Chapter 5 - Passive Transport
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biol 111
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
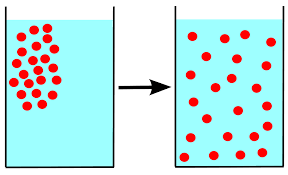
() is the tendency for molecules of any substance to spread out evenly into the available space
diffusion
() is the movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration by diffusion
passive transport
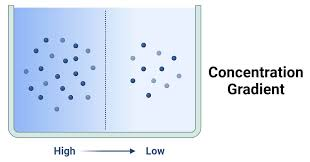
A concentration () is the difference in the concentration of a substance between two regions; this difference causes particles to naturally move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilibrium is ()
gradient, reached
The rate of diffusion is faster when: when the concentration gradient has a () difference, when temperature is (), when their solubility is (), when the surface area is (), when the distance to travel is (), when solvent density is (), when pressure is ()
greater, higher, nonpolar, greater, shorter, lower, greater
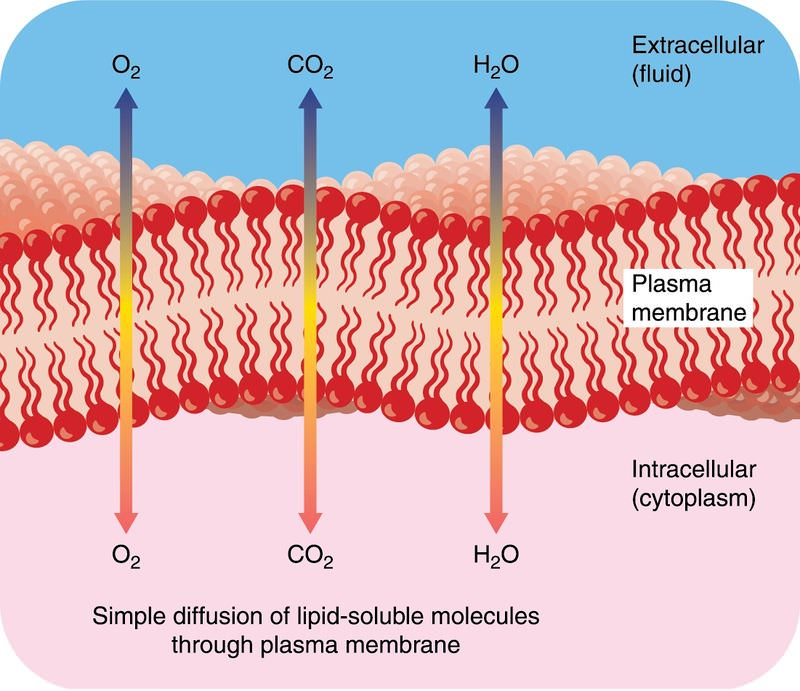
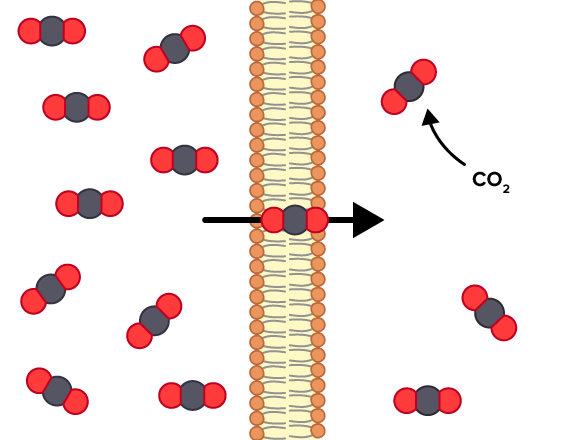
() requires no energy or protein assistance needed to move across the membrane
simple diffusion
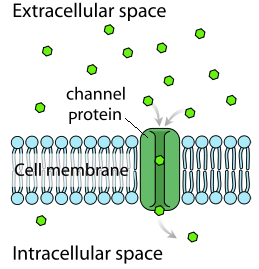
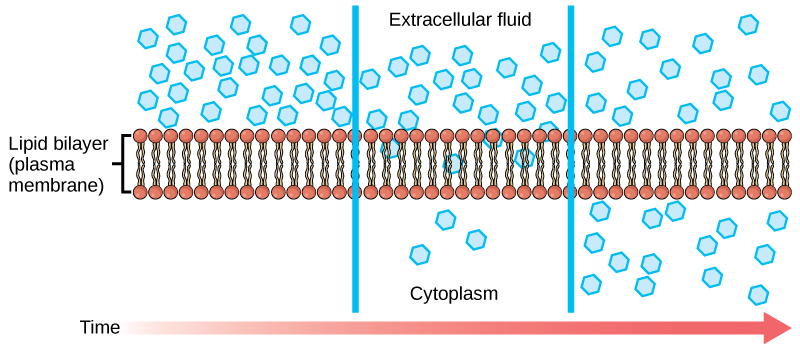
() requires the use of transmembrane proteins of which there are () proteins and () proteins; charged () and () polar molecules use this for diffusion.
