Grade 12 Biology Unit 2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36ATP
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical reactions in a cell or organism (continuous series of endergonic and exergonic reactions)
Energy
The ability to do work
Forms of Energy
Potential E:
Gravitational
Chemical
Elastic
Kinetic E:
Light
Sound
Thermal
Thermodynamics
The study of E (or flow of E) through living and non-living matter
First Law of Thermodynamics (Principle of Conservation of E)
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, instead converted from one form to another
Bond Energy
Measure of the stability of bonds, measured in kJ/mol (E required to break the bond)
The closer the e- is to the nuclei, the less...
Potential E it has
Breaking bonds=
E is absorbed
Forming bonds=
E is released
EA (subscript A)
Activation E
Transition State
Temporary unstable condition between old bonds breaking and new ones forming
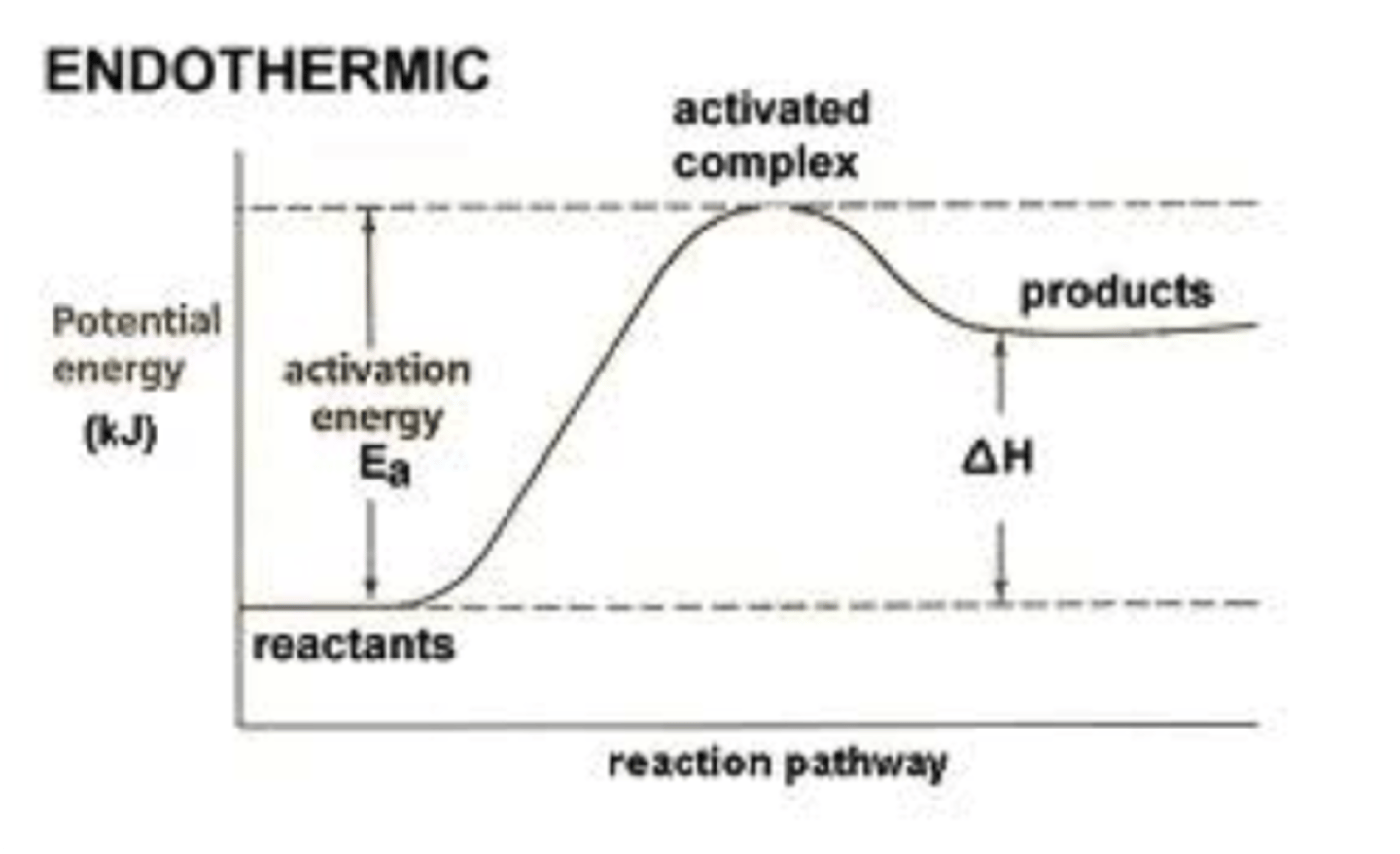
E required to break bonds > E released when forming bonds
Endothermic (Photosynthesis, +▲H)
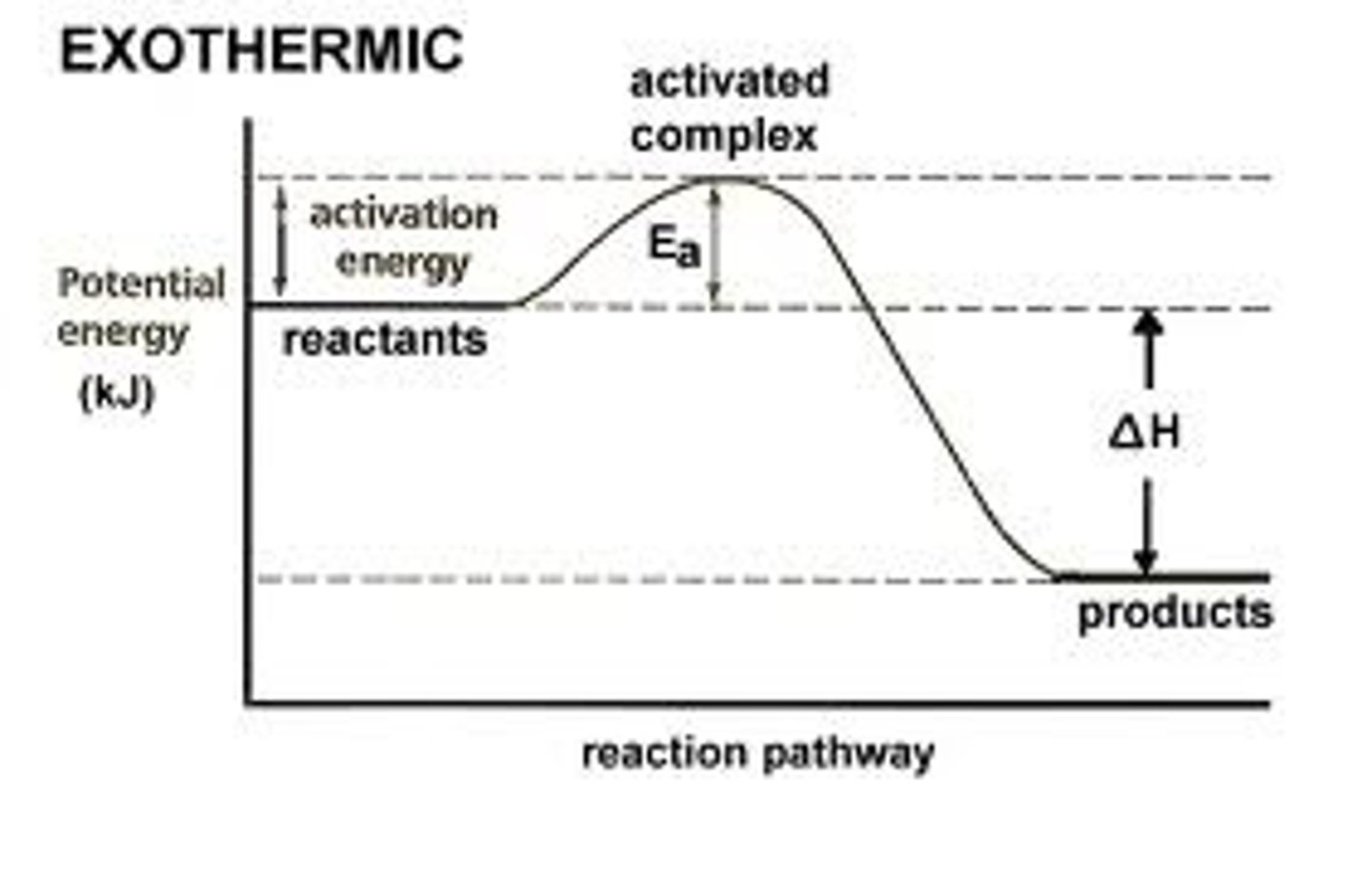
E required to break bonds < E released when forming bonds
Exothermic (Cellular respiration, -▲H)
Endothermic reaction
Photosynthesis
Exothermic reaction
Cellular Respiration
Enthalpy
Change in E of the products and reactants (▲H)
Second Law of Thermodynamics
In every energy transfer, some useful E in the system becomes unusable and randomness increases (mostly as heat)
Entropy
A measure of disorder in a system. (Natural tendency of the universe is towards increasing entropy)
Spontaneous reactions
Able to proceed on their own once enough E has been applied to get it started
Non-spontaneous reactions
