propedeutics small animals- neurologic exploration
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
light
mosquito
percussion hammer
what instruments are necessary for performing a neurological exploration?
only hindlimbs
if there is a spinal cord lesion between T2 and L4, what part of the animal do we expect to be affected?
between T2 and L4
if an animal has hind limb paralysis (paraplegia), we can add spinal cord injury to our differential diagnosis. where would we expect the injury to be?
front and hind limbs
an injury to the spinal cord that is cranial to C6 will affect what part of the animal?
8, 13, 7, 3, 5
the spinal cord is divided into segments: ___ cervical, ___ thoracic, ___ lumbar, _____ sacral, and ____ caudal
12
dogs and cats have _____ cranial nerves? (#)
1. mental status
2. posture and gait
3. postural reactions
4. cranial nerves
5. spinal reflexes
6. pain
what are the 6 important points we want to explore when examining an animal's neurologic condition?
1. alert
2. depression (decreased response)
3. disorientation (inappropriate response)
4. stupor (no response to normal stimuli, weak response to painful stimuli)
5. coma (no response)
what are the different levels of mental status that an animal might show?
it is a word used to describe the mental status of an animal. the animal has no response to normal stimuli, and a weak response to painful stimuli
what does stupor mean?
lack of response to any type of stimulus
what does coma mean in regards to the animal's mental status?
depression
what is the word used to describe an animal with decreased response to stimuli?
disorientation
if an animal has inappropriate responses to stimuli (ex- exaggerated), we call this_______
-rotation
-torsion (to the side)
-ventral flexion (head down)
what postural differences can we notice in an animal's head due to a neurological problem?
it is holding its head to the side
what does it mean if an animal is expressing "torsion" of its head?
the animal has a dorsal deviation of its spinal column
what does kyphosis mean?
kyphosis
what do we call this dorsal deviation of the spine?
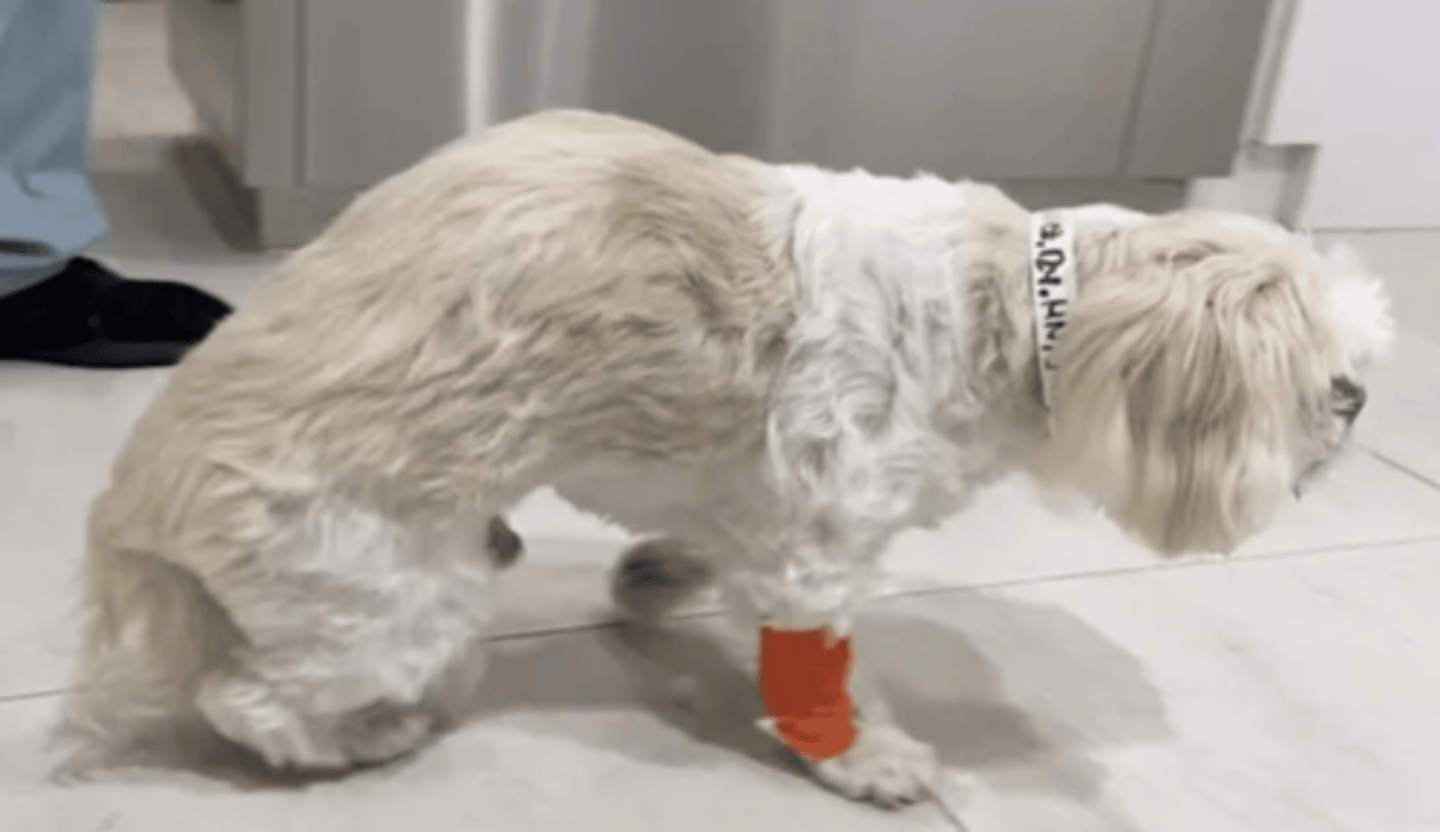

a ventral deviation of the spinal column
what is "lordosis"?
lordosis- ventral deviation of the spinal column
this dog is presenting what?
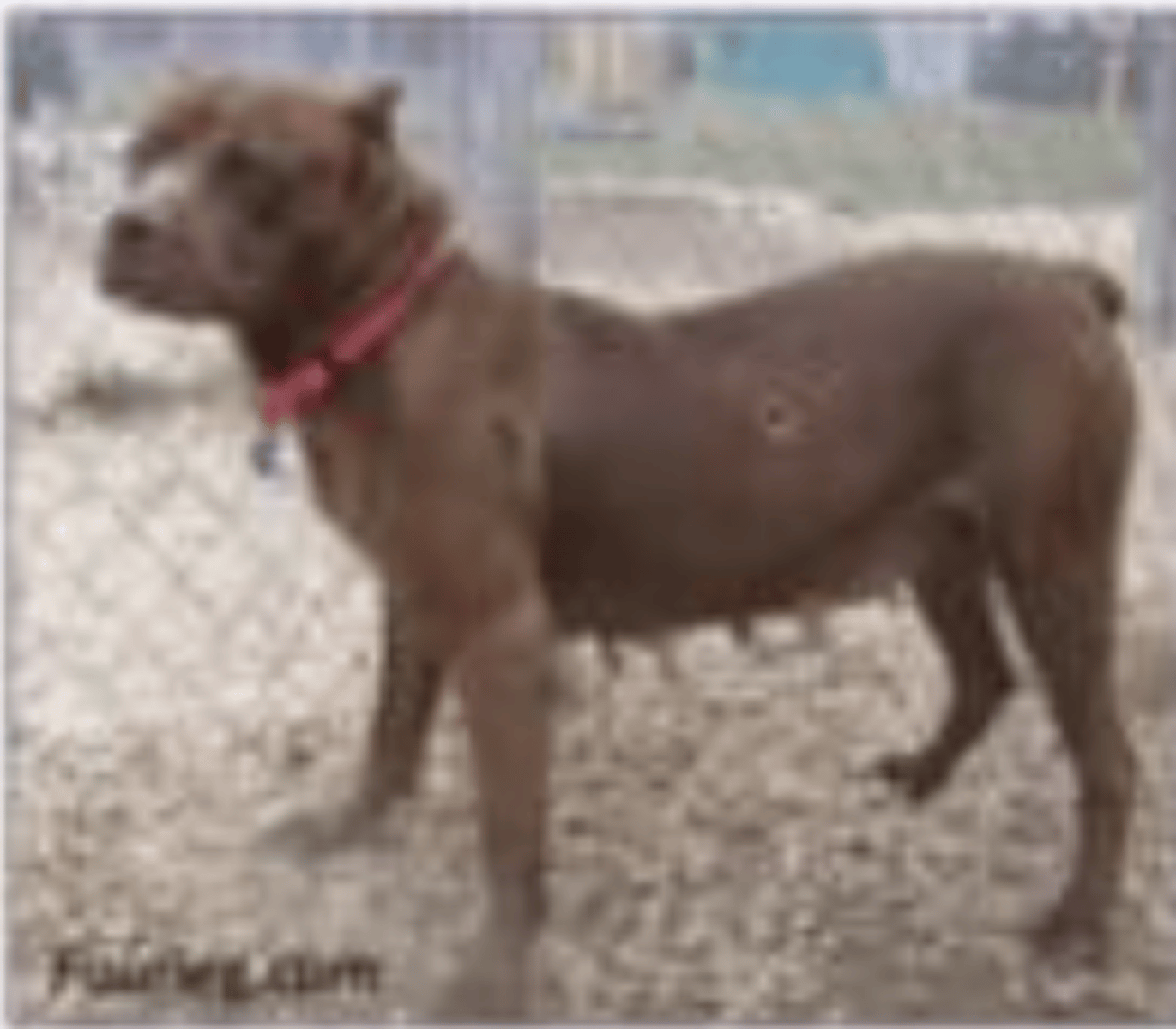

lateral deviation of the spinal column
what is scoliosis?
scoliosis
what type of postural difference does this dog have?
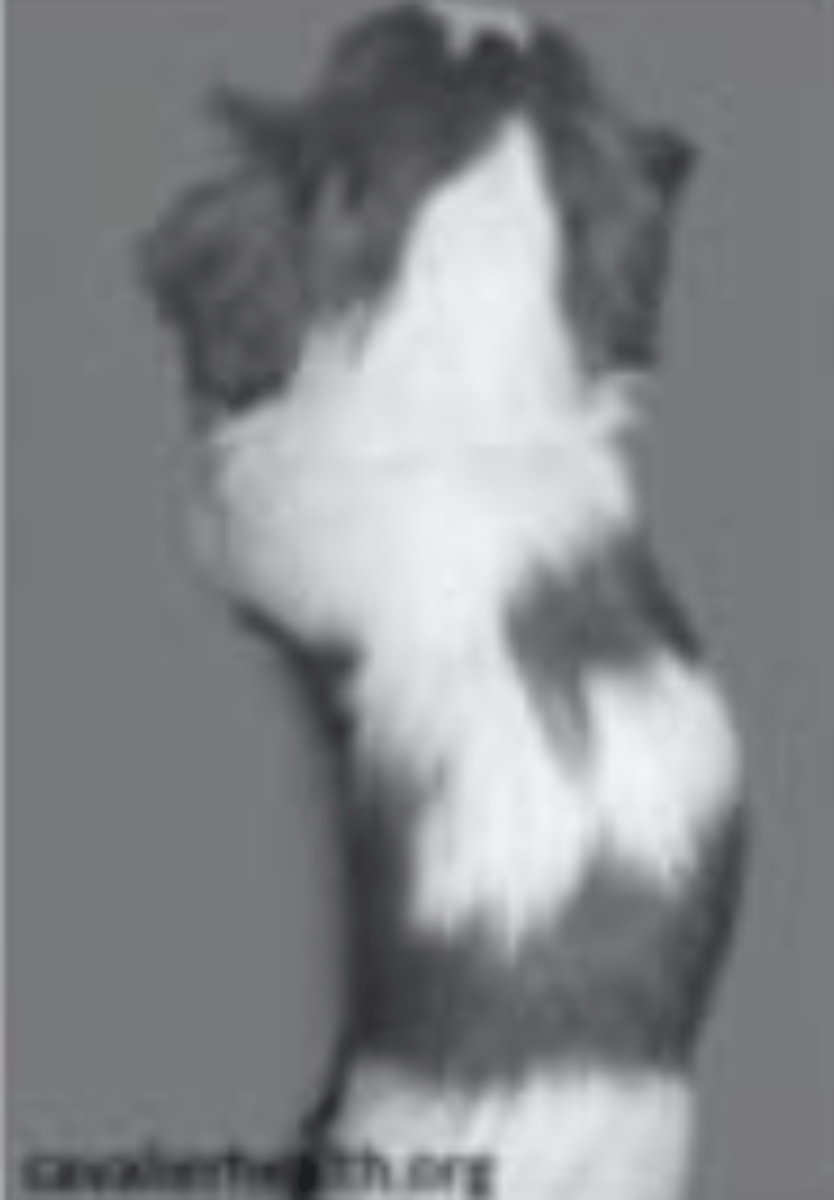

scoliosis
what is 1?

