
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
6.1 Metabolism
What is Metabolism?
total of an organism’s chemical reactions
ex/ food converting into energy is a chemical reaction. that’s why so many people say “i want high metabolism” because if you have that high metabolism that means there is more reactions and therefore more food gets converted into energy instead of fat
Metabolic Pathways
molecules altered via defined steps, catalyzed by specific enzymes
BARF
Break = Absorb
Release = Form
Catabolic Pathways
net release of energy = exergonic
digestive, breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones
ex/ hydrolysis

Anabolic Pathways
net absorption/
gain of energy = endergonic
synthesis, combine smaller molecules into more complex ones

Kinetic Energy
movement
thermal, heat
light
Potential Energy
stored
chemical energy: potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction
First Law of Energy Transformation (Thermodynamics)
energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be transformed
Second Law of Energy Transformation (Thermodynamics)
during energy transformation, some energy is converted into heat
ex/ lightbulbs are hot because the light energy transferred into the bulb and some is loss to heat —> which means lightbulbs are less efficient and wastes more energy
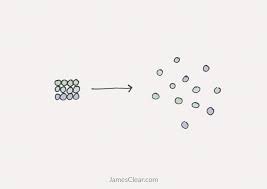
Universe is always trying to expand —> everything naturally increases in entropy
therefore, to decrease entropy, energy is necessary
this “reverses” it
Entropy = randomness, chaos
6.2
Gibb’s Free Energy
available energy that can perform work
net energy absorbed/released by reaction pathway
ΔG is less than 0
negative, energy released aka exergonic
exergonic = spontaneous —> increase of entropy
Catabolic Pathways
ex/ breakdown of glucose into CO2 and H2O has ΔG of -686k cal
ΔG is greater than 0
positive, energy gained/absorbed aka endergonic
entropy decreases —> not spontaneous
anabolic pathways
ΔG = 0
cellular death :(
chemical equilibrium - no work is being done
6.3
Energy Coupling
use energy released from exergonic rxn to drive an endergonic rxn
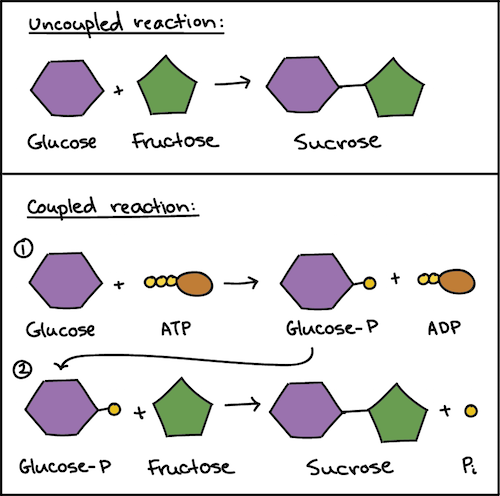
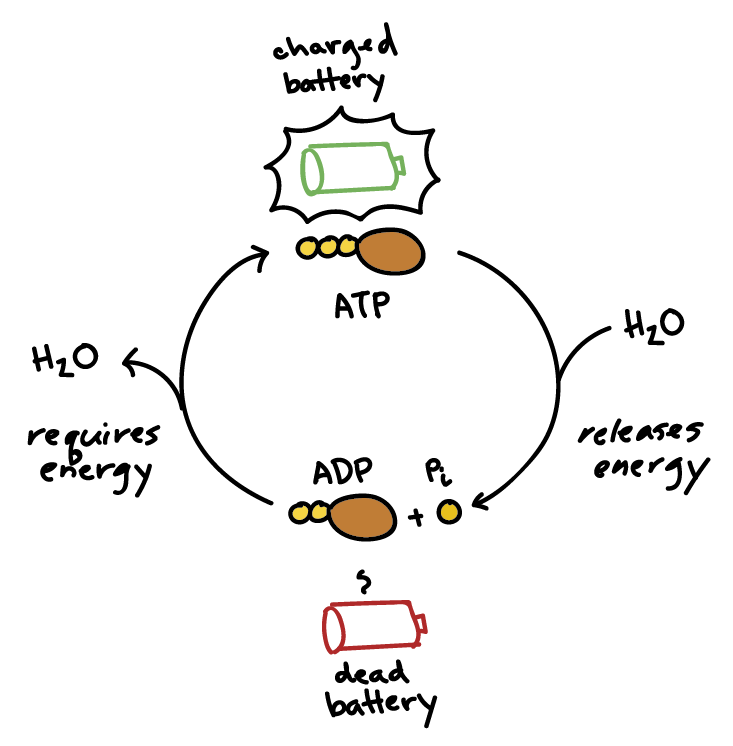
ATP
structure: adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups
ATP —> ADP + P
Phosphorylation
transfer of phosphate group from ATP to some other molecule/reactant, which is more reactive (less stable) than original molecule (changes shape)
ex/ when phosphorylation occurs in the sodium-potassium pump, the pump receptors change shape to fit the potassium atoms and will then release the sodium in and potassium out if ykyk
ATP regenerated by addition of phosphate to ADP; requires energy
6.4 ENZYMES
