Class 8-2: Exchange with the Environment
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what are the main ideas of exchange with the environment?
exchange = physical transfer across a surface
homeostasis & feedback
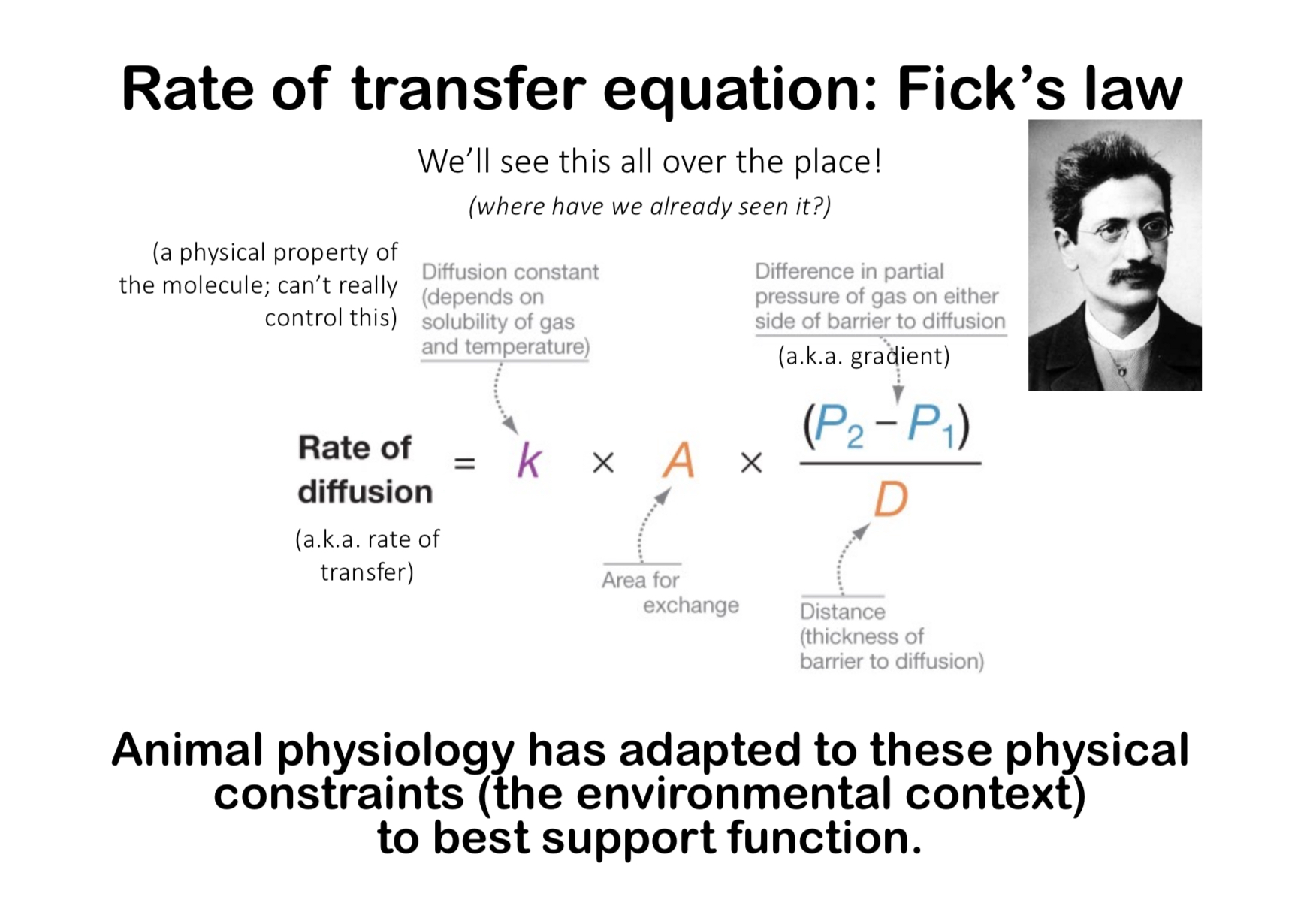
how does the small intestine maximize rate of transfer of nutrients (across a surface) into the body?
