Comprehensive Biology Exam Review: Cell Structure, Genetics, and Molecular Biology
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
What would an electron microscope be needed to view?
Ribosomes
What is present in all cells?
Cytosol, plasma membrane, ribosomes, DNA, central dogma
What factors affect seeing things clearly using a microscope?
Contrast, magnification, and resolution
When was the cell theory proposed?
1839
Who proposed the cell theory?
Botanist Schleiden and Zoologist Schwann
Which color of visible light gives the best resolution in a light microscope with a numerical aperture of 1.0?
Violet
What is serine?
An uncharged, polar amino acid.
How many nanometers are in 12 millimeters?
12,000,000
How many valence electrons are in carbon?
4
Which amino acid is INCOMPATIBLE with the formation of alpha helices?
Proline, because it has a ring structure.
Which statements about the plasma membrane of cells are correct?
None of the above is correct.
What is the maximum magnification of a standard light microscope?
Approximately 1,000x.
Which of the following is a disaccharide?
Sucrose.
Who proposed the fluid-mosaic model of the plasma membrane?
Singer and Nicholson.
What are the four types of proteins?
Storage, transport, structural, receptor.
What is the simplest amino acid?
Glycine.
Which chemical bond is due to the random accumulation of electrons?
Van der Waals interactions.
What is the resolution of a microscope using a light source with a wavelength of 600 nm and a numerical aperture of 0.5?
732.
Which chemical bonds act in protein folding?
All: Electrostatic attractions, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions, hydrophobic forces.
What are the four macromolecules of life?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
Which elements make up 96% of all living matter?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (CHON).
What is the percentage of water in cells?
Ranges from 75-95%.
What are the universal building blocks of all living things?
Cells.
Who demonstrated spontaneous formation of organic compounds in primitive Earth conditions?
Stanley Miller (1953).
What are the three domains of life?
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukaryotes.
Which type of microscopy can generate a 3D image?
Confocal, interference-contrast, scanning electron.
What is the role of cholesterol in cell membranes at normal body temperatures?
Makes cell membranes less fluid.
Which molecules have a glycerol backbone?
Phospholipids, triglycerides.
What is the charge of oxygen in a polar covalent bond with hydrogen?
Partial negative charge.
What is the strongest chemical bond in cells?
Covalent.
How many double bonds are in docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)?
6.
What are the basic amino acids?
Arginine, lysine, asparagine, and histidine.
What is the function of a protein domain?
Structurally independent part of a protein that folds on its own and performs a specific function.
Who demonstrated spontaneous formation of organic compounds in primitive conditions?
Stanley Miller
Name two basic amino acids.
Arginine (Arg) and Histidine (His)
What is a protein domain?
A structurally independent part of a protein that folds on its own and performs a specific function.
What percentage of the mass of most plasma membranes do proteins make up?
50%
What can the carboxyl group in amino acids do to lower pH?
Donate hydrogen.
Why must the phospholipid membrane of cells be a bilayer?
Due to the hydrophobic properties of the fatty acid tails and the hydrophilic heads.
What does scramblase do?
Transfers phospholipids randomly from one side of the lipid bilayer to the other.
What is the primary structure of a polypeptide?
The amino acid sequence.
Which polymers are created by dehydration or condensation reactions?
Polysaccharides, Polypeptides, Nucleic acids.
When did prokaryotes first appear on Earth?
Approximately 3.5 billion years ago.
How many oxygens and hydrogens does a monosaccharide with 4 carbons have? (CH2O)n
4 oxygens and 8 hydrogens.
What part is common to all amino acids?
Amino group.
How many fatty acid chains do phospholipids have?
2 fatty acid chains.
What is the carbohydrate in DNA?
Deoxyribose.
What is the role of cohesins and Histone H1 in interphase chromosomes?
Involved in condensing the interphase chromosomes.
What happens to cells in hypertonic environments?
They shrivel.
Does the RNA sequence need to be transcribed before making a peptide?
No, it does not.
What is the primary sequence of the peptide from the given RNA sequence?
5’ -GAUCCGGACAGAUGCAGACGGUUAAUUGCAGUCGAUAAACGGGUAGGUUCGA
Start Gln Thr ? Asn Cys ? Arg Stop.