So… what are enzymes
organic catalysts
Catalyst
speed up chemical reactions
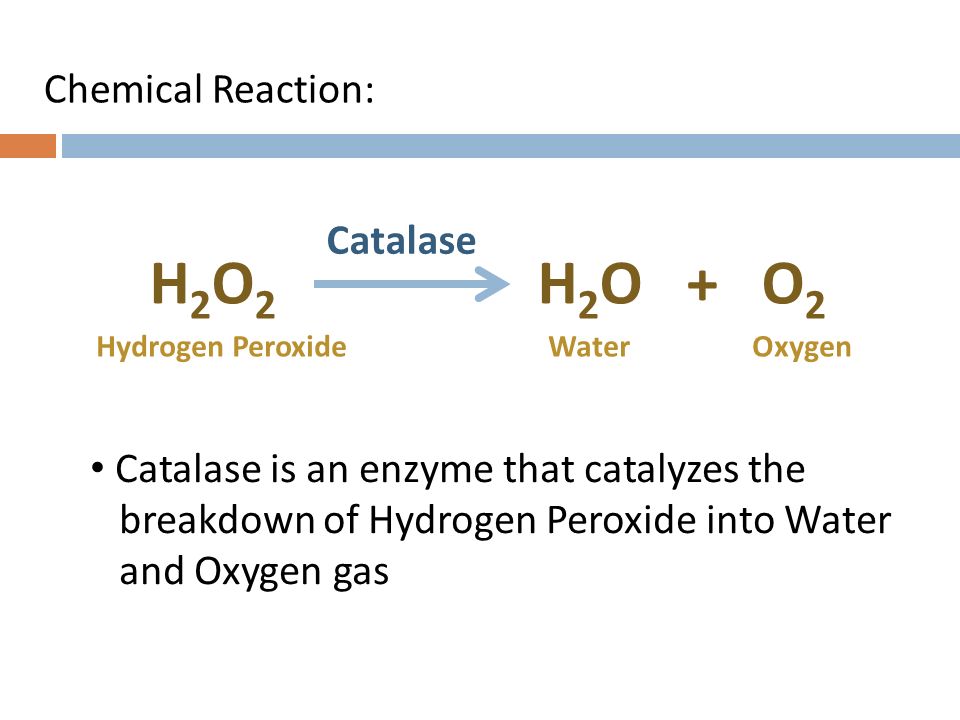
ex/ Catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into H2O and O2 and the catalase is the enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown
ex/ Hydrolysis (breakdown of compound due to reaction with water) can happen fast due to the enzyme SUCRASE

Activation Energy
initial investment of energy for starting a reaction (energy requited to contort reactant molecules so bonds can break)
often supplied by heat (thermal energy) absorbed from surroundings —> reactant molecules accelerate and collide more often and more forcefully
enzymes lower activation energy barrier
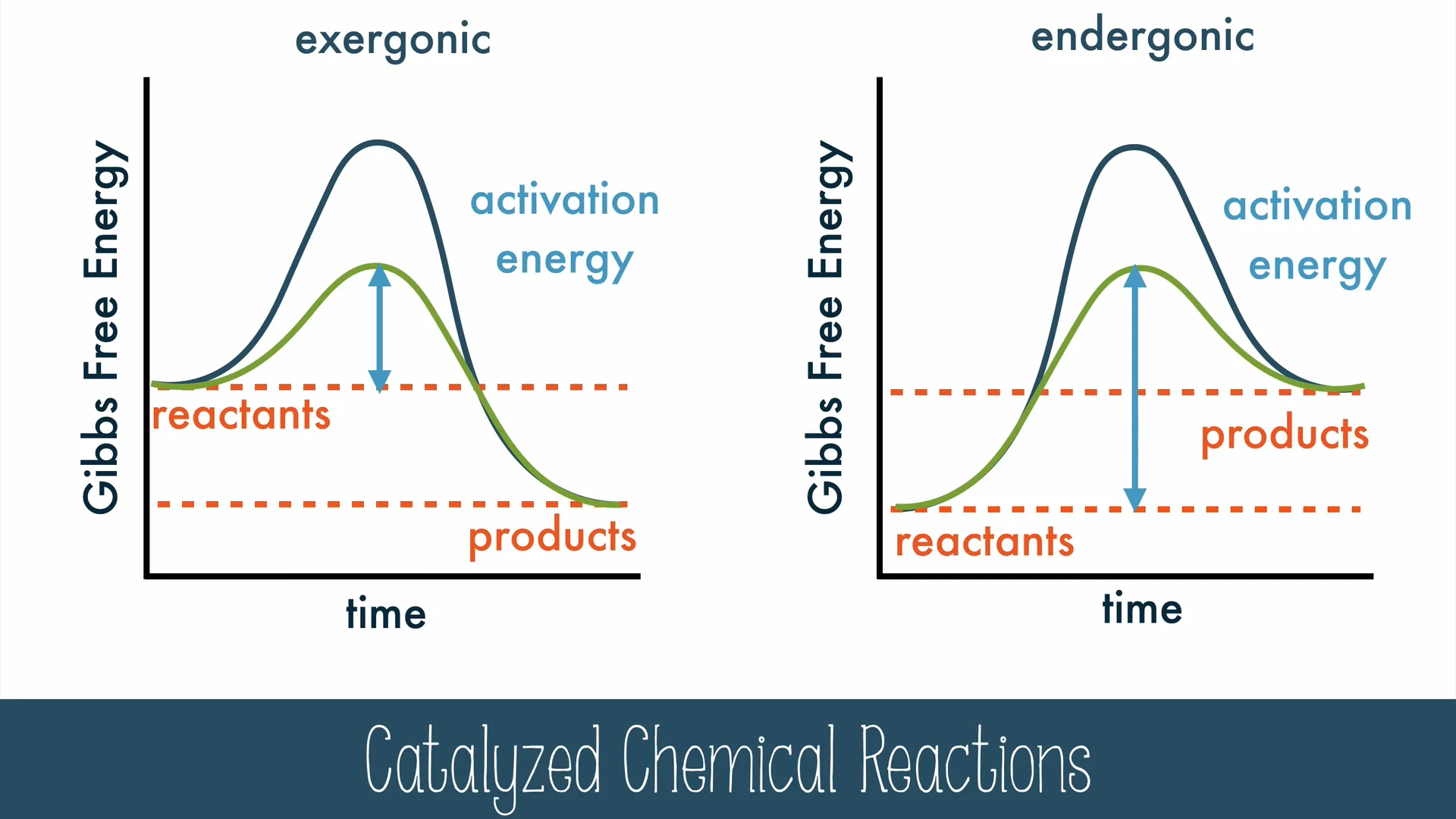
Enzymes in Activation Energy
provide template on which reactants (substrates) can come together in proper orientation
stretch substrate molecules, stressing/bending chemical bonds
provide conducive microenvironment for reaction (ex/ proper pH)
microenvironment = just in active site at enzyme, the bit gets altered, NOWHERE ELSE
Enzyme-Substrate Specificity
most enzymes names end in
active site of enzyme binds to substrate (pocket/groove enzyme surface) - complementary fit between shape of active site and shape of substrate
Induced fit - enzyme slightly changes shape to “hug” the substrate so it fits snug in active site.