facilitated diffusion, channel, carrier, ions, large
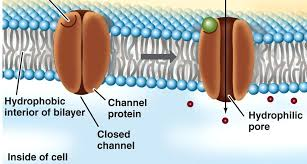
() proteins are hydrophilic in their () core to attract ions and or polar molecules; some are open all the () and others are () or only open when a signal is received.
channel, inner, time, gated
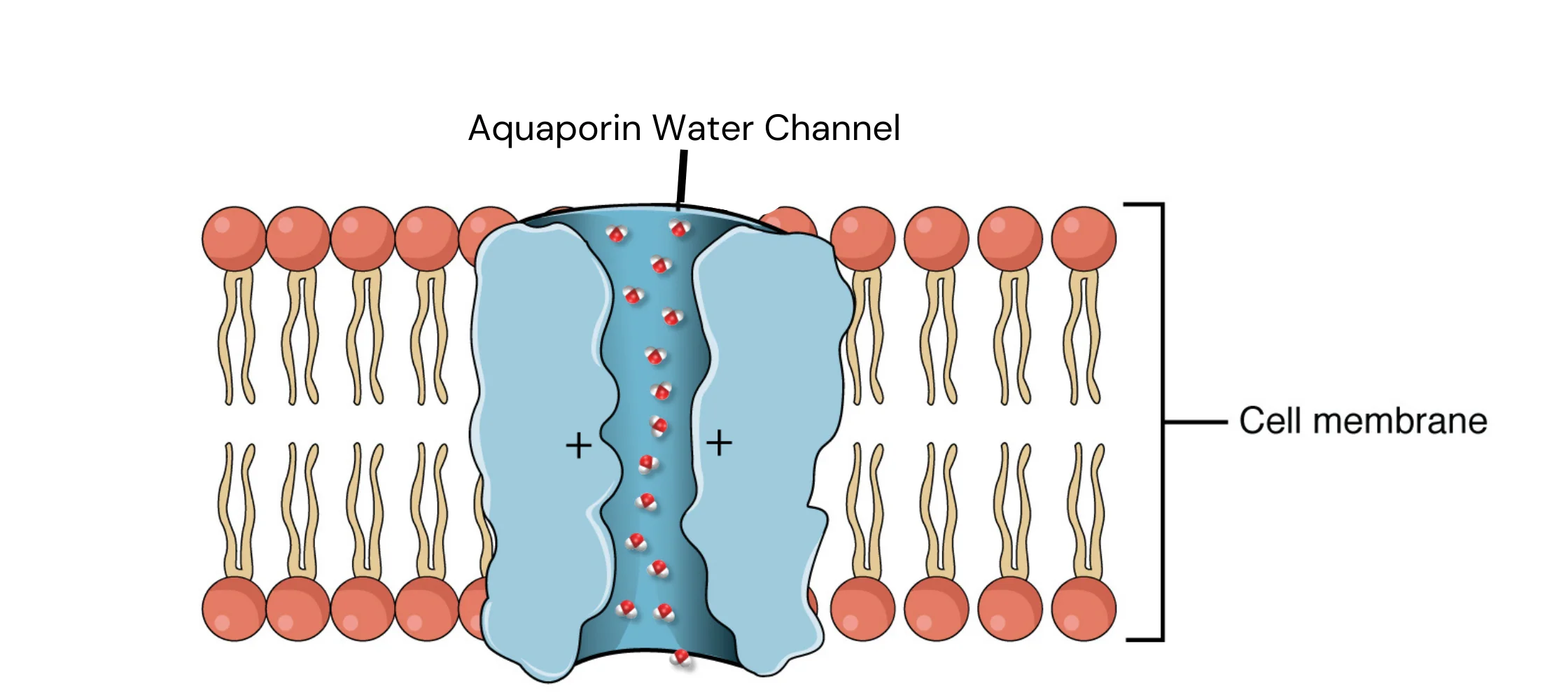
() are water channels that allow for the bulk transport of water across the hydrophobic plasma membrane
aquaporins
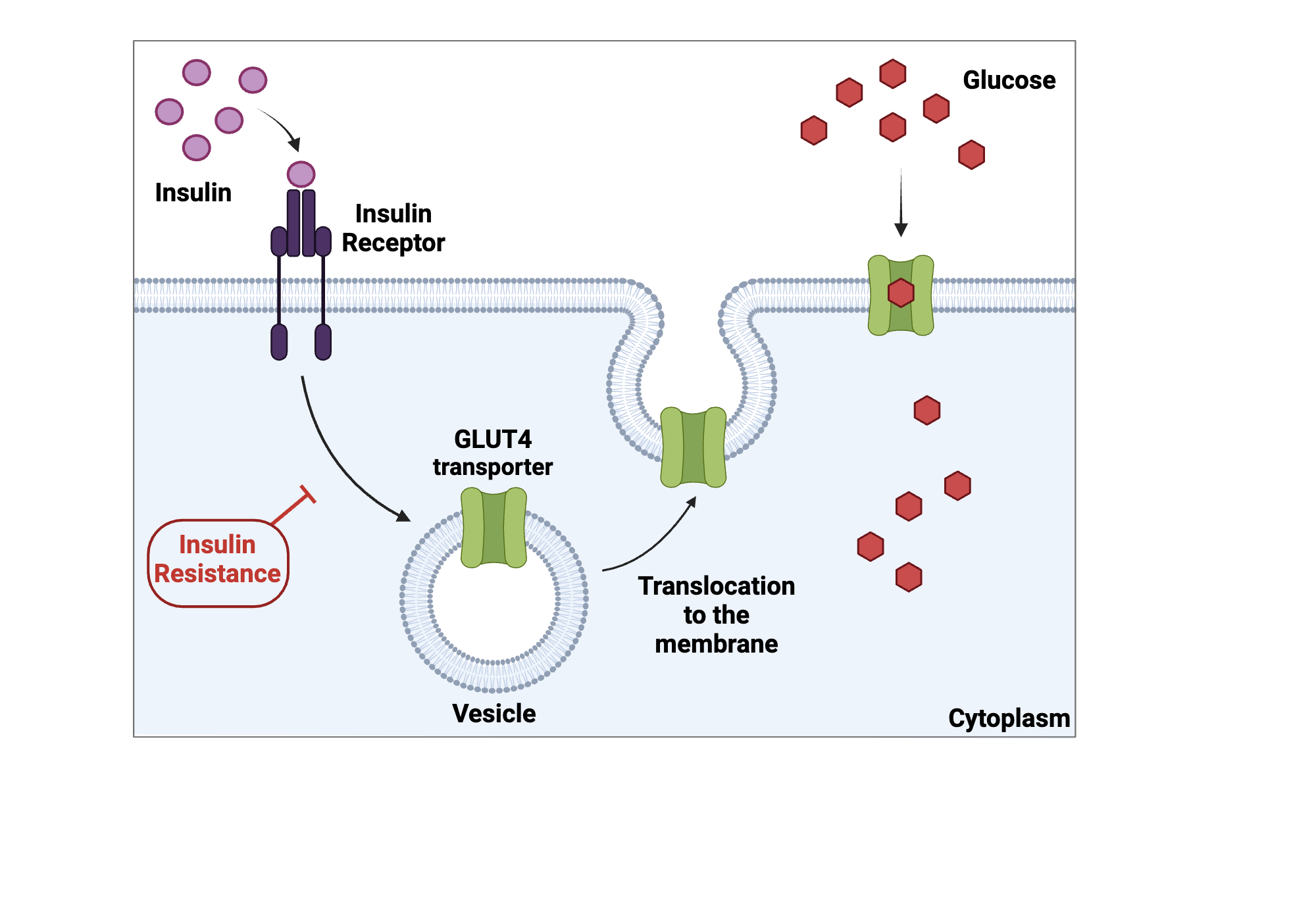
() proteins are specific to a () substance and bind to that substance then change () and “carry it” to the other side; many allow movement in either direction as concentration gradients ()
carrier, single, shape, change
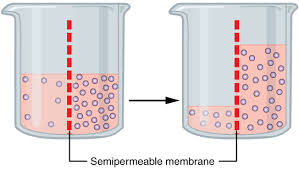
() is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane; direction is determined by solute concentration; water molecules move from areas of low () concentration to areas with a higher solute concentration