2
which animal has kyphosis?

lordosis
what is the term we use to describe 3?

wide base station
knuckle support
lying/sitting
what postural differences might we notice in an animal in their extremities?
torsion
this abnormal head position is called...
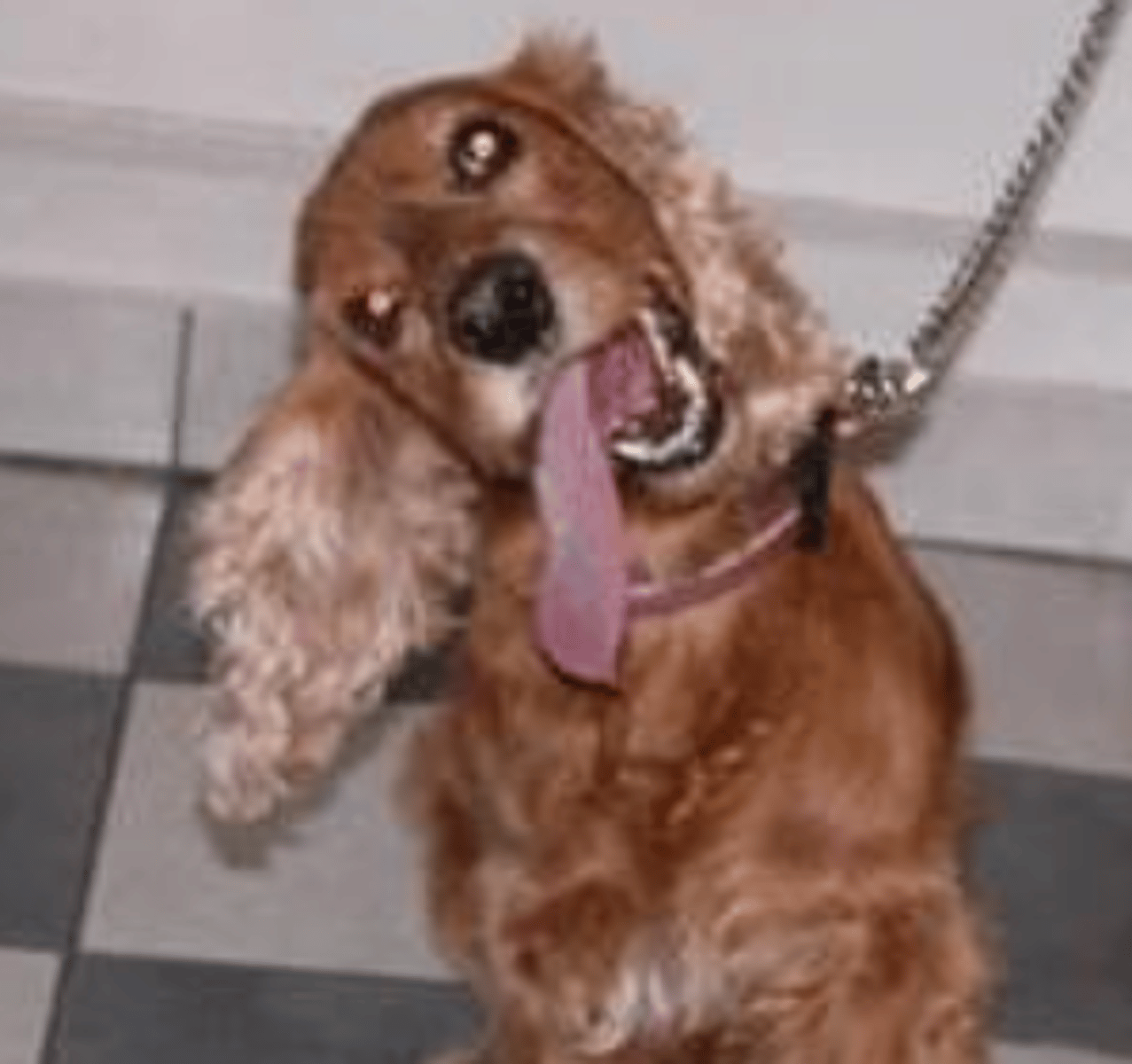

the animal's forelimbs and hindlimbs are spread
what does "wide base station" mean?
wide base station
what do we call this posture?
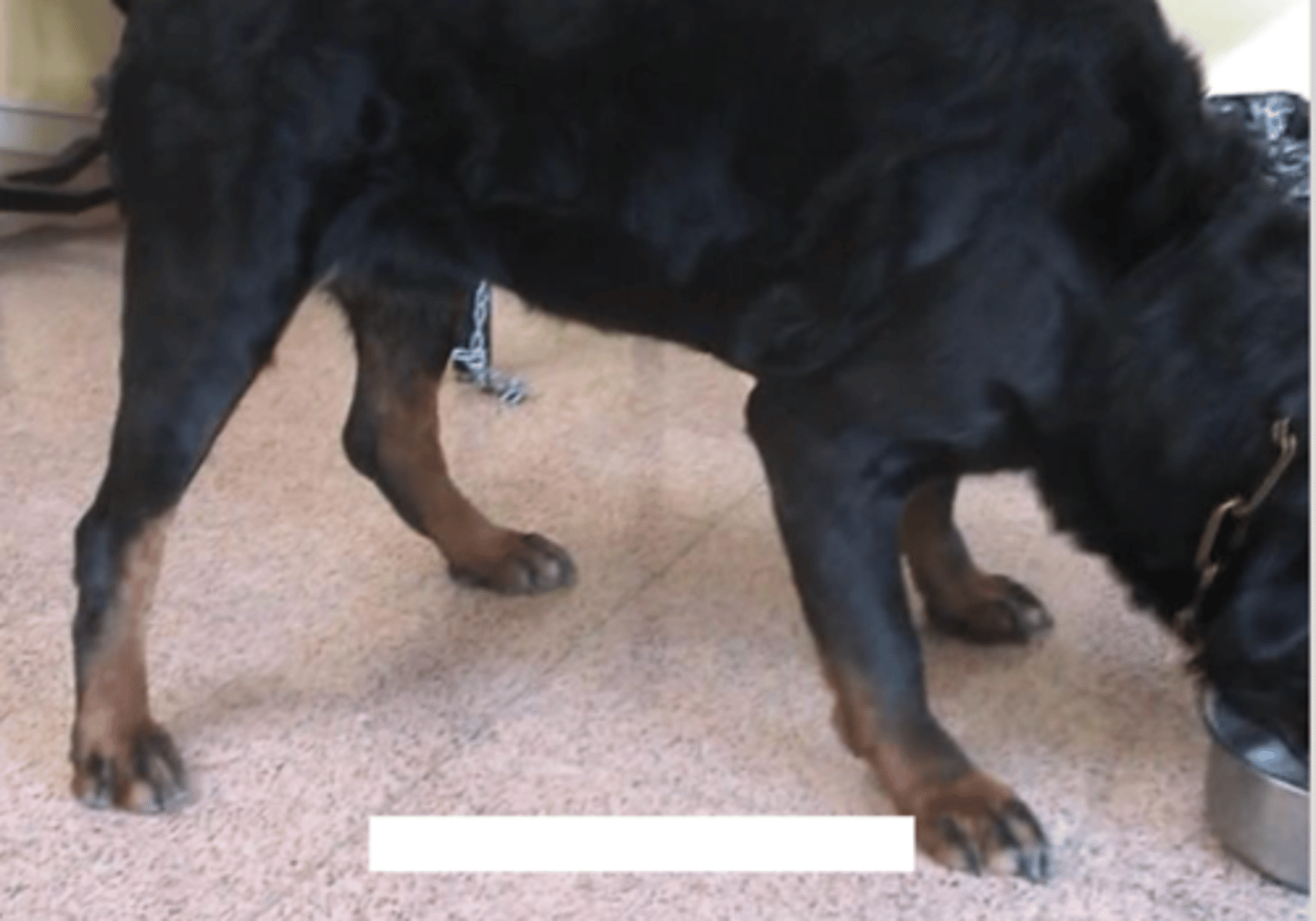

