Lecture 2: Introduction to Research (PSYC2009)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Why do we need statistical methods?
To count, chart, summarise, and otherwise describe what we’ve measured.
To understand and deal with risk.
To distinguish real patterns from random ones.
To enable us to make inferences from a sample of people.
What are the ideals of the scientific approach?
Universalism
Organised scepticism
Communalism
Transparency
Disinterestedness
Honesty
Universalism
Evidence-based claims are judged on the merit of that evidence; are based on the evidence itself (and nothing else).
Organised scepticism
All evidence-based findings are provisional/temporary and are bound to change.
Communalism (transparency)
All scientific findings (and processes) should be made transparent.
Disinterestedness
Researchers should approach their research question (and receive research questions) impartially; they should be emotionally detached from their work.This means avoiding personal biases or conflicts of interest, ensuring that findings are based solely on the evidence.
Honesty
Don’t lie, deceive, or conceal.
Continuum of scientific misconduct
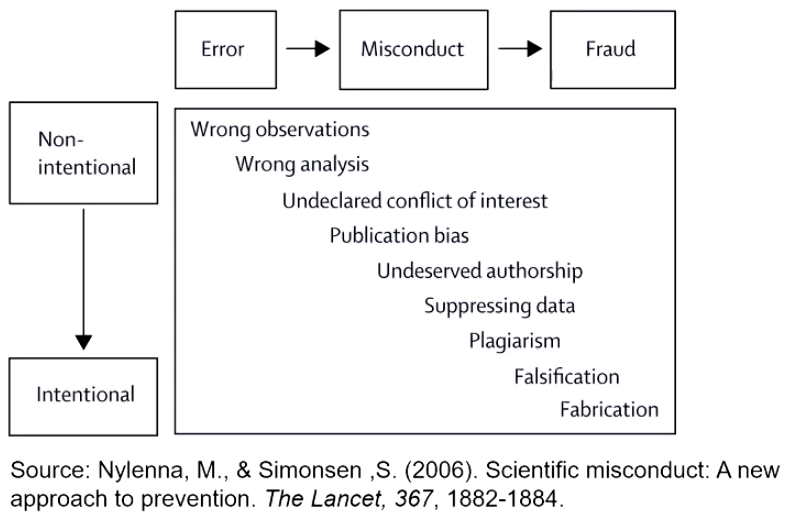
Aspects of ethics in research
Confidentiality, anonymity, and privacy.
Informed consent.
Involuntary participation.
Deception and debriefing.
Mental and physical stress and discomfort.
Choosing where, and what to publish.
Confidentiality
Not publishing data from participants/clients.
Anonymity
Keeping participant’s identity protected in publications.
Right to privacy
People’s expectations that personal lives will not be impacted by research participation.
Why are some people ‘anti-deception’?
When you deceive participants one time, you ruin them as participants. Every study after that, they’ll likely expect to be deceived again and question what’s actually happening.
What’s a purpose of deception?
To allow for true results. If you tell participants what you’re studying, their behaviour likely changes.
What must you do to minimise/prevent mental and physical stress and discomfort?
Debrief
Follow-up
Provide contact information
Bottom drawer filing
The fact that typically only fancy findings get published, and boring stuff where nothing happens don’t.
Predatory journals
Journals you have to pay lot’s of money to publish
Why is it considered worse to publish in a predatory journal than to not have published at all?
It involves no peer review process, and as long as you pay, regardless of the paper’s content, it gets published. People commonly perceive such paper’s to involve poor judgement and poor science.
What are four types of research?
Experimental
Quasi-experimental
Non-experimental (survey/correlational)
Case study
Definition of Experimental Research
A systematic attempt to manipulate theoretically relevant variables and to examine the effect of these manipulations on the outcome variable. (Haslam & McGarty)
Purpose of experimental research
Cause and effect
What does experimental research involve?
Active intervention and the manipulation of variables. This allows for one to make casual attributions/explanations. Also involves experimental and control groups.
Experimental group
The participants who are subjected to the treatment.
Control group
The participants who are not subjected to the treatment.
Independent variables (IV)
The variable you vary.
Dependent variable (DV)
The variable you’re measuring (i.e., the variable you think will change due to the manipulation of the IV).
Internal validity
The amount of control that you have over your experiments, and the degree to which you are sure that your X is causing the change in Y.
External validity
How true something is in the real world. Is always balanced with internal validity.
Confounds
Variables that look like your IV, but isn’t your IV.
Between-subjects
Different people exposed to different levels of the IV
Within-subjects
Levels of the IV differ within the same participants.
Examples of validity threats
Practice and fatigue effects
Advantages of experimental research
Causal inference
Control
Disadvantages of experimental research
Practicality
Reactivity effects
Validity (ecological and internal)
Quasi-Experimental research
Assignments to groups on the basis of pre-existing differences on the independent variable.
No manipulation
No random assignment
Disadvantages to quasi-experimental research
Hard to infer causality
Influence of extraneous variables
Advantages of quasi-experimental research
Good for studying variables that can’t be manipulated
Good ecological validity
Non-experimental research
“Survey” or “Correlational”
Advantages of non-experimental research
Ease of admin (faster, cheaper, more convenient for participants)
Many variables
Disadvantages of non-experimental research
Generalisability
Causal inferences (correlation is not causation)
When is case study research used?
When the phenomenon under study is rare.
Advantages of case study research
Can attain an in-depth exploration of theoretical ideas
Disadvantages of case study research
Conclusive statements are hard to make.