Macroeconomics Final Exam Study Guide
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the "fundamental economic problem" that exists in every economy?
Scarcity- satisfying unlimited wants with limited resources. Forces people to make choices.
Scarcity
Insufficiency of resources to satisfy people's unlimited wants
Economics
How people work to transform resources into goods and services to distribute and satisfy wants
Difference between Macro and Micro economics
Micro- study of individuals or specific firms or industries
Macro- study of the economy as a whole
What economic model depicts the flow of money, goods, and services between households and firms?
Circular Flow Model
Opportunity Cost
quantity of goods that must be given up to obtain another good
PPC - what is looks like and be able to determine opportunity cost and graph it
One good v another good
(look on study guide)
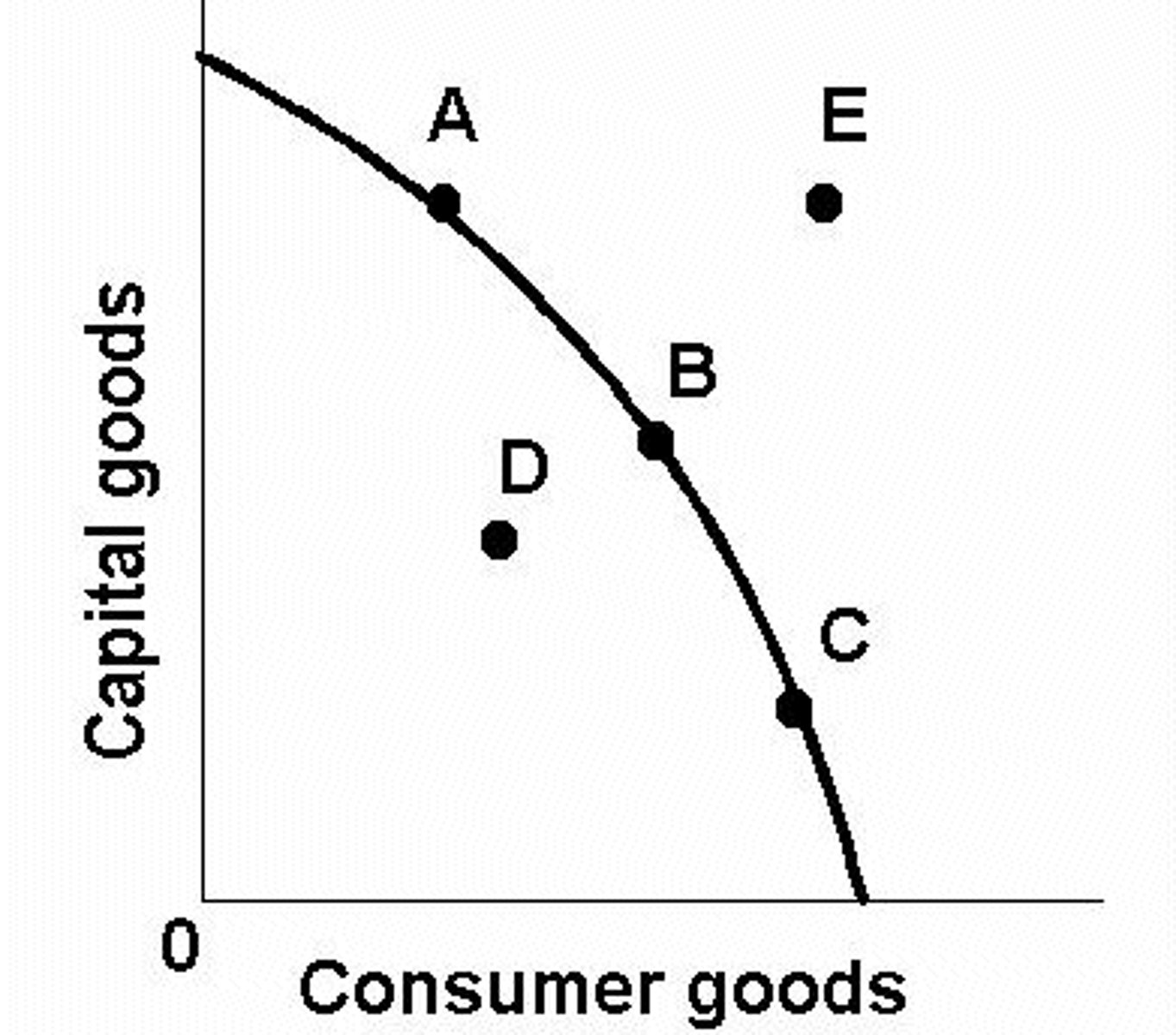
What shifts the PPC curve outward and inward
Inward- capital goods destroyed (natural disasters or war)
Outward- Innovations, new resources, new technology
Absolute v Comparative Advantage
Absolute- who can produce more of a good with fewer resources
Comparative- who can produce more of a good at a lower opportunity cost
Factors of Production
Land
Labor
Capital
Entrepreneurship
Define and Illustrate the Law of Supply and Demand
Demand- as price goes up, quantity demanded goes down and vice versa (inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded)
Supply- As price goes up quantity supplied goes up and vice versa (direct relationship between price and quantity supplied)
(See review for picture)
What causes a movement along the demand and supply curve
Changes in price
What are the determinants of supply and demand
Demand: change in income, taste/preferences, price of substitute/complementary goods, future expectations, population size
Supply: technology, resource prices, prices of related goods, number of suppliers, expectations of future prices
A Short-Run supply curve is drawn as _________ line. Long-Run is drawn as a _________line.
Upward Sloping,
Vertical
What does the horizontal segment of the aggregate supply curve indicate
Real GDP increase w/out affecting the economy's price level.
What are the determinants that would SHIFT the aggregate supply and demand curve
