Requirements and Business Process Modeling in Systems Analysis
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
What is the purpose of requirements determination in the SDLC?
To convert high-level business requirements into detailed requirements for model creation.
What is a requirement?
A statement of what the system must do or a characteristic it must have.
What are the two main types of requirements?
Functional requirements (related to processes or data) and non-functional requirements (related to performance or usability).
What is a requirements definition?
A document listing functional and non-functional requirements, which may be prioritized and defines the scope of the system.
What is the role of analysts in creating a requirements definition?
Analysts work with users to verify, change, and prioritize each requirement throughout the analysis workflow.
What is scope creep?
The addition of requirements that meet a need but are not within the current project scope.
What are some common problems in requirements determination?
Inadequate access to users, insufficient specifications, unknown requirements, and difficulties in verifying and validating requirements.
What are the steps involved in requirements analysis?
Understanding the as-is system, identifying improvements, and developing requirements for the to-be system.
What are some requirements analysis approaches?
Problem analysis, root cause analysis, duration analysis, activity-based costing, informal benchmarking, outcome analysis, technology analysis, and activity elimination.
What techniques are used for requirements gathering?
Interviews, questionnaires, observation, and document analysis.
What is the most popular technique for gathering requirements?
Interviews.
What types of questions are used in interviews?
Open-ended, closed-ended, and probing questions.
What are the steps for conducting a questionnaire?
Select participants, design the questionnaire, administer it, and follow up with results.
What is a good practice in questionnaire design?
Begin with non-threatening questions and group items into logically coherent sections.
What is the purpose of observation in requirements gathering?
To validate information gathered through other methods and to understand user behavior.
What is document analysis used for?
To gather information about the as-is system by reviewing technical and user documents.
What is sentence diagramming?
A text analysis technique used to clarify the structure of requirements.
What are user stories?
A way to express requirements in the format: 'As a
What is included in a system proposal?
