Test 3 Study Guide Political Science
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What is the general Ideology of Career Military Officers
They are generally overwhelmingly Conservative or Republican if they have served 10, 20, or 30 years of their life in the military
White Evangelical Christians (white born again christians) tend to vote on which Ideology.
Conservative or Republican
Which Ideology do Medical Doctor specialists in Rural or general suburban Areas tend to vote?
Conservative or Republican
College Professors in humanities and most social sciences tend to vote on which ideology?
Liberal or Democratic
Labor Union Members tend to vote on which Ideology?
Liberal or Democratic
Hispanics, Jews and African-Americans all tend to vote on which ideology?
Liberal or Democratic
Medical Doctors: General Practitioners that work in big cities or county Hospitals tend to vote in which ideology?
Liberal or Democratic
Rural Voters tend to vote under which ideology?
Conservative or Republican
White southern men tend to vote under which ideology?
Conservative or Republican
Wealthy Business people tend to vote under which ideology?
Conservative or Republican
Top Level Management tend to vote under which ideology?
Conservative or Republican
What are Purple States?
States with roughly equal mix of Republican and Democratic Votes
What are Red states?
States that are a majority of republican voters which are generally more conservative favoring smaller government and lower taxes
what are blue states?
States that are primarily Democratic or Liberal voters which are generally more liberal with policies often varying by state.
What is Political Socialization?
The process through which people come to think what they do about politics (their political beliefs)
how does what people think about politics come to be?
Generally based on what other people know as political Socialization is learned from someone else.
What is the difference between political Socialization and indoctrination?
Indoctrination is the process specifically meant to instill a set of strong believes usually in a short period of time, but Political Socialization takes time and is generally learned from other people.
What are the 4 agents of Political Socialization?
The family, The School, The Peer Groups, and The Media.
What are non-Violent forms of Political Participation?
Following Politics, Voting, Contacting Public Officials, Striking, Protesting, Marches and Rallies, Boycotts, Pickets (all have to be peaceful)
What are Violent forms of Political Participation?
Assassinations, Riots, Lynching, Terror and intimidation Campaigns, Suicide attacks, Pillaging, Revolutions, Wars
What is Political Efficacy?
A sense of being able to accomplish something politically
What is the relationship between Political Efficacy and Participation?
The more one feels one can accomplish things politically, the more one will participate.
How does party identification play a role in Participation?
The more attachment people have to a political party, the more they participate politically.
What happens when no presidential candidate wins a majority of electoral college votes?
The House of Representatives selects the President, one vote per state.
In Article II Section 1, Clause 3, if no person have a majority, then from the five highest on the lists the said house shall in like manner choose the president. but in choosing the president the votes shall be taken by the states and representatives from each state having one vote.
What was also added in 1804 regarding if no candidate wins a majority of electoral college votes?
The 12th amendment was ratified stating: “if no person have such majority, then from the persons having the highest numbers not exceeding 3 on the list of those voted for as president, the house of representatives shall choose immediately, by ballot, the president.”
Votes still taken from the state each having one vote.
What is Party Platform
it is the official statement that describes the party’s position on key public policy issues (however office holders are not required to follow the party platform and it is impossible to force them to follow it on every point.)
What correlates of presidential election results?
the state of the economy
incumbent approval ratings (even if incumbent is not running)
Partisan composition of the electorate
What are factors that don’t sway elections?
Celebrity endorsements, Television shows, YouTuber’s, and social media chatter
What organization is the chamber of commerce part of?
501c(6) - a category of non-profit organizations distinguished from the more commonly known 501c(3).
What are some characteristics and functions of 501c(6) entities?
Promote the common business interests of their members
improving business conditions rather than generating profit for an individual member
they are allowed to engage in unlimited lobbying as it pertains to their regular business interests (also political campaigns and activities though subject to taxation)
they are exempt from federal income tax on the portion of activities related to their mission. (members do not receive tax deduction for their dues unless their dues are used for lobbying or political activities)
funded through membership dues and are non tax deductible unless as a business
required to file annual reports (form 990) with the irs being transparent of finances, activities, and governance
common activities include industry networking events, educations seminars, publishing industry research, setting industry standards, and lobbying for legislation favorable to the industry.
what is narrowcasting?
the transmission of television programs, especially by cable, to a comparatively localized or specialist audience.
or
the political communication strategy of delivering tailored media messages to specific, targeted demographic or psychographic groups, rather than a broad, general audience
What are Open Primaries?
It means anyone can vote regardless of party affiliation, as long as they are registered to vote.
What are closed primaries?
It means only Officially registered party voters can vote.
What are Blanket Primaries?
Candidates of all parties appear on the same ballot. meaning votors vote for 1 candidate for each office. not taking into account of party affiliation.
