Income Tax Acc - Exam 2
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Income Tax Formula
Gross Income
Less: Deductions for AGI
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI)
Less: Deductions from AGI
Less: Qualified Business Income (QBI) Deduction
Taxable Income
Tax
Less: Tax Credits
Tax Liability
Less: Prepayments
Tax Due (or Refund)
Common Deductions for AGI (Exhibit 4-5)
alimony paid (pre-2019 divorce decree)
health insurance deduction for self-employed taxpayers
rental & royalty expenses
net capital losses (limited to 3k, only 1.5k for married filing separately)
one-half of self-employment taxes paid
business expenses
losses on dispositions of assets used in a trade or business
contributions to qualified retirement accounts (401k plans & traditional individual retirement accounts, IRAs)
Significance of AGI
important reference point that is used in other tax calculations
Examples of Itemized Deductions (Schedule A, exhibit 4-6)
medical & dental expenses
taxes
interest expense
gifts to charity
other miscellaneous deductions
Child Tax Credit Rules
qualify for $2,200 if under age 17 at yr end
qualify for $500 for qualifying dependents who do not meet the requirements for higher credit amount
Tests for Qualifying Child
Relationship
Age
Residence
Support
Test for Qualifying Relative
Relationship
Support
Gross Income
Other
Relationship Test for Qualifying Child
is taxpayer’s child, stepchild, foster child, sibling, half-sibling, stepsibling, or a descendant of any of these relatives
Age Test for Qualifying Child
younger than the taxpayer claiming the individual as a qualifying child
under age 19 or a full-time student under age 24
also anyone totally & permanently disabled
Residence Test for Qualifying Child
lives w/ taxpayer for more than half of the yr
includes temporary absences for things such as illness & education
Support Test for Qualifying Child
the qualifying child must not provide more than half of their own support
Relationship Test for Qualifying Relative
Taxpayer’s descendant or ancestor, sibling, stepparent, stepsibling, child of taxpayer’s sibling, sibling of the taxpayer’s parents, in-laws, & anyone else who has the same principal place of abode as the taxpayer for the entire year (even if not otherwise related)
Support Test for Qualifying Relative
taxpayer must have provided more than half of the support for the qualifying relative
Gross Income Test for Qualifying Relative
Gross income of the relative is less than $5,200 in 2025
Other Test for Qualifying Relative
must not be a qualifying child
Tiebreaking Rules for Qualifying Child
if the person is a qualifying child of a parent & a nonparent, the parent is entitled or has priority to claim the person as a dependent
if the individual is a qualifying child to more than one parent, the parent whom the child has resided for the longest period of time during the yr has priority
if the child resides w/ each parent for equal amounts of time during the yr, the parent w/ the higher AGI gets to claim the child as dependent
if the child is a qualifying child of more than one nonparent, the nonparent w/ the highest AGI gets to claim the child as dependent
What constitutes support / multiple support agreements?
no one taxpayer paid over ½ of the individual’s support for the yr
the taxpayer & at least one other person together provided more than half the support of the individual, & the taxpayer and the other person(s) would have been allowed to claim the individual as a dependent except for the fact they did not provide half the support individually
the taxpayer contributed over 10% of the individual’s support for the yr
each other person who provided over 10% of the individual support provides a signed statement to the taxpayer agreeing not to claim the individual as a dependent
commonly used in situations when siblings support elderly parents
Types of Filing Statuses
single
married filing separately
married filing jointly
qualifying surviving spouse
head of household
Requirements for Single Status
unmarried as of the last day of the yr
or legally separated from their spouse under a divorce or separate maintenance decree
does not qualify for any of the other filing statuses
Requirements for Married Filing Separately Status
taxpayers are legally married as of the last day of the yr
generally no tax advantage to filing separately (usually a disadvantage)
each spouse is ultimately responsible for paying their own tax
couples may choose to file separately (generally for nontax reasons)
Requirements for Married Filing Jointly Status
must be legally married as of the last day of the yr
if one spouse dies, the surviving spouse is considered to be married to decedent spouse at yr end
exception: the surviving spouse remarries before yr’s end
both spouses responsible for paying joint tax
Requirements for Qualifying Surviving Spouse Status
when a taxpayer’s spouse dies, the surviving spouse can file as a qualifying surviving spouse for 2 yrs after the yr of the spouse’s death if the surviving spouse remains unmarried & maintains a household for a dependent child