analogy: changing your cupped hand up to catch a speeding ball towards you
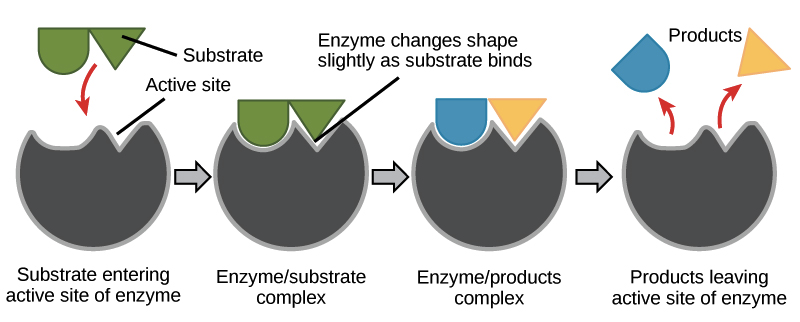
Enzyme-Substrate Specificity (continued)
substrate held in active site by weak interactions between R-groups of enzyme and substrate (H bonds and ionic bonds)
Single enzyme can act on about a thousand substrates per second
Enzymes can usually catalyze either forward or reverse reaction
Enzyme Saturation
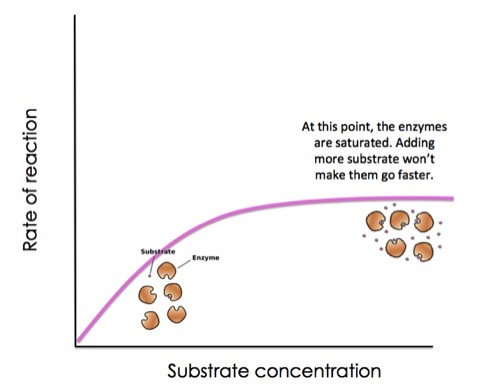
think of the toothpick activity
enzyme saturation = max rxn rate
overcome by just adding more concentration aka bring in a friend
Temperature and pH
thermal agitation of enzyme molecule disrupts weak interactions that stabilize active shape of enzyme = denaturation
Most human enzymes have optimal temps of 37°C
temperature decreases, slow down enzyme molecule
temperature increases, denatures molecule
pH increases or decreases, denatures molecule
Cofactors
nonprotein helpers that bind to enzyme
May be inorganic - Zn, Fe, Cu ions (trace elements)
May be organic - coenzymes
Enzyme Inhibitors
inhibit (stop) action of specific enzymes by binding to them
Competitive Inhibitor
fit into active site, blocking ability of substrate to bind
competes with substrate
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
allosteric inhibitors —> bind to the allosteric site —> this causes the enzymes active site to change shape and halt of its function (not denatured, just stop functioning) once it is removed its function resumes
Irreversible Inhibitors
inhibitor that makes it so the enzyme cannot return to its original shape
toxins and poisons (sarin, pesticides, penicillin, parathion, etc)
sarin —> inhibits muscular relaxation and tells diaphragm to contract and not relax
Toxins bind permanently to the allosteric site and this causes the enzymes shape to be permanently altered
Antibiotics inhibit bacterial growth, so that the immune system can turn them off more easily
Allosteric Regulation
enzyme’s function at active site affected by binding of a regulatory molecule to a separate site (allosteric site)
Activator: stabilizes shape with functional active sites (cofactor)
Inhibitor: stabilizes inactive form of enzyme (non competitive inhibitor)
Other regulation of Enzyme Activity
binding to one subunit of multi-subunit enzyme affects all subunits
A single activator or inhibitor molecule that binds to one regulatory site will affect the active sites of all subunits
Only need one activator/inhibitor to regulate all active sites
Feedback Inhibition
metabolic pathway switched off by inhibitory binding of its end product to an enzyme that acts early in the pathway