Top vote-getters participating in the primary then advances to general election.
declared unconstitutional (California Democratic Party v. Jones 2000 and Democratic Party of Washington v Reed 2003)
What are Invisible Primaries?
it refers to the pre-primary race to raise money and name recognition. The winner of the “invisible primary” almost always goes on to win the nomination.
Exceptions: Barack Obama defeating Hillary Clinton in 2008 Democratic primaries despite losing Invisible primary
What is Micro-targeting
it was first affectively used by republican President Geroge W. Bush in 2000 and 2004. More sophisticated during 2008 presidential campaign as democrats built extensive organization to contact and turn out voters.
its more so to use media and televised debates to allow candidates to communicate their policy goals and promises to a broad range of voters.
- Also very blunt becasue it is to send different campaign ds or messages t different demographic and ideological groups (suburban “soccer moms” will get ads different than “cowboy dads”)
What are Focus groups?
They are used to find out what is relevant to a particular group.
Statistical accuracy is not enough so relevance is also important and precedes accuracy.
believed they hold the key to winning elections or launching successful marketing campaigns
- use of a trained moderator
- structured interviews
- semi-structured interviews
Study this Diagram on media and politics
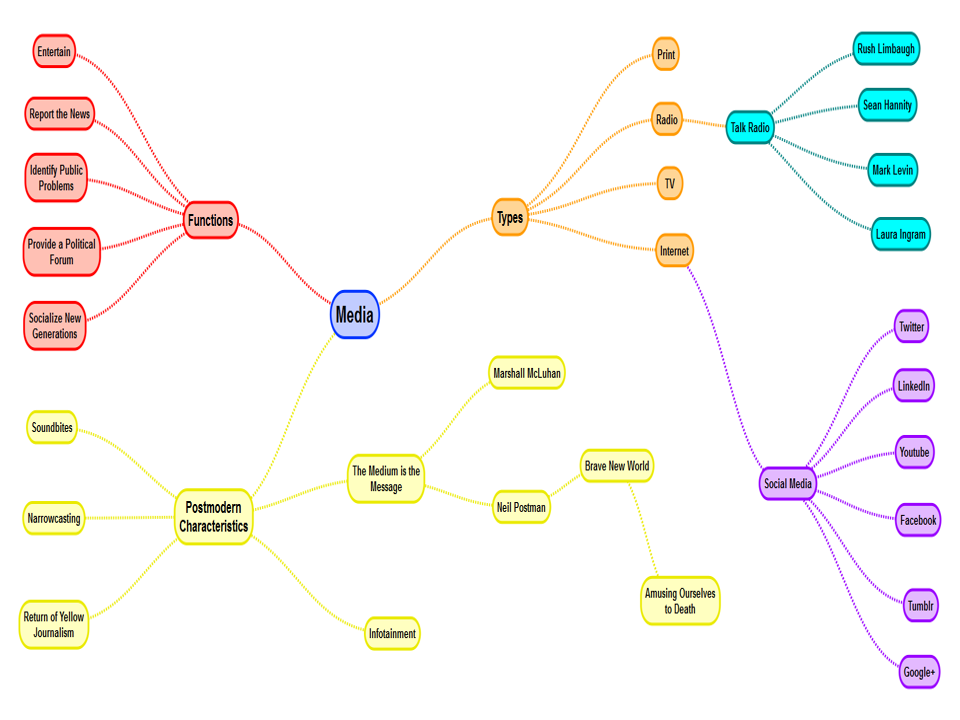
What is a Third Party?
A third party is the populists (or people’s) party, gave a nomination to General James B. Weaver.
its platform called for free and unlimited coinage of silver and government ownership of the railroads.
bot positions were crafted to appeal to the miners and farmers.
Weaver and the Populists became the first third party since 1860 to register electoral votes.
What are Political machines?
Known with “The Golden Age” of political parties in which parties were strong, stable, and dominant lasted from roughly 1876 to 1912
- from the end of the reconstruction era to the rise of the progressive era
Parties offered benefits to immigrants who arrived in large numbers (ireland, germany, greece, italy, russia) between late 1840’s and last 1880’s
- Jobs
- Food and clothes
- Bail bonds
- entertainment (torchlight parades, weekend picnics and community events)
What type of Environmental interest groups are stated in the slide
Sierra Club is what is stated but others include:
they also care about the environment and see economic development as being detrimental to the environment
League of Conservation Voters, National Wildlife Federation, and Natural Resources Defense Council
What does pluralism emphasize
Competition among diverse interest groups
The pluralist theory emphasizes competition among diverse interest groups for political influence, suggesting that power is not concentrated. This indicates that policy outcomes can vary significantly based on which groups are active on specific issues.
