Rheumatology Anatomy
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are rheumatic diseases?
structural disorders of the musculoskeletal system that are due to autoimmune disease (except for OA)
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
a chronic, inflammatory autoimmune disorder that affects joints
What are the most common joints affected by RA?
Wrists, feet, MCP, PIP joints of the hands
What is osteoarthritis?
degradation of joints induced by trauma
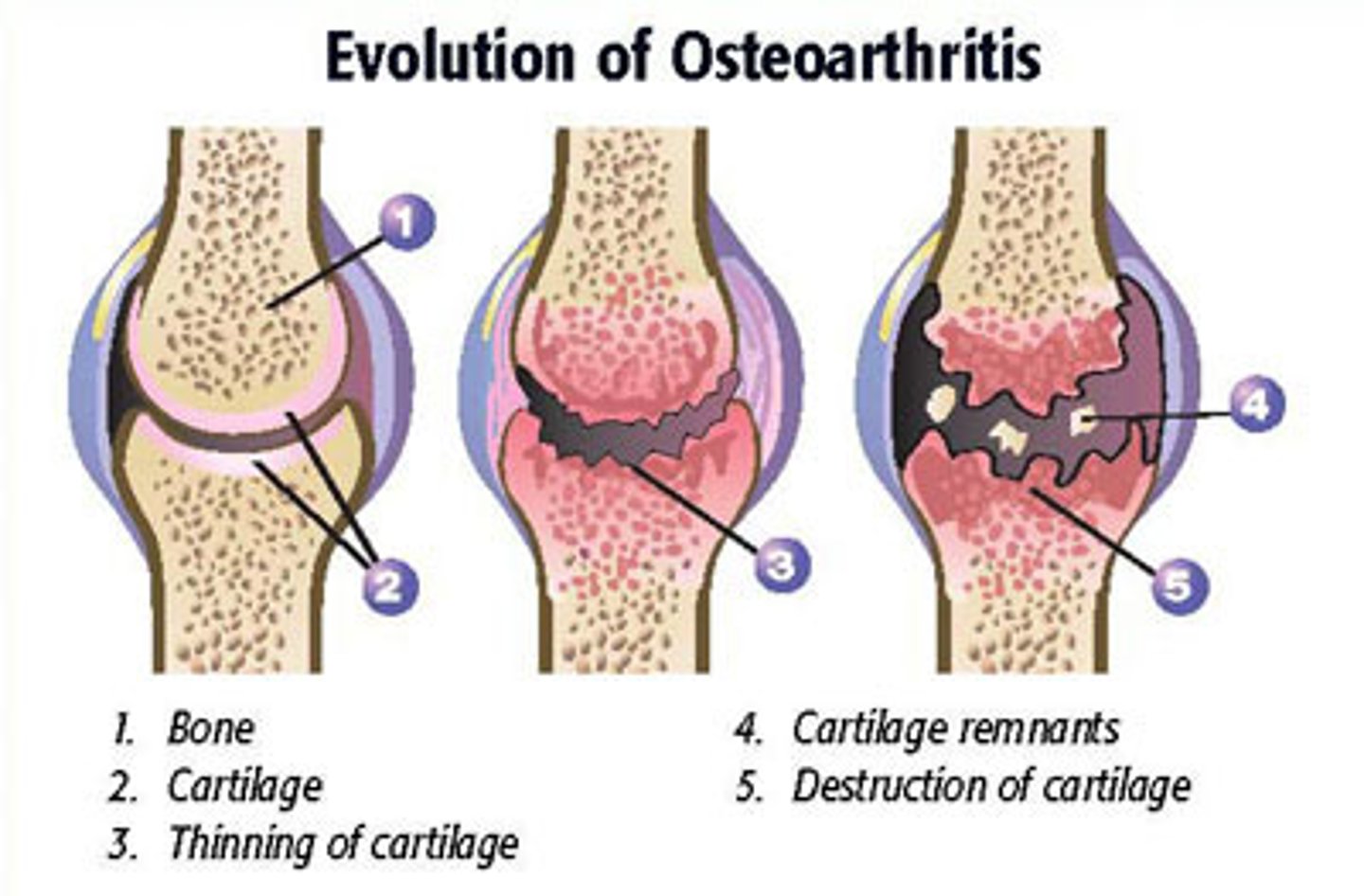
What are the most common joints affected by OA?
hands and weight bearing joints
What is gout?