enabling a continual gradient = amt on one side - amt on other side
between two things close together = distance across
over a large area = surface area
rate of transfer equation (ficks law)
define homeostasis
stability in the chemical & physical conditions within an organisms cells, tissues, and organs
regulated through negative feedback loops returning to a set point
what are examples of things that organisms regulate?
temp and blood pH
salt and water
blood glucose and calcium levels
blood pressure and hormones
why in general do organisms regulate anything?
to work within specific set of physical conditions where life works
what is thermoregulation?
an ectotherm coiled around an endotherm
endotherms vs ectotherms
endotherms: animals create their own heat from metabolism (mammals & birds)
ectotherms: animals receive heat from external sources (reptiles & fish)
what happens when mammals get hot?
start losing H2O & salt - kidneys respond to loss and sensory makes thirst
increase in metabolism therefore heat - pants, more blood flow, and heart rate inc
what happens when mammals are cold?
shiver & restricts blood flow to keep heat
circulatory system arranged in coutercurrent flow to minimize heat loss
concurrent vs countercurrent flow
concurrent: fluid flow in the same direction, less efficient large gradient disappears as fluids move
countercurrent: fluid flow in opposite directions, highly efficient maintain small exchange gradient along entire length
why don’t we look at osmotic stress?
they have to be adapted to be isotonic to their environment
diffusion & osmosis don’t affect their water and salt balance
what is the physiological challenge & response to osmotic stress in water in a hypertonic environment? (salt water)
fish lose water by osmosis & gain salts by passive transport
drink water & pump ions out
what is the physiological challenge & response to osmotic stress in water in a hypotonic environment? (fresh water)
gain water & lose salts
excrete water & bring in extra electrolytes
what are physiological solutions?
system of parts & processes that interact to produce a specific effect & solve the challenge in its environment
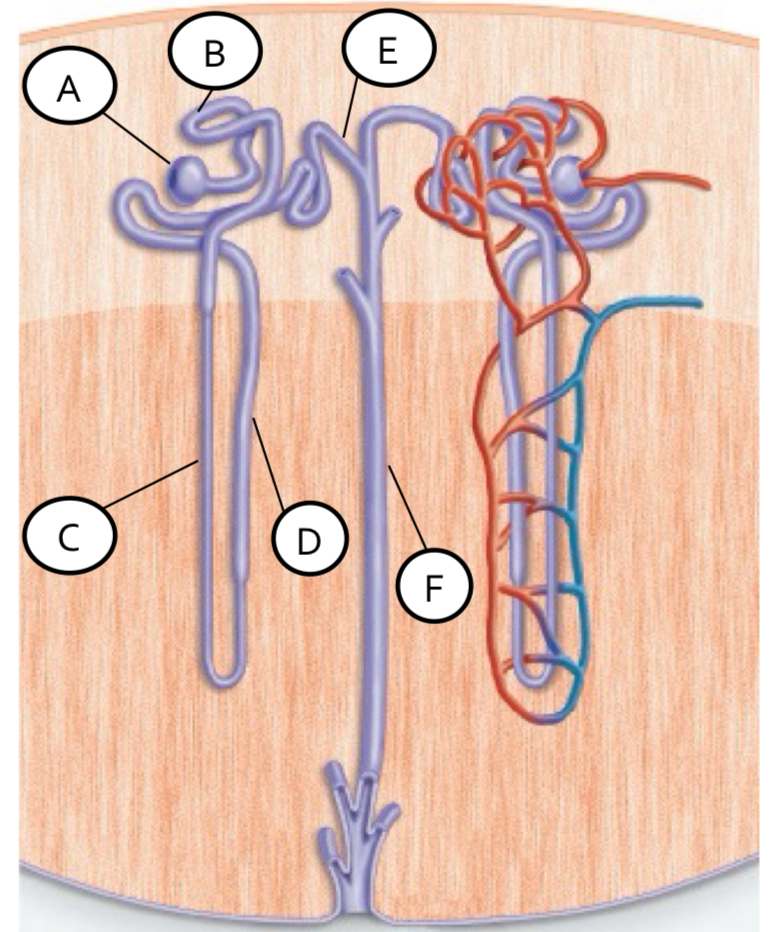
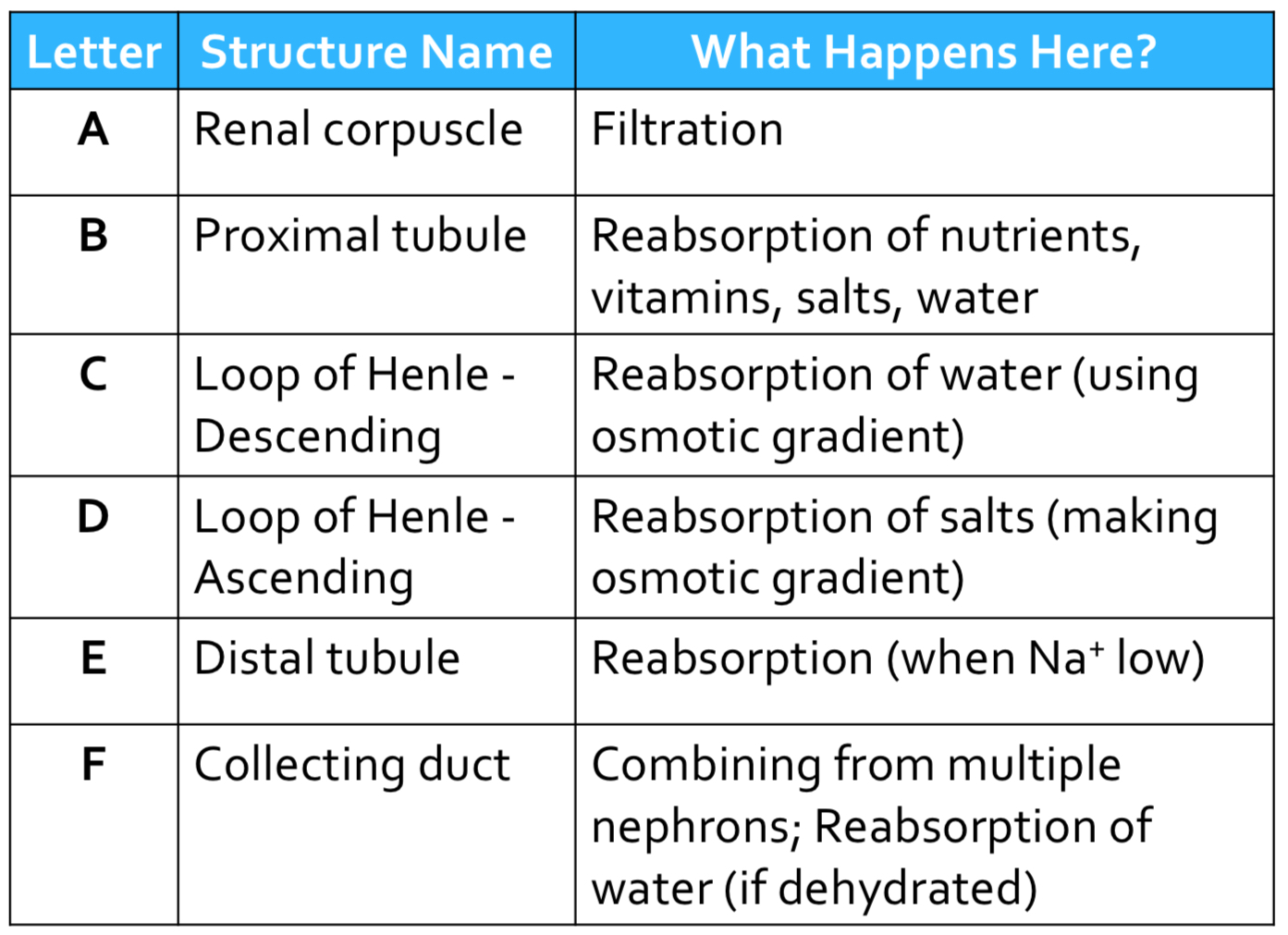
summarize filtration in the renal corpuscle
blood enters & filtration occurs as it passes through
pre-urine ie. filtrate
what is filtrate?
water & small solutes
all nutrients are reabsorbed (NaCl & water filtered by renal corpuscle)
descending vs ascending limbs
descending: water reabsorbed (aquaporins) using salt gradient
ascending: Na & Cl reabsorbed using and making salt gradient
what’s the role of the antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
production of concentrated or dilute urine
part of negative feedback loop returning system to a set point