What is Hyperpluralism
a theory of government and politics asserting that groups are so strong that government is weakened. Hyperpluralism is an extreme, exaggerated, or perverted form of pluralism
What is a 527 Committee/Organization
A group established for the purpose of political advocacy and required to report its source funding to the irs. Contributions are unlimited except for PAC’s
All committees including state, local, and federal candidate committeess, traditional politcal action comittees (PAC), Super PACs, and political parties are 527’s
What are Super PACs
They are “Independent expenditures only” committees. A type of PACs but cannot donate directly to candidates or coordinate their expenditures with those of a candidates campaign.
They can raise and end unlimited sums of money to advocate for or against a political candidate.
Where in the Constitution is the basis of the electoral College?
Article II Section 1, Clause 2: Each state shall appoint, a number of electors, equal to the whole number of senators and representatives to which the state may be entitled in the congress. but no senator or representative, shall be appointed an electors.
Who selects the electors?
controlled by political parties in each state, but generally the parties either nominate slates of potential electors or choose them by vote. This part results in each Presidential candidate having their own unique slate of potential electors.
What does the electoral college consist of?
It consists of the same number of senators and house of representatives members +3 for washington DC equaling a total of 538 total voters. Only needing 269 +1 vote in order to win the election (winner takes all)
How do blanket primaries weaken political parties?
Blanket primaries weaken political parties by reducing their control over nominations, blurring ideological lines, encouraging strategic interference, and undermining party loyalty and organization.
At which time was red and blue being assigned to the political parties consistently?
Since the 2000 election
When were the first colorful electoral maps on television broadcasted?
1976 however there were no consistency between networks on what colors were used for each party but red often stood for democrats and blue for republicans back then.
Using blue for a left-leaning party and red for a right-leaning party makes the united states odd among other nations why?
because red is often associated with political parties on the left and blue with conservative parties.
What is being referred to when the quote “The Medium is the Message” from Marshall McLuhan.
Political communication isn’t just about what politicians say, but how the medium itself changes what politics becomes. Based on different aspects like how the type of media changes the nature of political communication and power.
Types of examples on “medium” that is used by politicians.
Print media (newspaper, pamphlets), Radio, Television, and Social Media
What is Hard money?
Hard money refers to campaign contributions that are regulated and limited by law, given directly to a specific candidate’s campaign for federal office (like Congress or the presidency).
Why is it called “Hard” money
They are considered “hard” because they are hard to raise (due to strict limits and disclosure rules) and hard to spend illegally (because they are closely monitored by the Federal Election Commission — FEC).
Which presidents were elected in the 1920’s that receive a general name describing them in the 1920’s?
Harding elected in 1920
Coolidge elected in 1924
Hoover elected in 1928
What all did the 1920’s presidents have in common and what name were they given?
They were all Republicans and it was named “The Roaring Twenties”
What are types of Interest Groups mentioned?
Business (US Chamber of Commerce, Business roundtable, American Petroleum Institute)
Labor (AFL-CIO, Culinary Union)
Professional (AMA, BAR, AAUP)
Environmental (Sierra Club)
Demographic (AARP, NAACP, NOW)
Single Use (NRA)
What are incentives to join Interest Groups?
Economic, Social—regarding meeting new people, and Ideological (similar Ideologies)
Which branches of the Government are influenced by Interest Groups?
All branches of the Government
What do interest groups refer to specifically
They refer to a policy goal, with them being an organization of people with the same policy goal.
Most have one or just a few key policies they want to see implemented and they are not trying to appeal to everyone. though they may care about the public opinion about themselves or their issues
What were the first two parties in U.S. History?
Federalist and Democratic-Republicans with John Adams being the first president to officially belong to the federalist party.
Who was the first president to officially belong to a political party?
John Adams
What was the significance of Political Talk Radio?
It emerged as a platform for conservative voices countering liberal media
When did Political Talk Radio emerge?
Around the 1930’s
Why did Political Talk Radio begin to decline
The rise of television as the dominant medium
In good economic times, which party can be predicted to win the election?
The populous wants to conserve the economy and generally they don’t want to intervene with more taxes or regulations so people would generally vote Republican or Conservative
in bad economic times, which party can be predicted to win the election?
in bad economic times people want more help so people would generally vote Democratic or Liberal
Third parties do what when they are strong in presidential elections
They siphon votes from the major party that they are closest to.
Which political ideology glorifies the nation and often embraces violence as a legitimate means to achieve political goals?
Facisim:
Extreme nationalism: The nation is glorified above individual or group rights.
Authoritarianism: Strong centralized power with little tolerance for dissent.
Militarism/violence: Violence and war are seen as legitimate means to achieve national greatness.
Anti-democratic tendencies: Fascism opposes liberal democracy, emphasizing unity and obedience to the state.
Historically associated with regimes like Mussolini’s Italy and Nazi Germany.