Psych 291 - Lecture 8: Measurement Reliability and Validity
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Three Common Types of Measures
▪ Self-report - can be open ended or MC
▪ Observational - Researcher observing someone
Rich people have less empathy, less compassioniate (ted talk) the subjective feeling for feeling wealthy
▪ Physiological
Self-Report versus Observation
▪ Why might an observational paradigm be better than self-report measures?
▪ When (i.e., for what types of constructs/contexts) do you expect an observational paradigm to be better?
▪ Why might self-report measures be better than an observational paradigm? - may behave differently
▪ When?
a) Because they capture actual behavior, and avoid problems like lying, memory errors, or social desirability bias.
b) When measuring:
Non-verbal behavior (e.g., eye gaze, body language)
Infants/children who cannot self-report
Real behavior in natural settings
c) Because it can measure internal states (thoughts, feelings, attitudes) that are not visible from behavior.
d) When studying:
Emotions (e.g., anxiety, happiness)
Beliefs or opinions
Personal experiences (e.g., stress, pain)
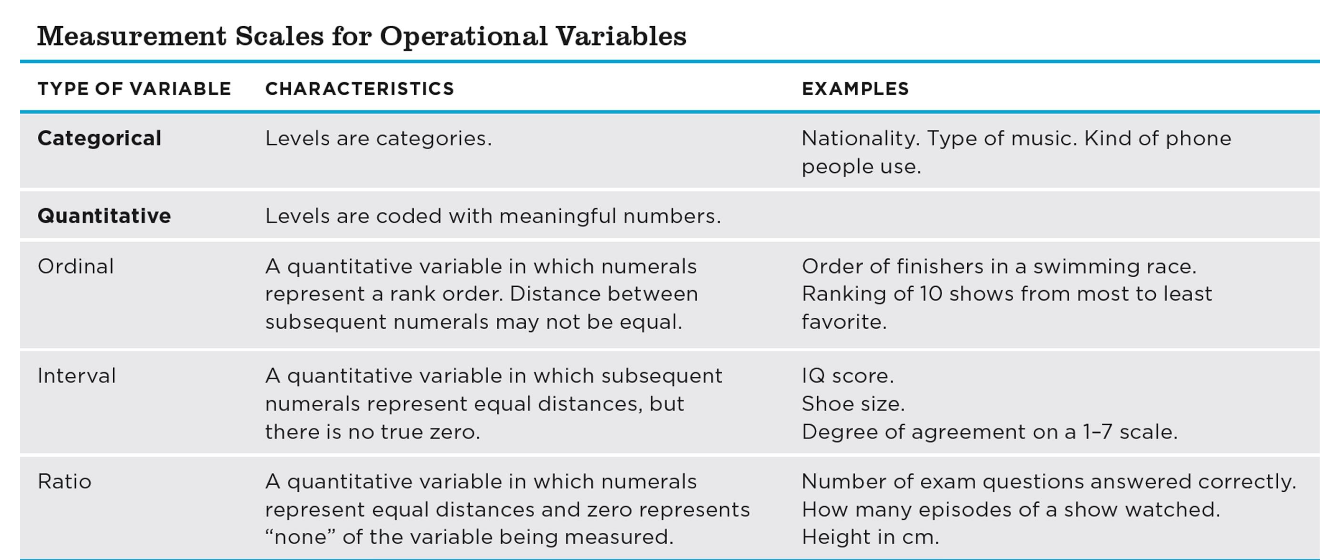
Scales of Measurement
Categorical (nominal) variables
Quantitative variables
▪ Ordinal scales
sets of rankings
▪ Interval scales
like a rank ordering but an equal interval between events, no true zero
▪ Ratio scales
like an interval scale but has a true zero point
Examples of Scales of Measurement
A geologist compares the mineral content of various soils using units of grams per metric ton. What kind of scale is this?
Every week, NHL teams are ranked. What kind of scale is this?
A class has 12% arts and business majors, 78% psychology majors, and 10% kinesiology majors. What type of scale is this?
Scores on standardized intelligence tests (IQ) are examples of what type measurement?
