1L1 DNA Structure & Organization
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Which experiment identified DNA as the genetic material?
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty (1944).
***AvEry Extracted the sEcret
Which experiment confirmed DNA is the genetic material using bacteriophages?
Hershey and Chase (1952).
***Hershey chases virus
What experiment revealed DNA’s double helix structure?
X-ray diffraction by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins,
interpreted by Watson and Crick (1953).
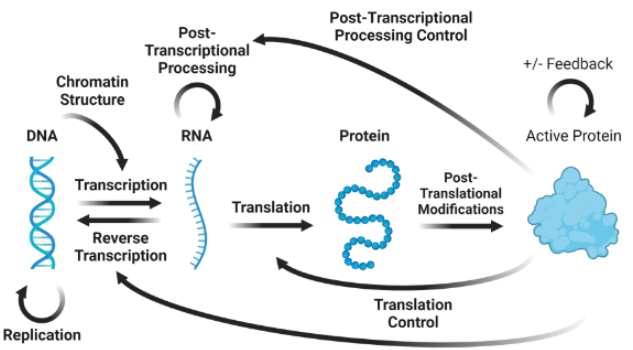
central dogma
DNA + transcription > RNA + translation > protein
DNA > 2DNA via replication
prokaryotes v eukaryotes
DNA in cytoplasm v. DNA in nucleus
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid (missing 2’ OH)
avery’s experiment
What type of molecule contains the genetic information of a cell?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Smooth cells produce a polysaccharide capsule, rough cells don’t
bacterial transformation
bacterial transformation
bacteria takes up external DNA to change morphology and physiology
cell-free extract
S cell heated to kill, fragments released as extract
extract is mixed with live R cells, R > S via transformation
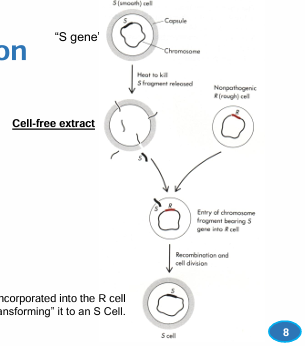
proteinase v rnase v dnase
degrades protein R > S
degrades RNA R > S
degrades DNA R X S
nucleotides
nucleoside + (1-3)P = nucleotide
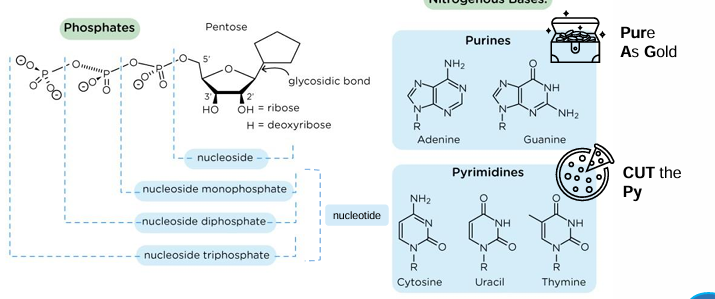
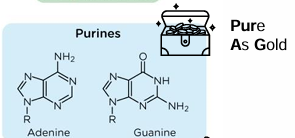
purine structures
2 rings
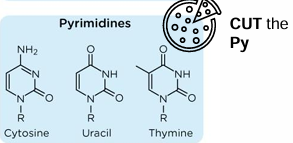
pyrimidine structures
1 ring
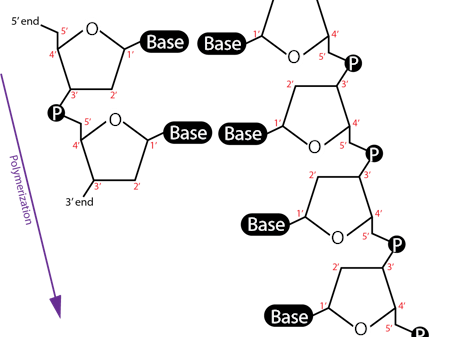
polynucleotides
DNA and RNA, 3’OH attacks 5’P and connects nucleotides (phosphodiester bond)
3’ end = free OH
chargaff’s rules
% A=T and G=C
Base composition varies between species. (human = 59% AT, yeast = is 64% AT)
Base composition is the same in different cells within an individual organism.
