Until 2 test bio
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Tissues
Group of cells that are working together for a specific purpose
What are the 4 main types of tissues in the body?
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous
Squamous
Thin, flattened cells
A type of epithelial tissue
Cuboidal
Cubelike, cells
A type of epithelial tissue
Columnar
Elongated cells
A type of epithelial tissue
Simple
Single layer of cells
Stratified
Two or more layers of cells
Striated Muscle
Muscle tissue that look striped
In skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle
Fibroblast
A type of connective tissue
most common fixed cells, large star-shaped cell; produce fibers by secreting proteins into matrix
Mast cells
A type of connective tissue
Near blood vessels; release heparin and histamine (inflammatory chemicals)
Macrophage
White blood cells; can move about; phagocytosis (cells eats large particles like bacteria, foreign substances, or dead cells)
A type of connective tissue
Heparin
fast-acting medication used to prevent and treat blood clots (blood thinner)
Histamine
released by mast cells in response to allergens and promotes inflammation
Collagen
an abundant protein source in the body and provides structural support and elasticity to connective tissues (skin, bones, tendons, ligament)
fibrosis
replacement of destroyed tissue with fibrous scar tissue
Regeneration
replacement of destroyed tissue with same type of tissue
Epithelial membrane
Comes in 3 types:
Serous
Mucus
Cutaneous
Serous Membrane
Lines body cavities
Made of epithelial and loose connective tissues
Lubcricates membrane surfaces
Mucus Membrane
Lines cavities and tubes opening to the outside
Made of epithelial and loose connective tissues
Secrete mucus
Cutaneous Membrane
External body covering called skin
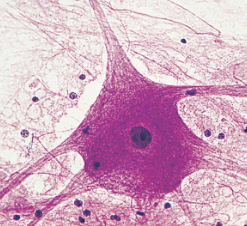
Neurons
Senses change and response by transmitting nerve impulses to other neurons or muscles and glands
fibrocartilage
very tough tissues; contains many collagenous fibers; shock absorber
Adipose tissue
Stores fat
Cushions and insulates
Hyaline cartilage
Most common type of cartilage
Ex,) Ends of bones (joints), soft part of nose
Elastic cartilage
Flexible; contains elastic fibers
Ex.) external ear
elastin
a protein that provides elasticity and flexibility to various tissues in the body
desmosomes
rivets, “spot welds” reinforce structural unit
ex. skin
Merocrine gland
release fluid products by exocytosis
ex. Salivary glands & sweat glands
Apocrine glands
lose small portions of their glandular cell bodies during secretion
ex. Mammary gland
Holocrine Glands
release entire cells (which later disintegrate)
Sebaceous glands in skin
microvilli
tiny, fingerlike projections that increase surface area for absorption (small intestine)
Goblet cells
secret mucus
Basement membrane
provides a framework for cells to adhere to and maintain their shape. secured to connective tissue
Tight junctions
Membranes of adjacent cells converge and fuse
ex. digestive tissue
Gap junctions
channels, link cytoplasm between cells
ex: heart muscle
Neuroglial cells
supporting cells that support, bind, supply nutrients, cell-cell communications
Inflammatory response
Mast cells release inflammatory chemicals
Capillaries dilate & become permeable
Swelling, heat, and redness make environment inhospitable to bacteria and viruses
White blood cells & plasma fluid containing clotting proteins & antibodies seep into area
Clotting proteins construct clot to stop blood loss, stabilize edges of wound & seal area
Area cleaned up by lymphatic vessels & macrophages (destroy extra, damaged and unwanted cells)
Immune Response
Resistance to a particular pathogen or toxin
Based on ability to distinguish foreign cells (non-self)
Cells recognize invaders and begin defending body
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
a non-cellular network of proteins and polysaccharides that surrounds and supports cells in tissues and organs
Axon
a long, slender projection of a nerve cell (neuron) that conducts electrical impulses, known as action potentials, away from the neuron's cell body
Granulation Tissue
new connective tissue and tiny blood vessels that form on the surface of a wound during the healing process, is formed.
Tissue engineering
Use of cells, engineering materials, and biochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions in an effort to advance medicine.
Synovial membranes
lining joints made entirely of connective tissue
Epithelial tissue
Which tissue is widespread throughout the body?
Epithelial tissue
Which tissue covers the organs?
Epithelial tissue
Which tissue forms inner lining of body cavities?
Epithelial tissue
Which tissues lines hollow organs?
Whats a carcinoma?
growths that originate in the epithelium
What are some characteristics of epithelial tissue?
Lacks blood vessels
Nutrients diffuse from connective tissue
Readily divide (skin cells, stomach lining cells)
Tightly packed (provides protective barriers)
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Common site of diffusion
Lines air sacs of lungs (O2/CO2 exchange)
Walls of capillaries
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Secretion (as in salivary glands)
Covers ovaries, kidney tubules
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Mainly protects
Has microvilli
Has goblet cells
Ciliated
in the female reproductive tubes
Nonciliated
in the uterus and digestive tract
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
nuclei are at 2 levels
May have cilia to move mucus
Lines respiratory system
Transitional Epithelium
Changes in response to tension
Inner lining of bladder that prevents contents from diffusing back
Glandular Epithelium
Has glands, exocrine glands, endocrine gland
Glands
cells that are specialized to secrete substances into ducts and bodily fluids
Exocrine gland
secrete products into ducts that open into internal/external surface
Endocrine gland
secrete products into tissue fluid or blood
What injuries stimulate tissue repair?
