DATA MINING MIDTERM
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Sum of squared residuals
We estimate the linear regression coefficients by minimizing the _____
RSE( Residual squared error)
The standard deviation of the error and accuracy of the model is measured using ____
P-Value
The _____ can be used to reject the null hypothesis if < 0.05
MSE
The ____ is reported in units of Y
K-Nearest Neighbor
The _____ approach is a non-parametric method that makes a prediction based on the closest training observation
Cross validation (either LOOCV OR K-Fold)
Performing _____ ensures that every observation is selected for the testing data at least once
Decision Boundary (Discriminant function)
Linear discriminant analysis uses a _____ to seperate observations into distinct classes
Prior Probability
The ______ measures the probability that a random chosen observation belongs to class
Posterior Probability
Refers to updated beliefs or probabilities after new data has been incorporated through Bayes' Theorem
Best Subset Selection
Performing ______ to sub-select predictors requires the user to check every possible combinations of predictors (2p).
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
The ______ is unsupervised method used to transform the predictors (p) to a linear combination of the predictors (M, p ≥ M).
Knot
A _____ is a location where our coefficients and functions change.
Regression spline
The _______ is a combination of step functions and polynomial regression.
Random Forest
The Decision Tree based model can be improved upon by using bagging and sub-selecting predictors at each split, typically called _______.
Pure Nodes
The goal of splits in trees is to produce homogeneous child nodes, often called ______.
We can relax the additive assumption of linear regression by adding interaction terms.
True
Linear regression is applicable to datasets where p is larger than n.
False
Naive Bayes classifiers assumes that all predictors are independent within classes
True
Classifiers typically return a probability that a given observation belongs to class k.
True
It is expected that the training error rate is lower than the testing error rate.
True
A confusion matrix is used to assess accuracy for classification and regression models.
False
It is good practice to prevent data leakage by reusing the same sample in both training and testing.
False
Both Ridge Regression and Lasso use a shrinkage penalty to regularize the coefficients to reduce the impact of the predictor on the model.
True
Forward and Backward Stepwise Selection are guaranteed to find the best possible combinations of predictors.
False
Cross Validation is often the best method to find the most optimal parameters.
True
Basis Functions are fixed, known functions (bk(X)) that transform X to allow us to use statistical tools like Standard Errors and Coefficient estimates.
True
For splines, it is best practice to use fewer knots to increase flexibility in regions where it may be necessary.
False
Generalized Additive Models allow us to use more than one predictor in our model.
True
Ridge Regression
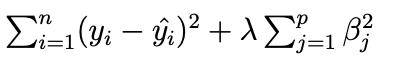
Smoothing Splines
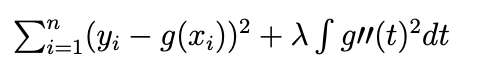
Linear Regression
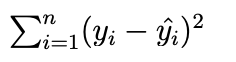
Lasso Regression
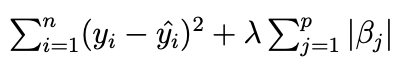
Linear Regression
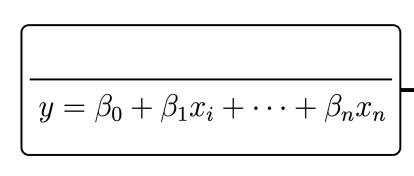
Logistic Regression
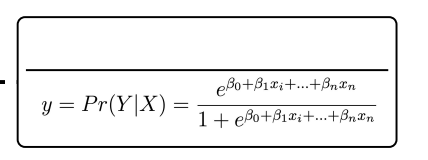
Ridge Regression
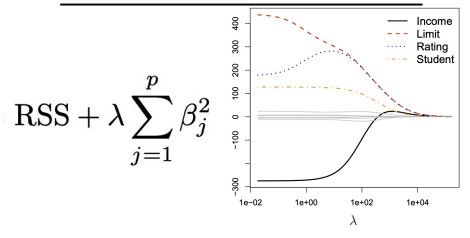
Polynomial Regression

Step Functions
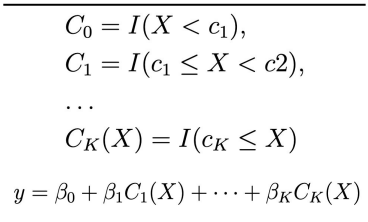
Lasso Regression
Regression Splines
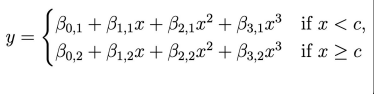
Tree Based Models
Non-Linear
Classification and Regression Trees (CART) (Decision Trees)
Goal of the decision tree is to split the data into like chunks or pure nodes
Then use the tree structure to make inferences on data
Makes few assumptions about the input dataset
○ No linearity assumptions!
