Genetic and Secondary Causes of Blood Pressure Variation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
distribution of bp in US and Canada- age related increase in bp
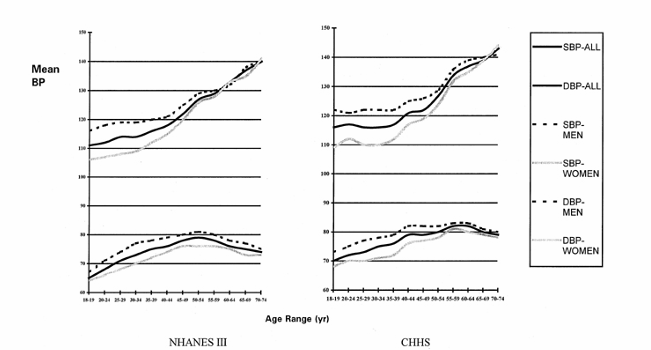
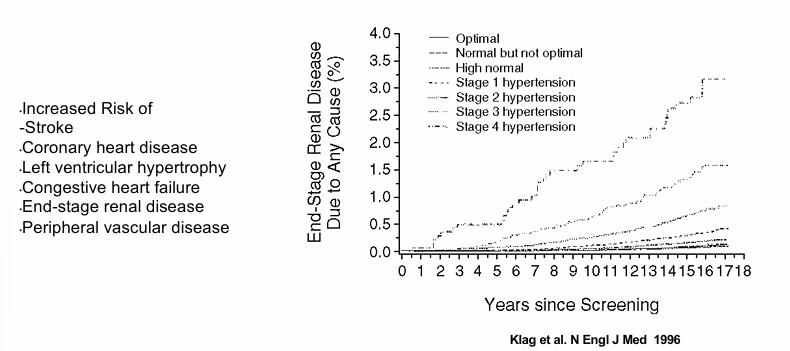
consequences of uncontrolled hypertension
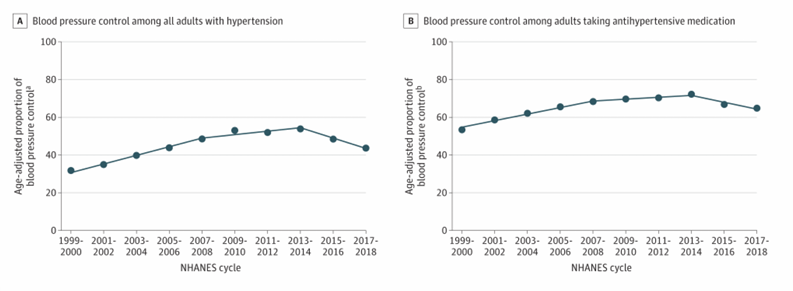
suboptimal blood pressure control among US adults with hypertension
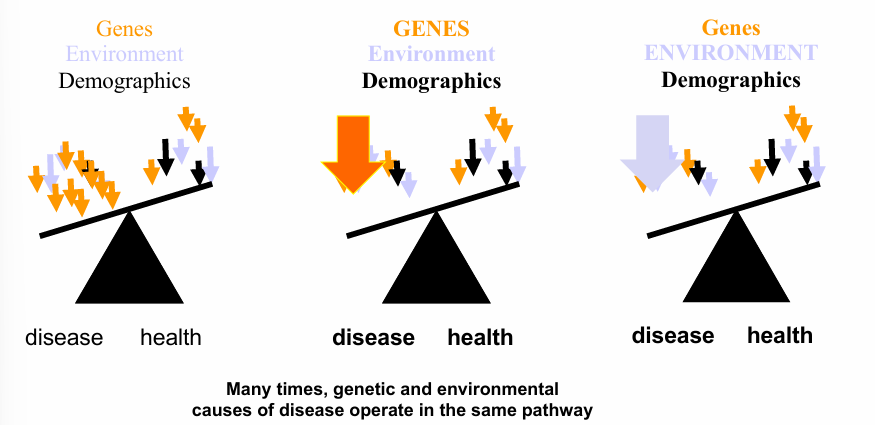
hypertension as a multifactorial disease
environmental causes of hypertension
-NSAIDs
-sympathomimetic agents (weight loss pills, decongestants, cocaine)
-amphetamine and amphetamine-like substances
