1.2.5 Elasticity of Supply
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What does Price Elasticity of Supply mean?
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES) is the responsiveness of quantity supplied for a product to change in it’s price.
What is the formula for (PES)?
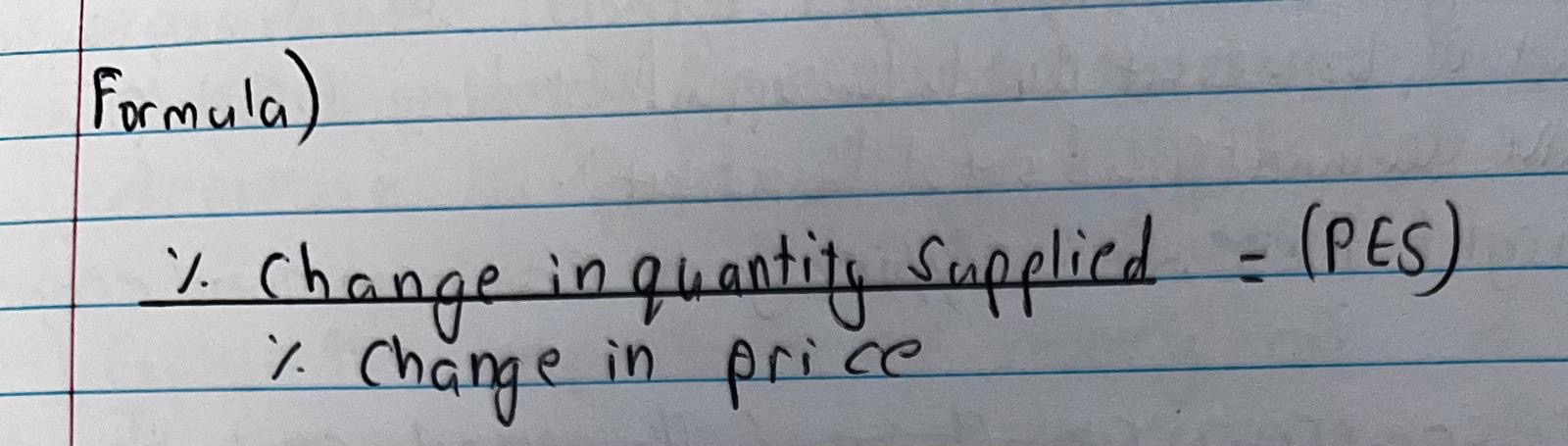
Why does the Supply Curve slope upwards?
The supply curve is upwards sloping so (PES) is always is a positive value.
What are the Numerical Values of (PES)?
Unitary
Relatively Elastic
Relatively Inelastic
Perfectly Elastic
What is Unitary elastic PES? Example?
Unitary PES is where PES=1 quantity supplied changes by exactly the same percentage as price.
Eg) A 7% increase in the price in the price of the bread led to a 7% quantity supplied, PES would be PES= (7/7=1.0)
What is Relatively Elastic PES? Example
Relatively elastic PES is where PES > 1 quantity supplied changes by a larger percentage than price so supply is relatively responsive to price.
Eg) A 2% decrease in the price of a Laptop led to a 12% decrease in quantity supplied, then PES would be: (-12/-2 = 6.0)
What is Relatively inelastic? Example?
Relatively inelastic PES is where PES<1 quantity supplied changes by a smaller percentage than price so supply is relatively unresponsive to price.
Eg) A 10% increase in the price of wheat lead to a 5% increase in quantity supplied then PES would be: (5/10 = 0.5)
What is Perfectly elastic? Example?
Perfectly Elastic is where PES=infinity a change in prices means that quantity supplied falls to 0 and supply is very responsive to price.
Eg) If price changes supply will go zero so price has to remain constant.
What is Perfectly Inelastic PES? Example?
Perfectly inelastic PES is where PES = 0 and a change in prices has no effect on output so demand is completely unresponsive to price.