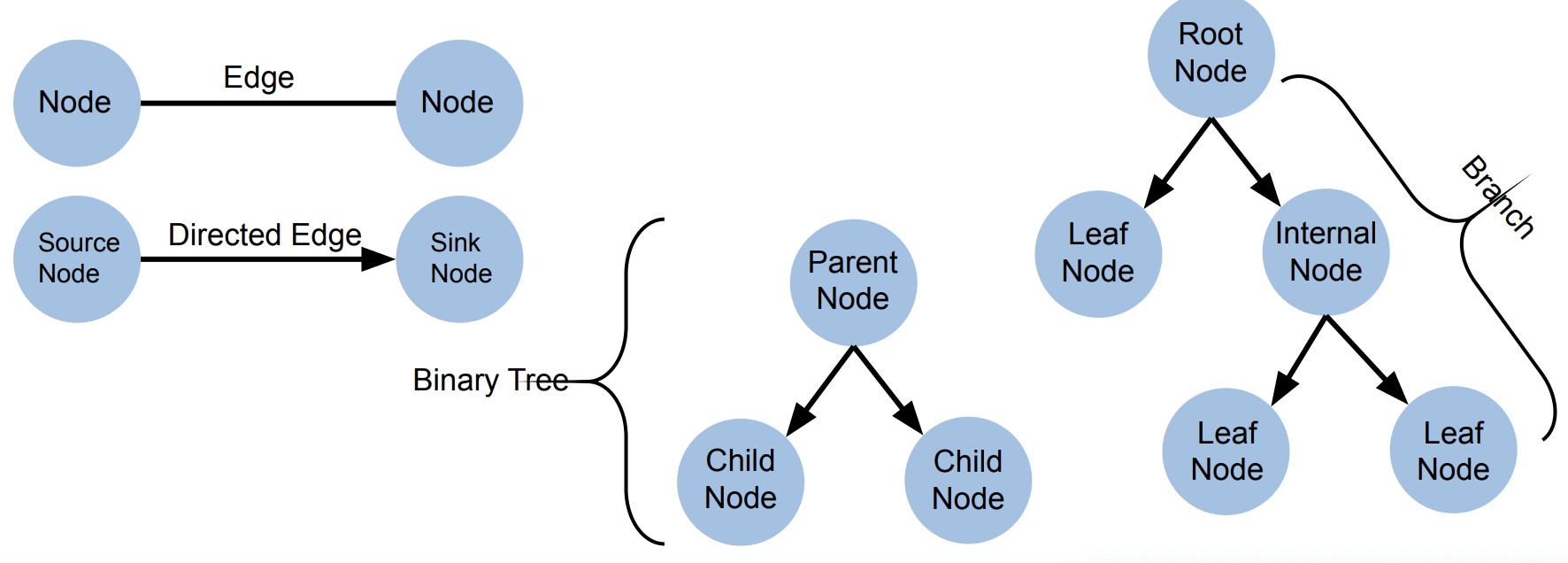
Graph Theory
Gini of Split
Used to split decision tree chunks
Want the split with the lowest possible Gini Impurity
If multiple are equal randomly choose one
Get for all predictors
How do we know to stop splitting?
Tree Depth - how many times do you want to split the data?
Minimum samples in leaf - how small do you want the leaf nodes?
Feature Importance
Tells us how much each input variable (feature) contributes to the prediction of a model
It helps us understand which features matter most in determining the output
Decision Tree Split Types
Classification - Gini, Entropy, Log Lost
Regression - MSE, Absolute Error, Poisson
Cost Complexity Pruning (Weakest Link Pruning)
A very large tree may overfit the data, want to prune the tree by removing some of the unnecessary branches
Start at full deep tree with many terminal nodes (𝛼=0), as 𝛼 increases the cost of having so many terminal nodes increases, and branches get pruned
Cross Validation to find optimal 𝛼, but 𝛼 and T are interacting so often people use them interchangeably
Improvement on Decision Trees
Decision Trees are weak learners with high variance
Eachs split will be very different from each other
We can use Decision Trees as the base for more complex models
Bootstrapping
Sub select the samples for the root node at random
Sampling without replacement, can be selected only once
Out of Bag (OOB) Error Estimation
Average the error across trees
Is a valid estimate of the test data since none of the individual trees have seen the given test sample
Random Forest (RF)
Sub-select the samples for the root node at random (using bootstrapping)
Sub-select the features at random at each split (sampling without replacement, can be selected only once)
Trees within the forest are not pruned
Boosted Trees
Builds trees sequentially
For each data point, calculate the difference between the predicted value and the actual value.
These residuals represent what the first tree did not predict correctly.
This way, it focuses on the mistakes of the previous tree.