Requirements for Head of Household Status
unmarried as of the last day of the yr
or legally separated from their spouse under a divorce or separate maintenance decree
not be a qualifying surviving spouse
pay more than half the costs of keeping up a home for the yr
have a qualifying person live in the taxpayer’s home for more than half the yr
excludes temporary absences for military service, illness, or education
if the person is the taxpayer’s parent, the parent is not required to live w/ the taxpayer
Qualifying Person Requirements for Head of Household Status
may not qualify more than one person for head of household filing status
if taxpayer can only claim a person as dependent bc of multiple support agreement, that person is not a qualifying person
if a custodial parent agrees under divorce decree to allow the noncustodial parent to claim the person as a dependent, the agreement is ignored for purposes of the head of household filing status test
Gross Income (IRC 61)
means all income from whatever source derived
includes income realized in any form, whether in money, property, or services
recognized when:
they receive an economic benefit
they realize the income
the tax law does not provide for exclusion or deferral
Economic Benefit
borrowed funds represent a liability, not gross income
Realization Principle
taxpayer engages in a transaction w/ another party
transaction results in a measurable change in property rights
Recognition
realized income is assumed to be recognized absent a deferral or exclusion provision
Accrual Method
income recognized when earned
expenses deducted in the period when liabilities are incurred
mostly used by large corps
Cash Method
income recognized when received
expenses deducted when made rather than when liabilities are incurred
mostly used by individuals
Constructive Receipt Doctrine
judicial doctrine that provides that a taxpayer must recognize income when it is actually or constructively received
deemed to have occurred if the income has been credited to the taxpayer’s account or if the income is unconditionally available (accessible w/o limits) to the taxpayer, the taxpayer is aware of the income’s availability, & there are no restrictions on the taxpayer’s control over the income
for cash method users
Claim of Right Doctrine
judicial doctrine that states that income has been realized if a taxpayer receives income & there are no restrictions on the taxpayer’s use of the income
addresses when a taxpayer receives income in one period but is required to return the payment in a subsequent period
potentially have to repay but currently no restrictions on the use of income
Assignment of Income
judicial doctrine holding that earned income is taxed to the taxpayer providing the service
income from property is taxed to the individual who owns the property when the income accrues
to shift income from property to another person, a taxpayer must also transfer ownership in the property to the other person
Earned Income
income from services
income from labor most common source of gross income
generated by the efforts of taxpayer
Unearned Income
income from property
includes gains or losses from sale of property, dividends, interests, rents, royalties, & annuities
depends on type of income & type of transaction generating income
Examples of Earned Income
wages
salary
fees that a taxpayer earns through services
unemployment compensation
Examples of Unearned Income
gains or losses from sale of property
interest
dividends
rents
royalties
annuities
Concept of Income from Flow-Through Entities
applies to legal entities, like partnerships, LLCs, and S corps, that do not pay income tax
income and losses from these entities are allocated to their owners
each partner & shareholder report their share of the entity’s income & deductions in proportion to their ownership % on their individual tax return
Alimony
a transfer of cash made under a written separation agreement or divorce decree
the separation or divorce decree does not designate the payment as nonalimony
in the case of legally separated (or divorced) taxpayers under a separation or divorce decree, the spouses do not live together when the payment is made
the payments cannot continue after the death of the recipient
types of payments that do not qualify:
property divisions
child support payments fixed by the divorce or separation agreement
if executed before 1/1/2019, alimony is included in gross income of the recipient & deductible for AGI by the payor
if executed after 12/31/2018, alimony is not taxable to the recipient or deductible by the payor
Prizes / Awards / Gambling
raffles, sweepstakes prizes, or lottery winnings are included in gross income
exclusions rules:
for scientific, literary, or charitable achievement under certain conditions
for employee length of service or safety achievement ($400 tangible property limit per employee per yr)
to Team USA athletes from US Olympic Committee on account of their competition in Olympic & Paralympic games (AGI limit applies)
What constitutes a prize?
