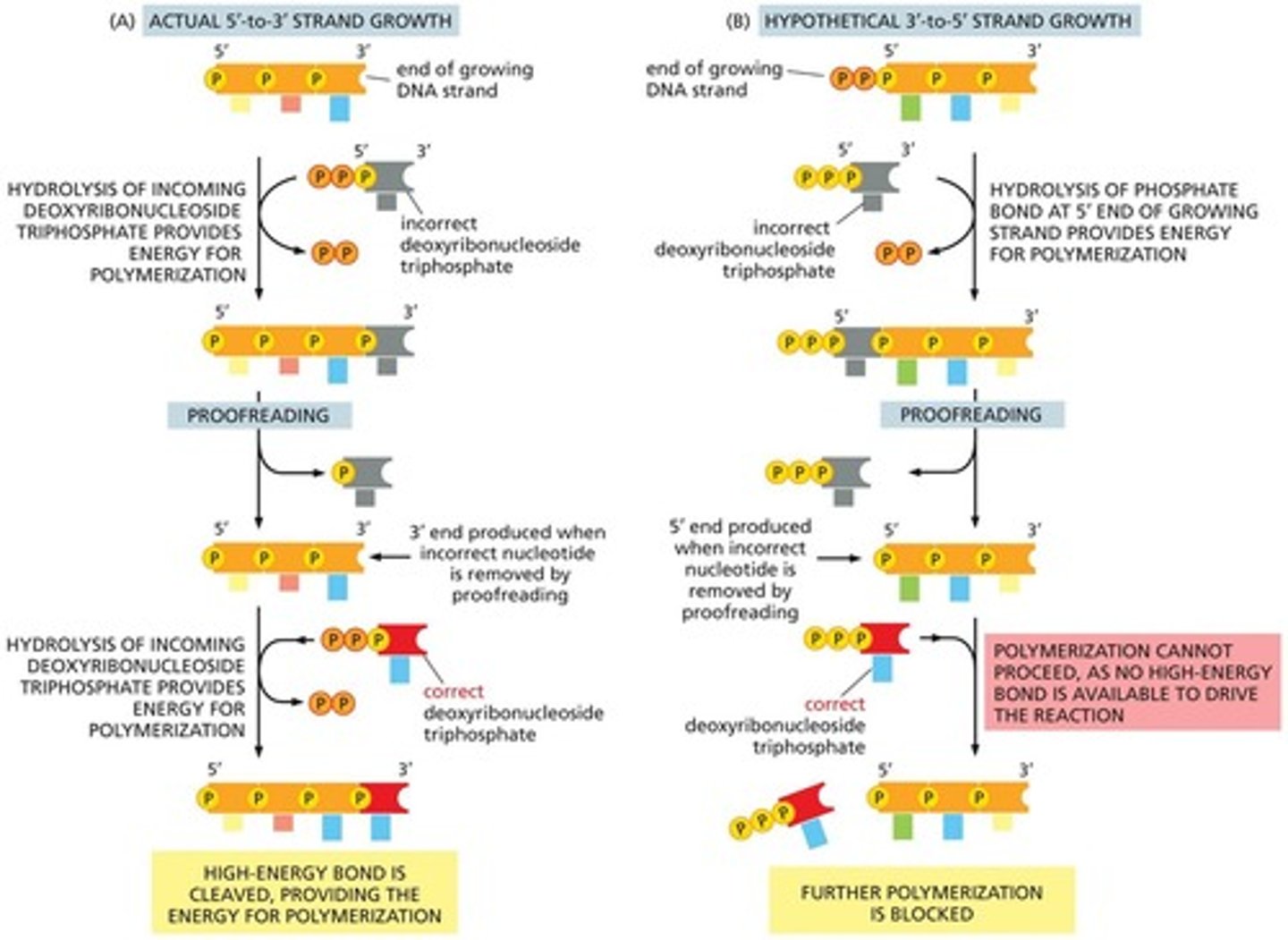
What is the function of DNA ligase?