A systemic disease caused by the buildup of uric acid in the blood leading to uric acid crystals in the joints
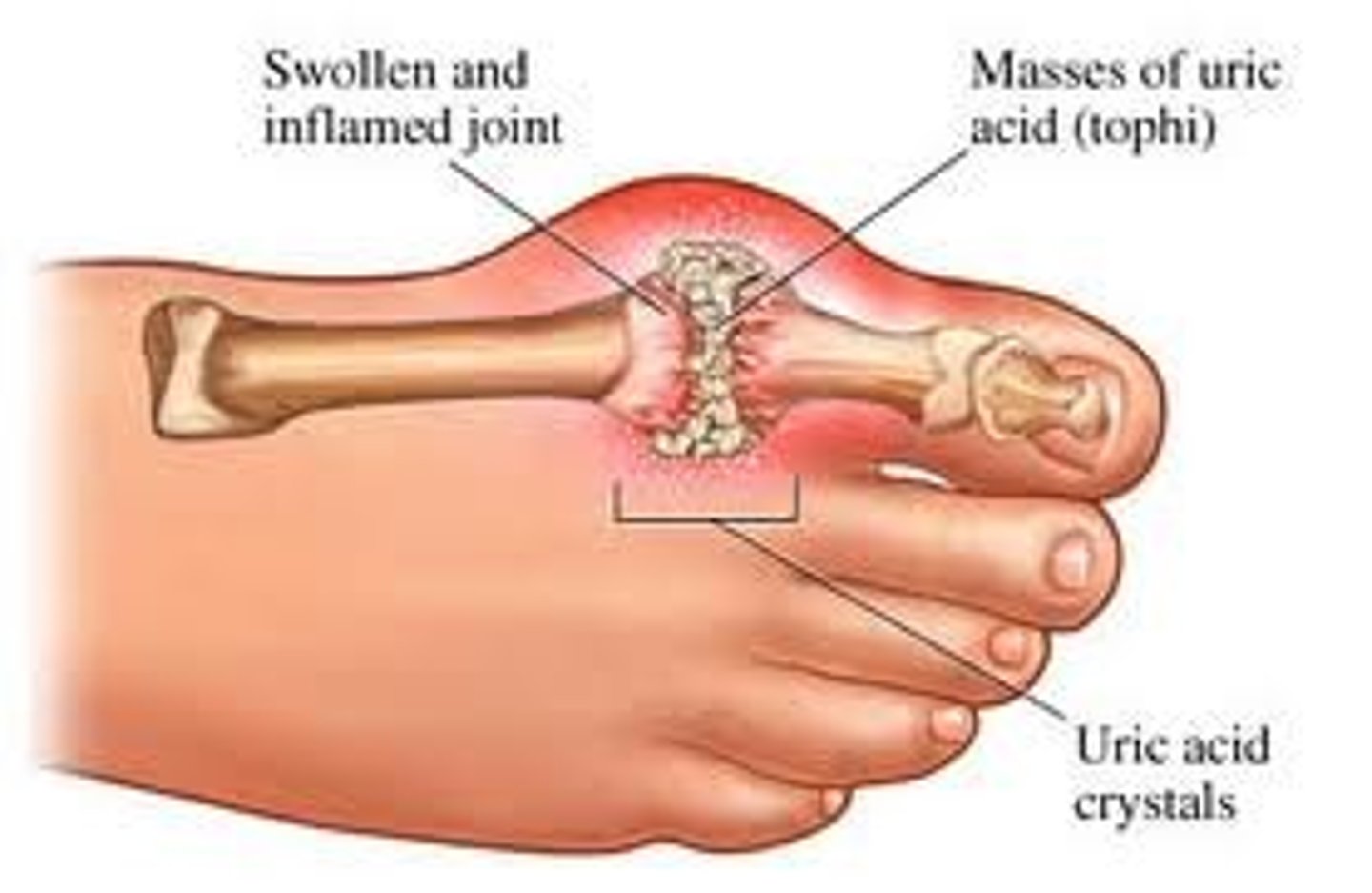
What is the most common joint affected by gout?