-exogenous glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
-antidepressants
-alcohol
-oral contraceptive pills and exogenous estrogen
-immunosuppressants
-erythropoietin
-natural licorice
-herbal agents ephedra or ma huang
environmental causes of hypertension- obesity
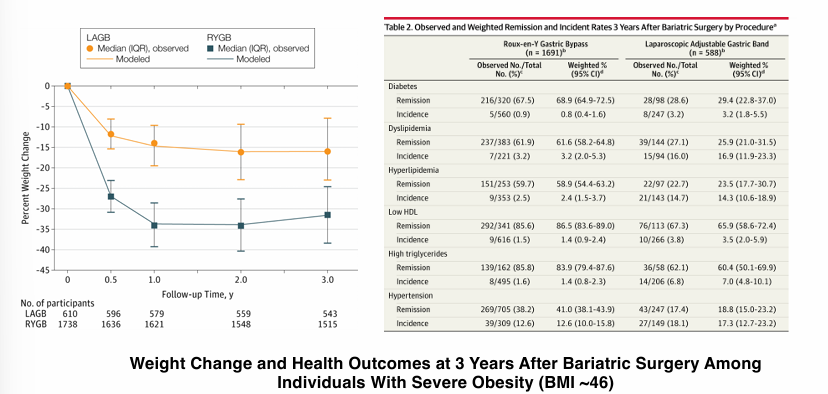
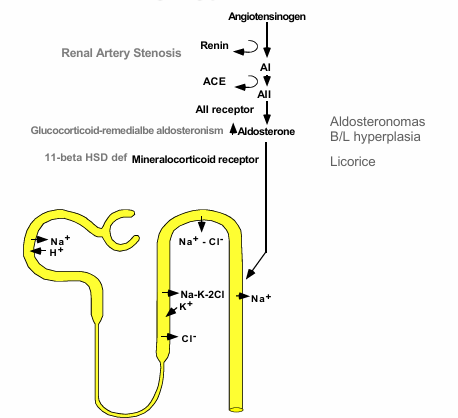
glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism
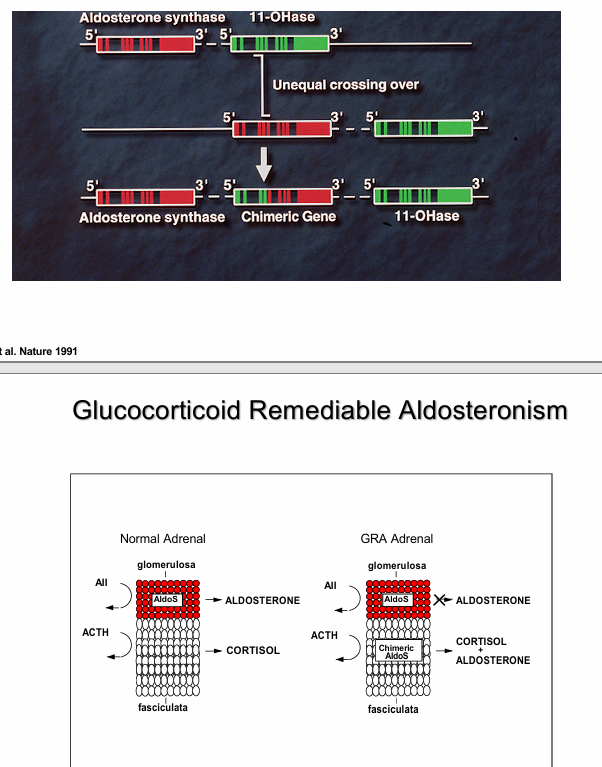
normal v. AME for lumen to blood
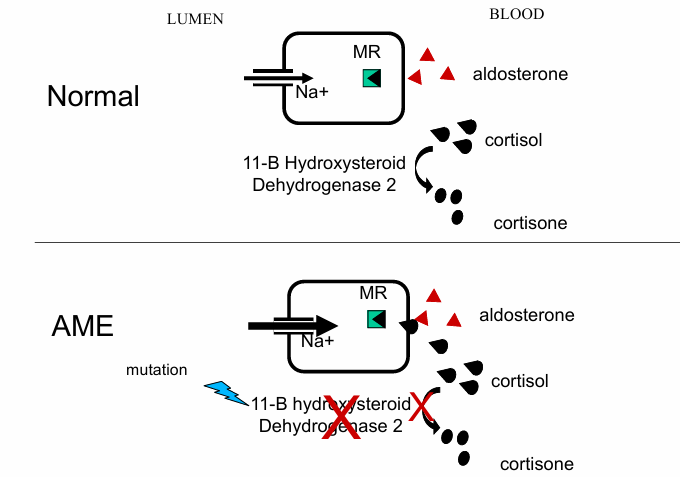
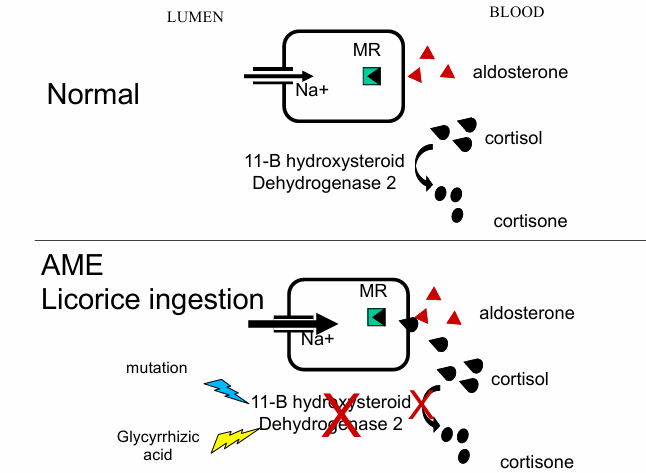
normal v. AME with licorice ingestion for lumen to blood
-adrenal hyperplasia
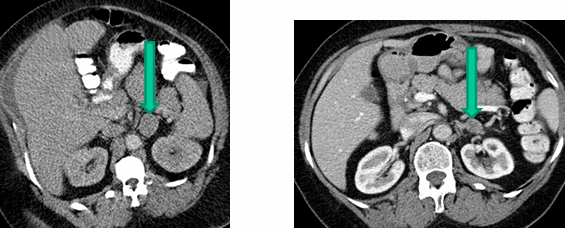
