cell division/DNA replication
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
purines
two ringed nitrogenous bases - adenine and guanine
pyrimidines
single ringed nitrogenous bases - thymine and cytosine
what is a nucleotide made of
a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base
where is DNA replication in a eukaryotic cell
in the nucleus
where is DNA replication in a prokaryotic cell
cytoplasm
when does DNA replication occur
during the synthesis phase of the cell cycle
what is the first step of DNA replication
initiation - helicase unzips DNA and primase adds short RNA primer
what is the second step of DNA replication
elongation - polymerase matches bases following complimentary rule
what is the third step of DNA replication
termination - ligase closes new DNA strand
what does helicase do
breaks hydrogen bonds and seperates DNA (in step 1)
what does polymerase do
matches nucleotides to new strand of DNA (step 2)
what does topoisomerase
keeps DNA stable while unwinding (present in all steps)
what does primase do
adds primer to attract polymerase (step 1)
what does ligase do
glues okazaki fragments together (step 3)
SSBP
stabilizes single strand DNA
chromatin
unwound DNA
chromosomes
packages of DNA
chromatids
each strang of a chromosome
centromere
point of attachment for two chromatids
centrioles
organize spindle fiber formation
what is the first phase of mitosis
prophase - centrioles migrate to poles, nuclear membrane dissolves
what is the second phase of mitosis