Not able to proceed on their own, needs a constant supply of E
Gibbs Free Energy
Remaining useful E that can do work (G)
▲G < 0
Spontaneous, exergonic
▲G > 0
Non-spontaneous, endergonic
Excess E from an exergonic reaction can be used to...
Drive an endergonic reaction
Catabolic reactions
The breaking down of molecules (exergonic)
Anabolic reactions
The building up of molecules (endergonic)
1P -> 2P -> 3P
AMP -> ADP -> ATP
ATP
Energy currency of the cell
Dephosphorylation
Release of E to do work, exergonic (breaking apart phosphates, ATP -> ADP + Pi)
Phosphorylation
Absorbing of E to form bonds, endergonic (adding phosphates, ADP + Pi -> ATP)
Activation energy of enzyme graph
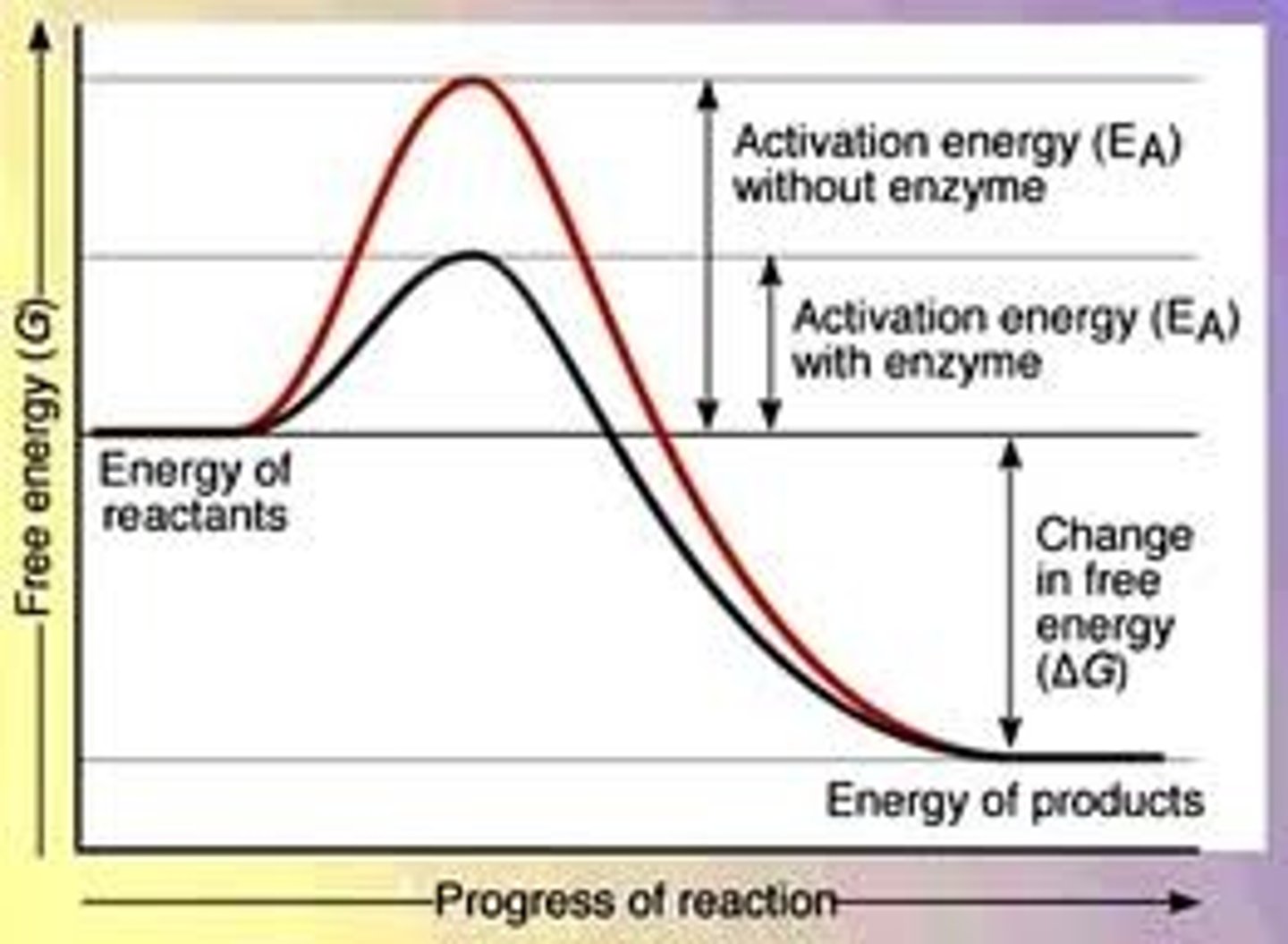
How do enzymes speed up reactions?
1) Bring substrates closer for rxn
2) Stress the bonds on the mlcl with ionic forces on enzyme, stressed bonds break more easily (induced-fit model)