An executive summary, system request, workplan, feasibility analysis, requirements definition, and current models of the system.
What is the significance of the executive summary in a system proposal?
It provides critical information in summary form to help executives determine which sections to read in detail.
What is the main objective of business process and functional modeling?
To identify business processes and create use-case diagrams and activity diagrams.
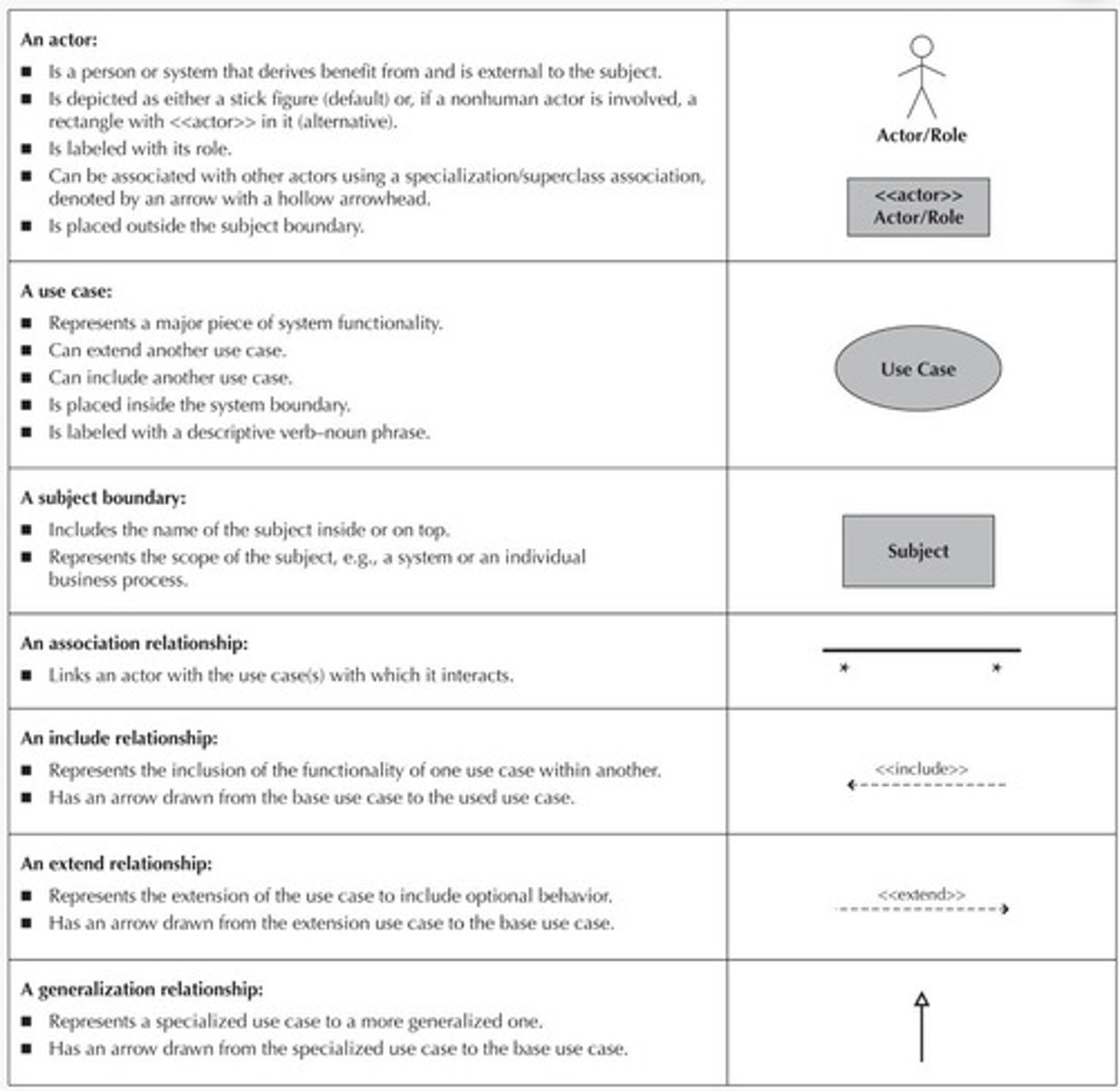
What are use-case diagrams used for?
To model business processes and illustrate the interactions between users and the system.
What is the role of activity diagrams in functional modeling?
To represent the flow of activities within a business process.
What guidelines should be followed when creating use-case descriptions?
Follow rules and style guidelines to ensure clarity and consistency.
What is the importance of critical thinking skills in requirements analysis?
They help analysts to effectively identify and solve problems within the requirements gathering process.
What is the purpose of use cases in business process identification?
Use cases help identify business processes to create a requirements definition.
How do use-case diagrams communicate system functionality?
They illustrate main system functions and user interactions at a high level.
What do use cases represent in UML diagrams?
Each use case represents one function of the system.
What is the difference between overview and detail use cases?
Overview use cases provide a high-level view, while detail use cases contain comprehensive information.
What are essential use cases focused on?
Essential use cases focus on core functionality, independent of implementation.
What do real use cases describe?
Real use cases describe specific steps using actual system details.
What do actors represent in a use case diagram?
Actors represent user roles or external systems interacting with the system.
How are associations depicted in use case diagrams?
Associations connect actors to use cases, showing interactions, often represented as lines.
What is a subject boundary in a use case diagram?
A subject boundary defines the scope of the system, distinguishing internal from external elements.
What is the first step in identifying major use cases?
Review the requirements definition to gain a complete overview of the business process.
What should be noted when identifying primary actors and goals?
Identify actors and their goals to determine system functionality.
What is the role of activity diagrams in business process modeling?
Activity diagrams describe activities that support a business process, often spanning multiple departments.