Fits each tree hard and may overfit, Boosted Trees are a slow learner
Fit each tree to the residuals of the previous tree instead of Ytrain
Iterative Random Forest (iRF)
The model is retrained multiple times, giving more weight to features that were consistently important in previous iterations.
This helps stabilize the identification of truly important features and reduce noise.
Basis Functions
Very simple extensions of linear models
Polynomial Regression
Step Functions (Piecewise-Constant Regression)
Splines
Basis functions b1 (X), b2 (X), … , bK (X) are fixed, known, and hand selected
Transforming X into something else
Like Linear Regression, all of the statistical tools are applicable here too
Standard Errors
Coefficient estimates
F-statistics
Polynomial Regression
The standard way to extend linear and logistic regression
Add polynomial terms (X d )
Typically d ≤ 4
Step Functions
Uses step functions to avoid imposing a global structure
Break X into bins, turn into ordered categorical variables/dummy variables
Good for variables that have natural break points
Ex: 5 year age bins
Are poor predictors at the breakpoints
Regression Splines
Type of basis function that is a combination of polynomial regression and step functions
Locations where the coefficients/functions change are called knots
More knots, more flexible method
Adding a constraint removes a degree of freedom, reducing complexity! (smoothing it out)
Natural Splines
Splines can have high variance at the outer range of X
Natural spline - adds boundary constraints, must be linear at the boundaries
Boundaries - the region smaller than the smallest K and the region larger than the largest K
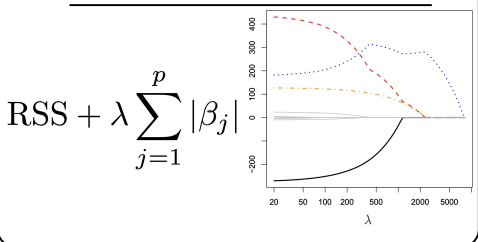
Smoothing Splines
Different approach, still produces a spline
Places a knot at every value of X
Uses penalty to determine smoothness
λ is the smoothing parameter controlling the trade-off:
Small λ≈0\lambda \approx 0λ≈0 → very flexible, almost interpolates data → high variance.
Large λ→∞\lambda \to \inftyλ→∞ → heavily penalizes wiggles → approaches a straight line → low variance, high bias.
Local Regression
Instead of fitting one global regression to all the data, this fits a regression only around the target point x0
Nearby observations have more influence on the fit at x0, while distant points have little or no effect.
Conceptually, this is similar to K-nearest neighbors (KNN), except:
KNN predicts by averaging nearby y-values.
Local regression predicts by fitting a weighted regression locally.
Generalized Additive Models (GAMs)
The model is additive:
The effect of each predictor is added together.
There are no interaction terms by default.
This keeps the model interpretable:
You can examine how each variable individually affects the response.
Allow you to use splines, natural splines, smoothing splines, or local regression for each predictor.
The only restriction: the contributions of predictors are added together, not multiplied or combined in complex ways (unless you specifically include interaction terms)
Subset Selection
Reducing the number of predictors by selecting a subset of the predictors and evaluating the performance of that subset compared to other subsets of predictors
Best Subset Selection
This model predicts the sample mean for each observation.
Try combinations of predictors to find the one with the smallest RSS or largest R squaredTotal of 2p possible models, computational intensive
If p is large (high dimensional data), may suffer from statistical problems for some models
Forward Stepwise Selection
Test all predictors seperately
Find the best predictor and tack on other predictors
Only adds predictors that are improving the model
Not guaranteed to find best possible combinations of predictors
Can be used in high dimensional data (n < p) with special considerations (Do not pass Mn-1)
Backward Stepwise Selection
Start with the full model (all predictors included).
Iteratively remove the least useful predictor (based on some criterion) one at a time.
Stop when removing more predictors would make the model worse.
Select the single best model using highest p-value (prediction error)
AIC BIC or R2
If p is large (high dimensional data), may suffer from statistical problems for some model
How to choose the best model?
Can measure this error:
Indirectly - by adjusting training accuracy measurements
Directly - by using a test/validation set, or KFold/LOO cross validation approach
Prediction focus? → CpC_pCp or AIC.
Simplicity & interpretability? → BIC.
Regression only, intuitive? → Adjusted R2R^2R2
Cp Statistic
Adds a penalty to training RSS
Penalizes models with more predictors
Lower CpC_pCp → better model.
Akaike Information Criterion (AIC)
Adds penalty, only defined for models fit by maximum likelihood
Lower AIC is better
Works when models are fit by maximum likelihood (e.g., regression, logistic regression)
Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC)
Heavier penalty when nnn is large.
Tends to select simpler models than AIC
Adjusted R 2
Essentially, a perfect fit would have only correct variables and no noise
Unlike plain R2, adding useless predictors decreases adjusted R2R^2R2.