What type of scale are you using if you said you came 120th place in a marathon?
Response Options:
A. categorical
B. ordinal
C. interval
D. ratio
1) Ratio
2) Ordinal
3) Categorical
4) Interval
5) Ordinal
Examples of Scales of Measurement
1. eye color
2. rating of well-being on a scale ranging from 1 to 5
3. order of finishers in a 5K race
4. parents’ marital status
5. blood alcohol content
6. distance from the stage in an auditorium
7. degree of pain felt
Response Options:
A. categorical
B. ordinal
C. interval
D. ratio
Categorical
Ordinal (not interval bc it’s subjective and space between numbers may not be equal)
Ordinal
Categorical
Ratio
Ratio
Ordinal (not ratio bc subjective and space between numbers may not be equal)
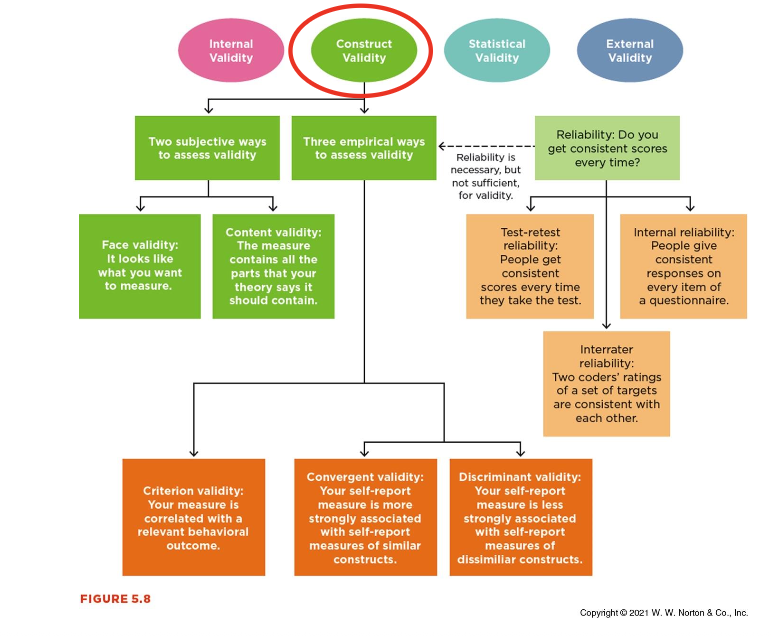
How do we decide whether a measure is “good”
Construct validity of a measure
Reliability of Measurement - What question does reliability address?
Validity of Measurement - What question does validity address?
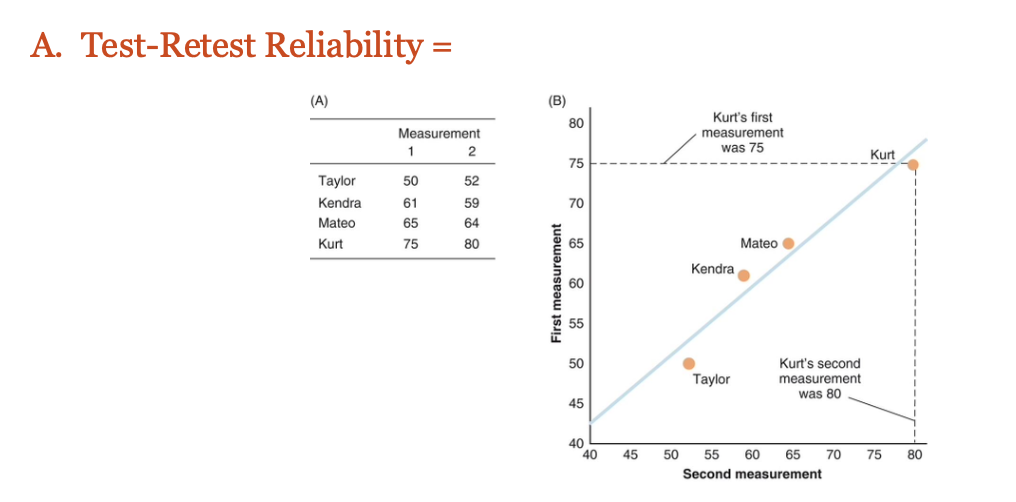
Test-Retest Reliability
Test–Retest Reliability means checking if a measure gives the same results when it’s used more than once on the same person under the same conditions.