uncoordinated gait
it can indicate lesions in the peripheral sensory nerves, spinal cord, brainstem, vestibular system, or cerebellum
what is ataxia?
proprioceptive
if an animal is dragging his limbs and walking on his knuckles, what type of ataxia is this?
dysmetry- different range and strength for each step.
an animal with a cerebellar lesion will show what type of ataxia?
when the animal is walking with an abnormal range/strength in each step. this is related with a cerebellar lesion.
hypermetry- exaggerated movements, excessive flexion, greater reach
hypometry- reduced flexion, reduced limb reach (small steps)
what is dysmetry? what are the different types?
when an animal walks with exaggerated movements, excessive flexion and a greater reach. very big steps.
this is related to a cerebellar lesion
what is hypermetry?
hypometry
cerebellar lesion
we notice an animal walking with abnormally small steps. what do we call this? what type of lesion is it associated with?
head tilt, falling, tilting and turning while walking, circling
if an animal has a vestibular lesion, what type of gait will it present?
vestibular system
if an animal is walking in circles, tilting and falling, where might he have a problem?
1 limb has reduced motor function
what is monoparesis?
the hind limbs have reduced motor function
what is paraparesis?
all 4 limbs have no movement
what does tetraplegia mean?
-plegia: total loss of voluntary movement
-paresis: reduced motor function
ex- hemiplegia, tetraparesis, etc
what is the difference between -plegia and -paresis?
the limbs of one side of the body have no movement
what is hemiplegia?
paraparesis- the hind limbs have reduced movement
paraplegia- the hind limbs have no movement
what is the difference between paraparesis and paraplegia?
tetraparesis
what is the word for reduced motor function of all 4 limbs?
hemiparesis
what is the word for reduced motor function of 2 limbs of the same side?
monoplegia
what is the word for NO motor function of 1 limb?
paraplegia
a dog comes to the vet, unable to move his 2 hind limbs. what do we call this?
monoparesis
a cat has reduced motor control over his front right limb. what is this called?
yes- if it is just a brain injury, this does not affect gait, only posture
can an animal with a brain injury have a normal gait?
left
brain injuries affect the opposite side of the body
if an animal has an injury on his RIGHT brain, what part of his body will have a postural defect?
right side
spinal cord injuries affect the same side posture and gait
if an animal has an injury on his RIGHT spinal cord, what part of his body will have a postural defect?
both
does a spinal cord injury affect the animal's posture or gait?
only posture
does a brain injury affect the animal's posture or gait?
spinal cord
-brain injuries only affect posture
if an animal has both postural and gait abnormalities, do we suspect a brain or spinal cord injury?
hemiwalking
paw replacement
hopping
wheelbarrowing
extensor postural thrust
visual and tactile placing
what are the different postural reactions for testing an animal's neurologic system?
paw replacement
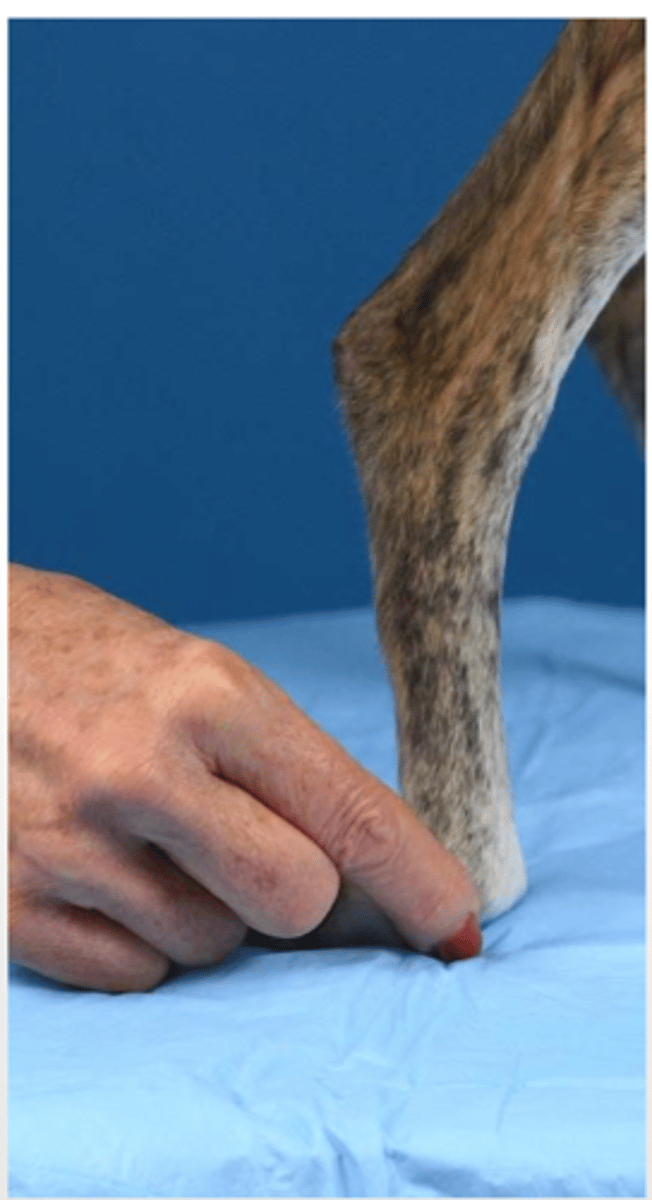
we flex the fingers of one limb so that the dorsal part of the fingers are resting on the table- a healthy animal should put his paw back to normal within 3 seconds.
what is this postural reaction test called? what is the expected result of a healthy animal?
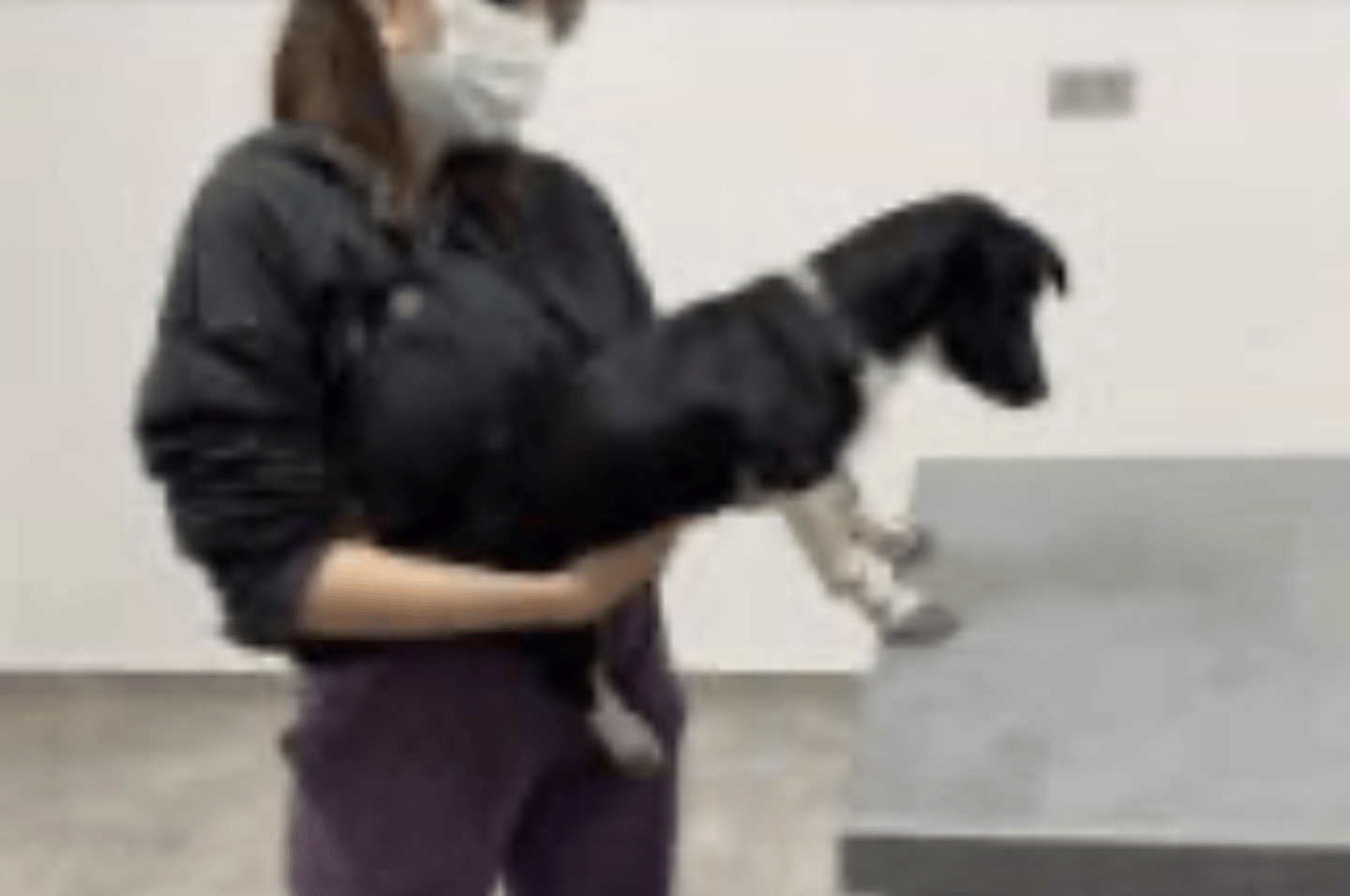
hemi walking
the animal should walk to the side with both limbs moving symmetrically
what is this postural reaction test called? what is the expected result of a healthy animal?
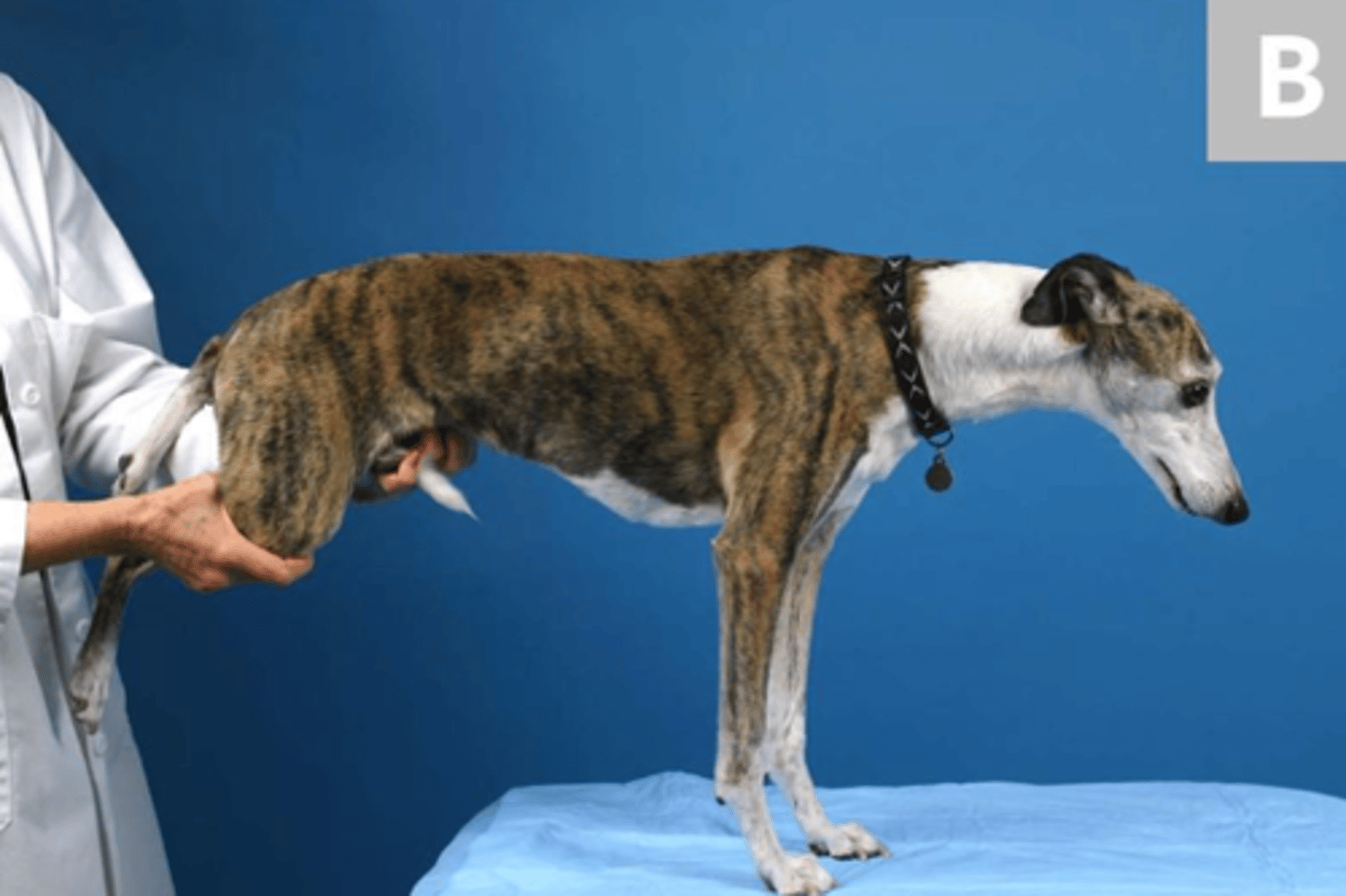
extensor postural thrust
we lift the animal and as we lower it to the ground, it should extend its hind limbs before contact the ground, and then hop backwards once it touches the ground
what is this postural reaction test called? what is the expected result of a healthy animal?
visual or tactile placing reaction
visual- allow the dog to see
tactile- covering the animals eyes
the animal should immediately place its feet on the table
what is this postural reaction test called? what is the expected result of a healthy animal?