any valuable item you receive from a contest, drawing, sweepstakes, or lottery that must be included in your gross income
this applies to both cash and non-cash items, regardless of their value
What represents income for income tax purposes?
wages & salary
self-employment income
investment income
retirement income
gambling winnings, prizes, awards
unemployment compensation
alimony received from a divorce or separation agreement executed before 1/1/2019
Imputed Income
income from an economic benefit the taxpayer receives indirectly rather than directly
for low interest loans, the amount of imputed income is the difference between the amount of interest using the applicable federal interest rate & the amount of interest the taxpayer actually pays
The borrower is deemed to pay imputed interest
(interest expense to borrower, interest income to lender),
and then the lender is deemed to have returned the
imputed amount (the tax consequences depend on
relationship between borrower and lender).Imputed interest rules do not apply to aggregate loans of
$10,000 or less between the lender and borrower
Forgiveness of Debt
amount of debt relief is included in gross income by taxpayer
exceptions exist for certain types of loans
a discharge of indebtedness is not taxable for insolvent taxpayers
taxpayers w/ liabilities exceeding their assets
if the discharge of indebtedness makes the taxpayer solvent, the taxpayer recognizes taxable income to the extent of his solvency
taxpayers w/ assets > liabilities
regardless of solvency, taxpayers are also allowed to exclude from gross income most discharges of student loans after 2020 & before 2026
Scholarships
ones that pay for required tuition, fees, books, & supplies are excludable
applies only if the recipient is not required to perform services in exchange for receiving the scholarship (limited exception for tuition waivers for student employees & teaching & research assistants)
does not apply to dorming
529 Plans
taxpayers allowed to exclude from gross income earnings on investments in qualified education plans as long as they use the earnings for qualifying educational expenditures
Series EE Savings Bond Interest
can elect to exclude interest earned when the redemption proceeds are used to pay qualified higher-education expenses
the exclusion of interest is restricted to taxpayers w/ modified AGI below specific limits
When is Social Security Taxable?
Single taxpayers: if modified AGI + 50% of Social Security Benefits > $25,000
Taxpayers filing married separate: taxable if living together
Taxpayers filing married joint: if modified AGI + 50% of Social Security Benefits > $32,000
Annuities
an investment that pays a stream of equal payments over a time period
a portion of each annuity payment declared as a nontaxable return of capital & the remainder as gross income
taxpayers use the annuity exclusion ratio to determine the return of capital (nontaxable) portion of each payment
Annuity exclusion ratio = original investment / expected value of annuity
Taxation of Annuities
Return on capital principal
exclusion ratio = original investment / expected value of annuity
return on capital = payment times exclusion ratio
taxable amount = payment times (1 - exclusion ratio)
Taxation of Property Distributions
Selling Price
Less: Selling Expense
Adjusted Selling Price
Less: Adjusted Basis
Realized Gain / Loss
Gifts & Inheritances
individuals may receive property as gifts or from a decedent’s estate (inheritance)
while the receipt of property is most certainly real income to the recipient, the value of gifts & inheritances is excluded from gross income because these transfers are subject to a federal gift & estate tax
Life Insurance Proceeds
amounts received due to the death of the insured are excluded from the income of the recipient
similar to inheritances, they are typically subject to the federal estate tax
if the proceeds are paid over a period of time rather than in a lump sum, a portion of the payments represents interest & must be included in gross income
Taxable Fringe Benefits
employees recognize compensation income on all benefits received unless specifically excluded by tax laws
