AP Biology: Unit 1 - Biochemistry
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Chemical Properties of Water
- polar molecule
- attract to opposite sides
- water's polarity allows it to hydrogen bond with other water molecules or other polar molecules
Water's Importance
- transports substances, needed for chemical reactions, keeps temperature constant
- universal solvent
Surface Tension of Water
- cohesion and adhesion
- resists being ruptured
- hyrdogen bond with nearby water molecules
Cohesion
water molecules attract and bond to other water molecules
Adhesion
water molecules are attracted and bond to other polar or charged molecules
Capillary Action
- Water adheres to the side of tubes that are lined with polar/charged molecules and "crawls" up the tube. The water molecules do not separate because of cohesion
- helps plants pull water from its roots
Water Resists Temperature Changes
- individually weak, collectively strong
- lots of hydrogen bonds
- a LOT of energy to break
- High Specific Heat Capacity
- maintain constant internal temperature for homeostasis
Solvency
substance that dissolves other chemical
Solvency of Water
- excellent solvent because it is polar
- pulls ionic compound into ions
Covalent Bonds
chemical bonds that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms
Ionic Bonds
type of linkage formed from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a chemical compound
Hydrogen Bonds
- An attraction between two atoms that already participate in other chemical bonds.
- One of the atoms is hydrogen, while the other may be any electronegative atom
Electronegativity
- different atoms attract electrons more than others
- atoms that pull electrons closer to them are more electronegative
- flourine, oxygen, nitrogen
Biomolecules
- organic molecules
- primarily made from carbon and oxygen
- required for life: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Carbon's Importance
- form 4 covalent bonds
- more structures = more shapes = more functions
Dehydration Synthesis
water is released to create a bond and forms a longer polymer
Hydrolysis
opposite of dehydration synthesis; water is used to break chemical bonds
Biomolecule Metabolism
series of chemical reactions that build up or break down biological molecules
Biomolecule Catabolism
- Reactions that break down materials
- Catabolic reactions break down polymers and release energy
Biomolecule Anabolism
- Reactions that make or build up materials
- Anabolic reactions make polymers and store energy
Carbohydrates
sugars; ratio of 1:2:1 (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen); linear and ring form structures
Monosaccharide
monomer of carbohydrates; joined via a glycosidic bond
Polysaccharide
polymer of carbohydrates; energy storing; in humans - glycogen, in plants - starch
Functions of Carbohydrates
short term energy source; energy storage; structure
Structural Polysaccharide
- linear structure and can stack to form stable structures
- used to make cell walls for plants
- we do not have enzymes to break glycosidic bonds
Functional Groups
clusters of atoms on a molecule that give the molecule polarity or acidity
pH
- how acidic something is
- acids give up H+ ions
- bases accept H+ or create OH-