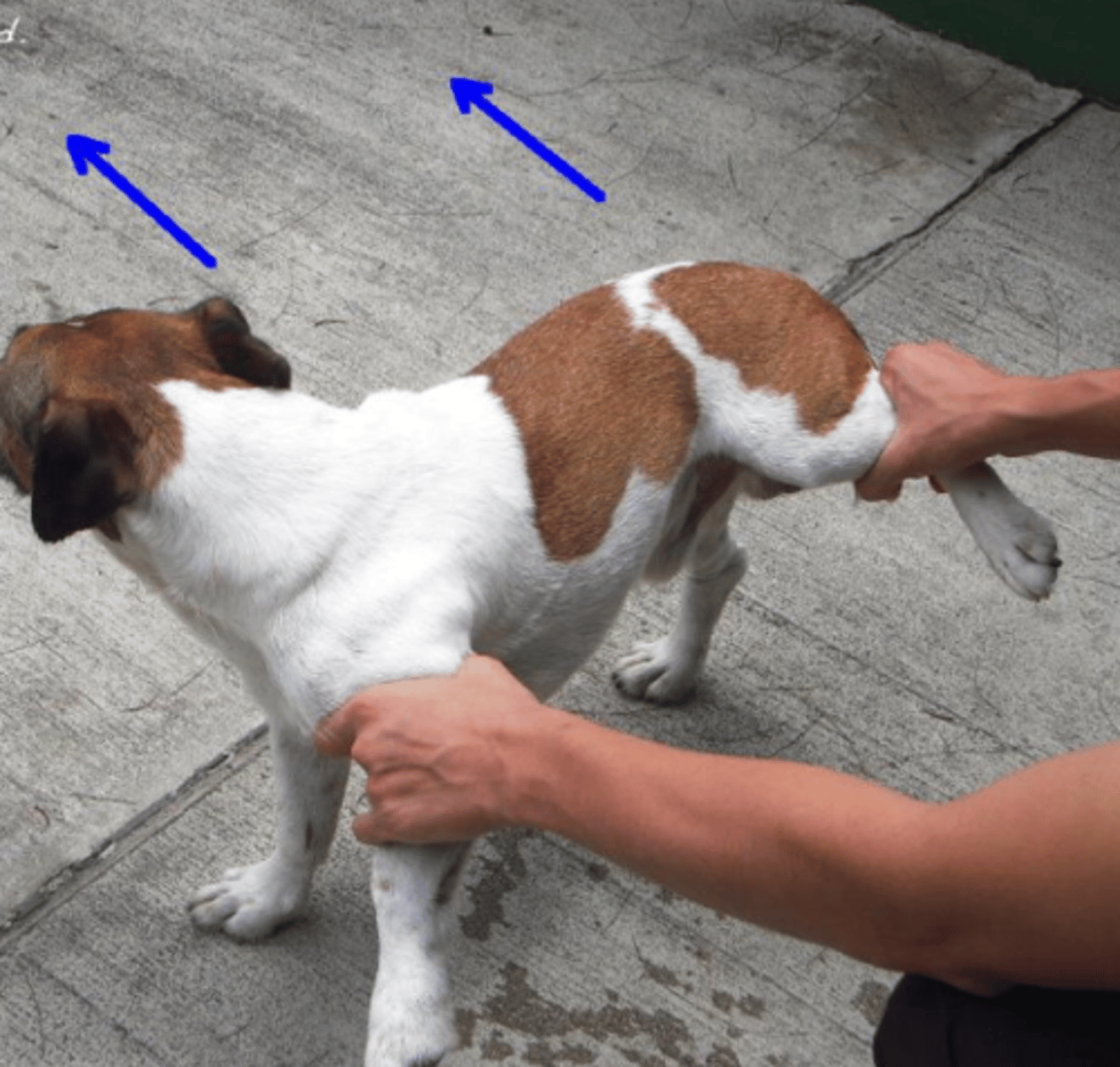
wheelbarrowing
the animal should walk symmetrically with its front limbs while we push it forwards
what is this postural reaction test called? what is the expected result of a healthy animal?
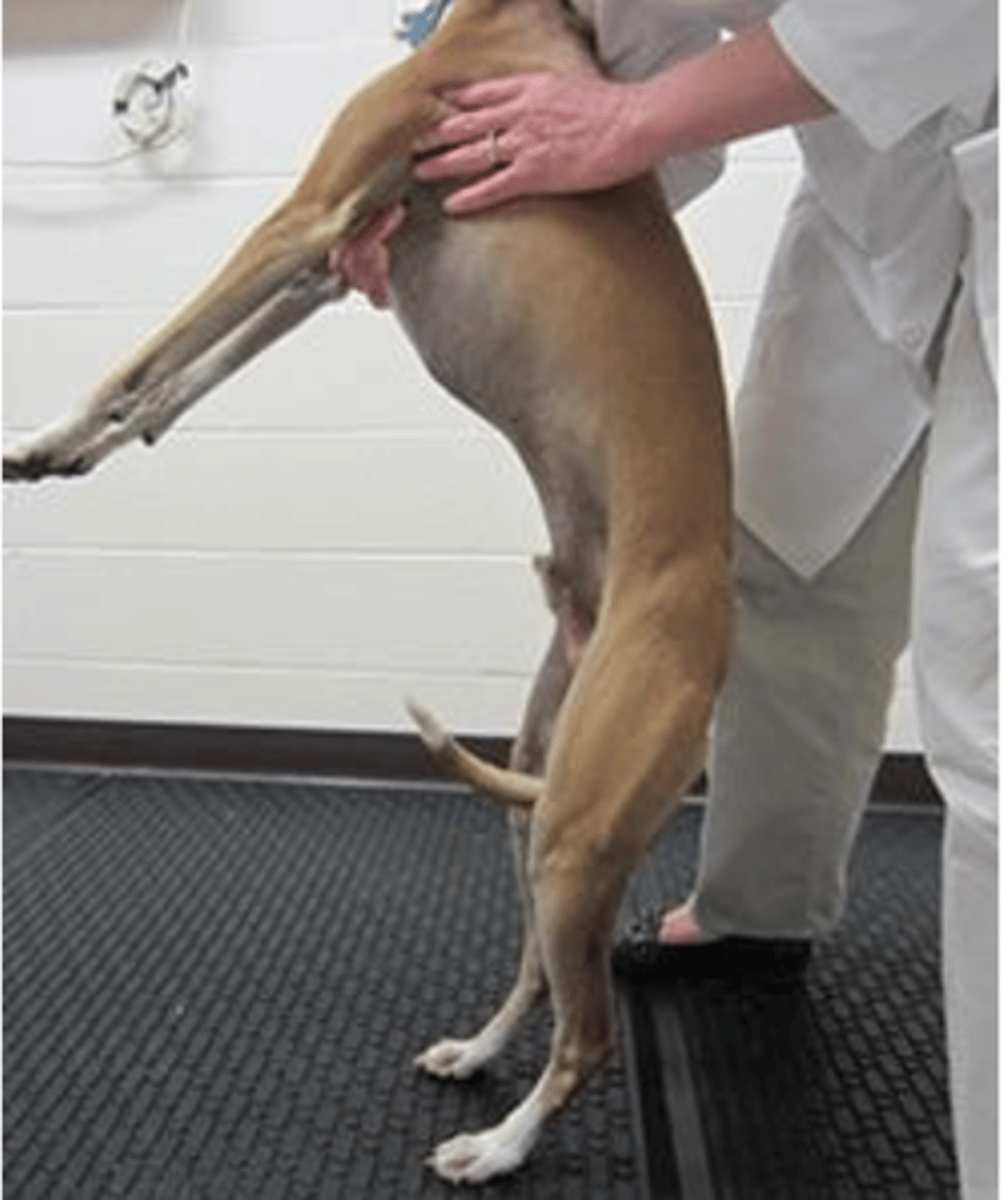
hopping
the animal should walk with the one limb that is not being held.
we should test all limbs.
what is this postural reaction test called? what is the expected result of a healthy animal?
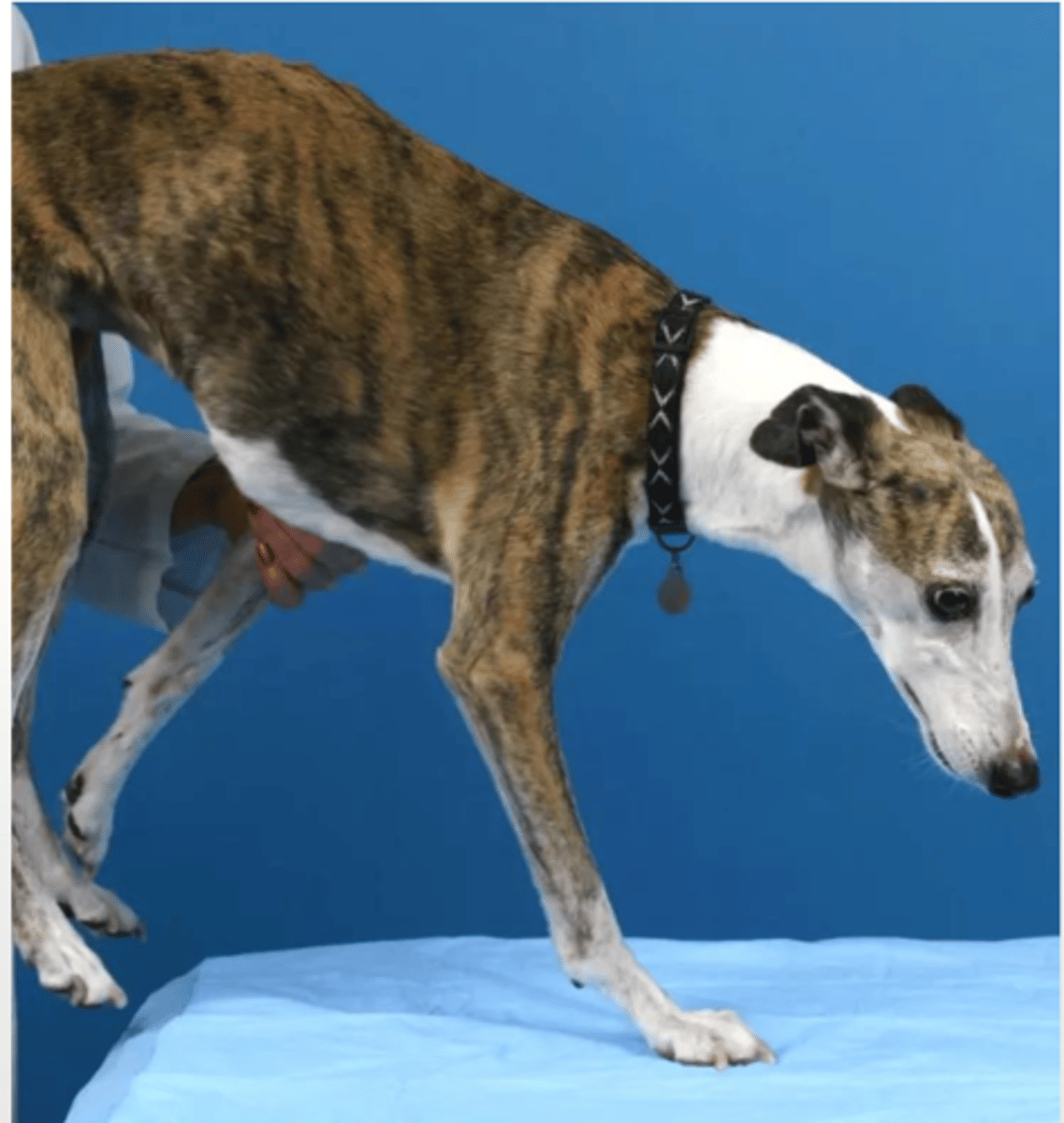
olfactory- I
what cranial nerve does this test?