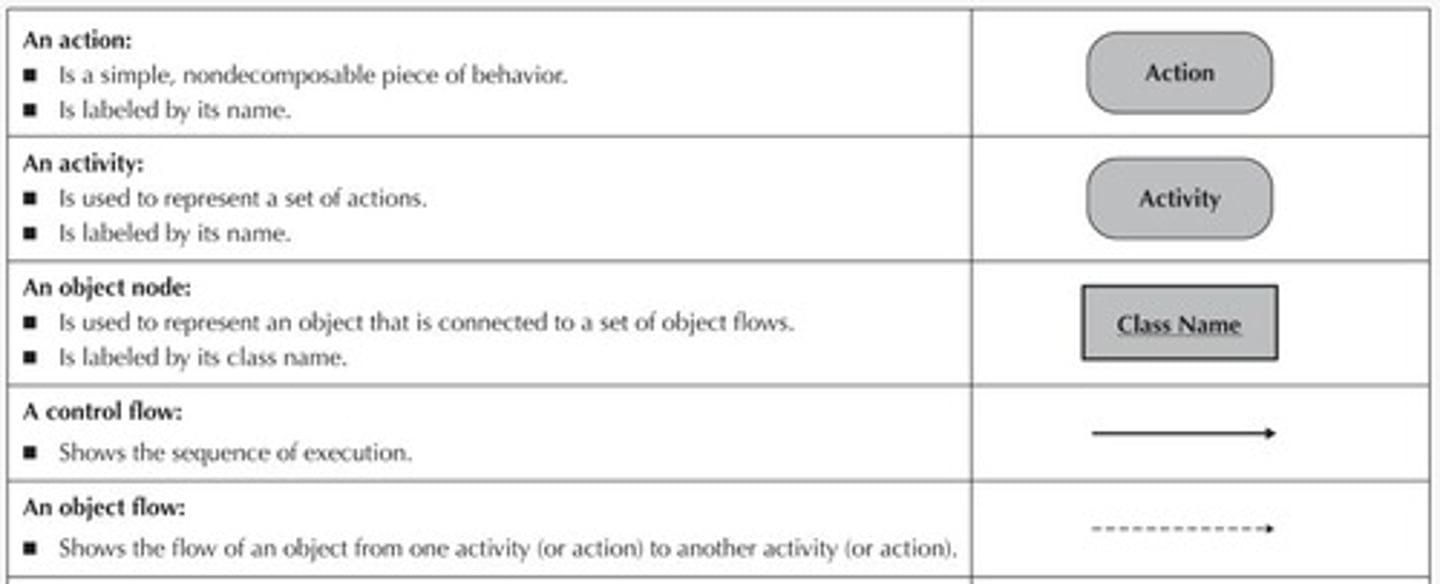
What do actions and activities represent in an activity diagram?
Actions and activities are performed for specific business reasons and can represent manual or computerized behavior.
How are object nodes represented in activity diagrams?
Object nodes are represented as rectangles with the name of the class of the object inside.
What do control flows represent in an activity diagram?
Control flows represent paths of execution through a process, shown as solid lines with arrowheads.
What is the difference between control flows and object flows?
Control flows represent execution paths, while object flows represent the flow of objects through a process.