Higher adjusted R2 → better model
Direct Measurement of Test Error
Report on the test/holdout/validation set of observations
Perform a cross validation (either LOO or KFold)
Advantages over indirect measurement, makes fewer assumptions about the true model
Shrinkage Methods
Aim to “shrink” or regularize the coefficients so that they are essentially equal to zero
Reduces the effect of the predictor on the model
Ridge Regression
As 𝜆 →∞, shrinkage penalty increases, shrinks coefficient close to 0, is only equal to zero when 𝜆 = ∞
All regression lines get close to 0 at the same time
Will always use all the predictors (but some may have small coefficients)
Does not use Beta 0
Lasso
coefficient estimates not only shrink to zero, some may be equal to zero and removed from the model entirely (variable selection)
Regression lines hit 0 at different times
Can use only a subset of the predictors (variable selection)
Which Shrinkage Method?
In general, ridge regression might be better if all of the predictors are contributing to the response at least a little bit, lasso may be better if certain that some predictors are equal to zero
Dimension Reduction
Here we will transform the predictors
Principal Component Analysis
Reduce number of predictors from p to M, by performing mathematical transformations to the existing predictors
Transform the original correlated features into a set of uncorrelated variables, called principal components
Adding any Zs will be automatically perpendicular or orthagonal to the last Z
Unsupervised
Principal Components Regression
When predictors X1,X2,…,XpX_1, X_2, \dots, X_pX1,X2,…,Xp are highly correlated, standard linear regression can become unstable.
Reduces the predictors to a smaller set of uncorrelated principal components (PCs) and then uses them as inputs for regression.
Doesn’t use the original predictors directly; it uses the top MMM components (usually the ones explaining most variance) as inputs for the regression.
Assumes that the principal components capturing most variance in Xare also the ones that matter for predicting Y
does use Y when computing ZM , is supervised
Classification
Assigns class info each sample (qualitative, categorical)
Logistic Regression
Models the probability that Y belongs to a particular category
Maximum Likelihood Estimation
Selecting 𝛽0 and 𝛽1 such that the predicted probability of (default = yes) is as close as possible the individual’s observed default status
Multinomial Logistic Regression
Allows for K > 2
Assumes that the odds for one class does not depend on the other
Predictors do not necessarily need to be explicitly independent, however low correlation between variables is preferred
K - 1
Runs idependent binary models
Banana vs Apple → binary model
Cherry vs Apple → binary model
Generative Models
If classes are too far apart
If X is approximately normal in each class and the sample size is small, generative models can be more accurate
Easier to extend to more than two response classes
Bayes Theorem
πk=P(Y=k) = probability that a randomly chosen observation belongs to class K.
Example:
πApple=05→ 50% of all fruits are Apples.
πBanana=0.3→ 30% Bananas.
πCherry=0.2 → 20% Cherries.
Linear Discriminant Analysis
Prior probability = your initial belief about a class.
Likelihood = how well the observed data fits that class.
Posterior probability = updated belief after seeing the data.
For each observation, calculate the discriminant for each class, assign to the class with the highest discriminant
To find the LDA decision boundary, find the point where these two discriminants are equivalent
Performs best with fewer observations, reducing the variance is important
Quadratic Discriminant Analysis
Like LDA, with the difference of a class specific variance rather an a common variance (how far they differ from the mean), allows for quadratic shaped decision boundaries
Performs best with large amounts of observations
Naive Bayes Classifier
Does not combine predictors in each class, but assumes they are independent
If Xj is quantitative:
○ Can assume within each class, the j th predictor comes from a normal distribution
In a line up of apples count every 5th apple as data
K-Nearest Neighbors
Non parametric
Many observations
Select a value of K, plot all training observations, for each test observation find the K nearest training observations, assign predicted value to test observation based on average known response value for the K nearest training observations
Generalized Linear Models
Useful when data is neither qualitative nor quantitative
○ Value more closely represents counts of a unit
○ Ex: CaBi ride share data, predicting number of riders
LDA & Logistic Regression
When it can be linear
Yes/No situation
QDA and Naive Bayes
Moderately non-linear boundaries
QDA allows each class to have its own covariance (curved boundaries).
Naive Bayes can capture more complex shapes depending on predictor distributions.
Non-parametric approach like KNN
Very non-linear boundaries
KNN does not assume any formula for the boundary. It decides based on local neighborhoods.
Linear Regression
Predicts a quantitative response
Assumes a linear relationship between predictor variables and the response variable
Parametric method
Estimate the parameters by minimizing the residual
𝛽0
Intercept
Starting point of the line
Unknown and Estimated
𝛽1
Slope
Unkown and estimated
Simple Linear Regression
Predicts a quantitative (numeric) response Y using a single predictor (independent variable) X
^
Indicates predicted value