blindfold the animal and place food in front, see if he reacts
how can we test the olfactory nerve (I)?
menace response
tests the facial (VII) and optic (II) nerves
what is this test called? what is it testing?
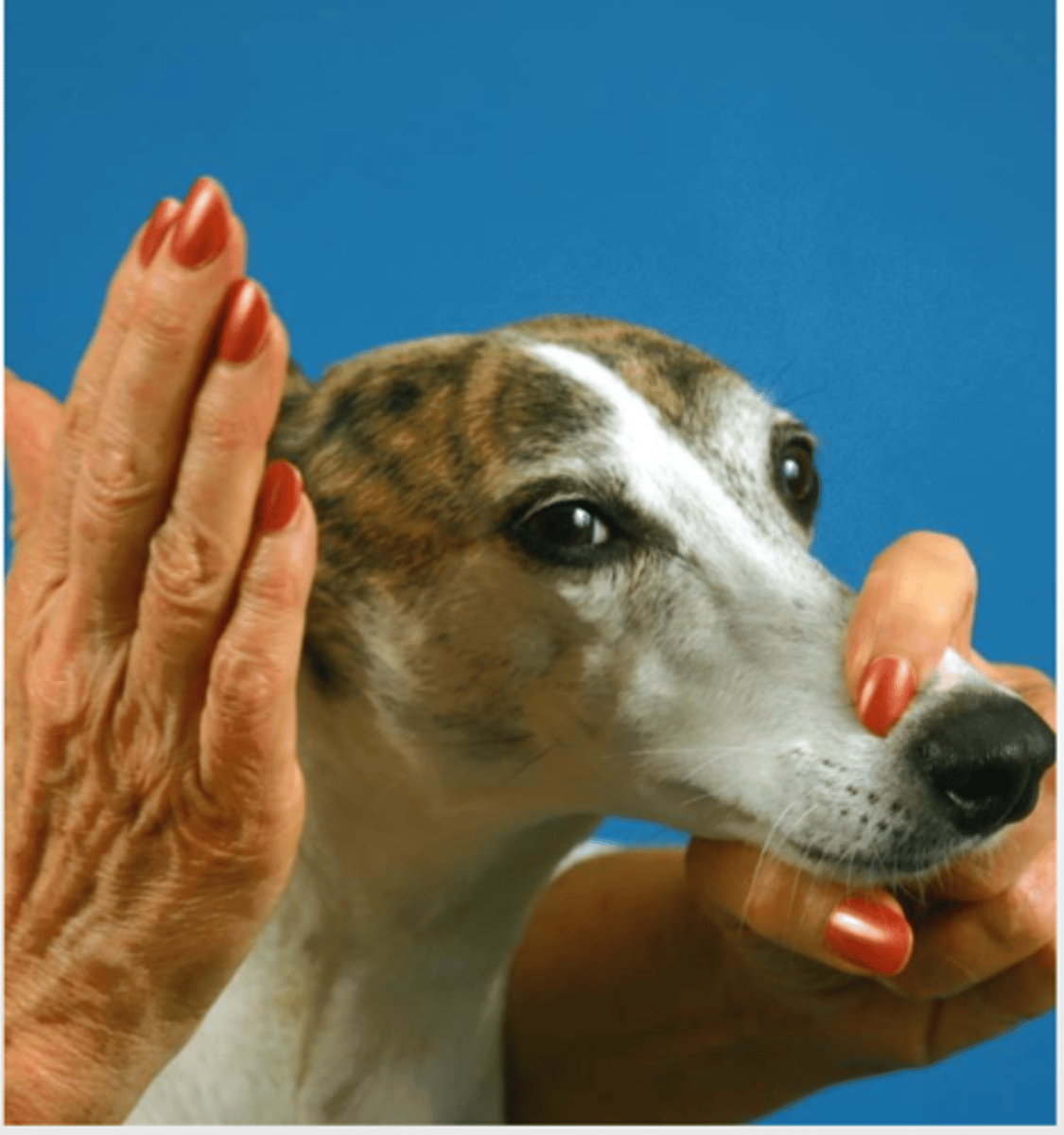

when we bring one hand gently towards the eye, we should observe the animal blink. this is not a reflex, but is a learnt behavior.
this tests the optic and facial nerves
what is the menace response?
direct/indirect pupillary reflex
tests optic and oculomotor nerves
what is this test for?
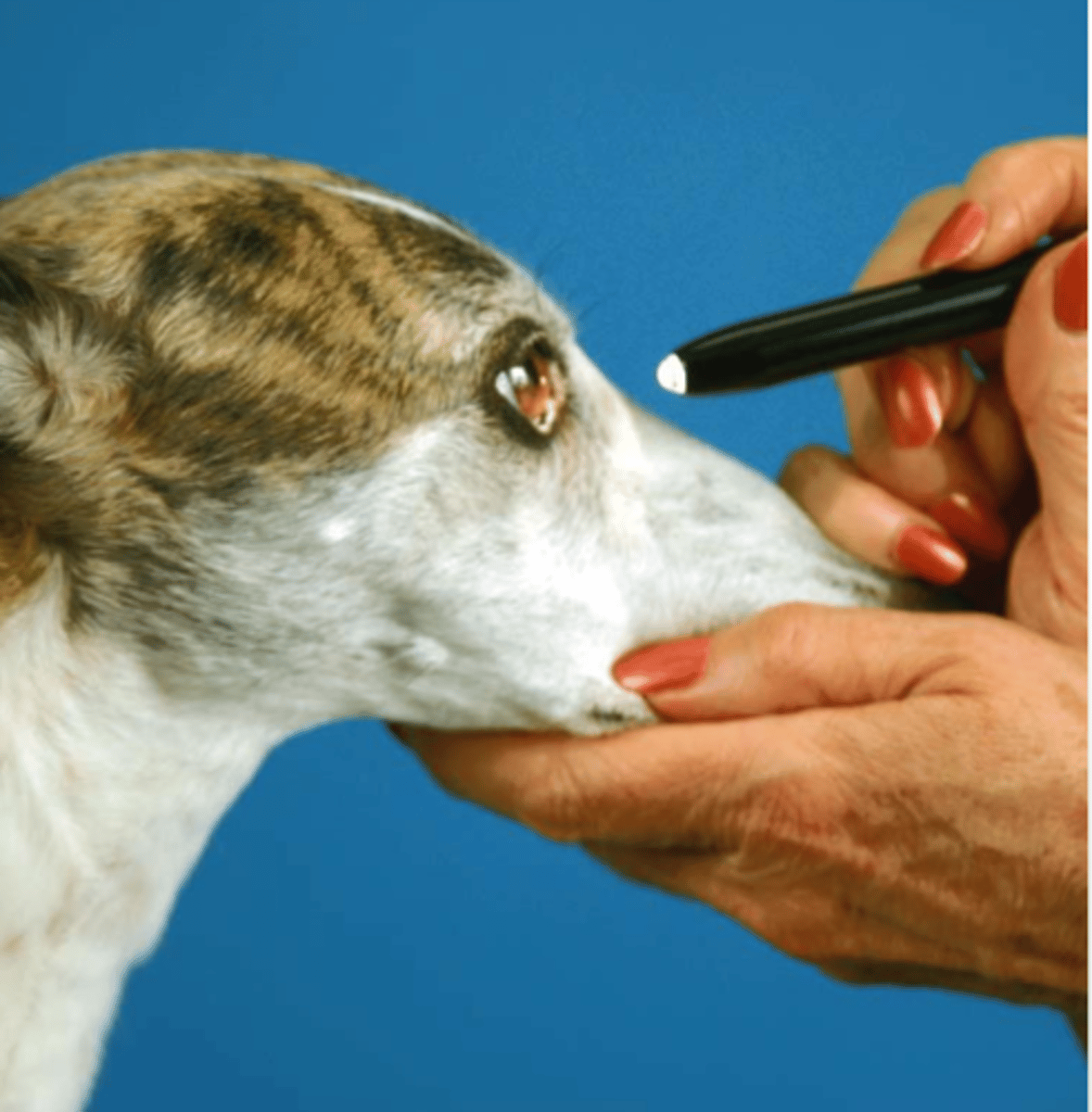

direct- the pupil of the eye that we shine the light into should contract
indirect- when we shine a light into one eye, the other eye should also have pupil contraction
what is the difference between the direct and indirect pupillary reflex?
oculomotor, trochlear, abducens
when we are observing the size and symmetry of the pupil, the opening of the eyelids, and the position and movement of the eyeballs, what nerves are we evaluating?
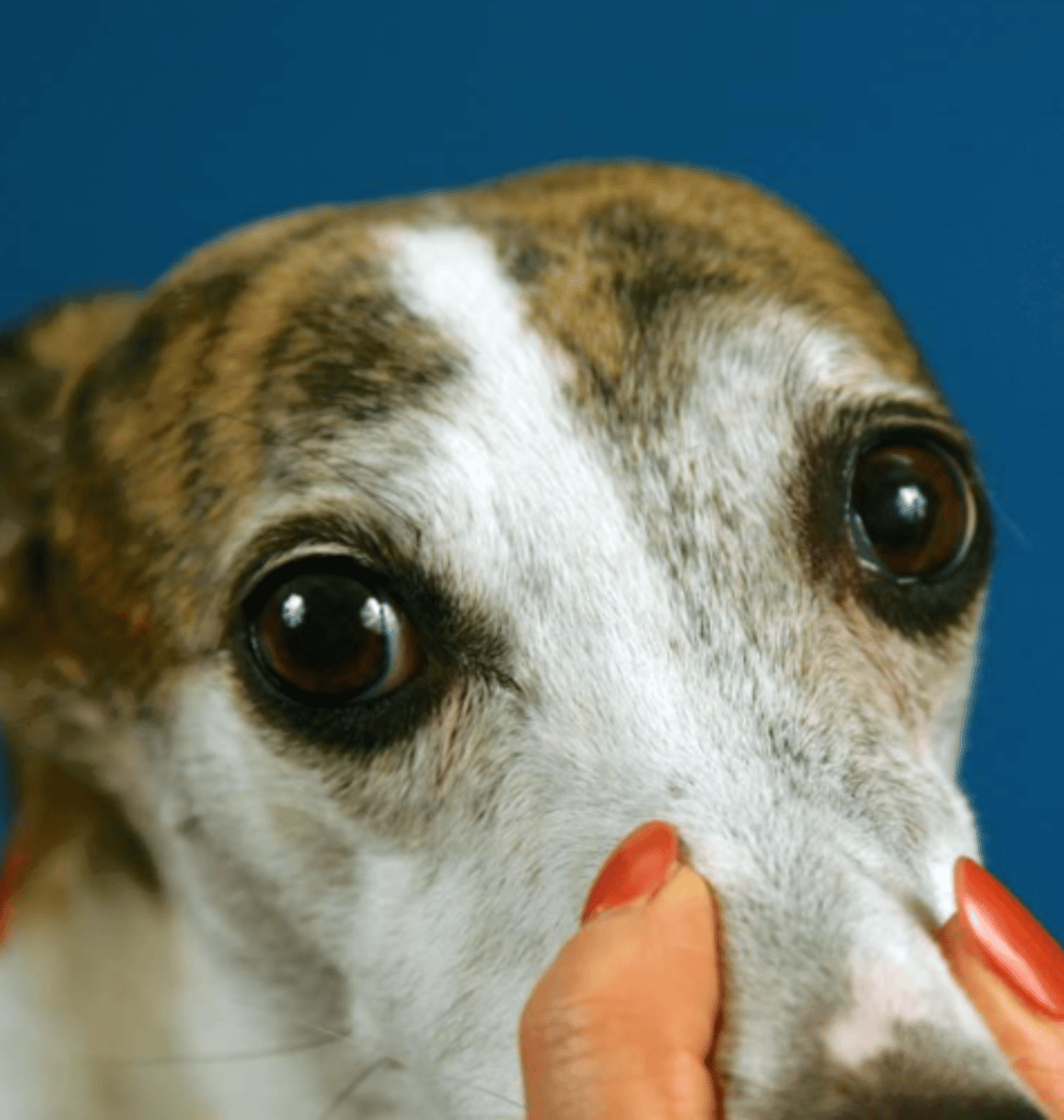