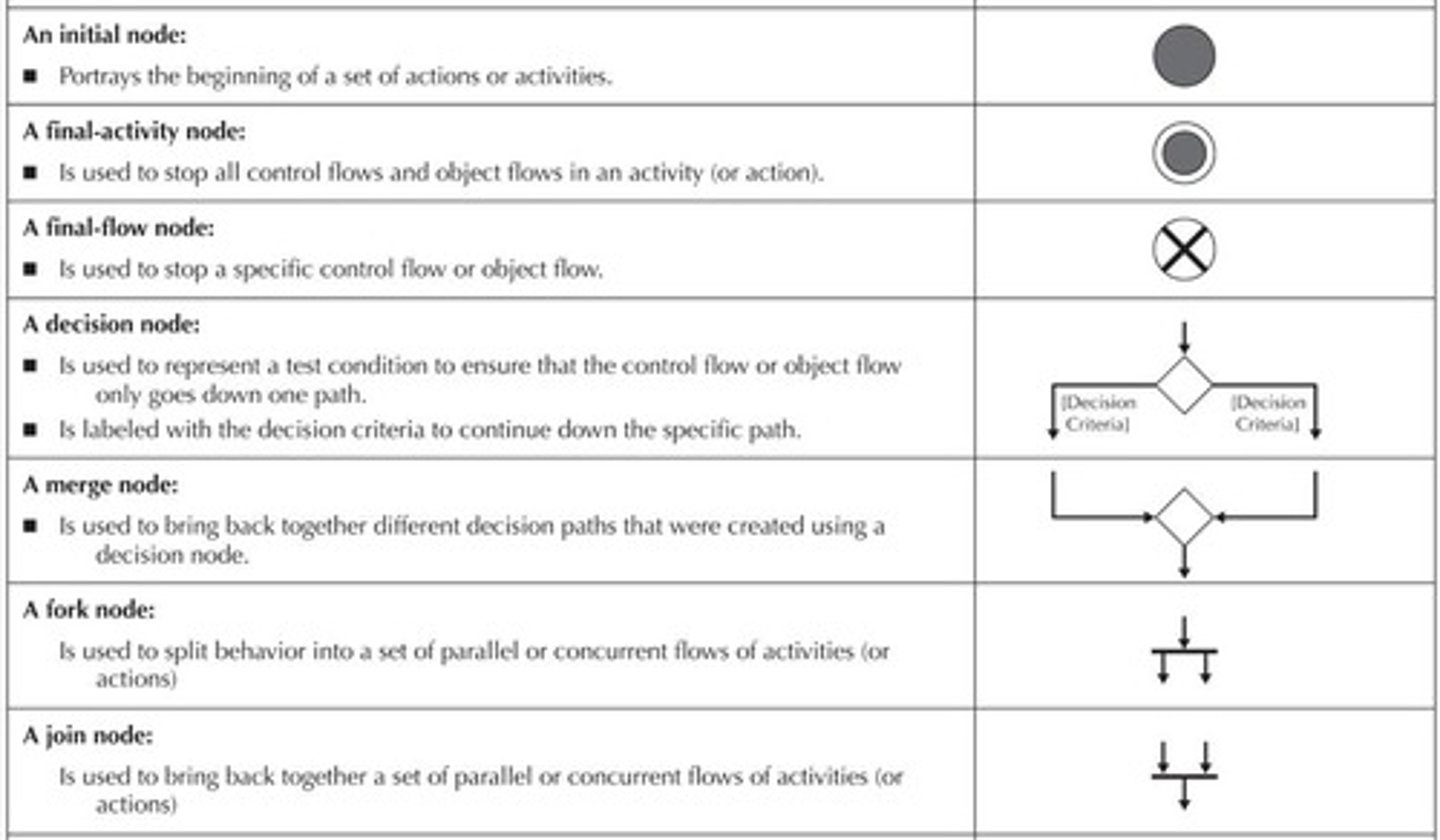
What marks the beginning of a process in an activity diagram?
The initial node, represented by a small filled circle.
What is the purpose of role-playing scenarios in use case modeling?
Role-playing scenarios help test system clarity and completeness.