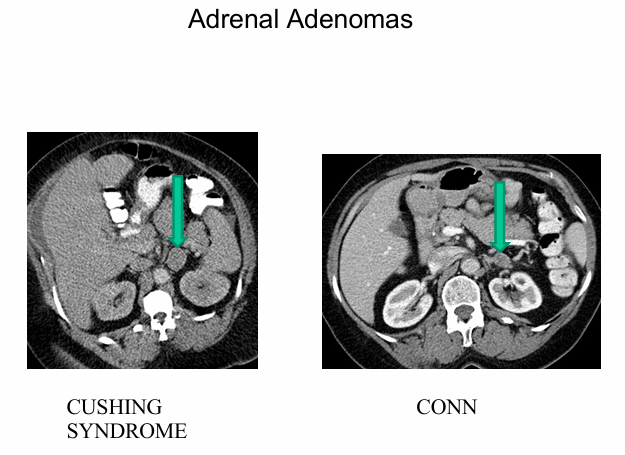
primary aldosteronism
-very common in patients with moderate to severe hypertension
-accounts for 10-20% of resistant hypertension
-40% of cases produced by aldosterone-producing adenoma (usually benign and unilateral)- curable by surgical removal of affected adrenal gland
-60% cases caused by bilateral hyperplasia- responsive to mineralocorticoid antagonists
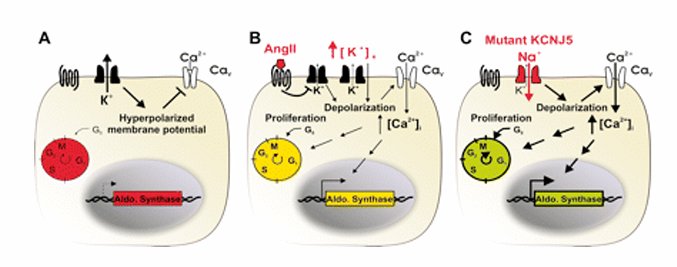
K-channel mutation in aldosterone producing adenomas
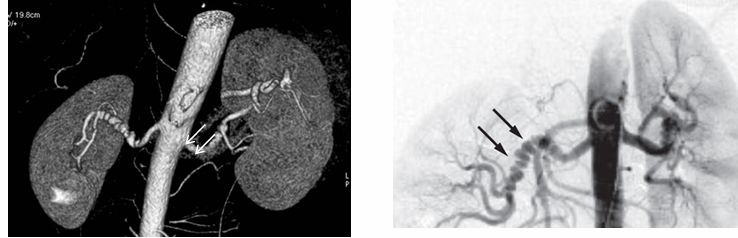
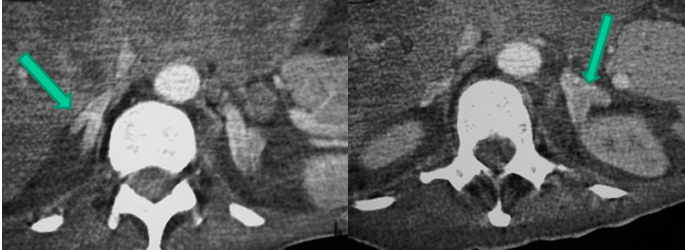
-”string of beads” characteristic of medial fibromuscular dysplasia
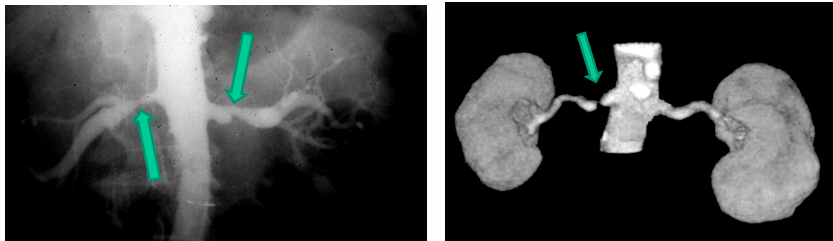