when we move the head to the left, right, up, and down and observe the rhythmical movement of the eyeballs in the direction that we are moving the head.
this tests the oculomotor, trochlear, abducens, and vestibulocochlear nerves
what is the positional nistagmus test? what does it test?
when we touch the eyelid of the animal, it must close its eye. this tests the trigeminal and facial nerves
what is the palpebral reflex?
the palpebral reflex
trigeminal and facial nerves
what are we testing here?
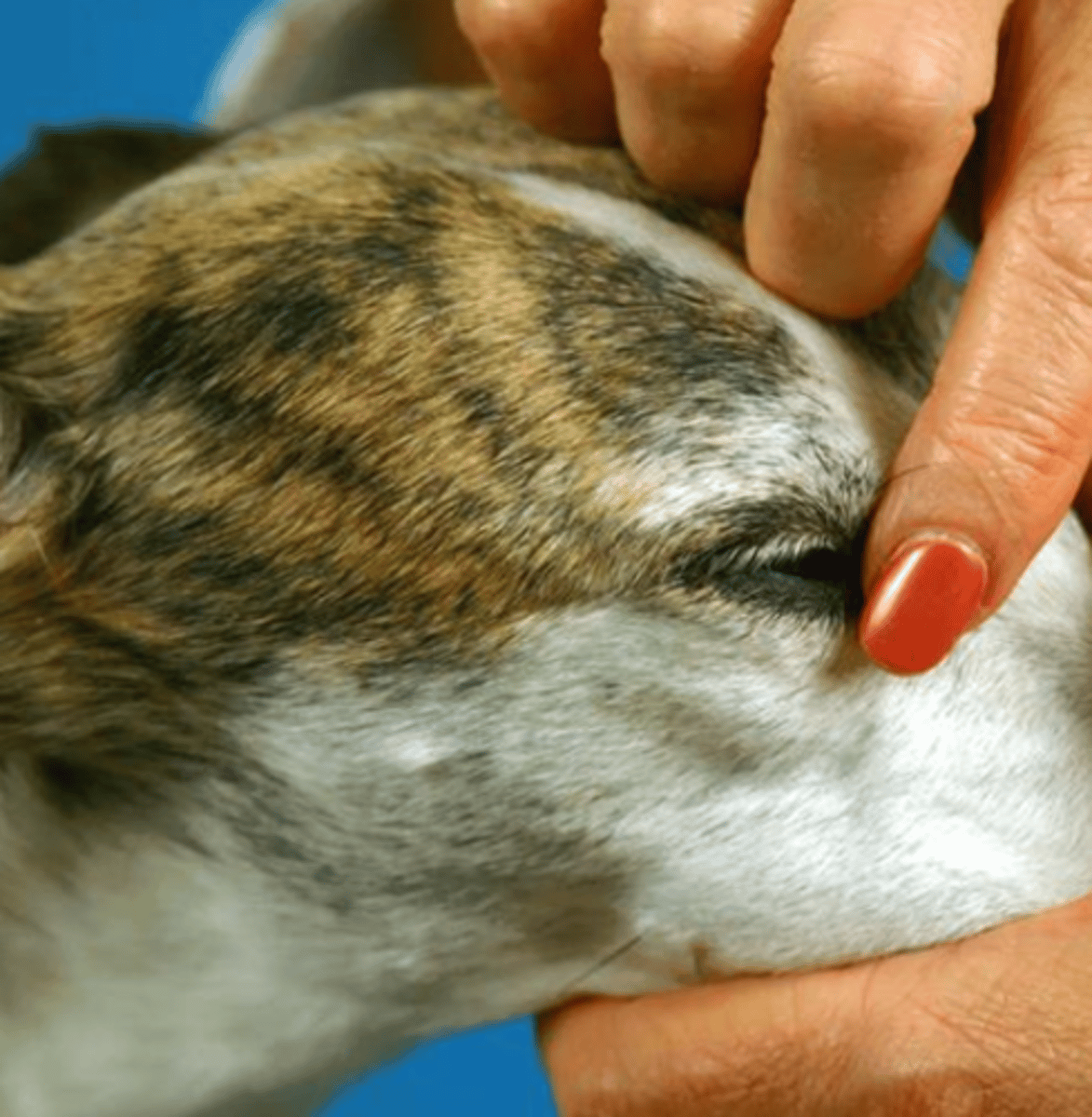
trigeminal
when we are palpating the masseter and temporal muscles, what nerve are we testing?
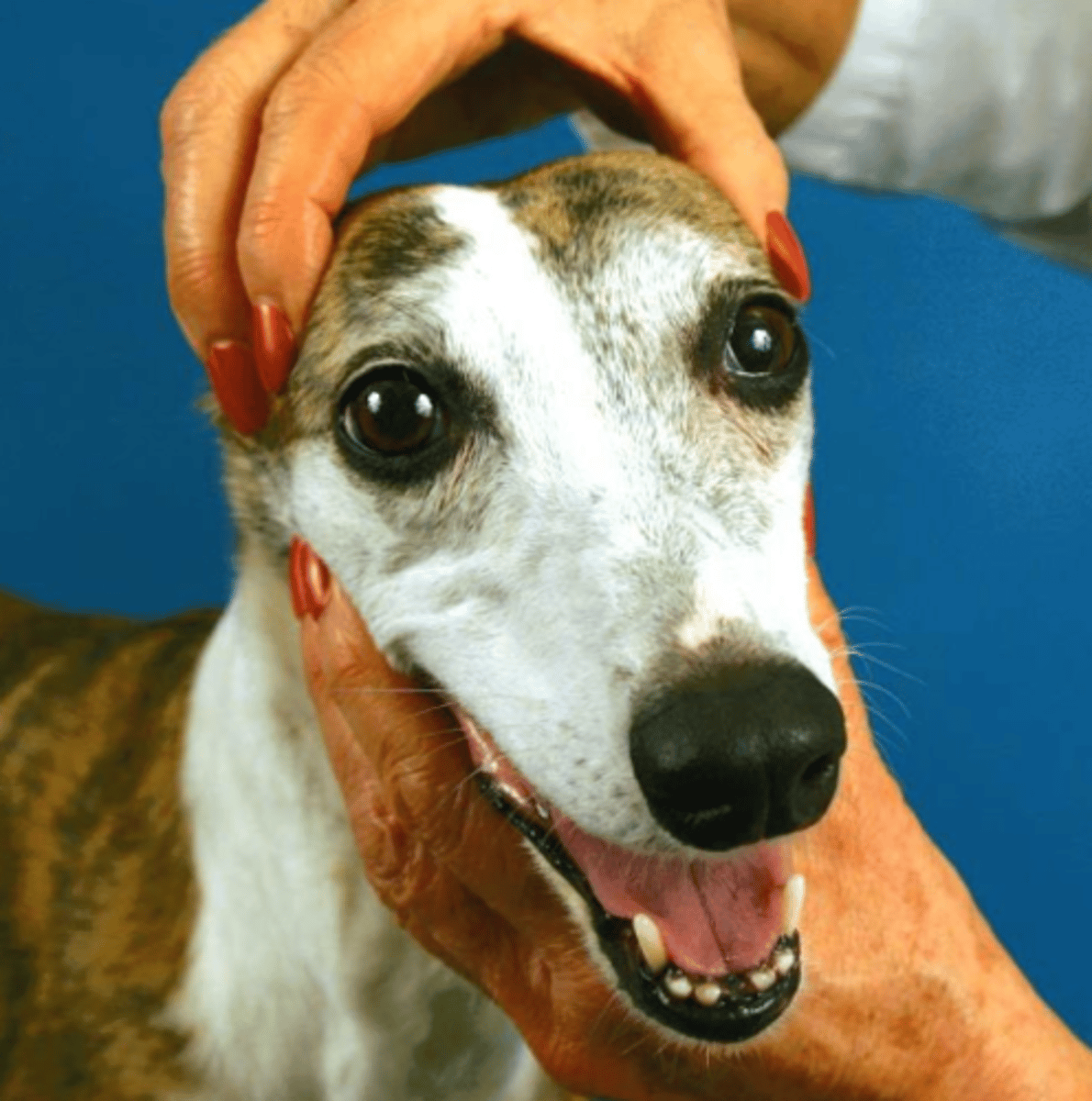