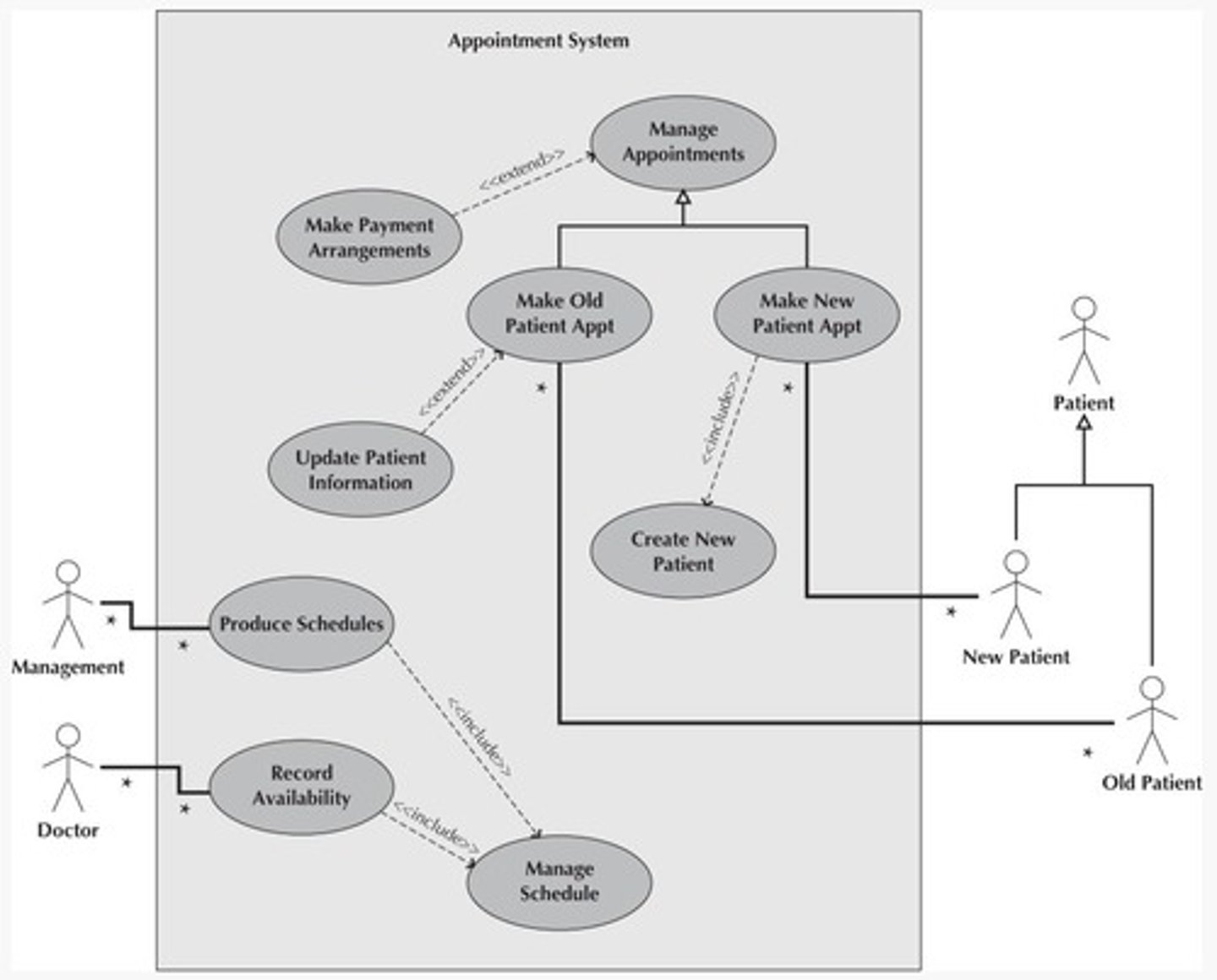
What is the significance of multiplicity in use case diagrams?
Multiplicity indicates many-to-many relationships, such as multiple patients managing appointments.
How should use cases be arranged in a diagram for clarity?
Higher-level use cases should be placed above lower-level ones to enhance understanding.
What is the iterative process in reviewing use cases?
It involves reviewing and adjusting use cases by splitting, merging, or adding new ones as needed.
What is the outcome of using business process models correctly?
They serve as powerful tools for communicating the analyst's understanding of requirements to users.
What is the purpose of a Final-Activity Node in an activity diagram?
It ends the entire process immediately when reached, shown as a circle with a small filled circle inside.
How does a Final-Flow Node function in an activity diagram?
It stops a specific path of execution but allows other concurrent paths to continue, represented by a circle with an X.
What does a Decision Node represent in an activity diagram?
It models a test condition that determines the path to follow, with each path labeled by a guard condition.
What is the function of a Merge Node in an activity diagram?
It combines multiple paths from earlier decisions into one, sometimes omitted for clarity.
What does a Fork Node do in an activity diagram?
It splits a process into multiple parallel or concurrent paths.
What is the purpose of a Join Node in an activity diagram?
It merges separate parallel or concurrent flows into a single path.