treats benefits received like taxable cash compensation
employer deducts cost & pays employee’s share of FICA taxes on benefit
employees must recognize a certain amount of gross income when employers pay life insurance premiums for the employee for policies w/ a death benefit in excess of $50,000
Employee Considerations for Taxable Fringe Benefits
employees may prefer it to an equivalent amount of cash when they benefit from employer-provided quantity or group discounts associated w/ the benefit
Computation for Annual Taxable Benefit
1) Subtract $50,000 from the death benefit of their employer-provided group-term life insurance policy
2) Divide the result in 1) by $1,000
3) Multiply the result in 2) by the cost per $1,000 of protection for one month from the table provided in the Treasury Regulations based on the taxpayer’s age
4) Multiply the result in 3) by 12 to annualize it
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits

Capital Assets
bought and held for appreciation potential
in general, an asset other than an asset used in a trade or business or an asset such as an account or note receivable acquired in a business from the sale of services or property
typically investment-type and personal-use assets
examples include:
artwork
corporate stock
bonds
personal residence
phone
Not Considered Capital Assets
asset used in trade or business
accounts or notes receivable acquired in business from sale of services or property
inventory
Amount Realized
the value of everything received by the seller in a transaction minus selling costs
Tax basis
the amount of a taxpayer’s unrecovered cost of or investment in an asset
generally the cost of acquiring the asset, including initial purchase price & other costs incurred to purchase or improve the asset
Tax Rates for Net Long Term Capital Gains
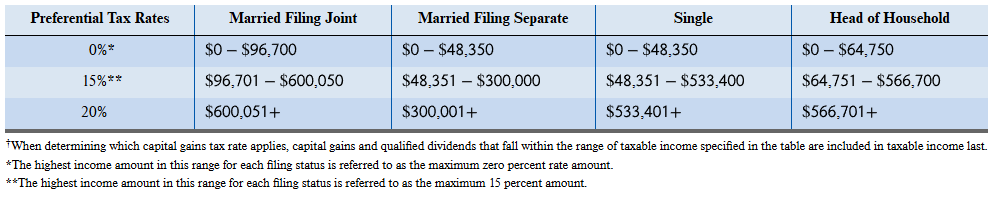
Tax Rate for Net Short Term Capital Gains
ordinary rates
Certain gains from the sale of depreciable real estate held long term are taxed at a maximum rate of _?
25%
Capital Assets taxed at 28%
collectibles: consists of art, rugs, antiques, metals, gems, stamps, coins, alcoholic beverages, or other similar items held for more than one yr
qualified business stock: stock received at original issue from a C corp w/ a gross tax basis in its assets both before & after the issuance of no more than $50,000,000 & w/ at least 80% of the value of its assets used in the active conduct of certain qualified trades or businesses
Exclusions of Tax for Qualified Business Stock Sold after being held for longer than 5 yrs
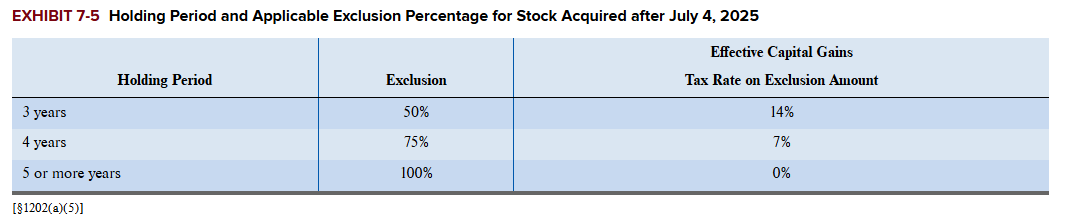
Netting Process for Capital Gains / Losses
1) combine ST gains/losses and separately combine LT gains/losses (including losses carried over from prior yrs)
2) if both ST & LT are both + or -, the net process is complete. ST taxed at ordinary & LT taxed at 0/15/20 percent
3) if ST & LT are not both + or -, then combine the results of ST & LT to get final net gain or net loss, depending on which outcome is greater determines whether it is ST or LT
Limits for Capital Loss Deductions
individuals can deduct up to $3,000 of net capital loss against ordinary income
remainder carries over indefinitely to subsequent yrs
Long-term requirments
held more than a yr
Short-term requirements
held for a yr or less
Appropriate Forms for Reporting Sales of Dispositions of Capital Assets
8949
1099-B
Schedule D
Losses on the Sale of Personal-Use Assets
gains are taxable as capital gains
losses are not deductible
Capital Losses on Sales to Related Parties
capital losses from sales to “related parties” are not deducted currently
the related party may eventually be able to deduct all, a portion, or none of the disallowed loss on a subsequent sale of the property
Wash Sale Rules
disallows the loss on stocks sold if the taxpayer purchases the same or “substantially identical” stock within a 61-day period centered on the date of sale
30 days before the sale
the day of sale
30 days after sale
intended to ensure that taxpayers cannot deduct losses from stock sales while essentially continuing their investment