Base composition does NOT change with age, nutrition, and environment
DNA v RNA structure
2’ OH is missing in DNA
Photo 51
previously only photos were of dehydrated DNA
xray diffraction to show location of atoms,
shows helix 34A long, 10 base pairs 3.4A apart
dNMP
2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-monophosphates
repeating unit of DNA
2D DNA structure
2 unbranched polynucleotide chains, antiparallel, held by H bonds
watson-crick-franklin base pairing = AT GC
sugar and phosphate backbone
DNA strand separation & annealing
denaturing/melting DNA (Tm = 50% denatured)
when cooled, DNA will anneal back together
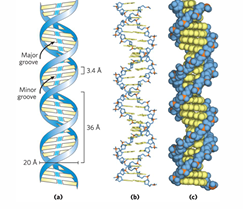
3D DNA structure
BDNA = 99% of DNA
right handed helix, 10.5 base pairs per turn
base pairs flat and perpendicular to backbone
Hphobic bases inside
base pairs exposed in major and minor grooves
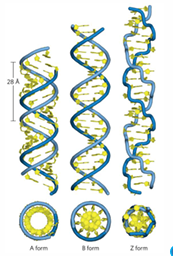
ADNA v ZDNA
ADNA = dehydrAted, structural model of dsRNA and RNA-DNA hybrids
ZDNA = <1% DNA, high GC content, left handed
cruciform, triplex, quadruplex
RNA structure
linear, single stranded
ribose sugar P backbone
U instead of T
GU wobble base pairing = RNA pairs with RNA
RNA complex structures
secondary and tertiary from internal base pairing
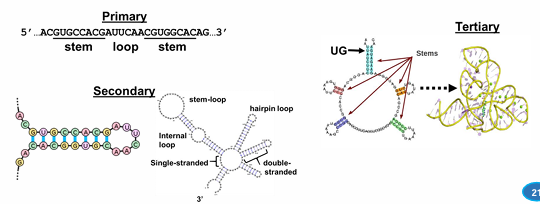
gene, genome, chromosome
gene contains DNA and regulatory elements
genome is all of the genes
46 chromosomes = helps position and organize genes in the genome
polynucleotide synthesis
always 5 > 3, NTPs as substrates
DNA polymerase = adds dNMP to 3’ end of DNA chain, requires primer
RNA polymerase = adds NMP to 3’ end RNA chain, can initiate de novo synthesis
reverse transcriptase = adds dNMP to 3’ end of DNA chain, requires primer
DNA polymerase
adds dNMP to 3’ end of DNA chain, requires DNA primer
RNA polymerase
adds NMP to 3’ end RNA chain, can initiate de novo synthesis
needs DNA template
reverse transcriptase
adds dNMP to 3’ end of DNA chain, requires primer and RNA template
nucleases digest polynucleotides
exonuclease = breaks Pdiester bond at one end
endonuclease = breaks Pdiester bond within chain
excinuclease = breaks 2 Pdiester bonds in single chain
exonuclease
breaks Pdiester bond at one end
endonuclease
breaks Pdiester bond within chain
sequence independent or specific
single strand (nick) or double-strand break
excinuclease
endonuclease; breaks 2 Pdiester bonds in single chain
restriction endonucleases / enzymes
endonuclease that breaks PDE bonds at specific restriction sites
palindromic sequences = same on both strands, forms sticky ends when cut
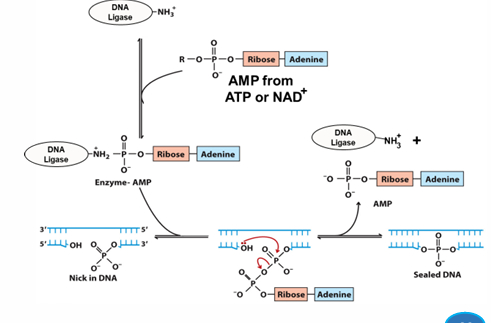
DNA ligase
links two existing DNA chains via PDE linkage
grabs AMP from ATP or NAD+
adds onto itself to activate
scans DNA for substrate (nick)
adds AMP to 5’P of DNA as a good leaving group (GLG)
3’OH attacks 5’P, forms PDE bond, remove AMP
bond is sealed
in vivo, seals nicks
recombinant DNA
new combos of DNA
restriction enzymes isolate new DNA, cut old DNA to match sticky ends, and DNA ligase fixes PDE bonds to form singular DNA
AT v CG bonds
AT has 2, CG has 3
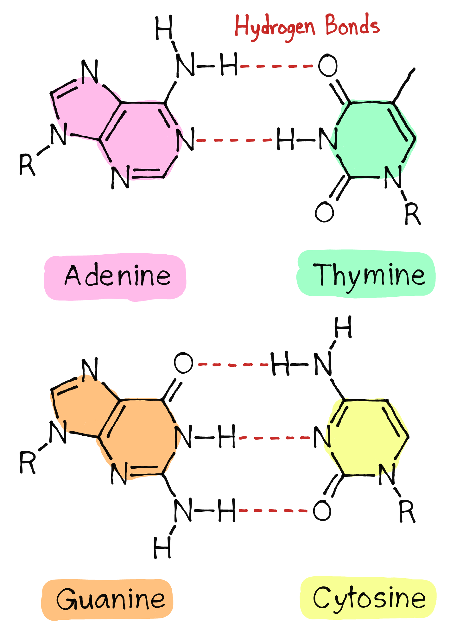
DNA detailed structure
3’OH forms PDE bond with 5’ phosphate in the ribose backbone,
1’ bases H bond together