L17 - T17C - S2 – Malware Payloads
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Payload Classification
Identifying what type of actions the code performs other than simply replicating or persisting on a host
Backdoor
Mechanism for gaining access to a computer that bypasses or subverts the normal method of authentication – (A+)
Allows attacker to e.g.
Access the PC | Upload/exfiltrate data files | Install additional malware tools.
Which can lead to
Using the computer to widen access to the rest of the network
To add it to a botnet and launch distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks or Mass-mail spam
Malware that create [____]s are referred to as “Remote Access Trojans (RATs)”
Command and Control (C2 or C&C)
Infrastructure of hosts and services with which attackers direct, distribute, and control malware over botnets – (A+)
Used by attackers to establish a connection with a compromised host
Whether the backdoor is used for standalone intrusion or a botnet management
Covert C&C Channel Creation Methods
Historical — The Internet relay chat (IRC) protocol
Modern — Use command sequences embedded in HTTPS or DNS traffic
Spyware
Software that records information about a PC and its users, often installed without the user's consent – (A+)
Can perform browser reconfigurations e.g.
Allowing tracking cookies, changing default search providers, opening arbitrary pages at start-up, adding bookmarks
Can also
Monitor local application activity
Take screenshots
Activate recording devices, such as a microphone or webcam.
Perform DNS redirection to spoofed sites
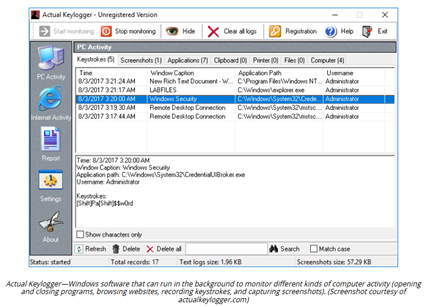
Keylogger
Malicious software or hardware that can record user keystrokes – (A+)
Attempts to steal confidential information by recording keystrokes
Attacker will usually hope to discover passwords or credit card data
Not only implemented as software
A malicious script can transmit key presses to a third-party website
Hardware devices to capture key presses to a modified USB adapter inserted between the keyboard and the port
True
This means the user must be confident enough in the installer package to enter the credentials or accept the User Account Control (UAC) prompt
Windows tries to protect the OS files from abuse of administrator privileges
True or False: In Windows, malware can only be manually installed with local administrator privileges.
Critical
Higher
_____ processes run with a _____ level of privilege (SYSTEM)
Consequently, Trojans installed in the same way as regular software cannot conceal their presence entirely
They will show up as a running process or service
The process name is often configured to be similar to a genuine executable or library to avoid detection
Trojan Persistence Methods
Using a registry entry
Creating itself as a service
True
True or False: Most techniques used by Trojans are relatively easy to detect and remediate
Rootkit Installation Methods
If hackers send malware by taking advantage of a serious security flaw, the malware might run automatically at the highest level of access (SYSTEM privileges) without needing permission
Alternatively, the malware may be able to use an exploit to escalate privileges after installation.
Rootkit
Class of malware that modifies system files, often at the kernel level, to conceal its presence – (A+)
Malware that runs using the highest level of access/privilege (SYSTEM) without needing permission
In theory there is nothing about the system that a [___] could not change.
Capability depends largely on
Adversary capability
Level of effort
True
An example of a mechanism that helps prevent misuse of kernel processes in Windows is code-signing
True or False: In practice, Windows uses other mechanisms to prevent misuse of kernel processes
True
True or False: The term “Rootkit” derives from UNIX/Linux where any process running as root has unrestricted access to everything from the root of the file system down
Things to be aware of when dealing with a Rootkit
Be aware that there is the possibility that the rootkit can compromise system files and programming interfaces e.g.
Local shell processes, such as Explorer or Task Manager on Windows, ps or top on Linux, and port-listening tools (netstat, for example), no longer reveal their presence (when run from the infected machine, that is)
A rootkit may contain tools for cleaning system logs,
This helps to conceal its presence