When one mlcl is oxidised...
Another must be reduced (Oxygen is often involved)
Oxidation is...
A series of enzyme-catalysed reactions that release a small amount of E that can be transferred to E carrying mlcls (like NAD+)
Why is the E from oxidation released in small bursts?
To prevent a big, destructive burst of energy (allowing it to be captured and stored in a usable form)
NAD+ is a...
Coenzyme
In the oxidation of glucose, NAD+...
Is reduced (NAD+ + 2H+ + 2e- -> NADH + H+)
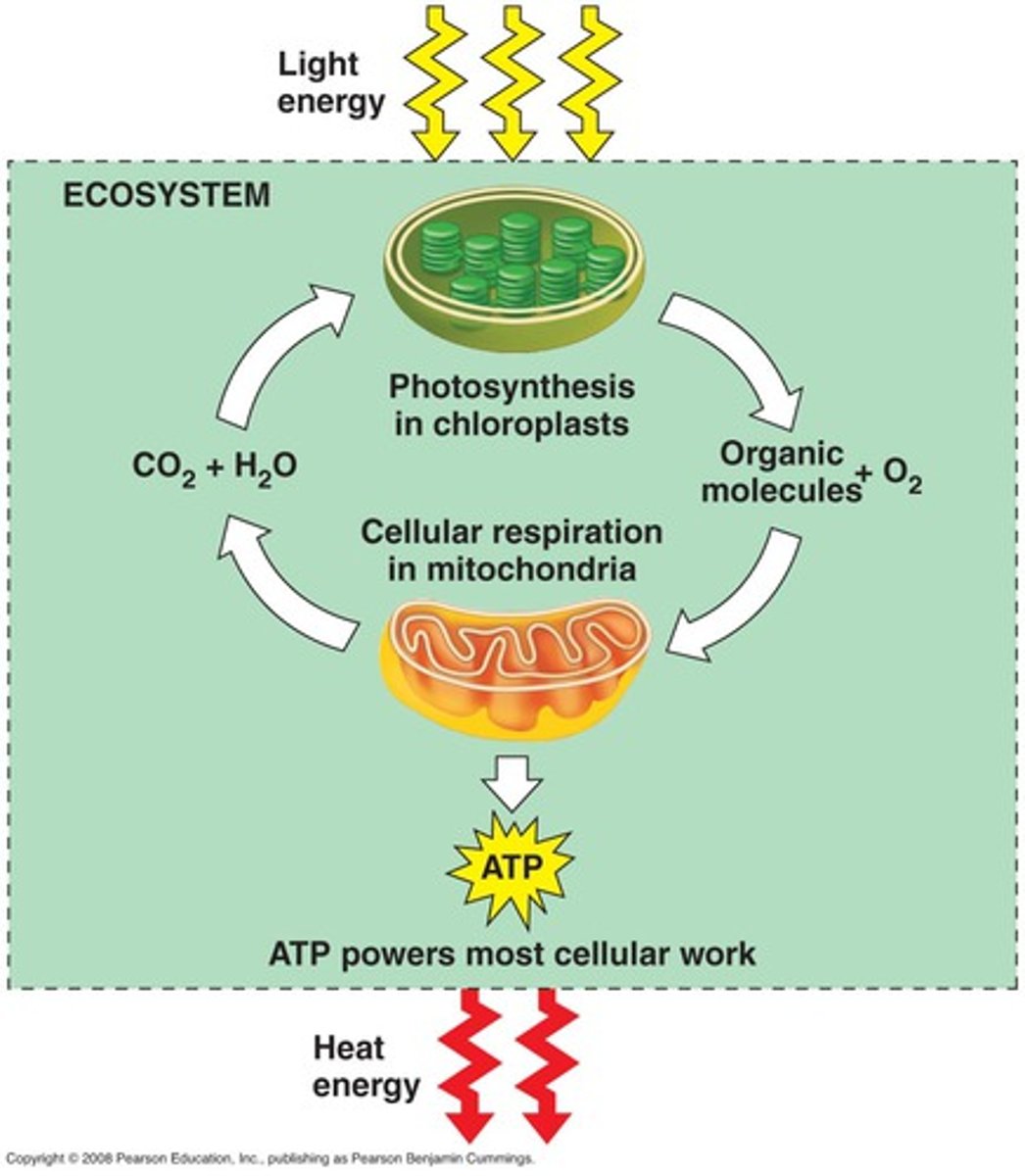
Flow of energy
Obligate aerobes
Requires oxygen for survival
The transfer of G to produce ATP from the oxidation of glucose can occur in two ways:
1) Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
-ATP formed by a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
2) Oxidative Phosphorylation
-NAD+ and FAD reduced
-NADH and FADH2 transfer E to ATP indirectly through a series of redox runs (electron transport chain)
4 Stages os Cellular Respiration
1) Glycolysis
2) Pyruvate Oxidation
3) Citric Acid/Krebs Cycle
4) Electron Transport Chain
Glycolysis consists of...
10 enzyme-catalysed reactions in the cytoplasm (does not require oxygen)
Pyruvate Oxidation
-Oxygen is required for pyruvate (3C) to enter the matrix through a transport protein in the inner mitochondrial membrane
1) Decarboxylation reaction of Pyruvate Oxidation
-Pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation
-Carboxyl group is removed as a CO2 mlcl
2) Dehydrogenation reaction of Pyruvate Oxidation
-Remaining 2C is oxidized
-NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+
3) End Result of Pyruvate Oxidation
Resulting acetate (2C) combines with CoA to form the 2C mlcl Acetyl CoA
Citric Acid Cycle consists of...