-renal artery stenosis
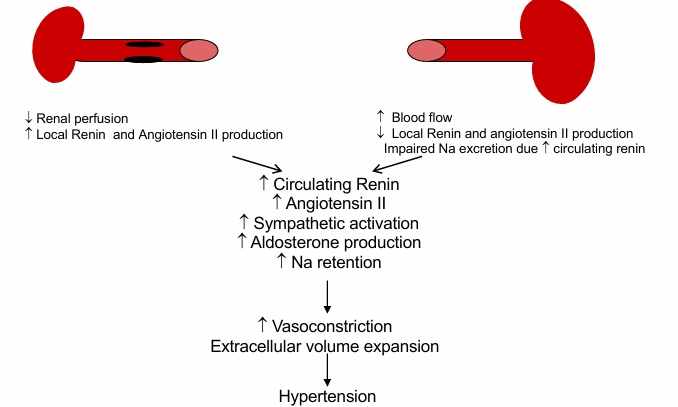
renovascular hypertension
-diagnosis: renin levels can be high but normal levels do not rule out renal artery stenosis
-imaging studies: sonography with duplex doppler, magnetic resonance angiography, CT angiography, angiography
-due to fibromuscular dysplasia in young individuals- treat with angioplasty
-due to atherosclerotic disease in older individuals with CV risk factors: suspect with pre-existing peripheral vascular disease or long history of smoking, recurrent flash pulmonary edema, treatment with angioplasty + stent placement
pathogenesis of many acquired or genetic forms of secondary hypertension