AS: input changes, change in productivity, changes in ACTION of government (Not gov't spending), environmental changes
AD: Changes in consumer spending, investment spending, gov't spending and net exports(exports-imports) *C+I+G+(X-M)*
When would demand-pull inflation most likely occur? Illustrate Demand-Pull Inflation on the aggregate model.
Aggregate demand curve increases pulling the price level up. Usually as a result of military expansion (increase in government spending)
(See study guide for graph)
Cost-Push inflation will most likely occur during? Illustrate Cost-Push Inflation on the aggregate model.
Aggregate supply curve decreases pushing the price level up. Usually as a result of an increase in cost of basic goods (OPEC in 1970's causes Stagflation in U.S.)
(See study guide for picture)
Be able to identify a shortage and a surplus using a supply and demand curve graph.
Surplus: QS >QD Shortage: QD > QS
(see graph on study guide)
__________ is the total value of all final goods and services produced in the economy (one country) during a given year, measured in current market prices.
___GDP____
The formula for GDP is GDP = C + I + G + (X - M). What does the C, I, G, X, and M stand for?
C = Consumer
I= Investment
G= Government
X= Export
M= Import
How does the "black market" impact GDP?
It is not included so it understates the actual value of GDP
What are the two different ways of counting GDP?
Expenditure Approach- total value of all goods and services (C+I+G+X-M)
Income Approach- total value of all resources used to make the goods and services
What is included in GDP and what is not counted in GDP?
Included: all FINAL goods and services
Not included: intermediate goods, value of housework, underground economy, cost of environmental damage, financial transactions, transfer payments, used goods, non-market activity
What is the difference between GDP and GNP?
GDP measures location (within a country's borders. Japanese owned company in U.S.)
GNP measures ownership (U.S. owned company overseas)
The Consumption Function equation C = a + bY is
a = autonomous consumption
b = marginal propensity to consume
Y = __LEVEL OF NATIONAL INCOME___
The part of national income that is not spent on consumption is defined as ____________.