Inflammatory: rapid & relatively non-specific
Immune: extremely specific, but slower to activate
High capacity regeneration
epithelial, bone, blood-forming
Moderate capacity regeneration
most connective
Weak capacity regeneration
skeletal & cartilage
Little functional regeneration
cardiac & nervous
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
Protections , Excretion, Absorption, Secretion
What cells are in blood?
red cells, white cells, and platelets in plasma
What does loose Connective Tissue do?
Binds to skin
Fills in spaces between muscles
Reticular Connective Tissue
Found in the walls of internal organs
intracellular junctions
What are tissues joined with?
Characteristics of connective tissue?
Most abundant tissue type by weight
Good blood supply; well-nourished
Cells farther apart with matrix (intercellular material) between them
Collagenous fibers
thick threads of collagen
major structural protein in body
found in ligaments (bone:bone) & tendons (muscle:bone)
Elastic fibers
bundles of thin fibers of elastin
stretch easily
found in vocal cords, air passages
Reticular fibers
thin collagenous
supporting networks
Dense Connective Tissue
Tendons & ligaments (poor blood flow)
What are the characteristics of muscle tissue?
Site of energy production
Generates body heat
Allows for movement
Skeletal Muscle
Attaches to bones; voluntary muscles
Contract when stimulated by nerve impulses
Long threadlike cells, striated with many nuclei
Facial expressions, write, talk…
Smooth Muscle
Walls of hollow internal organs
Shorter cells, single/central nucleus
Involuntarily controlled
Cardiac Muscle
Only in the heart
Branched cells, striated, single nucleus
Involuntarily controlled
Simple squamous epithelium
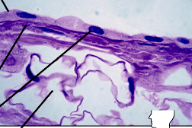
simple cuboidal epithelium
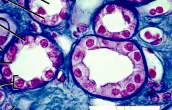
simple columnar epithelium
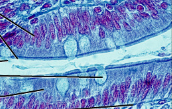
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
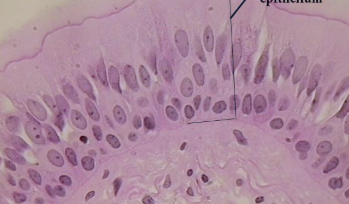
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
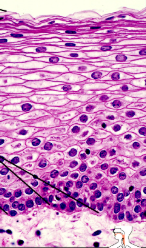
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
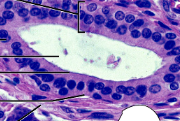
Transitional Epithelium
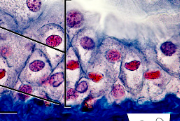
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
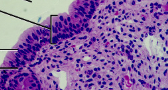
Loose connective tissue
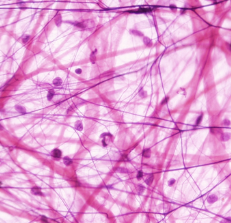
adipose tissue
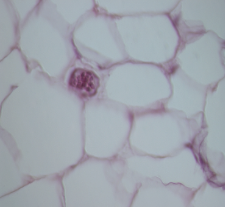
Reticular Connective Tissue
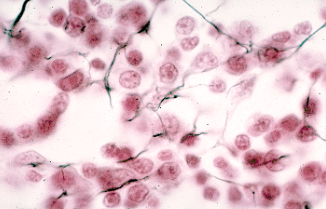
Dense connective tissue
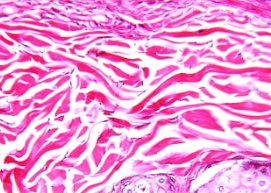
elastic connective tissue
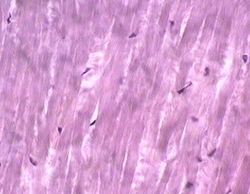
bone
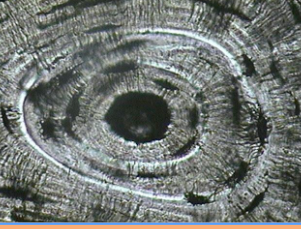
blood
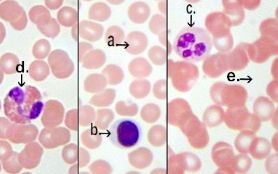
skeletal muscle
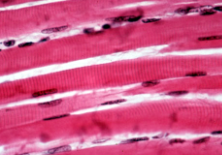
smooth muscle
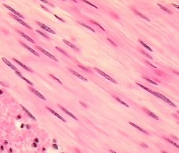
cardiac muscle
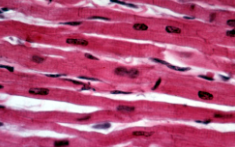
neuroglial cells
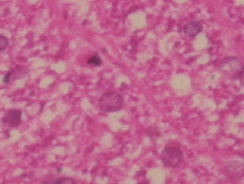
neuron