What are Swimlanes used for in an activity diagram?
They assign responsibilities to different actors, roles, or objects, improving clarity and organization.
What is the first step in creating an activity diagram?
Choose a business process to model from previously identified ones.
What should be identified after selecting a business process for an activity diagram?
Determine the necessary activities for the business process.
What is the role of control flows and nodes in an activity diagram?
They define the logic of the business process, including decision and merge nodes.
When should object nodes and flows be included in an activity diagram?
They should be included if the information captured in one activity is used later in the process.
What is a Use Case Description?
It offers comprehensive documentation of the functionality associated with each use case, linked to a specific user role.
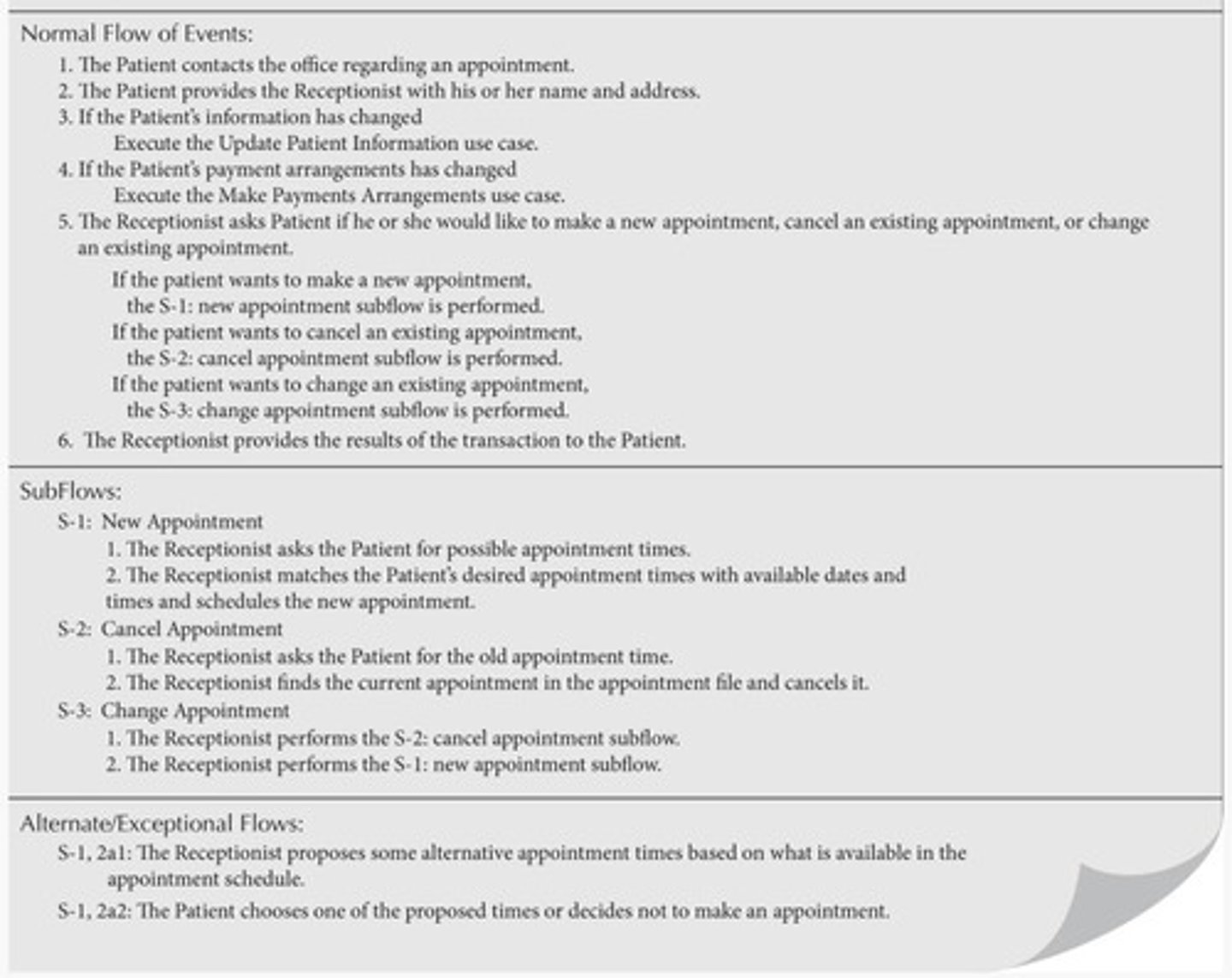
What is included in the Overview of Use Case Section?