Inter-Rater Reliability
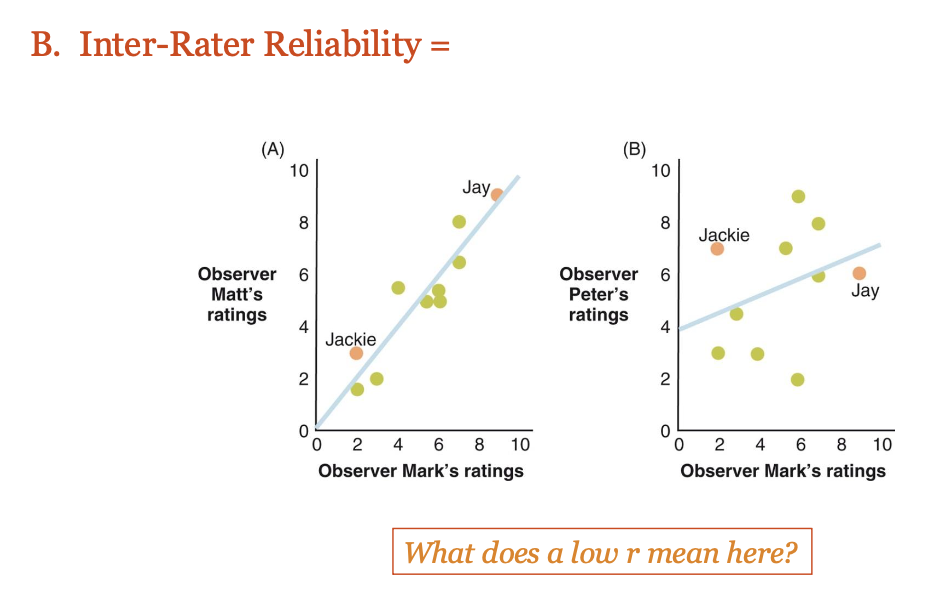
Inter-Rater Reliability means how much two or more observers agree when they are watching or rating the same thing.
A low inter-rater reliability (low r) means that the observers do not agree with each other.
Internal Reliability
▪ Consistency of people’s responses across the items of a multi-item measure
Split-half correlations
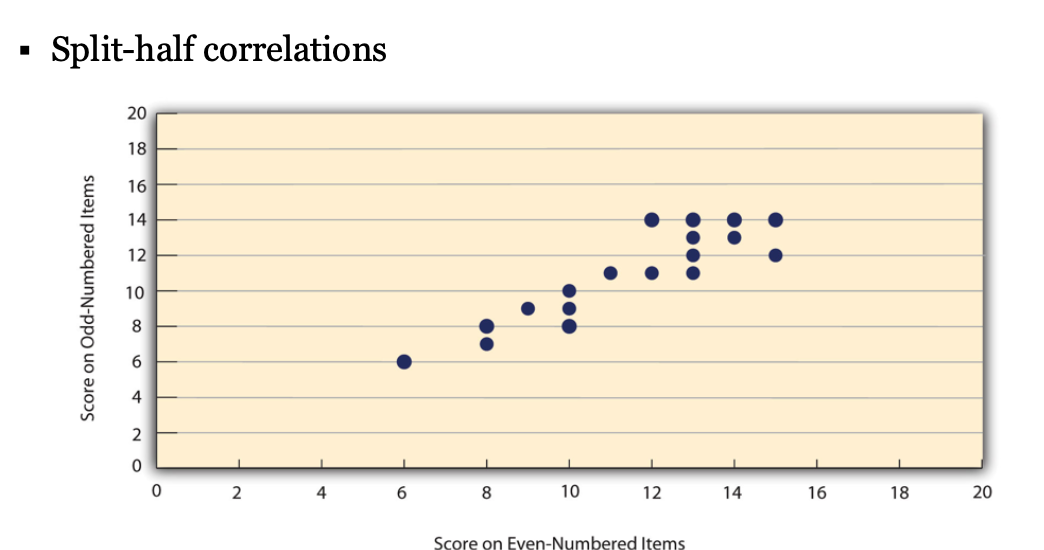
Internal reliability refers to how consistently the items on a questionnaire measure the same underlying thing.