trigeminal
when we are checking the mandibular tone, what nerve are we testing?
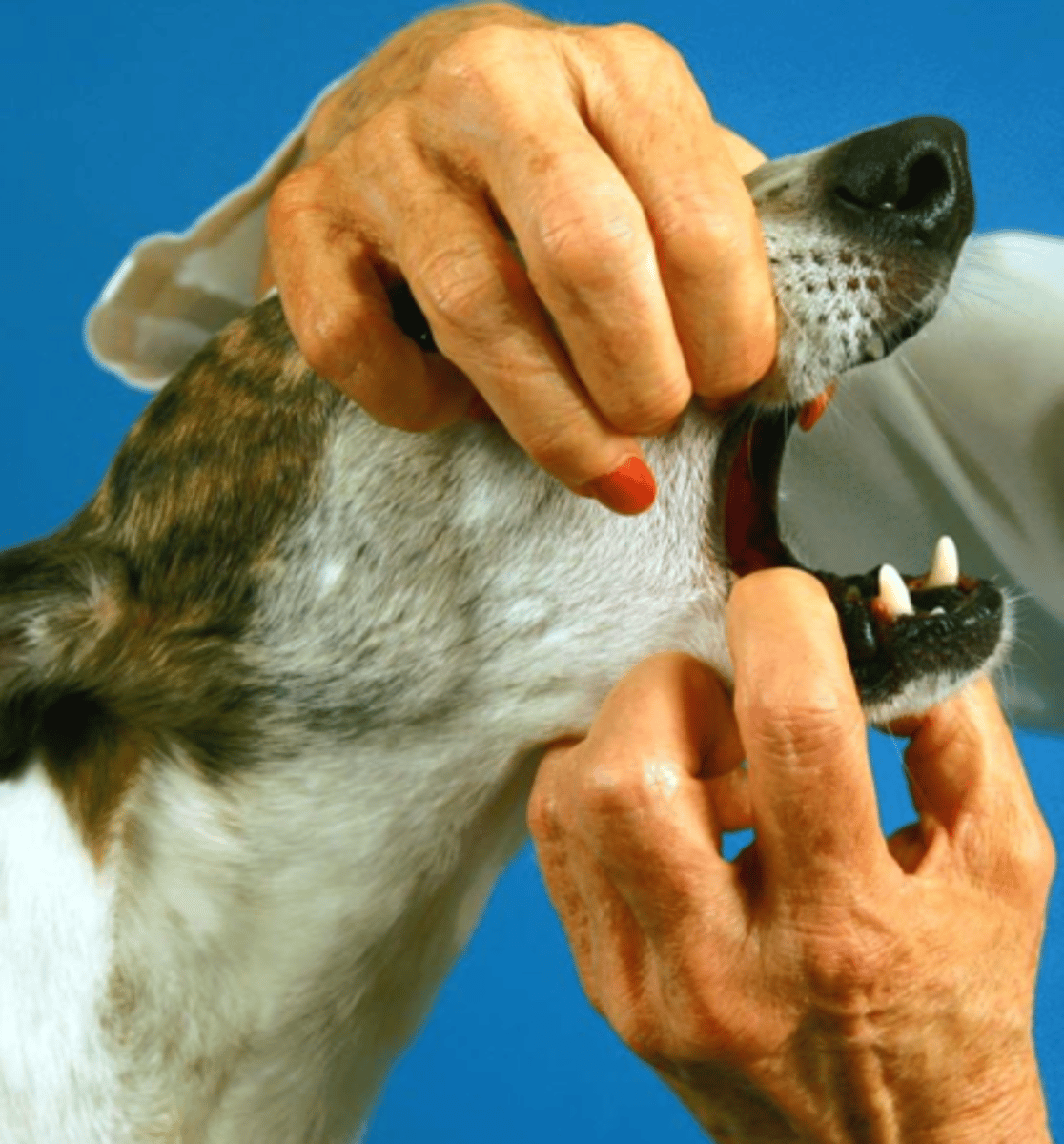
we tickle the inside of the pinna to see if the ear moves. this tests the facial nerve
what is the auricular reflex?
the auricular reflex
facial nerve
what reflex/nerve are we testing here?
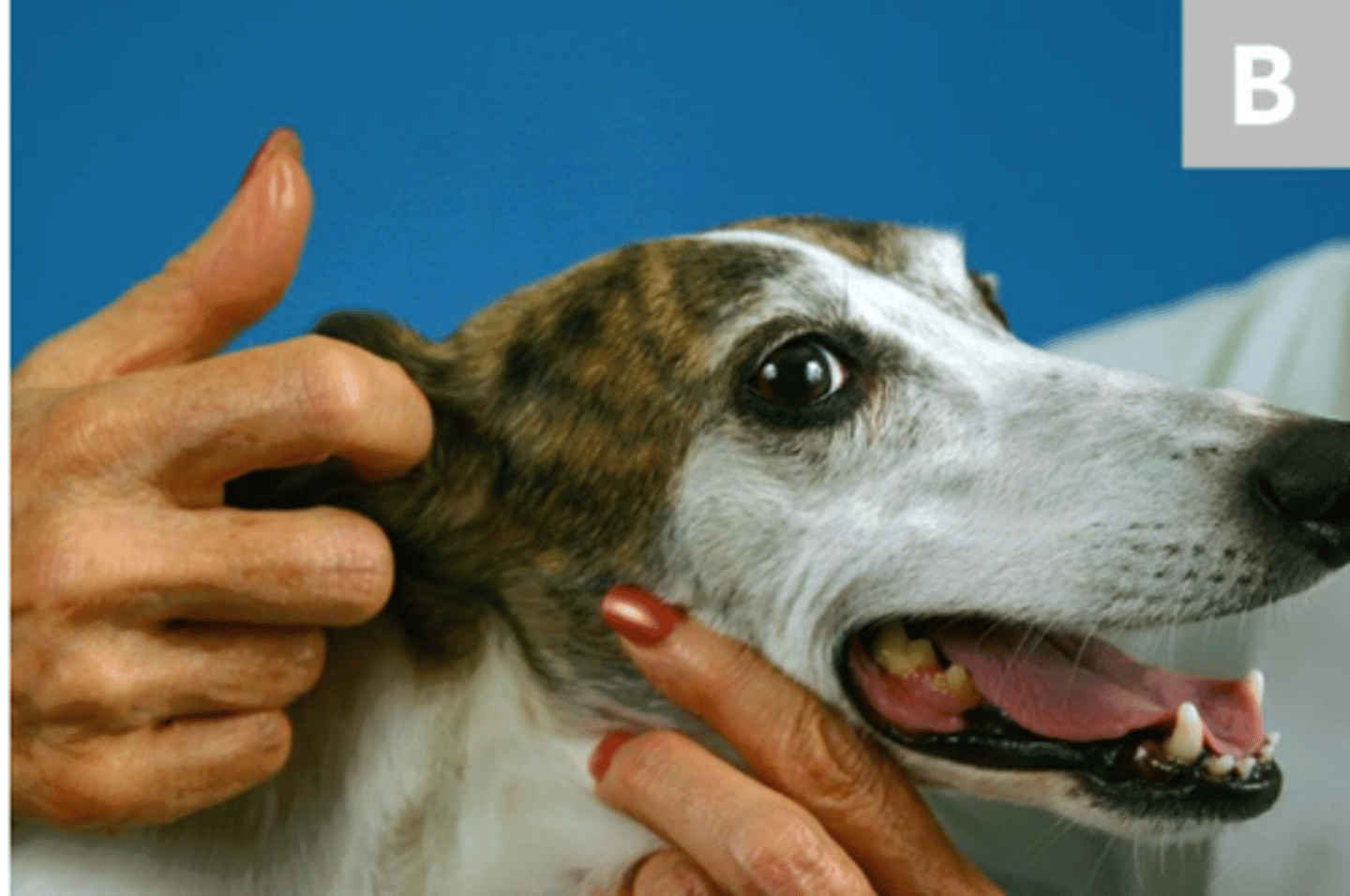
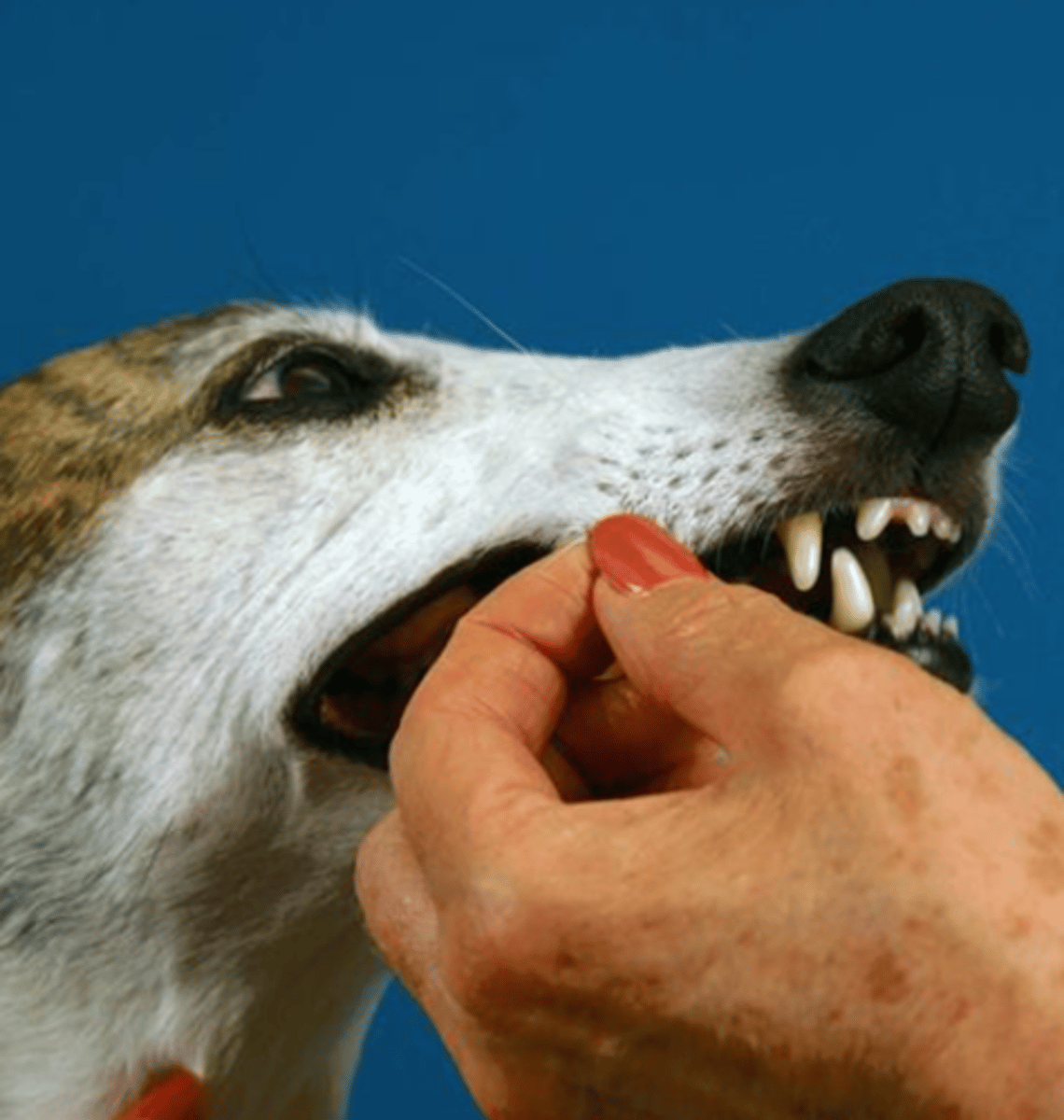
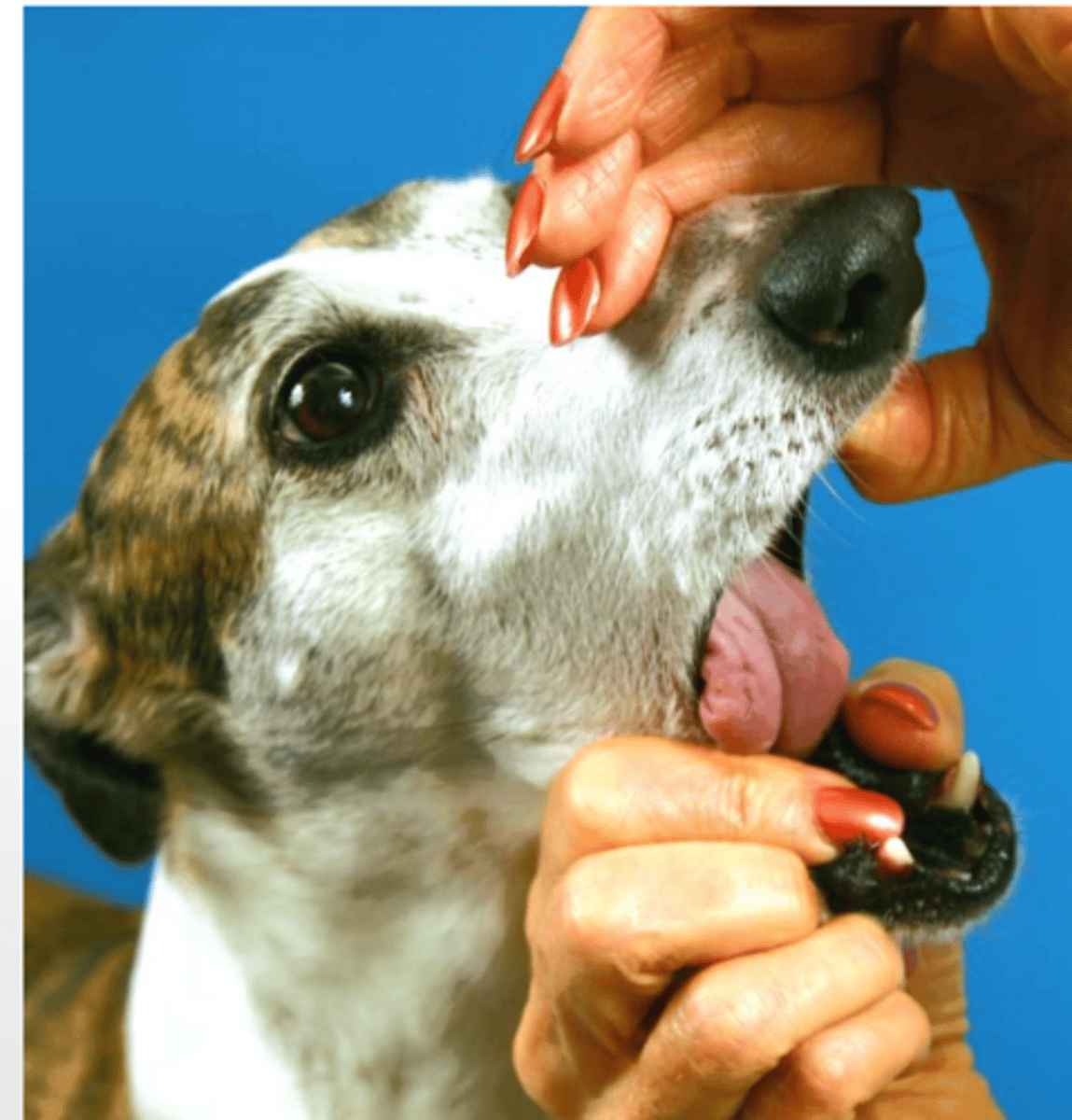
pinching the lip to assess the movement or withdrawal of the animal. this tests the facial and trigeminal nerves
what is the buccal reflex?
facial and trigeminal
this is the buccal reflex test
what nerves are we evaluating?