Lipids
fats, oil, waxes; long carbon-hydrogen chains; hydrophobic/nonpolar nature; insoluble in water
Triacylglycerols
glycerol head, 3 fatty acids
Phospholipids
- also glycerol head but with phosphate group and 2 fatty acids
- used to form cell membrane
- Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
Steroids
4 fused hydrocarbon rings; often used a signaling molecules
Saturated Fats
no carbon-carbon double bonds; long hydrocarbon chains can stack and have more intramolecular attraction; solids at room temperature
Unsaturated Fats
double bonds leading to bends in the chain; bends prevent stacking; liquids at room temperature
Proteins
- found in meats and muscles
- 20 amino acids
- 4 different structures
- carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
- wound repair, catalyzing chemical reaction
- enzymes speed up chemical reactions; maintain homeostasis
- found in cell membrane; transportation of materials
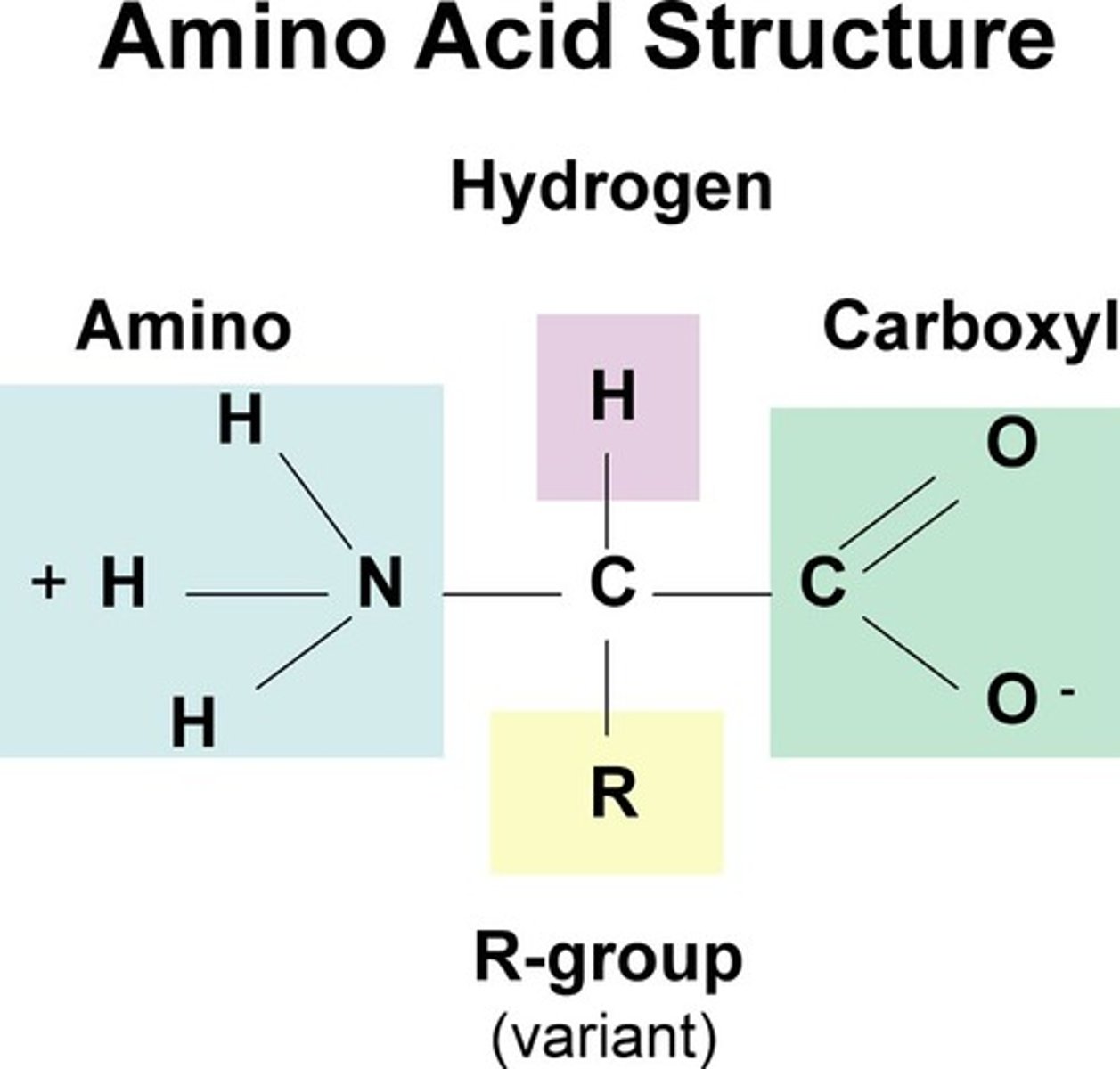
Basic Amino Acid Structure
carboxyl group (carbon double bonded to oxygen and OH), amino group (2 hydrogens bonded to a carbon), R-side chain
Primary Structure of Protein
sequence of amino acids determine how protein folds; change in sequence causes protein to misfold and not function properly
Secondary Structure of Protein
folding into alpha helices and beta sheets after the functional groups hydrogen bond; R-side chains are not involved
Tertirary Structure of Protein
finished folding; caused by interactions between R-side chains
Quaternary Structure of Protein
multiple polypeptide chains come together (not all proteins have this)
Protein Directionality
C-terminal (ends in carboxyl group) and N-terminal (ends in amino group)
Hydrophobic
scared of water
Hydrophillic
not afraid of water
Hydrophobic Collapse
major driving force behind the structure; hydrophobic inside the molecule and away from water
Other R Group Interactions
- hydrogen bonding between side chains
- charge attraction between acidic (-) and basic (+) charges
- hydrogen bonds are sensitive to temperature and pH
DIsulfide bridges
strong bonds between sulfure atoms on cystine amino acids (increase stability)
Denaturalization
changes in temperature causing disruption ahd breaks the protein
Nucleic Acids
genetic materials; carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous
Nucleotide Structure
phosphate group, 5 carbon sugar, nitrogen-containing organic base (A, T, C, G)
Function of Nucleic Acids
- store genetic information
- DNA and RNA
- antiparallel (5` and 3` ends)
- carbons in sugars are labeled by direction
DNA Structure
- eukaryotes - long structure, prokaryotes - circular structure
- deoxyribose
- more stable than RNA
- found in nucleus
- sugar phosphate formed by phosphodiester (covalent) bonds
- twisted into a double helix due to repulsion of negative charge
- linked together by hydrogen bonding
Pyrimidians and Purines
- A, G and purines and have double carbon rings
- C, T, U are pyrimidines and have single carbon ring
Base Pairing Rules
A - T, C - G
C - G are connected with 3 hydrogen bonds so they are stronger
RNA
- single-stranded
- A, U, C, G
- ribose
- used as a copy of DNA to make proteins
- make ribosomes, bring amino acids together