Oral Biology Unit 2 Test
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Components of periodontium
Gingiva, cementum, PDL, alveolar bone
Gingiva
Attaches to underlying bone, surrounds the cervix and fills inter proximal space
3 parts of the gingiva
free gingiva, interdental papilla, attached gingiva
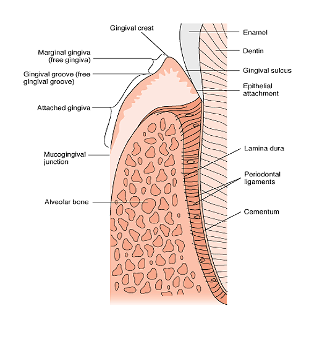
Free gingiva
not attached to the underlying bone, forms a sulcus space between gingiva and tooth
Free gingival groove
A shallow groove that separates free gingiva and attached gingiva
Groove runs parallel to gingival margin
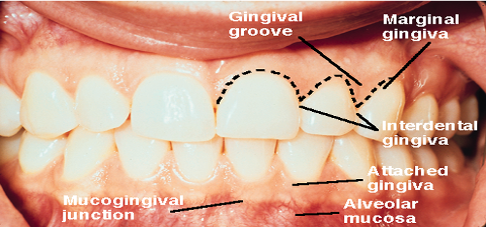
Gingival margin
edge of the gingiva nearest to the crown of the tooth
marks the opening of the gingival sulcus
Gingival sulcus (crevice)
space between the free gingiva and tooth
Attached gingiva
Adheres tightly to bone beneath it
Merges with alveolar mucosa at mucogingival junction
stippled
Alveolar mucosa
movable tissue attached to underlying bone
non-keratinized thin epithelium
not on palate
Interdental papilla
occupies interproximal areas between two adjacent teeth in a healthy mouth
Col
Depression between lingual and facial papilla
Junctional epithelium
Provides a seal at the base of the sulcus
cuff like band that attaches to cementum in a healthy gingiva
1 mm below CEJ
Mucogingival junction
attached gingiva meets with alveolar mucosa
found on facial surface of all quadrants and lingual surface of mandibular arch
no mucosa on palate
Cementum
attaches tooth to bone by means of periodontal ligament
Compensation
Formation of secondary cementum
periodontal ligament
soft CT that surrounds the root of tooth
surrounds the root of the tooth
comprised of fibers, ligaments that suspend tooth in alveolus
connects to alveolar bone
vascular
Functions of PDL
formative
supportive
protective
sensory
nutritive
resorptive
5 Sharpey’s fibers PDL