metaphase - centrioles are on opposite sides of the cell, chromosomes line up in middle
what is the third phase of mitosis
anaphase - centromeres divide, chromatids goto opposite sides of the cell
what is the fourth phase of mitosis
telophase - nuclear membrane forms, new cells are formed
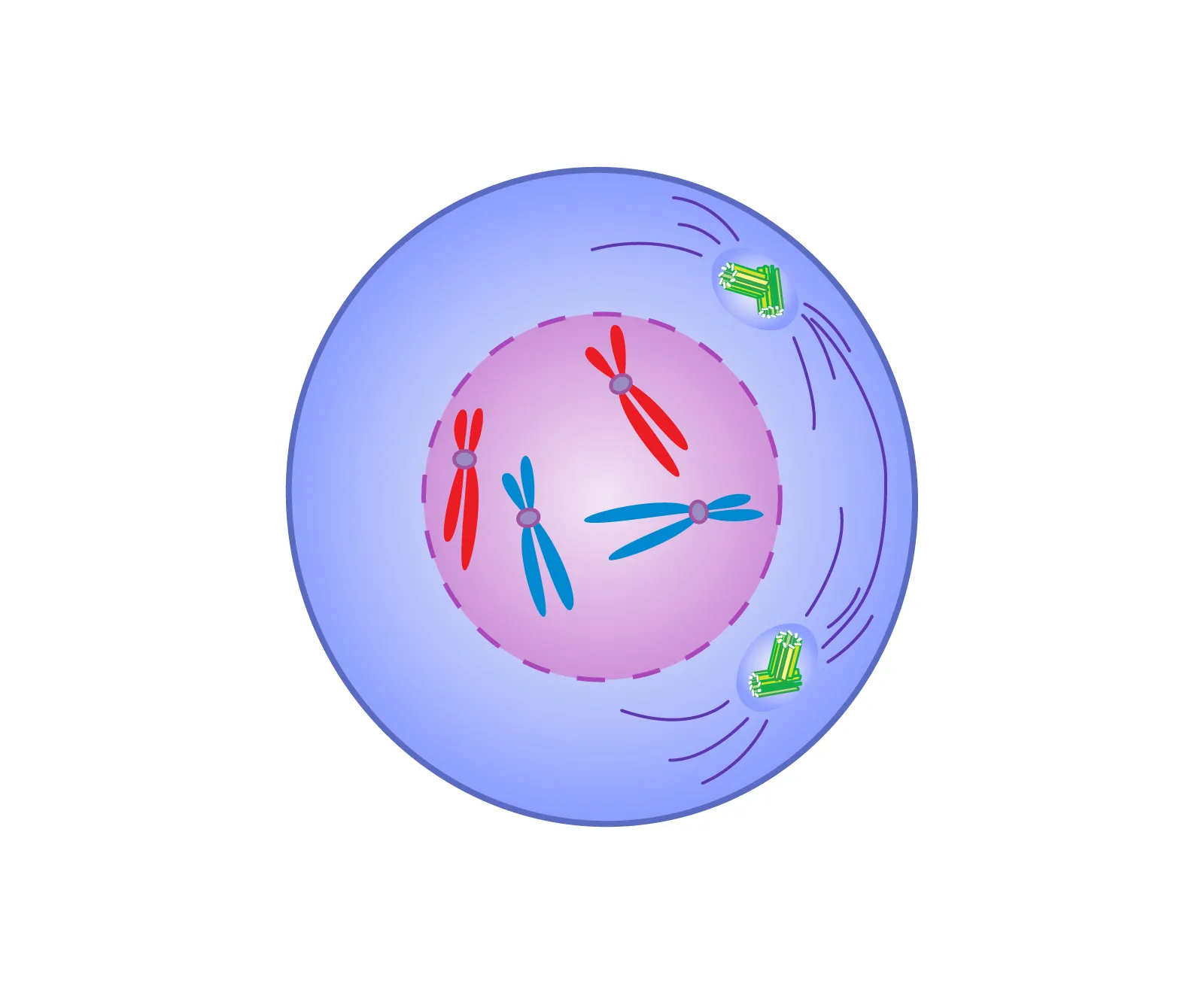
prophase
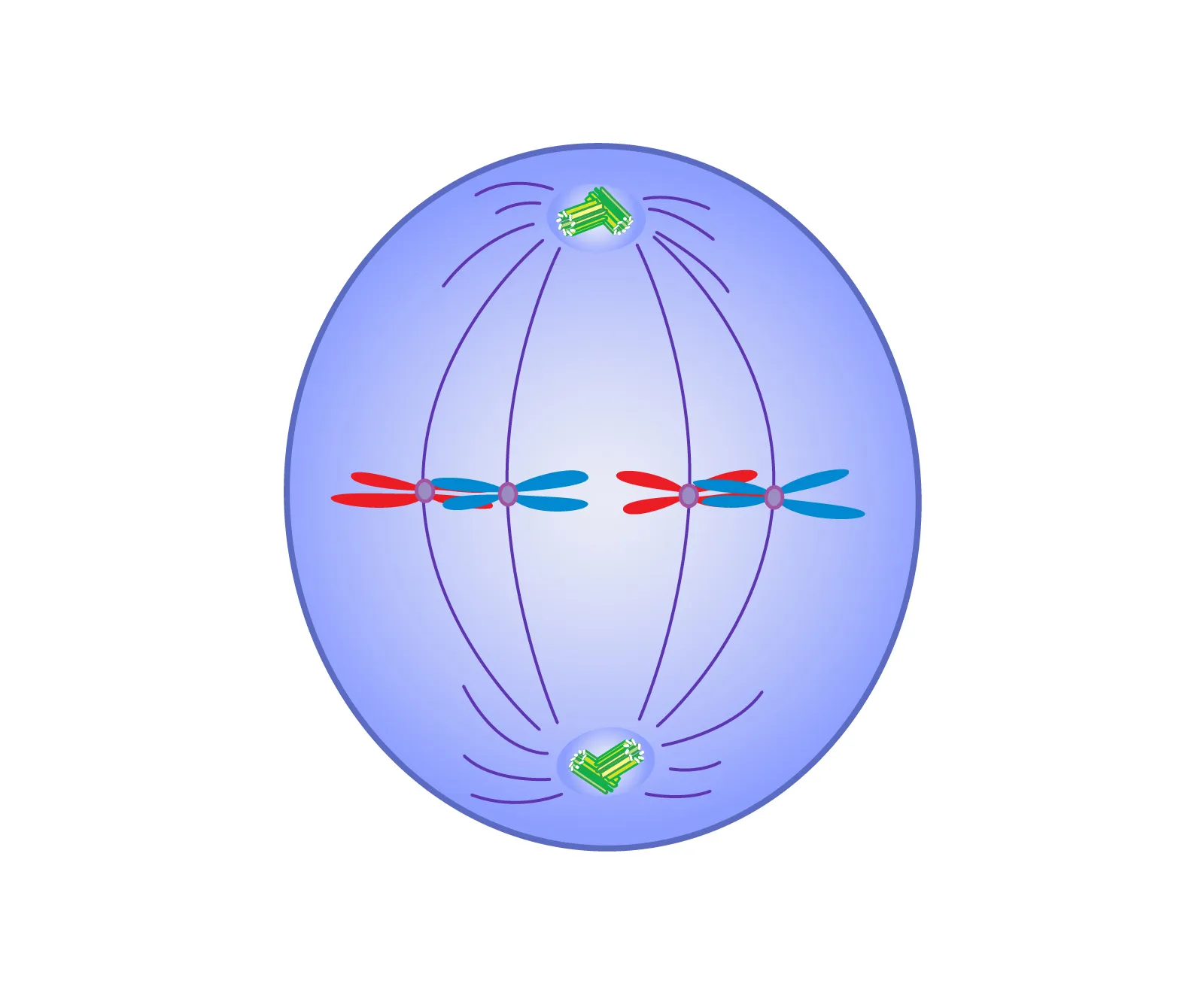
metaphase
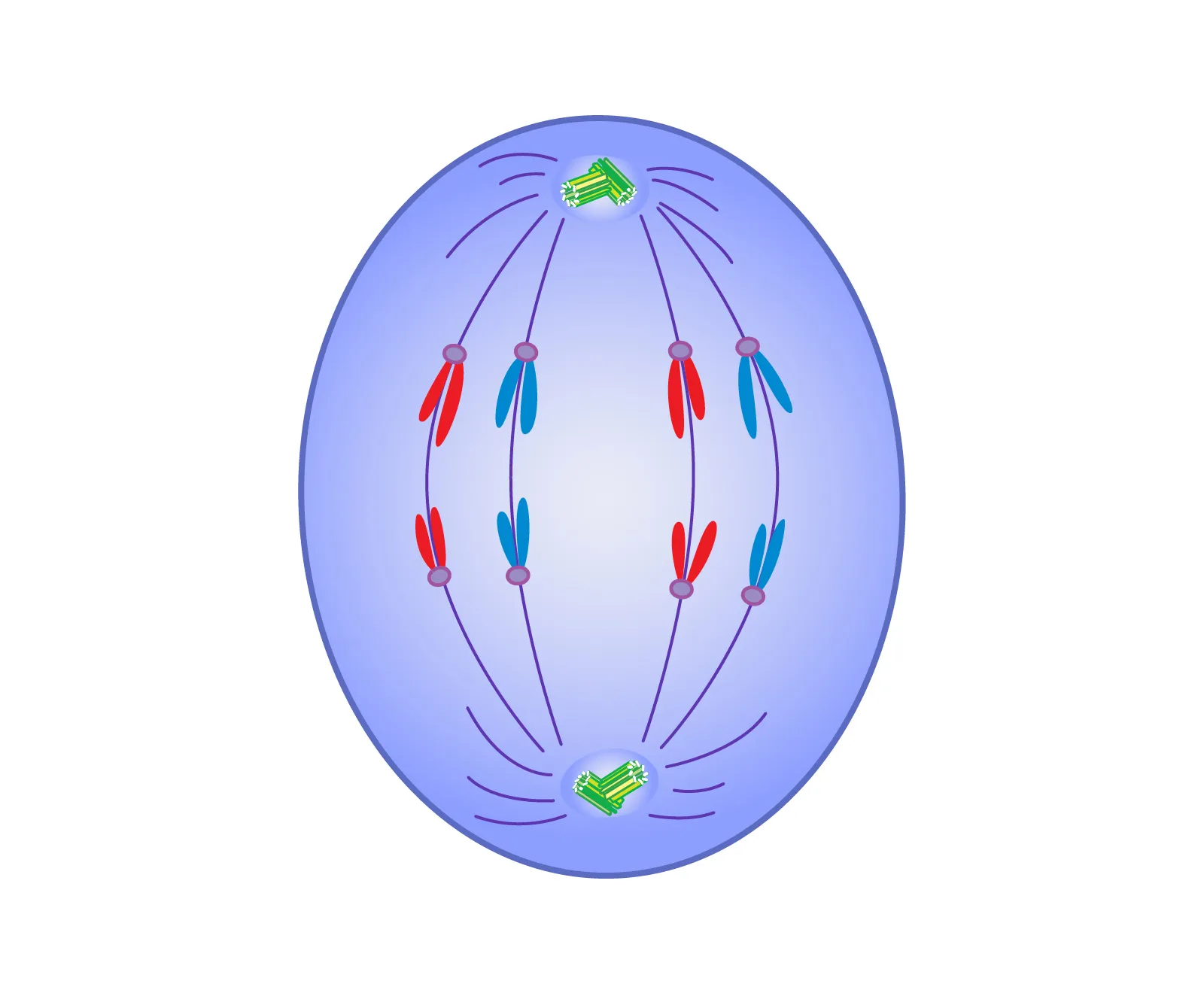
anaphase
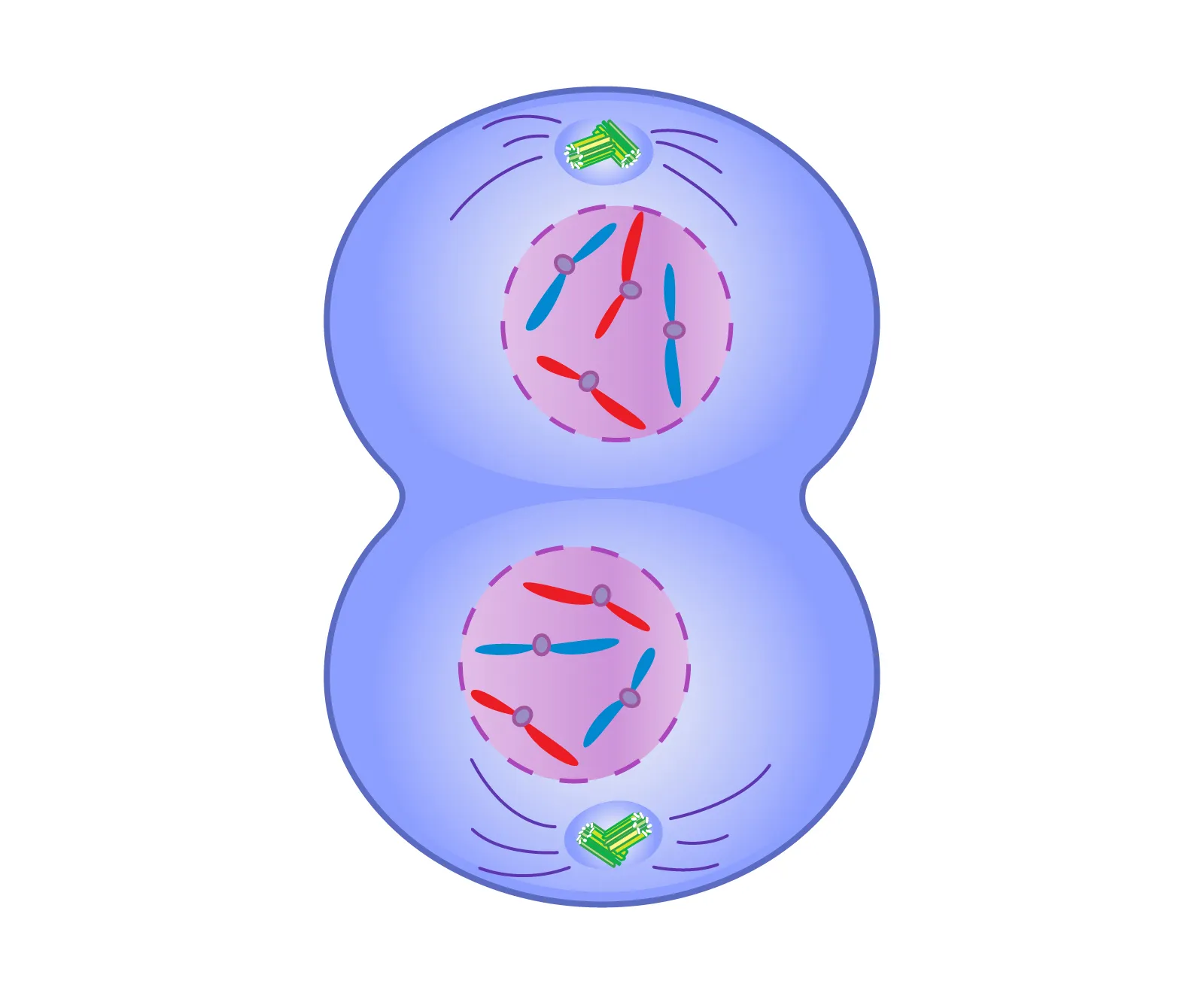
telophase