Organic Chemistry- Chapter 5
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Alkenes: Bonding, Nomenclature, and Properties
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
A molecule containing one or more carbon-carbon double or triple bonds; fewer hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon than in an alkane; contains alkenes, alkynes, and arenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Benzene and its derivatives
Arene
A group derived by the removal of a hydrogen atom from an arene
Aryl group
When the aryl group substituent on a parent chain is a benzene ring, it is called a ______ group
Phenyl
What is the bond angle of an sp² hybridized atom?
120
A C=C bond contains ___ sigma bond and ___ pi bond
One; one
Does any rotation around a C=C bond occur under normal circumstances? Why or why not?
No, because of the presence of the overlapping pi orbitals
In an open chain alkene, are cis or trans isomers more stable? Why or why not?
Trans; there is steric strain present on alkyl substituents on a cis isomer that is not present on the trans isomer
Name the following alkenyl group:
=CH2
Methylene
Name the following alkenyl group:
-CH=CH2
Vinyl
Name the following alkenyl group:
-CH2CH=CH2
Allyl
True or False:
Smaller alkenes are well-known by their common name rather than their IUPAC name
True
In the E,Z naming system, a compound of (E) configuration has high priority groups on ________ side(s)
Opposite
In the E,Z naming system, a compound of (Z) configuration has high priority groups on ________ side(s)
The same
When naming a cycloalkene, the carbon atoms of the ring’s double bond are numbered _ and _ in the direction that gives the substituent encountered first the _______ number
1;2; smaller
True or False:
Cyclopropene-cycloheptene are too small to have trans isomerism
True
Why can’t cyclopropenes-cycloheptenes have trans isomerism?
There would be too much angle strain
True or False:
Cyclooctene and larger ring sizes can experience cis isomerism, but not trans
False
True or False:
Most of the time in alkenes, trans isomerism is more stable than cis, and the same is true with cyclooctene and larger ring sizes
False
For an alkene with n C=C, __ stereoisomers are possible
2^n
When counting C=C to determine the numbers of stereoisomers a compound has, do you count double bonds that are in cycloalkenes smaller than 8? Why or why not?
No, because those double bonds do not show trans isomerism
Alkenes are essentially ________
Nonpolar
What is the only force present in alkenes?
Dispersion forces
Alkenes are _________ in water
Insoluble
Alkenes are _______ in one another, other nonpolar organic molecules, and in ethanol
Soluble
Benzene rings are very ______ and ______
Strong; stable
In organic chemistry I, are benzene ring substituents reactive?
No
List the formula used for finding the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (degrees of saturation)
(H reference-H molecule)/2
What is the molecular formula of the reference compound when finding the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency?
Cn + H2n+2
Rules pertaining to the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency:
For every halogen present (F, Cl, Br, I)…
Add one additional H
Rules pertaining to the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency:
For group 6 elements (O, S, Se)…
No correction is necessary
Rules pertaining to the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency:
For each atom of Group 5A (N, P, As)…
Subtract one hydrogen
What information does finding the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency give you?
The total number of double bonds/rings present in the molecule
When counting the number of double bonds and rings present in order to determine the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency, do you count double bonds/rings that are smaller than cyclooctene?
Yes
Double bond stability _________ with increasing alkyl substitution
Increases
True or False:
Cis alkenes are more stable than trans alkenes
False
Having both R groups on one carbon of a disubstituted alkene is ____ stable than having an R group on each carbon
More
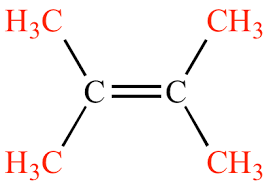
What degree of substitution is this alkene?
Tetrasubstituted
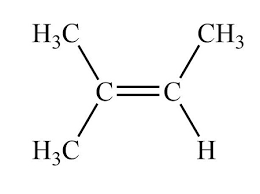
What degree of substitution is this alkene?
Trisubstituted
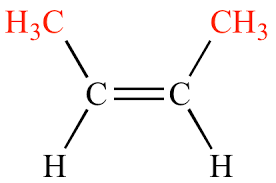
What degree of substitution is this alkene?
Disubstituted
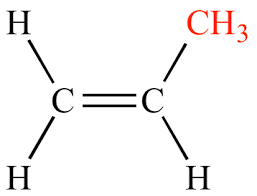
What degree of substitution is this alkene?
Monosubstituted
Rank the following from lowest stability to highest stability:
Disubstituted alkene
Tetrasubstituted alkene
Monosubstituted alkene
Trisubstituted alkene
3, 1, 4, 2
When naming alkenes, the first carbon of the double bond should have the ________ number possible
Smallest
True or False:
When naming alkenes, giving the C=C a smaller number takes precedence over giving the first substituent the smallest possible number
True
Methylene, vinyl, and allyl are all common _______ groups
Alkenyl
True or False:
Rather than following the same priority rules as the R,S naming system in alkanes, the E,Z system has its own set of priority rules
False
An alkene with two double bonds has what infix?
-adien-
Alkenes containing several double bonds are often referred to as…
Polyenes
In small-ring cycloalkenes, the configuration of the double bond is ___ because such rings are not large enough to accommodate a _____ configuration
Cis; trans
True or False:
Trans configuration in a cycloalkene is only possible if there are 8+ carbons present in the ring
True
In alkenes, melting and boiling points ________ as the number of carbons increases due to _________ surface area
Increase; increased
True of False:
Alkenes have relatively low melting and boiling points
True
Why can an sp² hybridized C accommodate slightly more negative charge than an sp³ hybridized C?
The sp² hybridized C has more s character
The more carbons present in an alkene, the ______ the boiling point
Higher
The higher the surface area of an alkene, the ______ the boiling point
Higher
What is made up of a carboxylic acid with long alkyl groups?
Fatty acid
The building blocks of fats
Fatty acids
List the degree of saturation:
A molecule only containing carbon-carbon single bonds
Saturated
List the degree of saturation:
A molecule containing one carbon-carbon double bond
Monounsaturated
List the degree of saturation:
A molecule that contains at least two carbon-carbon double bonds
Polyunsaturated
In an omega-3 fatty acid, the double bond occurs at the _____ carbon from the ___ of the alkyl group
Third; end
In an omega-6 fatty acid, the double bond occurs at the _____ carbon from the ___ of the alkyl group
Sixth; end
Increasing the number of double bonds in a fatty acid _________ the melting point of the fat
Decreases
The ______ the number of cis double bonds, the ____ kinks in the hydrocarbon chain
Larger; more
What fat is generally a solid at room temperature and contains only single bonds between carbon atoms?
Saturated fat
What fat is generally a liquid at room temperature and has one or more double bonds between carbon atoms?
Unsaturated fat
The process of adding hydrogen atoms to double bonds, thus converting the double bonds to single bonds
Hydrogenation
True or False:
Trans fats in nature are common and cis fats are extremely rare
False
Most trans fats are ___-____, created during the _____________ process
Man-made; hydrogenation
Does a trans or a cis alkene have a slightly higher boiling point?
Cis
Increasing the number of double bonds in the fatty acid _________ the melting point of the fat
Decreases
The more double bonds in a fatty acid, the more kinks. This leads to poor ________ and less van der Waals forces, leading to _____ melting points
Stacking; lower