SHS 300: Module 5
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
bones that form the nasal skeleton
-frontal bone, nasal bones, maxillae, palatine bone
bones that form the nasal septum
ethmoid and vomer bone
3 pharyngeal divisions
nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx
boundaries for nasopharynx
anterior: nasal b
posterior: posterior pharyngeal wall
superior: cranium
inferior: velum
oropharynx boundaries
anterior: oral cavity
posterior: posterior pharyngeal wall
superior: velum
inferior: hyoid bone & anterior epiglottis
hypopharynx boundaries
anterior: base of tongue and laryngeal inlet
posterior: posterior pharyngeal wall
superior: hyoid bone and anterior epiglottis
inferior: cricoid cartilage
4 paranasal sinuses
maxillary, front, ethmoid, sphenoid
paranasal sinsuses functions
lighten skull, voice resonance, air conditioning, mucus production, protection2
2 structures that form the velum
soft palate and uvula 3
3 main functions of velopharyngeal-nasal apparatus
ventilation, speech production, swallowing
possible movements of the pharynx
-lengthening/shortening
-inward/outward
-forward/backward
possible movements of the velum
-upward and backward
-downward and forward
how can velopharyngeal closure be acheived
elevate and retract velum
move the lateral pharyngeal walls inward
1+2
1+2+ move the posterior pharyngeal wall forward
velopharyngeal movement when producing oral sounds
closed
velopharyngeal movement for producing nasal sounds
open
3 velopharyngeal-nasal control variables
-airway resistance
-sphincter compression = muscular pressure
-acoustic impedance
cranial bones
front, parietal, occipital, temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid, nasal, mandible`
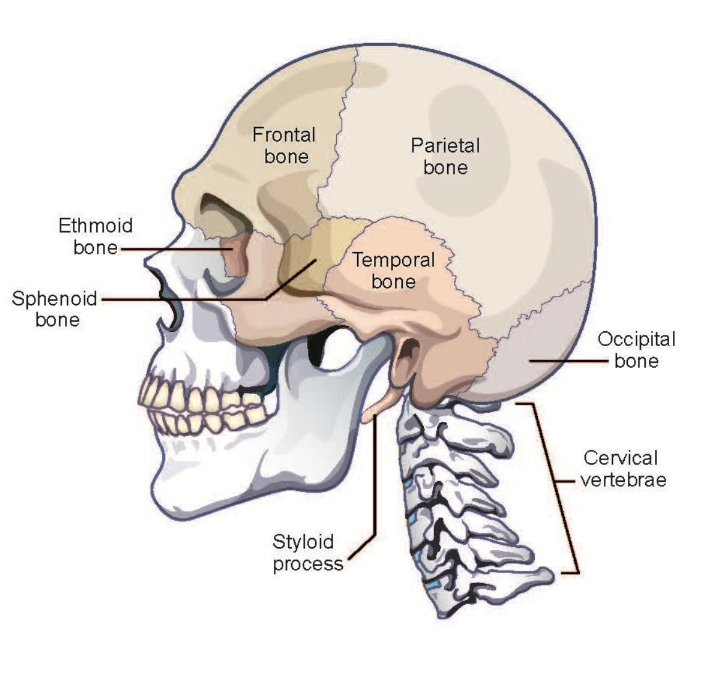
specific parts of temporal bone
zygomatic, styloid, mastoid

hard palate bones
alveolar ridge
palatine process
palatine bone
superior pharyngeal constrictor
CN IX, X
assist with velopharyngeal closure
middle pharyngeal constrictor
CN IX, X
move posterior wall of pharynx forward and narrows diameter
inferior pharyngeal constrictor
CN IX, X
narrows diameter
salpingopharyngeus
CN IX, X
shortens and elevates pharynx
stylopharyngeus
CN IX, X
move the laterall walls of pharynx upward and inward
palatopharyngeus
CN IX
elevates pharynx and larynx
widen pharynx
levator veli palatini
CN IX, X
elevate and retract velum to close VP port
tensor veli palatini
CN V
musculus uvulae
CN IX, X
shorten and elevate velum
palatoglossus
CN IX, X
lower soft palate and elevate back of tongue
palatopharyngeus
CN IX, X
lower velum and narrow upper pharynx