Eg) A 10% increase in the Price of a Product led to no change in quantity supplied, then PES would be: (0/10 = 0.0)
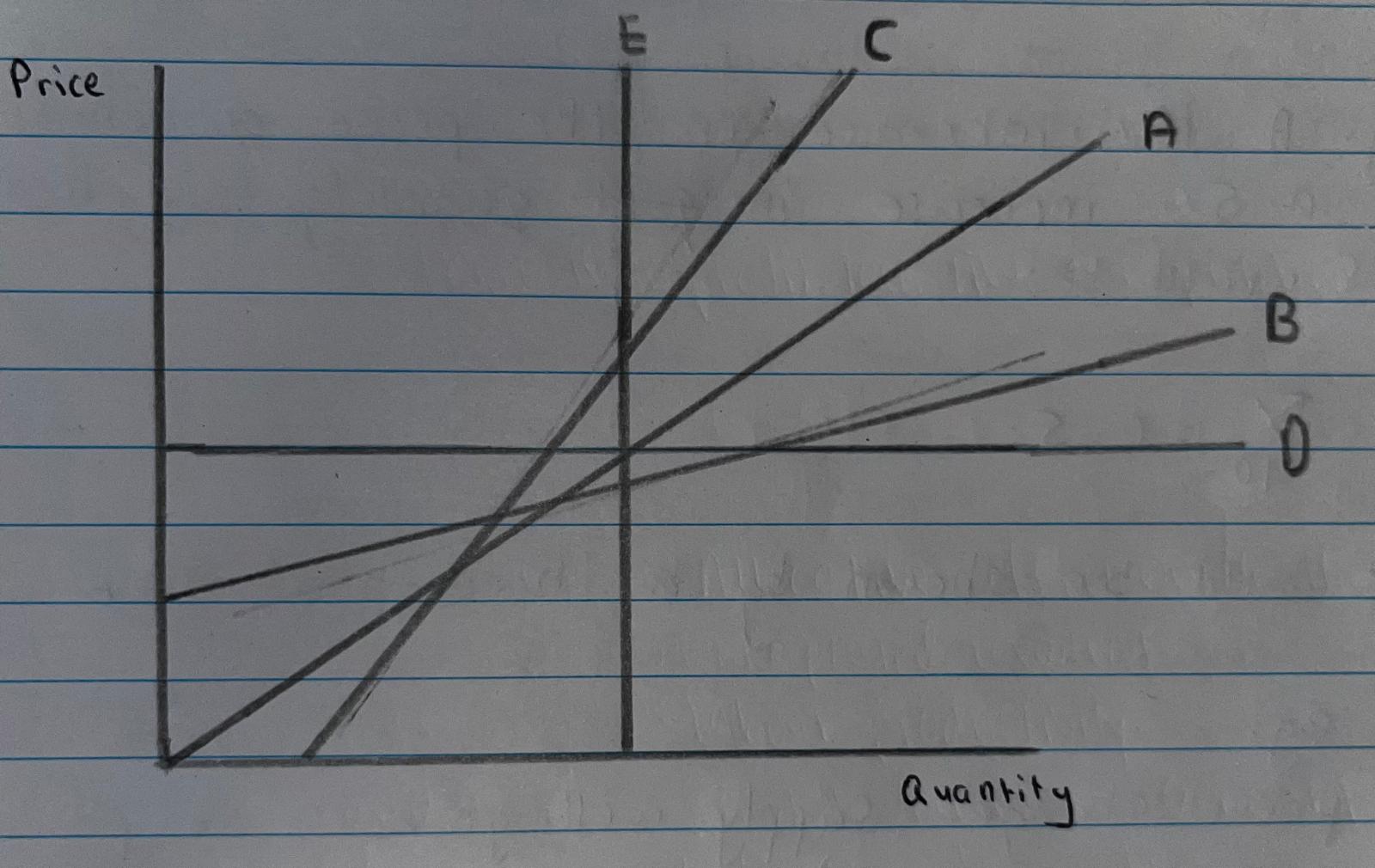
A = Unitary/ B = Relatively Elastic/ C = Relatively Inelastic/ D = Perfectly Elastic/ E = Perfectly Inelastic
What factors affect PES?
Time, Availability of Stocks, Availability of Substitutes
How does Time affect PES?
In the Short Run, at least one factor of production is fixed, so supply tends to be inelastic.
While in the Long Run, firms can adjust all factors of production making supply more elastic. The more time producers have to respond to price changes, the more elastic the supply becomes.
How does Availability of Stocks affect PES?
If firms hold large stock of goods, they can respond quickly when prices rise, making supply more elastic.
For goods that cannot be stored for long periods, such as perishable goods like bread, supply is more inelastic.
The greater the availability and durability of stock, the more elastic the supply will be.
How does Availability of producer Substitutes affect PES?
If producers can easily switch to making alternative products, supply will be more elastic.
For e.g. if a car manufacturer can quickly change from producing one model to another, supply is elastic.
When it is difficult to switch production between goods, supply is more inelastic.
Evaluation Factors affecting PES?
Time: Supply is more elastic in the LR. Some industries face delays (e.g. construction and planning, laws)
Stock : Building Stock will cause Firms to pay admin costs.
F.O.P: Skilled Labour will require extra training and increase in costs.