Mammals and Sound
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Define communication
The process of exchanging information through scent, sound, visual displays, and more.
Why do mammals communicate?
courtship
warnings
food
territorial defense
social play
parental care
Describe what sound is
Sound is a vibration that carries through air, water, or ground. The vibrations cause a chain reaction of compressions (high pressure) and rarefactions (low pressure) that radiate outward from the source. When these waves reach the ear, the vibrations are converted into signals that the brain interprets as sound.
It moves fastest to slowest through ground → air → water
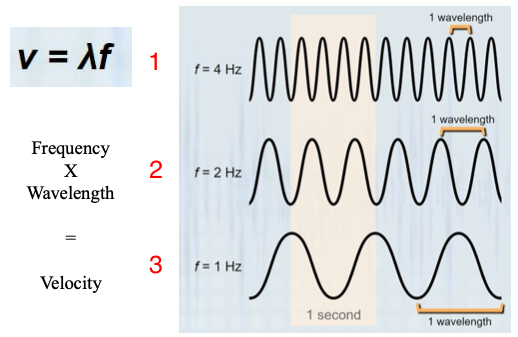
What kind of sound is coming from each of these numbers and give an example for each of an animal that makes them.
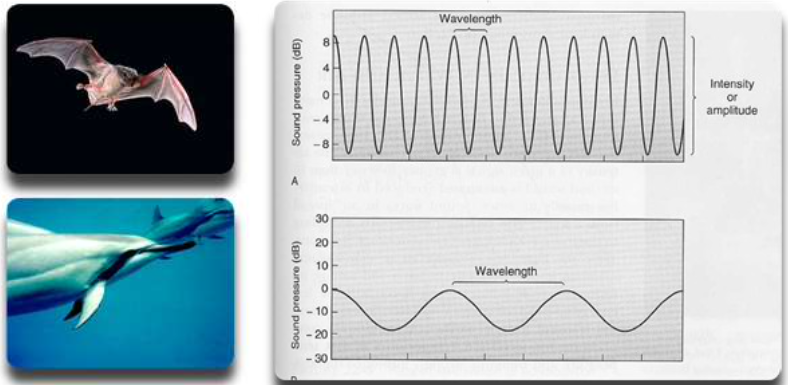
ultrasonic sound waves (dolphins + bats)
beyond human hearing
audible sound waves (humans)
sounds of daily life, from speech and music to environmental sounds
infrasound waves (elephants)
imperceptible to humans but can carry over long distances and through various mediums
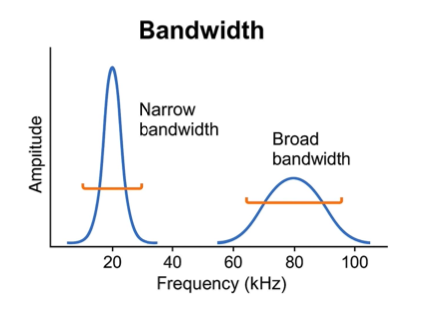
difference between the two?
narrow bandwith + high amplitude = short, high-pitched sound
broad bandwith + low ampltitude = long, low-pitched sound
attenuation
the reduction in the intensity or strength of a sound wave as it travels through a medium or is blocked by materials
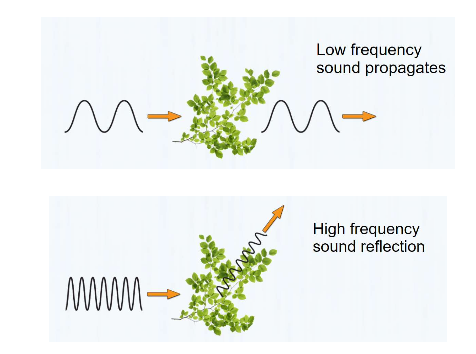
High frequency sounds attenuate _____ over a long distance.
Low frequency sounds attenuate _____ over a short distance.
Why?
High frequency sounds attenuate more over a long distance.
more likely to reflect off of (bounce off) something
Low frequency sounds attenuate less over a short distance.
more likely to propagate (go through) something
Advantages and disadvantages of using sound as a communication method.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Works when visibility is low | Reveals position to predators or rivals |
Can travel around obstructions | Noise can cover up message |
Allows for complex messages | Can be energetically costly |
Quick transmission | Limited directionality |
Can be detected from a distance | Info can get lost over long distances |
Low-frequency versus high-frequency sounds
Low-Frequency (elephants) | High-Frequency (bats) |
Large body size = low-pitched sound | Small body size = high-pitched sound |
Sound is used to communicate | Sound is used to find prey |
Sound travels farther | Sound travels short distances |
Live in open areas = less likely to reflect | Live in cluttered areas = very likely to reflect |
Explain how elephants detect low-frequency vibrations through the ground and why this is vital to their social communication.
Elephants feel them with their trunks and feet, which travel up the trunk or leg into the brain, where the sound is interpreted. They will use these calls to warn others of predators.
Echolocation in bats vs. odontocetes
Bats | Odontocetes |
Use a series of calls | Use a series of clicks |
High frequency - travels farther in the air | Low frequency - travels farther underwater |
Varied calls | Invariable calls |
Terminal buzz present | Terminal buzz present |
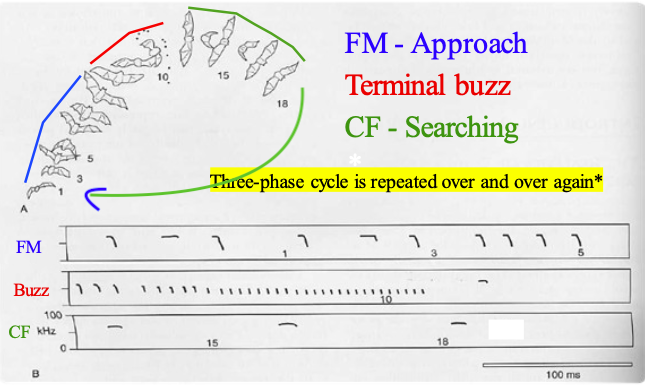
Identify and explain the stages of a bat’s echolocation call during foraging.
Constant Frequency (CF) - Searching
constantly calling, waiting for the call to bounce off of prey
not detailed, low-bandwidth, constant
Frequency Modulation (FM) - Approach
CF bounced off of prey
uses to approach and begin to zero in on prey
detailed, high-bandwidth, varies
Terminal Buzz (TB) - Kill Shot
zero in and swooping to catch prey
very short, frequent calls
very detailed, high-bandwidth, constant
Advantages/disadvantages of echolocation
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Efficient hunters | Energy cost |
Reduces chances of colliding with things | Only bits of info at a time - low resolution |
Unique niche = little competition | Limited sound range |
Recognize key insect adaptations that allow them to detect and respond to bat echolocation.
Moths hear the bats coming and produce their own ultrasound back at the bats to disguise their location by “jamming the bat sonar”
sound-producing structures on their thorax or the tip of their abdomen/genitals
Batesian mimicry: send messages to bats telling them they taste bad, some do taste bad, others are bluffing
bats are very picky so this works