big toe
What is lupus?
a very complex, inflammatory autoimmune disease with a diversity of symptoms and multi-organ involvement
How long does it take to diagnose lupus?
nearly 6 years
What is psoriatic arthritis?
inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis prior to joint involvement
What are the 5 types of PsA?
1. oligoarticular (asymmetric): less than 3 joints
2. polyarticular (symmetric): 5+ joints
3. mulitans
4. spondyloarthritis: joints of the spine
5. distal interphalangeal: fingers and toes
Why is hard to diagnose between psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis?
They present very similarly, but PsA has spine involvement and previous psoriasis
What does the immune system target in RA?
synovial tissue
What does trauma lead to degradation of in OA?
cartilage
Where does the immune system target in PsA?
joints
What are synarthrodial joints?
immovable joints; where 2 bones meet closely
ex. sutures of the cranial (skull) bones
What are amphiarthrodial joints?
generally non-moveable joints or slightly moveable joints; joined by cartilage
What are diarthrodial joints?
freely moveable joints
What are the 4 key structures of diarthrodial joints?
1. articular cartilage
2. synovium
3. joint capsule
4. synovial fluid
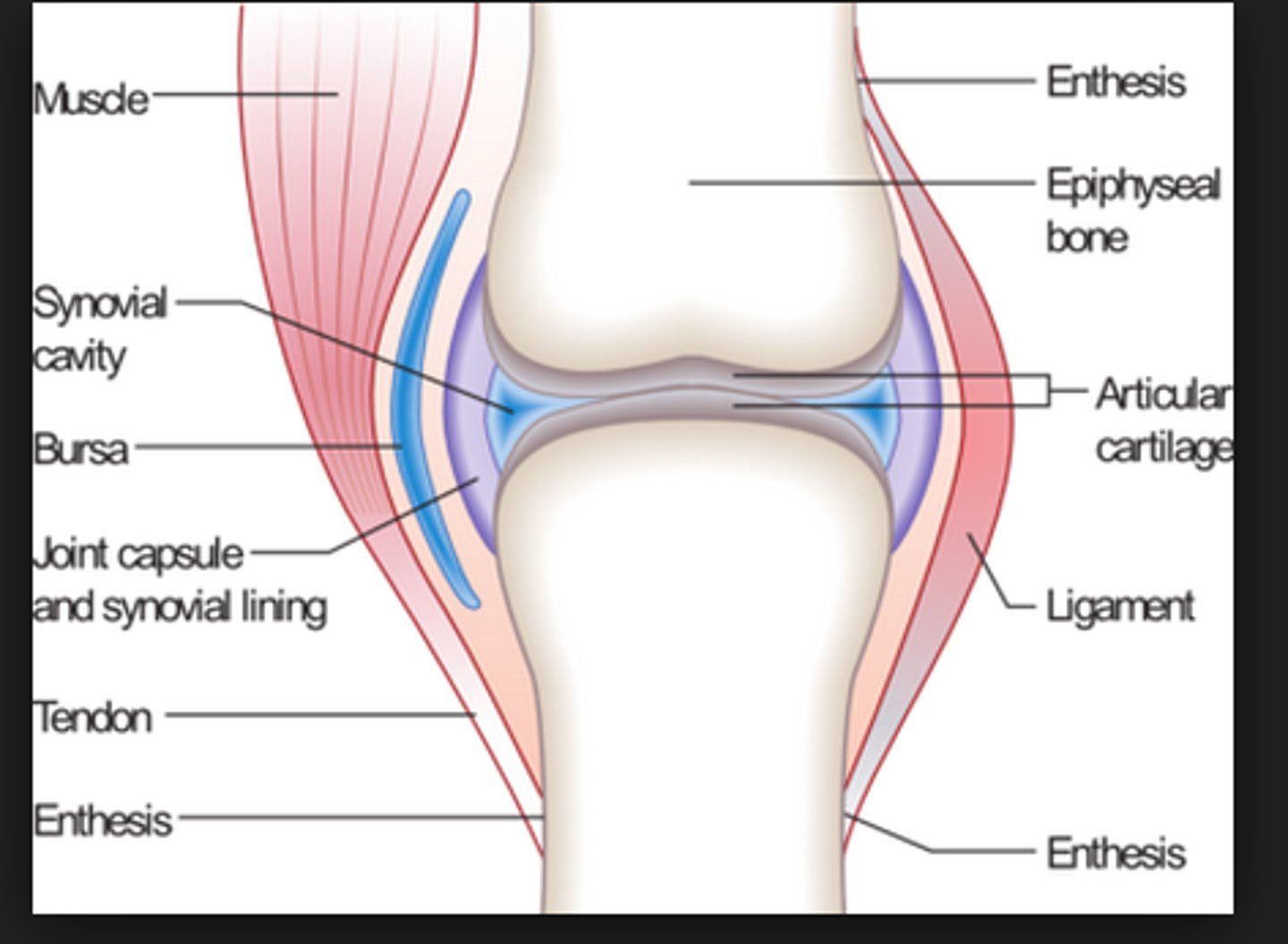
What is articular cartilage? What are its characteristics?
smooth, white connective tissue that covers the ends of bones where they come together to form joints; it has no vasculature or nerves, but it has chondrocytes and an extracellular matrix containing collagen and proteoglycans
What is the synovium?
connective tissue that lines joints, tendons, and bursae, but not cartilage; contains thin, loosely constructed proteoglycans, lots of hyaluronan, and macrophages and fibroblasts
What is the joint capsule? What is it made of?
a thin sac that surrounds the joint and synovial fluid; is made of collagen type I and fibrillar type III
What is synovial fluid?
transudate of plasma in the joint capsule that is low in protein and cell content; has hyaluronan to create a high viscosity
What is the WBC content of synovial fluid in individuals without disease?
less than 200 cells/mm3