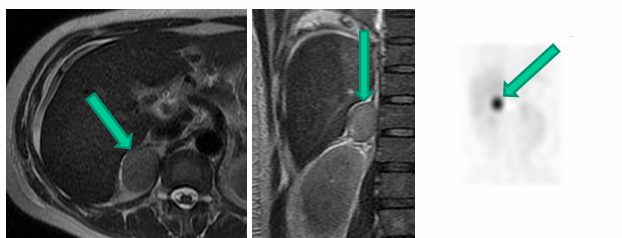
-pheochromocytoma

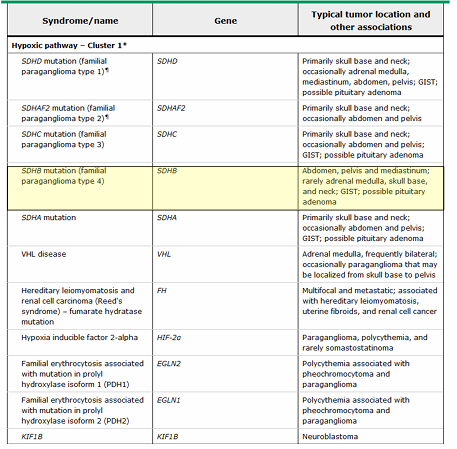
germline mutations associated with pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma
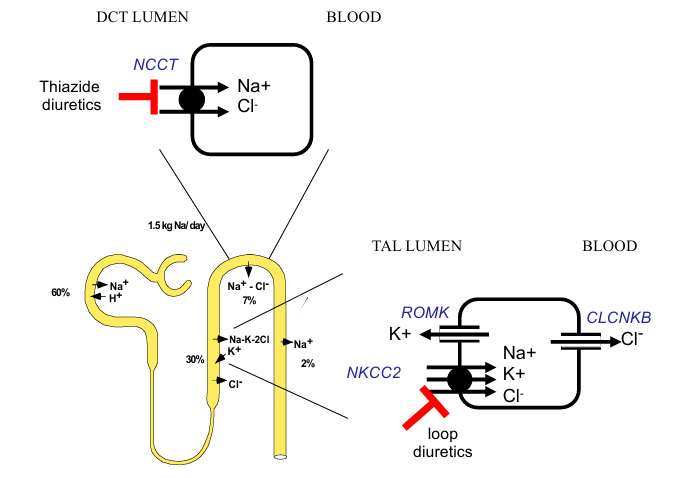
tubules with thiazide and loop diuretics
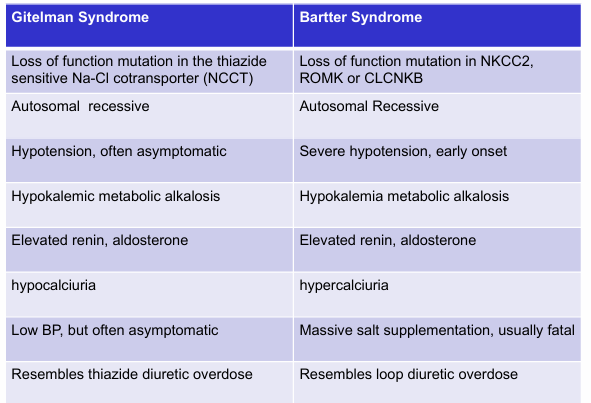
hypotensive disorders with hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis- Gitelman syndrome, Bartter syndrome
___ is a common cause of hypertension
-chronic kidney disease
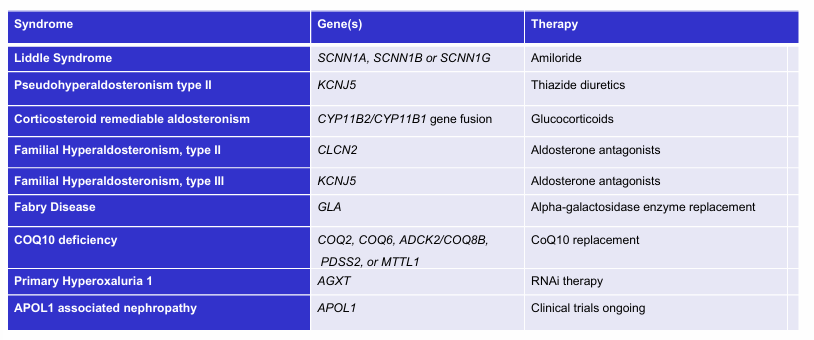
monogenic kidney disease with specific therapies- syndrome, gene(s), therapy
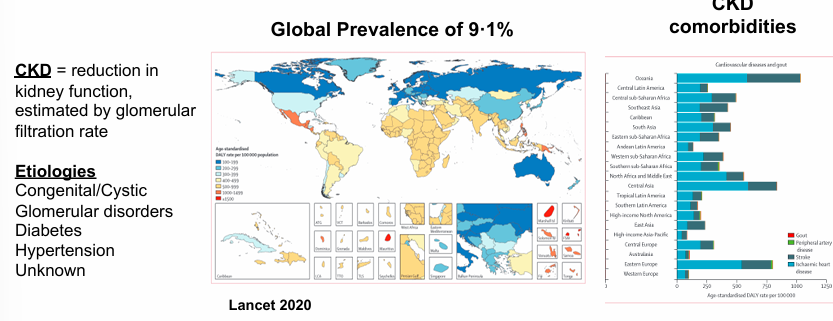
summary