To join Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand

What problem arises at the ends of linear chromosomes during replication?
Loss of 50-100 nucleotides when removing the RNA primer
What are telomeres?
Regions at the end of linear chromosomes that do not contain genes, consisting of repeating units of 5' TTAGGG 3'

What is the function of telomerase?
To extend telomeres and allow completion of DNA synthesis at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes
Where is active telomerase typically found?
In cells of reproductive organs that undergo meiosis
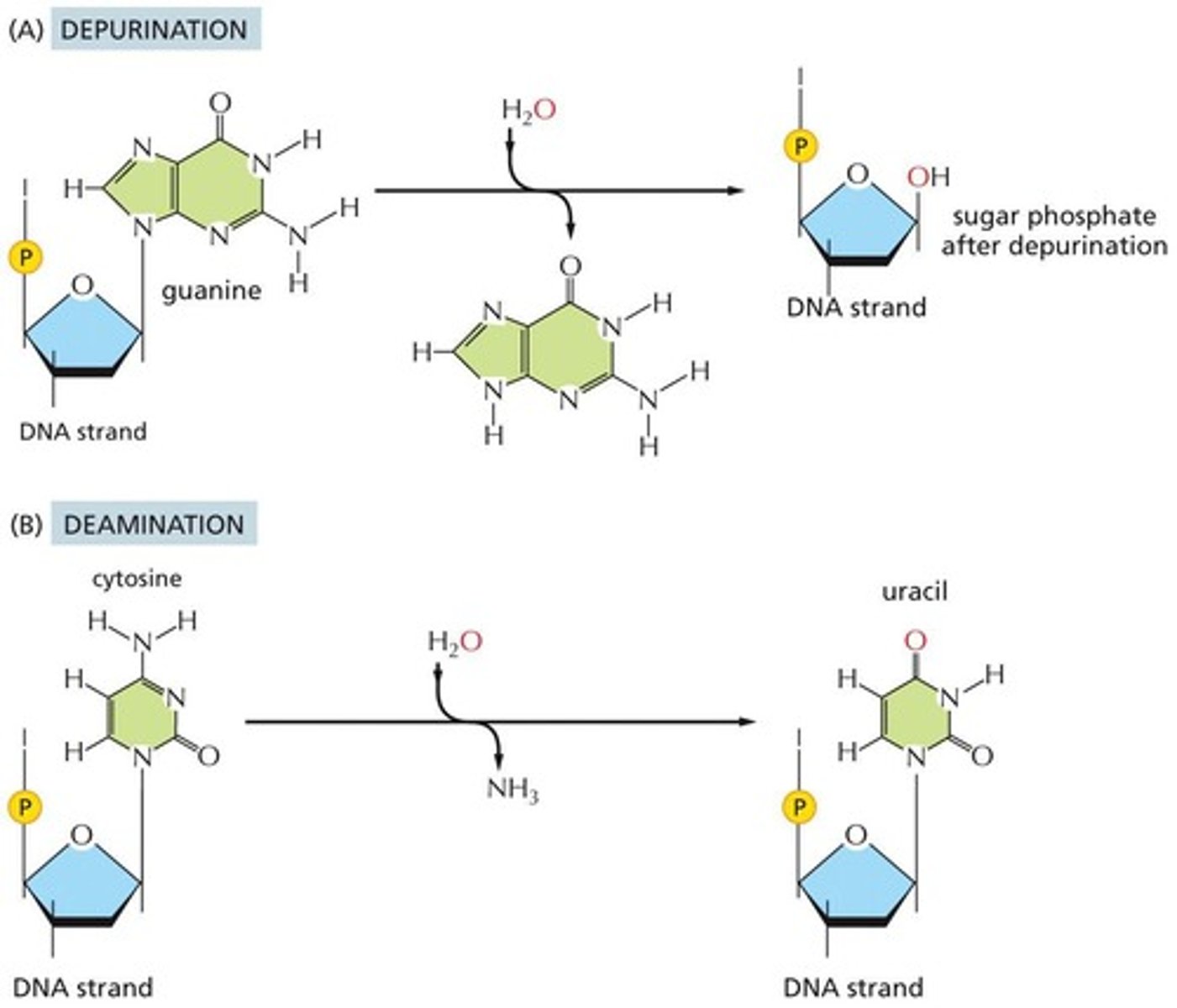
What spontaneous changes can occur in DNA?