What is the WBC content of synovial fluid in individuals with non-inflammatory conditions like OA?
less than 2000 cells/mm3
What is the WBC content of synovial fluid in individuals with inflammatory conditions like RA?
greater than 2000 cells/mm3
What causes changes in intrasynovial pressure seen in RA?
change in cell and protein composition in the synovial fluid
What causes joint deformities in RA and why?
alteration of intrasynovial pressure that causes joints to assume position of least pressure
What factors lead to acute joint inflammation?
1. vasodilation
2. edema
3. neutrophilic infiltration
4. depolymerization of hyaluronic acid
5. synovial fluid volume increase
6. synovial ischemia (hypoxia)
What happens with cytokines (IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1) all leave the synovial fluid and enter the blood?
They enter systemic circulation and can cause osteoporosis, anaemia, thrombocytosis, fever, fatigue, depression, acute phase response and systemic inflammation
What are the primary lymphoid organs?
bone marrow and thymus
What are the secondary lymphoid organs?
spleen and lymph nodes (liver not technically but incredibly important)
Where are T cells produced? Where do they mature?
produced in bone marrow, but migrate to thymus for maturation
Where are B cells produced? Where do they mature?
produced in bone marrow, stay in bone marrow for maturation
What is the site of immune activation?
the lymph nodes
What happens in the lymph nodes?
antigens are transported through lymph fluid to LNs via dendritic cells which then present the antigens to the B and T cells
Why is the spleen important?
it is the site of immune response to blood borne pathogens
What happens if someone doesn't have a spleen?
LNs take over immune response to blood borne pathogens, although they are not specifically designed for this so it may make them more susceptible to bacteria like pneumococci and meningococci
Why is the liver also important in immune response?
the liver produces proteins responsible for innate immune responses
What can cause autoimmune reactions?
an overactive immune system, genetic predispositions, viruses, malfunctioning of the immune system