Basic background information, use-case name, ID, type, primary actor, and importance level.
What does the Trigger in a Use Case Description signify?
The event that starts the use case, which could be external or temporal.
What are the three categories of event flows in a Detailed Use Case Section?
Normal Flow of Events, Subflows, and Alternative or Exceptional Flows.
When should events be factored into subflows in a use case?
If the normal flow is too complex to be easily understood.
What are some optional characteristics included in a Use Case Description?
Complexity level, execution time, system, data flows, attributes/constraints, preconditions, and guarantees.
What is the first step in creating a Use Case Description?
Select a use case to document based on its importance level.
What should be described in the normal flow of events?
Focus on what the business process does, listing steps in order from first to last.
What is the significance of Swimlanes in an activity diagram?
They help clarify who performs what activity in the process.
What is the purpose of the Importance Level in a Use Case Description?
It helps prioritize use cases based on their significance for the system's version.
What does the term 'Association' refer to in Use-Case Relationships?
Communication between the use case and its actors.
What does the 'Extend' relationship in use cases indicate?
Optional behavior that extends the functionality of a use case.
What is the goal when creating use cases and diagrams?
To ensure clarity and usability while maintaining an effective level of detail.
What is the purpose of creating a Use Case Description?
To outline the normal flow of events and ensure steps match corresponding activities.
How many steps should ideally be included in a Use Case Description?
Between 3 to 7 steps.
What should be done with large steps in a Use Case Description?
Break them down into smaller, manageable steps.
What is the SVDPI format used for in defining flows?
It maintains a structured format for clarity and consistency.
What should be reviewed to ensure accuracy in a Use Case Description?
The use case should be reviewed with users to confirm each step is correct.
What is the role of role-play testing in validating Use Cases?
It helps confirm the validity of the use case steps by having users act them out.
What is the relationship between activity diagrams and use-case descriptions?
Each activity in the diagram must correspond to an event in the use-case description.
What must be ensured regarding actors in use-case diagrams?
All actors in the use-case description must appear in the use-case diagram.
What are the three types of relationships that should be included in use-case descriptions?
Include, extend, and generalization relationships.