Depurination and deamination, leading to loss of nucleotides
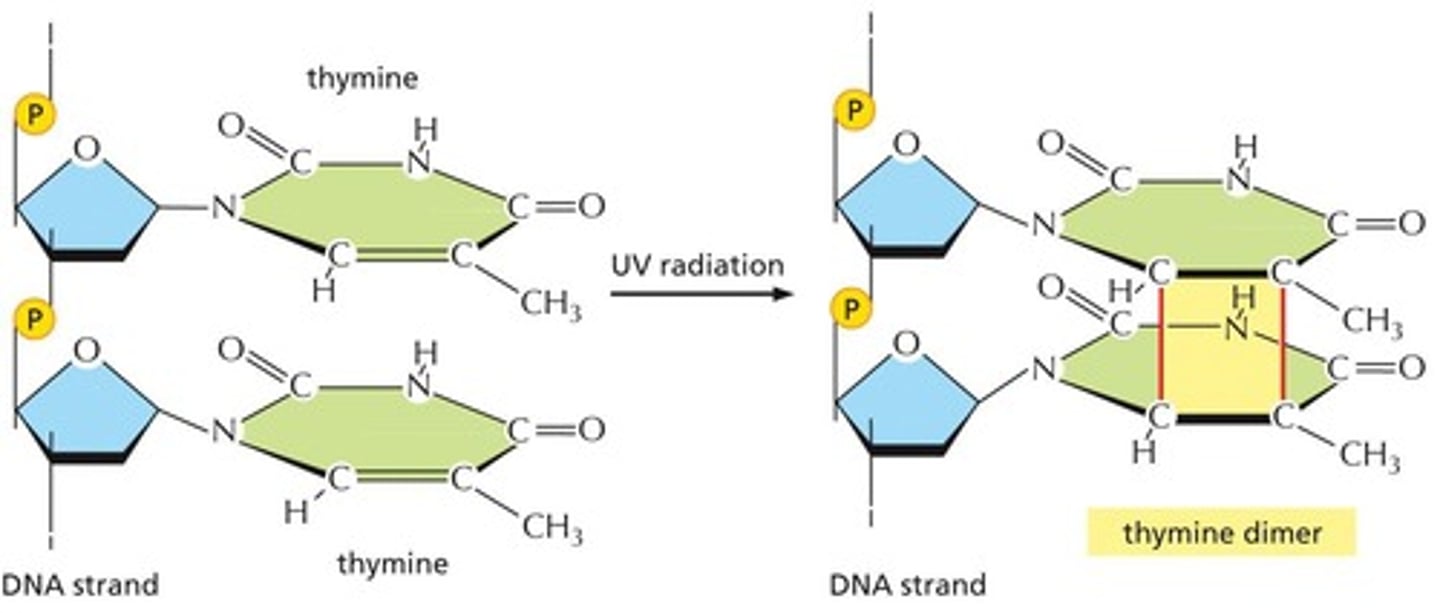
What effect does UV radiation have on DNA?
It can cause covalent bonds between pyrimidine bases, leading to mutations
How does DNA repair typically work?
Using the undamaged strand to accurately repair the damaged strand

What is a major problem when repairing double-stranded breaks in DNA?
Loss of genetic information if the damaged strand contains genes
What is the consequence of leaving chemical modifications of nucleotides unrepaired?
They can produce mutations