glossopharyngeal, hypoglossal, and vagus nerves
this is the swallowing reflex
what nerves are we evaluating?
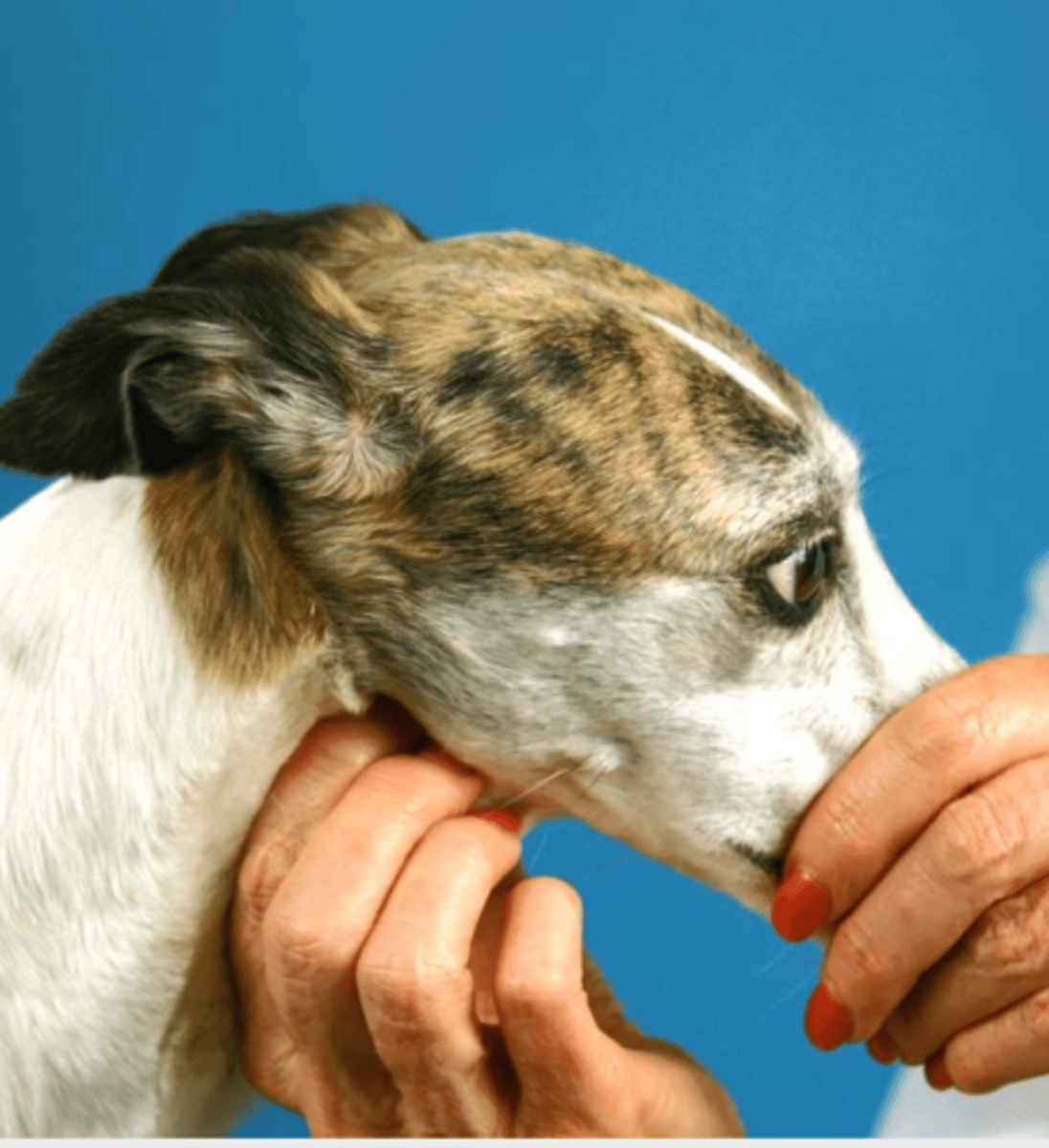

glossopharyngeal, hypoglossal, and vagus nerves
what nerves does the swallowing reflex test?
evaluate the movement and strength of the tongue
swallowing reflex
how do we evaluate the hypoglossal nerve?
hypoglossal
when we evaluate the tongue, what nerve are we checking?
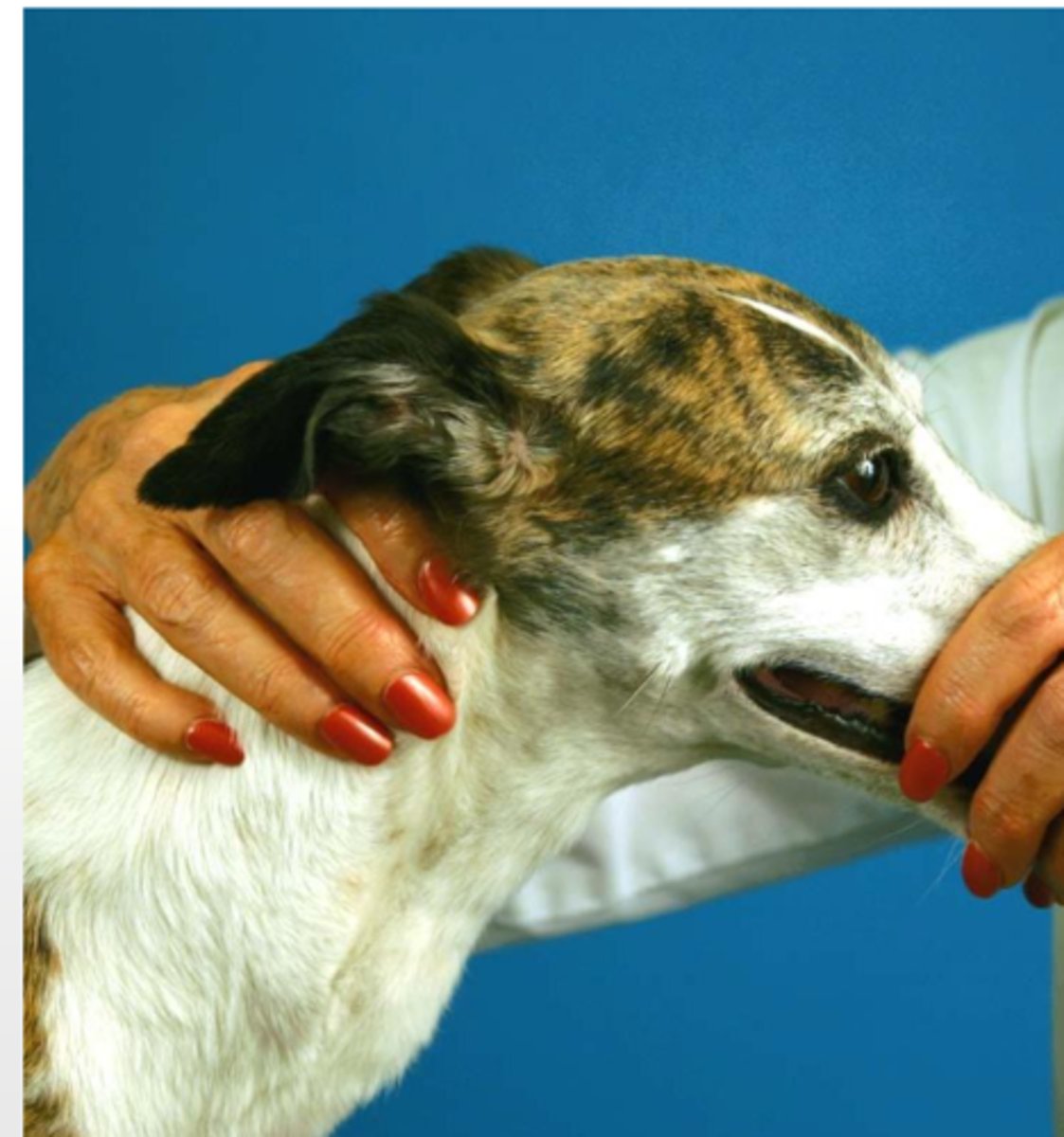
accessory nerve
when we palpate the trapezius muscle, what nerve are we testing?
hyporeflexia
if the animal has decreased spinal reflexes, we call this _____
the absence of spinal reflexes
what is arreflexia?
hyperreflexia
what is it called when an animal has increased spinal reflexes?
using a percussion hammer
the animal must be relaxed, in lateral decubitus
how do we check the spinal reflexes?
C6-C8
what nerves does the biceps reflex assess?
C7-T1
if we are assessing the animal's triceps reflex, what nerves are we evaluating?
extensor carpi radialis
withdrawal reflex
what reflex would we assess if we want to check for an injury between C7 and T2?
C6-T2 (front limb)
L4-S3 (back limb)
what nerves does the withdrawal reflex relate to?
T2-L5
what nerves do we assess when evaluating the cutaneous tunici muscle reflex?
L4-L5
what spinal nerves does the patellar reflex associate with?
L7-S1
what nerves are we evaluating if we test for an animal's gastrocnemius reflex?
L6-S2
what nerves is the cranial tibial reflex associated with?
S1-S3
what nerves do we evaluate with the perineal reflex?
an exaggerated reaction to painful stimuli
what is hyperesthesia?
anesthesia
if we perform a painful stimulus on an animal and he shows NO reaction, what is this called?
slow or weak response to a strong painful stimulus
what is hypoesthesia?
hyperesthesia
if we perform a painful stimulus on an animal and he shows a very exaggerated reaction, what is this called?
CSF analysis
Xrays
Myelography
Ct scan
MRI
Electroencephalogram
what complementary tests can we use to evaluate the nervous system?