What can damage DNA?
Carcinogens, Increased thermal collisions, Oxygen free radicals, UV light.
What does telomerase do?
Extends the end of the lagging strand in DNA.
Why is the sodium-potassium pump important to cells?
It uses about 30% of the ATP within the cell and regulates sodium and potassium concentrations.
How many chromosomes and nucleotide pairs are in the human genome in somatic cells?
46 chromosomes and 3.1 billion nucleotide pairs.
Which type of DNA repair requires replicated chromosomes to be close?
Homologous recombination.
How many nucleotide pairs wrap around the histone core in nucleosomes?
147 nucleotide pairs.
What occurs during the depolarization stage of an action potential?
Sodium ions enter the cell.
Where do proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum enter in the Golgi apparatus?
Cis cisterna.
What determines if a ribosome will attach to the endoplasmic reticulum?
Polypeptide.
What are mechanisms by which substances move into organelles?
Direct transport across membrane, pore proteins, & vesicles.
How often does DNA polymerase make errors after proofreading?
About one error in every 1x10^9 nucleotide pairs.
Which RNA polymerase transcribes all protein-coding genes in eukaryotes?
RNA polymerase II.
What does semiconservative DNA replication mean?
Daughter cells have one old strand from the parent cell and one newly synthesized strand.
What happens at axon terminals to transmit signals between neurons?
Neurotransmitters packaged in vesicles LEAVE the presynaptic neuron via secretion.
Which organelle helps cells maintain their shape?
Cytoskeleton.
What role do tRNA molecules play during protein synthesis?
They are adaptors between mRNA and amino acids.
Which organelle is NOT part of the endomembrane system?
Mitochondria.
Where are anticodons found?
In tRNA.
What are some differences between RNA and DNA polymerases?
RNA polymerases don't proofread whereas DNA polymerases check before addition, and proofread after.
RNA polymerases are more prone to mistakes. Errors occur every 1 in 104 nucleotide pairs, whereas DNA polymerase occurs every 1 in 107 nucleotide pairs
DNA polymerase is involved in replication, RNA polymerase is involved in transcription
Where are lipids synthesized?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the error rate of DNA polymerase?
1 in 10^7 nucleotide pairs
What synthesizes lipids in cells?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Who were involved in determining that DNA is the genetic material?
Fred Griffith, Martha Chase, Oswald Avery
What do nucleases do when DNA damage is detected?
Cut out the damaged area in the DNA
What does the serial endosymbiosis theory suggest about mitochondria?
They formed from aerobic bacteria uniting with pre-eukaryotic cells
What is required for the movement of a large 100 kD protein into the nucleus?
Import protein, dilation of the nuclear pore opening, localization sequence in the protein
What are RNA molecules that catalyze chemical reactions called?
Ribozymes
Which molecules can most easily pass through the phospholipid bilayer without assistance?
Steroid hormones
What is the most widely used and abundant activated carrier?
ATP
Which proteins are part of the DNA replication machine?
DNA polymerase, helicase, primase, sliding clamps
What does the codon table allow us to determine?
The polypeptide sequence from the mRNA sequence
Why is the movement of sodium ions into human cells more powerful than potassium ions moving out?
Sodium moves down its concentration gradient and with its voltage gradient toward a negative environment
Who led the research group that discovered the first DNA polymerase?
Arthur Kornberg (1956) found 1st DNA polymerase in E Coli.
What is TFIID?
A general transcription factor found in eukaryotes that binds to TATA boxes and interacts with RNA polymerase II
How long is one turn of the DNA helix?
~3.4 nm
What do histone-modifying enzymes add to histones?
Acetyl, methyl, and phosphate groups
What is catalase?
An oxidative enzyme found in peroxisomes (peroxisomes are organelles that carry out oxidative reactions using molecular oxygen)
What is located at positions A, B, C, and D?
Sodium-driven glucose symport, tight junction, sodium-potassium pump, passive glucose uniport
What does aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase do?