8 enzyme-catalysed reactions in the matrix where citrate is decarboxylated and dehydrogenated (oxidised with reduction of NAD+ and FAD)
Substrate-level phosphorylation in the Citric Acid Cycle
Dephosphorylation of GTP -> GDP, converts ADP -> ATP
Citric Acid Cycle Steps
1) Oxaloacetate -> Citrate
2)
3) NAD+ -> NADH, -> CO2
4) NAD+ -> NADH, -> CO2
5) GTP -> GDP, ADP -> ATP
6) FAD -> FADH2
7)
8) NAD+ -> NADH
Products of Citric Acid Cycle with 2 mlcl of Acetyl CoA
-6NADH
-2FADH2
-2ATP
-4CO2
Electron Transport Chain transfers electrons, which...
-Releases G, causing H+ in the matrix to be pumped into the intermembrane space
-This creates a concentration gradient of H+
-This creates the proton-motive force, which is from the potential energy of the electrochemical gradient, harnessed to do work
-Which leads to chemiosmosis, the ability of cells to use the proton-motive force to do work, thus synthesising ATP
Concentration gradient
Concentration of one side is higher than the other
Proton-motive force
The potential energy of the electrochemical gradient used to do work
Chemiosmosis
Ability of cells to use the proton-motive force to drive ATP synthesis
UnCouPler (UCP) protein
Embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that allows passage of H+ without going though ATP synthase
Thermogenesis
E is dissipated as heat instead of ATP, maintaining body temp in babies and helping revive animals from hibernation
Ionophores
Lipid-soluble chemicals that reversibly bind ions, to transport them across the membrane
NADH produces...
3 ATP
FADH2 produces...
2 ATP
Net ATP in Glycolysis
2 ATP
Net ATP in Pyruvate Oxidation
2NADH from glycolysis -> 2FADH2 -> 4 ATP
2NADH from pyruvate oxidation -> 6 ATP
Net ATP in Citric Acid Cycle
6 NADH -> 18 ATP
2FADH2 -> 4ATP
2 ATP
Net ATP of Cellular Respiration
36 ATP
% Efficiency of Cellular Respiration Formula
mol ATP made x E in kJ/mol of ATP
÷
total E in glucose
Regulation of ATP
-ATP inhibits (allosteric inhibition-reversible non-competitive inhibitor) phosphofructokinase
-Also inhibits the citric acid cycle
Regulation of NADH + Citrate
NADH and citrate allosterically inhibits (reversible non-competitive inhibitor) phosphofructokinase
Activation of ATP synthesis
Breaking down of ATP to AMP allosterically activates phosphofructokinase
Fat (Extra E for Cellular Resp.) enters cell as...
Glycerol -> Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (G3P)
Fatty Acids -> Acetyl CoA
Protein (Extra E for Cellular Resp.) enters cell as...
Amino Acids -> Pyruvate, Acetyl CoA, in Citric Acid Cycle
Sucrose (Extra E for Cellular Resp.) enters cell as...
Glucose -> Glucose
Fructose -> Fructose-6-phosphate -> Glucose
Starch (Extra E for Cellular Resp.) enters cell as...
Glucose -> Glucose
Glycogen (Extra E for Cellular Resp.) enters cell as...
Glucose-1-phosphate -> Glucose
Fermentation occurs when...
Oxygen is not available
Fermentation is a means of...
Regenerating NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue on in the absence of oxygen (to produce ATP)
Lactic Acid Fermentation (humans)
Glucose -> (ADP -> ATP) (NAD+ -> NADH) 2 Pyruvate -> (NADH -> NAD+) Lactic Acid
Lactate Threshold
The point at which lactate production is too high for transport out of muscles to keep up (can be improved with endurance training)
Oxygen Debt
The amount of oxygen your body needs after intense exercise to return to its resting state
Alcoholic Fermentation
Occurs in yeast in anaerobic conditions to produce ethanol and CO2 to regenerate NAD+
Glucose -> (ADP -> ATP) (NAD+ -> NADH) 2 Pyruvate -> (-> CO2) (-> CO2) 2 Acetaldehyde -> (NADH -> NAD+) Lactic Acid