osmosis, solute
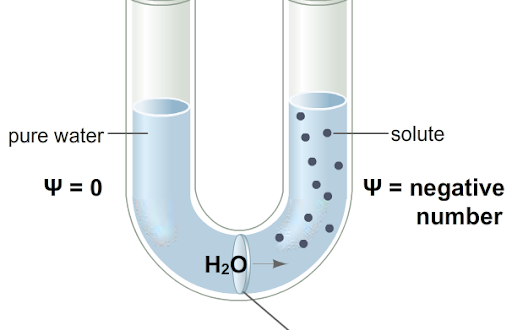
() is the tendency of water to move from one place to another, this is affected by solute concentration, pressure, and gravity; () pressure is pressure required to stop the net movement of water; () pressure is the positive pressure caused by movement of water into a cell
water potential, osmotic, turgor
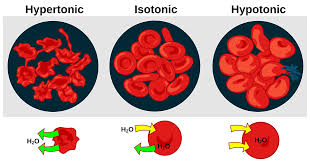
() is the ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water, it changes the volume in a cell by (); has a great impact on cells without cell (); there can be three states of tonicity: isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic
tonicity, osmosis, walls
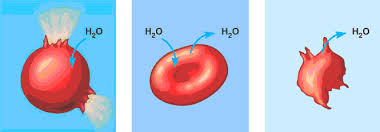
() is when the solution and the cell contain the same concentration of measured solute; there is not net movement of water which makes the exchange rate ()
isotonic, equal
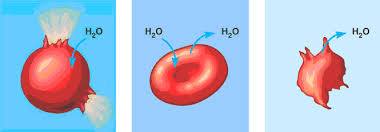
A solution is () when it has a lower solute concentration than the cell it surrounds; this causes water to move () the cell
hypotonic, into
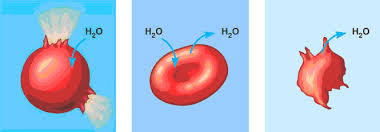
A solution is () when it has a higher solute concentration than the cell it surrounds; this causes water to move () the cell
hypertonic, outside
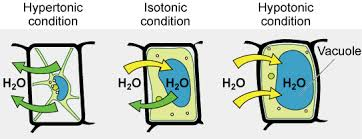
Cell () help maintain water balance in plant cells; they are firm or (); plant cells are generally healthiest in a () environment; the uptake of water is eventually balanced by the elastic () pushing back on the cell
walls, turgid, hypotonic, wall
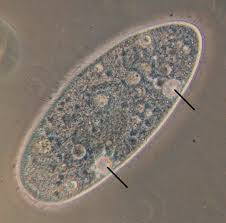
() is the process of maintaining a stable balance of water and solutes (like salts) in an organism's body fluids to achieve homeostasis; for example freshwater protists like amoebas have () vacuoles that pump water out of their cell to prevent bursting
osmoregulation, contractile