Adds amino acids to tRNA via covalent bonding
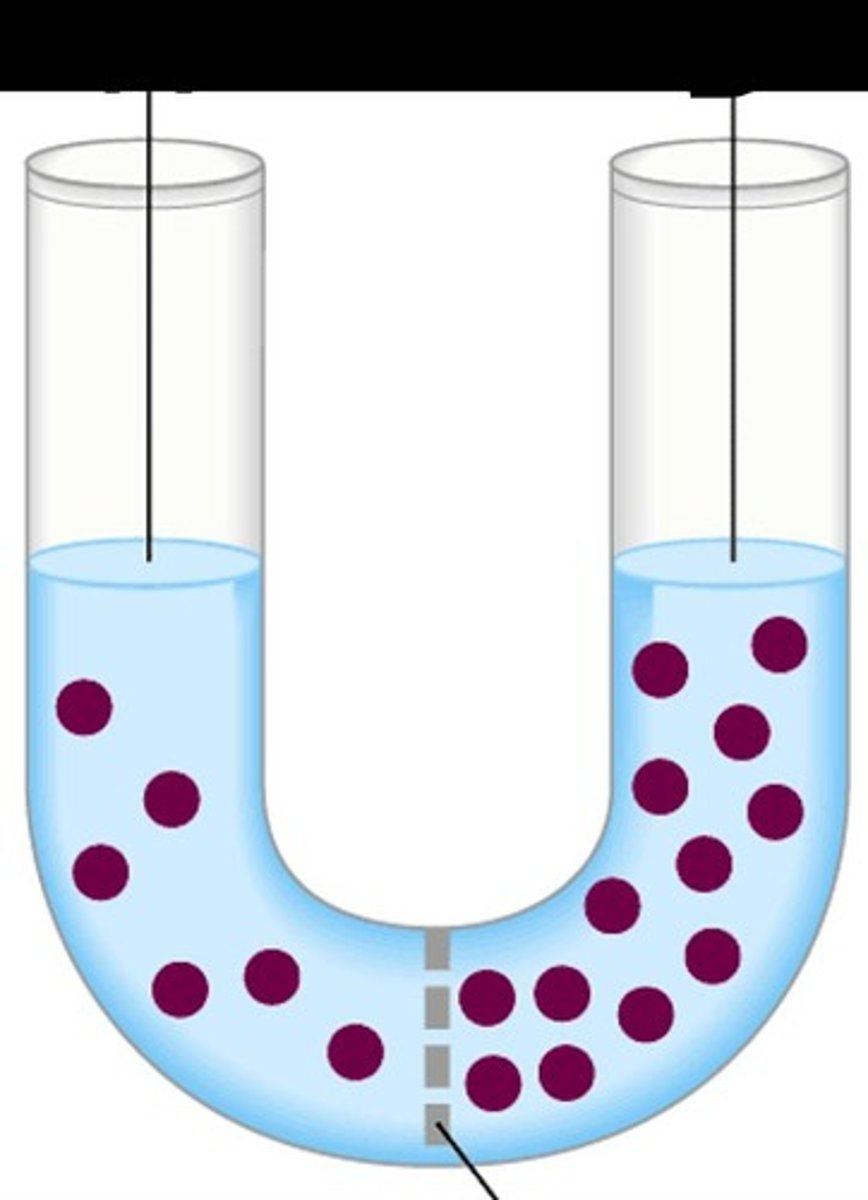
In the pictured situation, which side is the hypertonic solution?
B
What do gradient-driven antiports do?
Use the diffusion of one substance into the cell to provide energy for moving a second substance out of the cell
What is the resting membrane potential of most human cells?
About -70 mV
What does DNA polymerase add nucleotides to?
The 3-prime hydroxyl of DNA
Where can ribosomes be found in eukaryotic animal cells?
Cytoplasm, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, rough ER
Which eukaryotic DNA polymerase allows the replication fork to move past thymine dimers?
Pol eta
What happens to cytosine during deamination?
It changes into uracil
What is the charge on the intracellular side of the membrane in resting cells?
More positive due to high sodium concentration inside and low potassium concentration outside
According to the simple rule of diffusion, where does a substance move?
From high concentration to low concentration
Where is very condensed chromatin found?
Heterochromatin, inactivated X chromosome, telomeres, except euchromatin