What is a class in object-oriented systems development?
A general template used to create specific instances or objects in the problem domain.
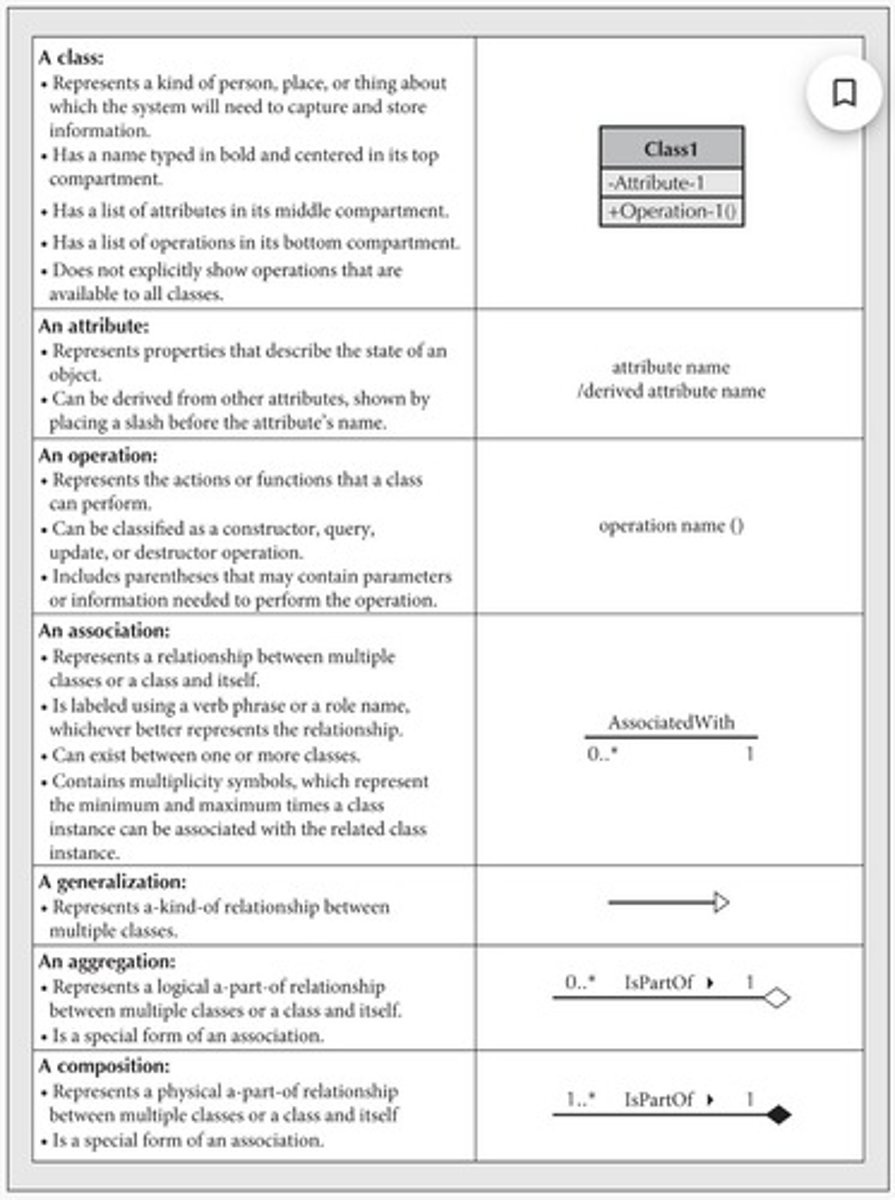
What distinguishes concrete classes from abstract classes?
Concrete classes create objects, while abstract classes are useful abstractions that do not exist in reality.
What does an attribute represent in a class?
A piece of information relevant to the class's description within the application domain.
What is the purpose of an operation in a class?
To describe the actions that instances of the class can respond to.
What are generalization and specialization relationships?
Generalization is a relationship where one class is a broader category, while specialization is where a class is a more specific instance.
What is an association class?
An association treated as a class in a many-to-many association because it has attributes that need to be remembered.
How is the unique identifier for an association class formed?
By concatenating the keys of the attached classes.
What is the significance of UML rules in activity diagrams?
They ensure that different types of nodes and flows adhere to established standards.
What should be done if the key for an association class cannot be formed correctly?
The model is considered incorrect and needs to be revised.
What is the main focus during the iteration of the use case process?
To refine and improve the use cases while adapting to changes.
What is the importance of documenting sufficient use cases?
To ensure enough information is available to proceed with structural modeling.
What is the purpose of peer review in the walkthrough process?
To validate the fidelity of functional models to the requirements.
What is the expected outcome of a walkthrough session?
To identify inconsistencies and errors in the models.
What should be done to simplify complex use cases?
Look for opportunities to decompose them into smaller, more manageable cases.
What is the relationship between structural models and functional models?
Structural models must be verified and validated against functional models for consistency.
What is the role of attributes in an association class?
Attributes in an association class store additional information relevant to the relationship.
What is the unique identifier for a CourseEnrollment association class?
The concatenation of CourseNumber, SectionNumber, and Student ID.
What does it indicate if a key cannot be formed by concatenating endpoint keys in an association class?
It indicates that the model is incorrect.
What is a whole-part relationship?
A relationship where one class is a component of another class.
What is aggregation in object-oriented design?
A whole-part relationship where the component can exist separately and be removed.