_____SAVING_____
The formula for the Marginal Propensity to Save is
*1-MPC*
MPS = Change in ____SAVING_____ / Change in _____NATIONAL INCOME______
Define aggregate expenditure
Spending by consumers on consumption goods, spending by businesses on investment goods, spending by government and spending by foreigners on net exports
Define unemployment and the four different types of unemployment.
Unemployed: not having employment (a job) but actively seeking one.
(1) Frictional- brief, voluntary quit to seek better employment. Also includes initial job hunt after high school or college
(2) Structural- fundamental changes in production or substitution of new goods for customary ones
(3) Cyclical- associated with downturns and recession phases of business cycle
(4) Discouraged worker- given up after persistent rejection. NOT counted as part of labor force
Underemployed: employed in jobs not utilizing talents or experience
Who loses from inflation? Who Wins?
Losers: people on fixed income, landlords, workers with union-negotiated mulit-year fixed wage contracts, savers
Winner: borrowers and the government
Adam Smith identified four factors that contribute to the nation's economic growth.
Size of labor force, degree of labor specialization, size of capital stock, level of technology
Exchanging one good for another without the use of money is known as?
Barter system
What are the three primary functions of money?
Medium of exchange, measure of value, store of value
Liquidity
Degree to which an asset can easily be exchanged for money
M1 currency includes
Currency, demand deposits, travelers checks
M2 currency includes
M1 + savings accounts, money market mutual funds, money market deposit accounts, repurchase agreements, small-denomination time deposits
M3 currency includes
M2 + large-denomination time deposits and large repurchase agreements
Rank the least liquid to the most liquid forms of money
M3, M2, M1
The amount of assets that a bank must hold at all times is determined by what
Legal reserve requirement (set by the Fed)
What is the Legal Reserve Requirement? Be able to determine the growth of the money supply as a result of the Legal Reserve Requirement.
Sets the amount of currency from demand deposits banks must keep in vaults or at Fed district banks
Increase in LRR: decrease in $ supply
Decrease in LRR: increase in $ supply
What is the FED?
Federal Reserve- the central bank of the United States. 12 district banks across U.S.
What is the formula for the potential money multiplier?
1 / the _LEGAL RESERVE REQUIREMENT____
How much money will the FDIC insure demand deposit accounts for? What does the FDIC stand for
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. $100,000 (present day $250,000)
This is the responsibility of the ________ to hold bank reserves, provide banks with currency and loans, and clears checks.
____FED_____
What is the money supply? Be able to graph the money supply.
Supply of currency, demand deposits, and travelers checks used in transactions
(See study guide for graph)
What is the result of an increase and a decrease in the money supply?
What happens to interest rates? INC in $MS = DEC ir DEC in $MS = INC ir
What happens to investment? INC in $MS= INC in I DEC in $MS = DEC in I
What is the impact of GDP? INC in $MS = INC in GDP DEC in $MS = DEC in GDP
Two examples of automatic stabilizers are:
Unemployment
PERSONAL/CORPORATE INCOME TAXES (PROGRESSIVE TAXES)
The dominant school of thought from the late 19th century until the Great Depression of the 1930's was the ________.
_____CLASSICAL______
After the Great depression of the 1930's since WWII until the 1970's the ideas of the ____________ school became conventional wisdom.
____KEYNESIAN_____
Supply - side economists believe that lowering corporate income taxes will result in:
Increased after-tax profit, which induces suppliers to increase aggregate supply. This encourages people to work longer, which increases aggregate supply and tax revenue
Appreciation of U.S. currency means what? Depreciation of U.S. currency means what?
Appreciation- a rise in price of U.S. currency relative to foreign currency (stronger) Imports become less expensive
Depreciation- a fall in price of U.S. currency relative to foreign currency (weaker)
Imports become more expensive
What is the foreign exchange market?
Market where currencies of different nations are bought and sold
Define a Quota and a Tariff? Why are these used?
Quota- limit the quantity of a specific good that can be imported (increases domestic prices)
Tariff- tax on imported goods (domestic prices rise, quantity imported falls, domestic production increases)
To slow down international trade and restrict imports to boost domestic production