Internal Reliability
▪ Cronbach’s α (alpha) reflects the average of the inter-item correlation
▪ What would a low Cronbach’s α suggest about the measure?
Cronbach’s alpha tells us whether the questions in a multi-item scale are all measuring one single concept.
If α is high → the items are consistent and “hang together.”
If α is low → the items do not match well and may be measuring different ideas.
What a low α suggests
Some questions may be confusing or poorly written
Some items may be measuring different constructs (not the one they're supposed to)
Respondents are not answering the items in a consistent pattern
Classify each of the following results as an example of internal reliability, interrater reliability, or test-retest reliability.
1. A researcher finds that people’s scores on a measure of extraversion remain stable over 2 months
2. An infancy researcher wants to measure how long a 3-month-old baby looks at a stimulus on the right and left sides of a screen. Two undergraduate research assistants watch a tape of the eye movements of ten infants and time how long each baby looks to the right and to the left. The two sets of timings are correlated r = .95.
3.A researcher asks a sample of 40 people a set of five items that all capture agreeableness. The Cronbach’s α for the five items is found to be .65.
Test–retest reliability
Inter-rater reliability
Internal reliability
Measurement Validity (2), (2) (3)
▪ Validity can be assessed subjectively or objectively
▪ Subjective Validity Measures:
▪ Face Validity: Does the measure look like it measures what it’s supposed to measure?
This is about first impressions.
▪ Content Validity : Does the measure cover all parts of the concept it’s supposed to measure?
This requires expert judgment, not just first impressions.
▪ Objective Assessments of Validity
▪ Criterion Validity
▪ Extent to which a measure is associated with a concrete behavioral outcome with which it should be associated
Does the measure actually predict or relate to real-world behavior?
▪ Assessed via correlation
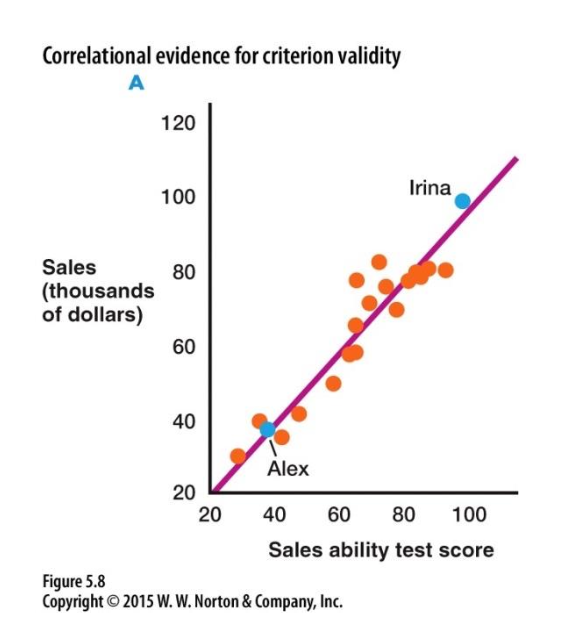
▪ Known-groups comparison
▪ Evaluate whether the measure of interest can discriminate among groups whose behavior has already been confirmed - people that have been diagnosed with anxiety should score higher on anxiety tests
Objective Validity Measures (cont)
▪ Convergent Validity
▪ Measure should correlate with what?
Measure should correlate with similar constructs (depression and tiredness)
▪ Discriminant Validity
▪ Measure should not correlate with what?
Measure should NOT correlate with unrelated constructs (height and depression)
Relation between Reliability and Validity?
Reliability is necessary but not sufficient for validity