41. Acute renal failure – causes, diagnostic, management
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
How can causes of acute renal failure be classified?
Prerenal
Renal
Postrenal
Reduced renal perfusion (hypovolaemia, shock, trauma, embolism, DIC, ACE inhibitors, dehydration, impaired cardiac output)
Increased protein catabolism (necrosis, starvation, infection, fever)
Direct or indirect damage to the nephrons, causing inadequate perfusion and obstruction.
This includes infectious agents (leptospirosis, Lyme disease), inflammatory diseases (immune-mediated glomerulonephritis, lupus), and nephrotoxic substances
What are clinical signs of acute renal failure?
General: sudden onset lethargy, anorexia, decreased water intake, dehydration, normal body condition
Urinary: oliguria/anuria (or polyuria during recovery), asymmetrically enlarged, firm, painful kidneys
GIT: vomiting, +/- diarrhoea, tongue necrosis, mm ulcers (increased urea in blood → bacteria change urea to ammonia → ulcers)
Respiratory: tachypnoea, uraemic breath
Cardiovascular: bradycardia
CNS: ataxia, seizures
History and anamnesis (sudden onset of anorexia, lethargy, vomiting, ataxia, seizures, known toxin or drug exposure, reduced water intake, oliguria)
Physical examination
Laboratory examination
Biopsy
Urinalysis
Imaging
Increased calcium, phosphate, phosphorus, total protein, BUN, and creatinine
Decreased bicarbonate
Increased haematocrit/PCV and lymphopenia. Typically not anaemic.
What are important biomarkers when evaluating kidney function?
Cystatin C
SDMA
What is a hallmark finding in urine for acute kidney disease (AKD)?
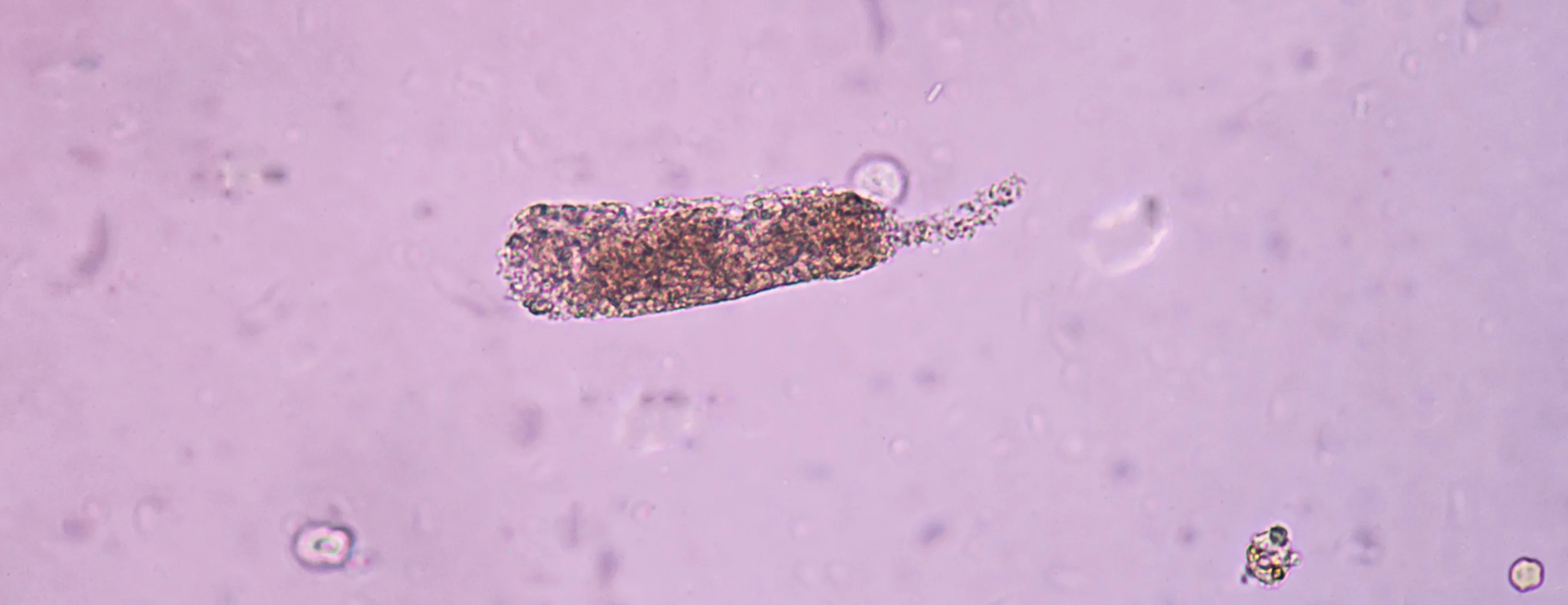
Inability to concentrate urine (≤1.020)
Mild-to-moderate proteinuria
Glucosuria
RBCs, WBCs, pathogens
Calcium oxalate crystals
What is hypersthenuria?
Urine specific gravity > 1.012-1.035, indicating dehydration
What is the normal pH of urine in dogs?
6-6.5 (acidic)
What does low pH of urine suggest?
Metabolic acidosis
How is ARF managed?
Removal of the toxin (emesis, activated charcoal, antidote)
Fluid therapy (to correct hypovolaemia)
Treatment of acidosis (bicarbonate)
Re-establishing urination (diuretics like mannitol and furosemide)
Antiemetics (Cerenia {maropitant]), H2 blockers (Famotidine), proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole)
Renal food (less protein)
Antibiotics (if pyelonephritis is present)